Phase regulator malfunction
Malfunctions of the phase regulator may include the following: it begins to make unpleasant cracking sounds, freezes in one of the extreme positions, the operation of the solenoid valve of the phase regulator is disrupted, and an error is formed in the ECU memory.
Although you can drive with a faulty phase regulator, you need to understand that the engine will not operate in optimal mode. This will affect fuel consumption and engine performance. Depending on the problem that has arisen with the clutch, valve or the phase regulator system as a whole, the symptoms of the malfunction and the possibility of eliminating them will differ.
Causes of phase regulator malfunction
Malfunctions are divided directly into the phase regulator and its control valve. So, the reasons for the malfunction of the phase regulator are:
- Wear of the turning mechanism (blade/vane) . Under normal conditions, this happens for natural reasons, and it is recommended to change the phase regulators every 100...200 thousand kilometers. Contaminated or low-quality oil can accelerate wear.
- Displacement or mismatch of the set values of the phase regulator rotation angles . This usually occurs due to the fact that the rotating mechanism of the phase regulator in its housing exceeds the permissible rotation angles due to metal wear.
But the reasons for VVT valve failure are different.
- Failure of the phase regulator valve seal . For Renault Megane 2 cars, the phase regulator valve is installed in a recess in the front of the engine, where there is a lot of dirt. Accordingly, if the oil seal loses its tightness, then dust and dirt from the outside mixes with the oil and enters the working cavity of the mechanism. The result is jamming of the valve and wear of the rotating mechanism of the regulator itself.
- Problems with the valve electrical circuit . This could be a break, contact damage, insulation damage, a short to the housing or to the power wire, a decrease or increase in resistance.
- Ingress of plastic shavings . On phase regulators, the blades are often made of plastic. As they wear out, they change their geometry and fall out of their seat. Together with the oil, they enter the valve, disintegrate and are crushed. This can lead to either incomplete valve stem travel or even complete jamming.
Operating principle of the phase regulator
To understand why the phase regulator cracks or its valve jams, it makes sense to understand the principle of operation of the entire system. This will give a better understanding of breakdowns and further actions to repair them.
The engine does not perform the same at different speeds. Idle and low speeds are characterized by so-called “narrow phases”, in which the exhaust gas removal rate is low. Conversely, high speeds are characterized by “wide phases”, when the volume of gases released is large. If “wide phases” are used at low speeds, then the exhaust gases will mix with the newly incoming ones, which will lead to a decrease in engine power, and even stop it. And when “narrow phases” turn on at high speeds, it will lead to a decrease in engine power and its operating dynamics.
There are several types of phase control systems. VVT (Variable Valve Timing), developed by Volkswagen, CVVT - used by Kia and Hyindai, VVT-i - used by Toyota and VTC - installed on Honda engines, VCP - Renault phase regulators, Vanos / Double Vanos - system used in BMW. Next, we will consider the principle of operation of the phase regulator using the example of a Renault Megane 2 car with a 16-valve K4M engine, since its failure is a “childhood disease” of this car and its owners most often encounter a non-working phase regulator.
Control occurs through a solenoid valve, the oil supply to which is regulated by electronic signals with a discrete frequency of 0 or 250 Hz. This entire process is controlled by an electronic control unit based on signals received from engine sensors. The phase regulator is switched on when the engine load increases (rpm value from 1500 to 4300 rpm) when the following conditions are met:
The phase regulator returns to its original position when the speed decreases under the same conditions, but with the difference that zero phase shift is calculated. In this case, the locking plunger blocks the mechanism. Thus, the “culprits” for a malfunction of the phase regulator can be not only the phase regulator itself, but also the solenoid valve, engine sensors, malfunctions in the motor, and malfunctions of the ECU.
General information about the operation of phase regulators
Modern power units made in Europe and Japan, including the Peugeot 307 engine, are equipped with various electro-hydraulic systems that change the degree of filling of the cylinders due to the level of valve closing or opening. By adjusting the valve timing it is possible to change the volume of new charges and parts of the residual exhaust gases.
Based on the speed of the crankshaft and the level of throttle valve actuation, the degree of the combustible mixture entering the cylinder and the exhaust gases leaving it greatly changes. By modifying the valve timing, it becomes possible to make the necessary adjustments based on the crankshaft speed and the level of filling of the cylinders with the combustible mixture.
