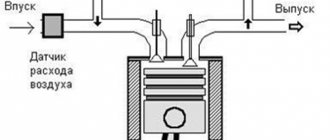
The stability of power units and their degree of environmental friendliness depends on the presence of the EGR system. Its main task is to return part of the exhaust gases to the intake channels to improve ignition of the combustible mixture. Installed on diesel engines and some models of gasoline power units.
The USR device has a positive effect on engine operation, reduces fuel consumption, and less toxic substances enter the atmosphere. Today the article will tell you about the USR in a diesel engine, what it is and answer the question posed.
System task
For normal operation of engines, low levels of nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases are required. They are formed in the high temperatures of diesel engines, creating saturation of the fuel mixture with nitrogen oxides. As a result, a negative interaction of oxides with oxygen occurs. This is the result of such interaction.
Oxygen, instead of being completely burned, is partially used to form undesirable elements. As a result, the diesel engine lacks power, the volume of fuel consumed increases significantly, and a large amount of harmful substances enters the outside air. Air pollution occurs.
Reduces the level of negative phenomena by returning some of the exhaust gases back into the chamber, thereby lowering the temperature. Recirculation of internal combustion engine exhaust significantly reduces the formation of nitrogen oxides.
The return of programmed exhaust fractions to the chambers has virtually no effect on the regulatory requirements for fuel preparation. On the contrary, it receives a positive effect, since the power increases with obvious savings in diesel fuel.
How is EGR system flow controlled?
The controller periodically tests the EGR system along with other emission control systems. If the flow rate is higher or lower than expected, the ECU detects a malfunction and turns on the Check Engine light on the instrument panel.
EGR with temperature sensor
There are different ways to control EGR flow. Some vehicles use an EGR temperature sensor installed in the intake portion of the EGR system. When the EGR valve opens, the temperature on the intake side rises from the hot exhaust gases.
EGR with DPFE sensor
Older Ford vehicles used a DPFE (Delta Pressure Feedback EGR) sensor, which measures EGR flow based on the pressure difference on either side of the meter port in the exhaust portion of the EGR system.
EGR with electric valve
Modern cars use an electric exhaust gas recirculation valve. Some cars also have an EGR cooler.
The ECU controls EGR flow by opening or closing the EGR valve using a stepper motor.
EGR flow is controlled by the manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor, mass air flow sensor (MAF) and oxygen sensor.
Previous entry Oxygen sensor (Lambda probe) - what it is, how it works, problems, symptoms, replacement
Next entry Gasoline vapor recovery system EVAP
Should I turn off the EGR or not?
In United Europe, where there is one car for every resident, air pollution is treated extremely negatively, let’s say, with reverence. There, the question of whether to disable and use EGR is not discussed. In post-Soviet countries, heated debates arise about this on the Internet in specialized forums and special periodicals.
The argument for disabling the USR is the opinion of some “experts”, they say that the system depresses the functionality of power units, prematurely rendering them unusable.
It becomes clear where such reviews come from by analyzing in detail the reasons why the USR system is ineffective. This partly happens when the system really “suffocates” the engine: the power plant becomes low-power. But this happens when drivers stop maintaining the system correctly. For example, the inlet channel clogged with dirt is not cleaned in a timely manner. Negativity occurs when sensors and valves go out of functional condition.
It has been established that EGR is vulnerable to the use of low-quality diesel fuel, which causes the appearance of large soot. Diesel fuel and gasoline regularly increase in price, which leads to a situation where substandard diesel or cheap gasoline is poured into fuel tanks. To remove carbon deposits, you need to spend a lot of money. And many drivers, not ready to endure the costs, consider it rational to turn off the system. The expediency of such a decision worries them little.
Signs of a malfunctioning EGR valve
Signs of a malfunction of the USR valve will be frequent engine stopping, floating engine speed at idle, detonation and “triple”, jerking when the car is moving, loss of power in the engine during acceleration. In a diesel car, the EGR valve requires more attention than in a gasoline car. It is recommended to clean it of carbon deposits and deposits regularly after 60-100 thousand mileage, since diesel fuel contains more impurities that settle at high temperatures on the walls and valve curtain, which leads to malfunction and breakdown.
Valve mechanism jammed
The most common reason for the EGR valve not working is the jamming of its mechanical part. This happens when it is open or closed, depending on the specific situation:
- in the first case, jamming usually leads to the fact that the exhaust vapors, after some time, enter the cylinder with all the ensuing consequences;
- in the second, the danger in the form of the release of harmful substances threatens the environment, but the car should not be harmed.
The culprit of jamming of the mechanical part of the valve is usually soot deposited on the part - an integral companion of the combustion products of gasoline and diesel fuel. For this reason, to avoid jamming of the mechanism, monitor the quality of the fuel used in the car and change the oil on time. Fuel your car at large gas stations of well-known supplier brands and avoid unknown stations.
The mechanical part of the USR valve has a service life ranging from 150 to 180 thousand kilometers. These figures are correct only under conditions of proper care and operation of the unit in tandem with a motor running on high-quality fuel.
Faulty engine
The culprit for a breakdown of the recirculation system may be the engine. Among the most common engine problems potentially responsible for failure of the EGR valve:
- untimely replacement of the air filter;
- occurrence of piston rings.
If the recirculation unit fails and you suspect a motor malfunction, first of all, diagnose the internal combustion engine. Eliminate any problems found, and then proceed to repair (replace) the recirculation valve.
Physical deterioration
After working for a certain period of time, the exhaust gas recirculation system may fail due to its physical aging. The wear rate of the unit is directly proportional to the amount of soot deposited on it.
Particles accumulating on the device are a normal phenomenon, since soot is formed during combustion in any case, while the amount of nitrogen oxides increases with increasing temperature, and the volume of soot particles increases with decreasing temperature.
To achieve the golden mean, internal combustion engine engineers are forced to make various technical tricks when designing USR systems. However, it has not yet been possible to avoid the problem of EGR valve wear due to the impact of very aggressive soot deposits on it.
The seal is broken
Violation of the tightness of the vehicle's recirculating system threatens failure of both the USR valve itself and other engine components. The worst thing is that the engine control program does not see the air entering the block. The driver may remain unaware of the presence of this malfunction for a long time.
Electronics problems
Malfunctions of the electronic part of the car can also damage the EGR valve. Problems usually arise when the power supply circuits of electronic components are broken. Sometimes the valve position sensor is to blame for problems.
Operating principle of the USR
The EGR valve of a diesel power plant and its gasoline counterpart operate differently. That is, there is a direct dependence on engine models.
EGR operation on gasoline and diesel engines:
- The valve that controls the supply of fresh air when the diesel engine is idling allows it to flow 2 times less. When loads increase, the valve doses exhaust gases into the intake manifold - allowing a smaller volume to pass through. If the internal combustion engine reaches peak loads, the system valve completely shuts off the flow of exhaust gases. It does not come off during the start of the power plant. This is the algorithm for the functioning of the USR installed on a diesel power unit.
- As for the valve installed on a gasoline power plant, the operating principle is different. It does not operate when the engine is idling and at the moment of its maximum torque. In other situations, it limits up to 90% of fresh air intake.
Recirculation operates in a special mode. The valve of a gasoline engine is controlled in two ways - by a controller using electric current or pneumatically.
Today on highways it is easy to see cars where exhaust exhaust is cooled in a special way. The valves are integrated into the OD (engine cooling) system. The result is a complex system, compensated by a significant decrease in the volume of nitrogen oxide.
What is an EGR valve
The operation of the valve is quite simple - part of the gases from the exhaust system is mixed with air from the exhaust manifold. If the percentage of nitrogen oxide is too high, this leads to high temperatures in the combustion chamber. We all know from school that oxygen acts as a catalyst for combustion. And gases from the intake manifold, mixing with the air flow, minimize the percentage of oxygen. As a result, the combustion temperature decreases and toxicity decreases.
The main objectives pursued by the USR system
When using a system valve, part of the exhaust gases from the cycle is returned through the intake manifold for subsequent combustion. At the same time, power units operate more softly and smoothly, and in gasoline engines there is a noticeable decrease in the level of detonation.
Advantages of using a recirculation system:
- Improving the performance of diesel and gasoline internal combustion engines.
- Reduced fuel consumption.
- Reducing exhaust toxicity.
The process of formation of harmful oxides under the influence of high temperatures consists of the following stages:
- Active increase in the percentage of nitrogen oxides in fuel-air mixtures.
- Interaction of oxygen and nitrogen under the influence of high temperature.
- The entry of air into the combustion chamber causes active formation of nitrogen oxide.
- Replacement of oxygen by the resulting nitrogen oxides.
- Lack of oxygen causes incomplete combustion of the working mixture.
- Loss of engine power.
- Increased consumption of diesel fuel or gasoline.
- Increased toxicity of exhaust gases in internal combustion engines.
The return of part of the exhaust gases to the intake manifold contributes to a noticeable decrease in the combustion temperature of fuel mixtures. As the temperature decreases, the intensity of the formation of nitrogen oxides decreases.
When gases that have gone through a full cycle enter the combustion chamber, it does not disrupt the quantitative balance of the main components involved in creating fuel-air mixtures, the power indicators of power units do not change when operating in various modes, and fuel is saved.
Functions of the gas recirculation valve
The EGR valve in a diesel engine is the main element of the recirculation system. The functioning of the entire system is based on its work. Using this device, the exhaust gases partially enter the manifold for mixing with the incoming air. An increase in the amount of oxygen in the chamber leads to an increase in the combustion temperature of the working mixture. The added exhaust gases reduce the percentage of oxygen, which helps reduce operating temperature and the amount of nitrogen oxides in the exhaust gases.