Taken together, this makes it possible to achieve certain positive dynamics in the functioning of the power unit of the Peugeot 308 and 307:
- increasing the power output of the power unit;
- improvement in torque indicators over fairly wide speed ranges;
- reducing the level of harmful exhaust emissions;
- saving fuel consumption;
- reduction of engine noise.
Standard power units use a rigid crankshaft and camshaft connection. In the classic Peugeot 308 and 307 engines, a phase regulator is installed, which allows you to adjust the location of the camshaft and crankshaft in order to change the degree of valve overlap. Electric or electrohydraulic mechanisms are responsible for the degree of rotation of the camshaft. Moreover, in simple devices, it is possible to install the shaft in clearly defined positions. In more modern phase regulators, it has become possible to smoothly adjust the camshaft in relation to the crankshaft.
In a classic engine, the exhaust valve opens approximately 10-35 degrees before the piston moves to extreme top dead center. In turn, the valve closes after 40-85 degrees when the piston passes the bottom dead center.
In order to obtain the highest power indicators, a certain amount of advance angles must be ensured when opening and, conversely, a delay at the moment of closing the intake valves. The highest revolutions of the power unit are accompanied by the filling of the cylinders with inert gas flows with the intake valves not yet closed at the moment the pistons rise. In turn, at minimum speeds, the delay in closing the valves plays an important role, leading to partial squeezing of the new fuel mixture from the cylinders.
Dismantling and cleaning the phase regulator
The operation of the phasic can be checked without dismantling. But to check the wear of the phase regulator, it must be removed and disassembled. To find where it is located, you need to navigate along the front edge of the camshaft. Depending on the design of the motor, dismantling the phase regulator itself will differ. However, in any case, the timing belt is thrown through its casing. Therefore, access to the belt must be provided, and the belt itself must be removed.
After disconnecting the valve, always check the condition of the filter mesh. If it is dirty, it needs to be cleaned (rinsed with cleaner). To clean the mesh, you need to carefully move it apart where it snaps into place and remove it from its seat. The mesh can be washed in gasoline or other cleaning liquid using a toothbrush or other non-rigid object.
The phase regulator valve itself can also be cleaned of oil and carbon deposits (both outside and inside, if its design allows) using a carb cleaner. If the valve is clean, then you can proceed to check it.
How to check the phase control valve on a Renault
I’ll start with what the phase regulator valve is actually needed for. The solenoid control valve supplies oil under pressure to the camshaft phase adjuster. When the supply of control voltage to the solenoid valve from the ECU is stopped, the phase regulator returns the camshafts to the position of minimum retardation of the intake valves, providing maximum torque effect at low speeds.
The following picture shows the principle of operation of the phase regulator valve:
On a Renault Megane 2 car, the phase regulator solenoid valve is installed on the cylinder head cover near the oil filler neck. Before removing it, it would be advisable to wipe everything around it to avoid dirt getting inside the cylinder head.
To remove it, you need to disconnect the connector and unscrew the bolt with an 8mm head in my case (everywhere on the Internet they write that it is 10mm).
After removing the valve, we look at the small filter mesh. It must be clean. When I removed the valve for the first time, it was with a mileage of about 160 thousand km. The mesh was heavily soiled. This time, she is also dirty, but not much.
To clean the mesh, carefully move it in different directions where it snaps into place and remove it.
I cleaned my mesh with a toothbrush dipped in gasoline. Cleans very well. I didn’t wash the valve itself; the inside turned out to be clean.
Just wiped the outside. By the way, small grains of sand and pebbles got on the valve when it was removed, so don’t pay attention to them. If the inside of the valve is dirty, wash it with carburetor cleaner and blow it with air.
Checking the phase regulator valve on Renault Megane 2
Using a multimeter, in ohmmeter mode, measure the resistance at the valve terminals. According to the Renault technical note “Engine and its systems”, the resistance value at a temperature of 20 degrees should be in the range of 6.7 - 7.7 Ohms . If the resistance is different, the valve is faulty.
For a longer life of the valve and the phase regulator itself, I advise you to change the oil as often as possible.
I’m posting a photo with the numbers of the phase regulator valve, maybe it will be useful to someone. Good luck.
Next, I suggest you read the information on replacing the phase regulator valve seal in the post “Replacing the phase regulator valve seal on Renault Megane 2”.
How to check the phase regulator
There is one simple method for checking whether the phase regulator is working in the engine or not. To do this, you only need two thin wires about one and a half meters long. The essence of the check is as follows:
The phase regulator solenoid valve must be checked using the following algorithm:
The resistance can be measured without dismantling, but the mechanical component of the valve must also be checked. For this you will need:
Phase regulator error
If on Renault Megane 2 the control unit has generated error DF080 (camshaft characteristic change circuit, open circuit), then you must first check the valve using the above algorithm. If it works normally, then it is necessary to “ring” the wire circuit from the valve chip to the electronic control unit.
How to Check the Phase Regulator of Renault Megane 2 ~ VESKO-TRANS.RU
Renault Megane Black Barracuda again › Logbook › No. 87 - (!) Malfunctions of the Megane II phase regulator.
Changing the valve timing is the main task of the phase regulator. The 16-valve engine with a volume of 1.6 (1598 cm3) K4M, which is installed in the Renault Megane 2, is equipped with a phase regulator. The kit also includes a bolt and a bolt cover for the phase regulator.
Renault Megane regulator is controlled by the injection system computer via an electric valve, which is installed on the cylinder head cover. crankshaft speed within the range of 1500 -4300 rpm.
At higher rotation speeds , the power is cut off, so the cylinders are filled at the highest crankshaft speed . How to remove the heater fan for Renault Megan 2 Phase regulator Renault Megan 2. The locking plunger blocks the mechanism in this position.
Replacing the Renault Megane 2 and 3 fuel filter, despite its importance. 5000 rub. How to recognize if the phase regulator is Renault Megan, the oil pressure sensor is Renault Megan 2.
The phase regulator of Renault Megane 2 engines (f4r and k4m) is located on the camshaft of the intake valves and serves to more completely fill the cylinders with the fuel mixture in all of them.
In the initial position, the solenoid valve is closed and the oil passage opens under the following conditions: there are no malfunctions of the camshaft position sensors, the crankshaft, there are no problems in the injection system, after starting the engine, the engine speed should be about 1500-4300 min–1 The load should not be more than 87%.
Part 9: how to check the phase control valve for Renault Megane ll
THANKS FOR WATCHING SUBSCRIBE TO MY YOUTUBE CHANNEL!
Renault phase control valve. Why are there no singles? How to check it? Error DF080 | Video lecture
Operating principle of the phase regulator
on a
Renault
.
How to check
the mechanical and electrical parts. If consumption increases, throttle response decreases, starting is difficult, extraneous engine noise appears, the so-called “diesel” noise, most likely this is due to a malfunction of the phase regulator.
The Renault Megane 2 phase regulator optimizes the filling of the cylinders depending on the crankshaft . remove the battery on Renault Megane 2, how to open the door on Renault Duster without a key.
What lighting devices are used in Renault Megane 2 and how to choose the right new lamp. Torque at medium loads and power at high crankshaft speeds increases. Faulty phase regulator for Renault Megane 2.mp4 -.
This results in a later arrival of an additional portion of the fuel mixture due to the high speed of movement. Replacing a ball joint for Renault Megane 2 But at low rotation speeds, the inertia of the charge is small.
By closing the exhaust valves early, poor cylinder filling and loss of torque due to displacement of part of the fresh mixture charge can be avoided. Phase regulator Renault Megan phase regulator Renault Megan 2 with when it is required and how. Renault Megane repair manual figure 2.228.
Camshaft phase regulator. Replacing the fuel filter for Renault Megane 2. Fuel filters for Megane 2 diesel fuel. Thus, the closing of the intake valves should occur later, the higher the crankshaft speed.
Found it on vsepoedem.com/ It’s written clumsily, but the meaning is clear.
Now I’m faced with the same problem. The fazik, as before, occasionally crackles when starting the engine. But now the consumption has increased - 10-11 in the city. The throttle response has dropped, i.e. accelerates like a vegetable.
And sometimes the consumption returns to normal, with it the throttle response returns and it begins to seem that the 1.6 is not so bad when it presses you into the seat during acceleration.
Then again it all disappears somewhere, and it has nothing to do with cod.
Disabling the phase regulator
Many car enthusiasts are concerned about the question: is it possible to drive with a faulty phase regulator? The answer is yes, you can, but you need to understand the consequences. If for some reason you decide to turn off the phase regulator, then you can do it like this (considered on the same Renault Megane 2):
Conclusion
Automakers recommend changing phase regulators every 100...200 thousand kilometers. If it knocks earlier, first of all you need to check its valve, as this is easier. It is up to the car owner to turn off or not turn off the phasic, as this leads to negative consequences. Dismantling and replacing the phase regulator itself is a labor-intensive task for all modern machines. Therefore, you can only perform this procedure if you have experience and the appropriate tools. But it is better to seek help from a car service center.