EURO 4 requirements
On diesel power plants, the European standard EURO-4, which controls exhaust gas pollution levels, requires the diesel engine to be equipped with valves set to high pressure.
- The standard has approved a scale of harmful particles contained in exhaust gases. Nitric oxide should be 0.25 grams per kilometer.
This is achieved by the recirculation system. Exhaust gases are removed directly in front of the turbine unit. Then there is redirection to the intake devices.
Types of diesel recirculation systems
For a diesel engine, several types of EGR exhaust gas recirculation systems are used, the collection of which is determined by the environmental standards of the vehicle. Currently there are three of them:
- High pressure (meets Euro 4 standard). The EGR valve directly connects the exhaust (installed in front of the turbocharger) and intake manifolds. This scheme uses an electro-pneumatic drive. When the throttle valve is closed, the pressure in the intake manifold is reduced, resulting in a higher vacuum. This leads to an increase in the incoming flow of exhaust gases. On the other hand, the intensity of turbocharging decreases, since less exhaust gases enter the turbine. When the throttle is fully open, the EGR does not operate.
- Low pressure (complies with Euro 5 standard). In this arrangement, the valve is connected to the exhaust system in the area between the particulate filter and the muffler, and in the intake system - in front of the turbocharger. Thanks to this connection, the temperature of the exhaust gases is reduced, and they are also cleaned of soot impurities. In this case, in comparison with the high-pressure circuit, turbocharging is performed at full power, since the entire gas flow passes through the turbine.
- Combined (complies with Euro 6 standard). It is a combination of high and low pressure circuits, each with its own recirculation valve. In normal mode, this circuit operates through the low pressure channel, and at increased load, the high pressure recirculation channel is connected.
On average, the EGR valve lasts up to 100 thousand kilometers, after which it can become clogged and fail. Further, in most cases, motorists, not understanding why recirculation systems are needed, simply remove them completely.
Technological process
In a diesel engine, the recirculation valve returns some of the exhaust gas back to the engine. The valve device is brought into normal operating condition due to the rarefied environment of the inlet channel created by a special pump. In addition, magnetic forces act on the valve, that is, the electromagnet is controlled.
Recirculation processes acquire intensity or passivity depending on the stage of engine operation. The appearance of intensity is recorded when the throttle is closed, since the intake pressure is completely reduced. At this moment, there is a decrease in the flow of exhaust gases directed to the engine turbine compressor.
The USR does not show activity when the engine is idling at maximum open throttle during periods of warming up and bringing the car to the programmed temperature.
Types of EGR valves
Location of EGR in a car
Currently, there are three types of EGR valves, differing in the type of drive:
- Pneumatic - the simplest (outdated) exhaust gas recirculation drive system. In fact, the valve control in this circuit is carried out by creating a vacuum in the intake manifold of the car.
- Electropneumatic . The EGR pneumatic valve is driven by an electrovalve controlled by the vehicle's engine ECU based on data from a set of sensors (exhaust back pressure, temperature, valve position, intake pressure, coolant temperature). It connects and disconnects the vacuum source to the EGR valve, having only two positions. In turn, a vacuum in such a system can be created by a vacuum pump.
- Electronic . This type of EGR valve is driven directly by the vehicle's engine ECU. It has three positions, which provides smoother control of the exhaust gas flow. The position of the electronic EGR valve is switched by solenoids that open and close it in various combinations. In such a system, vacuum is not used.
How does electronics control the USR?
The electronics located in the ECU carefully “monitor” the operation of the recirculation “activity”. The valve is activated precisely by the received signal from the electronic control center.
The valve positions are controlled by pulses generated by pressing the throttle valve. And the spatial position of the throttle is controlled by a special sensor. In short, a complex control system.
EURO 5 has introduced new environmental requirements for motorists. Today, the standard requires that nitric oxide levels not exceed 0.18 grams per kilometer. The recommended result is obtained by integrating a reduced EGR into the diesel fuel system.
Drivers received information about the location of the element through a news alert. It goes directly behind the diesel power plant particulate trap. The exhaust gases are then directed to a flow redirection device for additional temperature reduction. The next stage is the entry of exhaust gases through the valve device and then to the turbine unit.
EURO-5 and its advantages
The emergence of new European and international standards is motivated by the emerging difficult environmental situation in the countries of the United Europe, whose air basin is “overloaded” with automobile exhaust gases. The only way to improve the situation is through prohibitive measures, which is what Europe is doing. The introduction of a new prohibitive standard has undeniable advantages over previous analogues:
- large volume of retained soot;
- lowering the temperature of exhaust gases;
- an obvious decrease in the level of nitrogen oxide found in exhaust exhaust.
In net terms, the power of diesel engines does not decrease one iota.