Source
Renault Megane Meganych › Logbook › Phase regulator valve. Unclear…
Hi all! I realized that my phase regulator is not working. There is no diesel in the morning, but if you look at Piren, something like this opens up:
SCO 99.9, Need 12, in fact 1-2. By the way, these 1-2 actually appear if you turn on the gas at a low coolant temperature, that is, when the phase regulator is not yet turned on (SCO 0). This can indicate that the phase regulator is not working. Moreover, if you increase the throttle to 4k, then the values, on the contrary, become larger than necessary. There is, of course, a possibility here that the phase adjustment turns off a little earlier, and the tooth does not have time to transmit the correct values. The timing belt was changed 3k ago, the phasic itself most likely never changed. I decided to remove the valve, see if there was any oil there at all, clean it, and change the oil seal - since everything was like this:
Now the most interesting part 1. Oil in the connector. After washing it comes out again. If you start the engine without a valve, oil appears, but not quickly if after a long period of inactivity. If you do it right away, it will splash out 2. There is no net, it looks like it’s under a Kamaz truck. Looks like he was dealing with barbarians.
4. I stupidly threw back the valve chip... and nothing changed, the engine worked as it did, the readings were as crooked as they were, and remained exactly the same. Well, almost nothing - the following error got into alive (I put it back - it went away). Which makes me wonder whether a signal is sent to the valve at all. How to check?
5. On the panel, the service and Jackie Chan did not light up (Jackie Chan never burned out, the service with a pregnant woman burned out) What the hell...
In general, does anyone have any ideas besides the fact that the phasic and the valve are dead. If only they were the problem, then in principle they could be replaced.
Added:
I remove the chip from the valve - there is no check, in others there is. Well, I have an alarm error on the adsorber. Do you get the idea? I look carefully at my own photos... The chip for the valve is black... and the connector is gray, and where is the gray chip? Adsorber! I remove the chip from the adsorber and oops - Injection check, camshaft error. Flipped it around, erased the mistakes - Voila
Added 2:
I took the valve off and cleaned it again. So far it’s working, I gased it on the spot. went to work. The car feels more responsive and smoother, most noticeable in 2nd gear. Consumption has dropped slightly. The valve in the Prince worked, because instead of the adsorber valve, after 3k revolutions the phase regulator valve approximately opened to full))
Source
What is a phase regulator?
- Files
- Engine
General description of the phase regulator
Modern European and Japanese engines use various electro-hydraulic systems that make it possible to change the cylinder filling ratio by changing the valve overlap. Thanks to adjustable valve timing, it is possible to influence the amount of fresh charge and the proportion of residual exhaust gases. Depending on the crankshaft speed and the degree of opening of the throttle valve, the behavior of the charge entering the cylinder and the exhaust gases leaving it change greatly. When setting constant valve timing, gas exchange can only be optimized for a certain range of rotational speeds. Adjustable valve timing allows adjustments to be made taking into account changes in crankshaft speed and different filling of the cylinders with the mixture.
All this results in the following advantages:
– increased engine power output – better torque performance over a wider rpm range – reduced CO emissions – reduced fuel consumption – reduced engine noise
In a conventional engine, the crankshaft and camshafts are rigidly connected to each other mechanically (by a timing belt or chain)
In engines with a phase regulator, it is possible to adjust the position of the camshaft and crankshaft to change the valve overlap. The camshaft is rotated using an electric or electro-hydraulic drive. Simple devices can only install the shaft in one of two positions. More complex phase regulators allow smooth adjustment of the camshaft relative to the crankshaft.
It will be useful: Where are the fuses on the Toyota Corolla E150 and how to replace them yourself
In modern engines, the opening of the intake valve occurs on average 10-35 degrees before the piston reaches TDC, and closing 40-85 degrees after BDT. The exhaust valve closes 10-30 degrees after passing the T.M.T. But these figures can be changed either up or down.
To obtain maximum power, it is necessary to ensure maximum values of the opening advance and closing angles of the intake valves. At high engine speeds, the cylinder is filled due to the inertia of the gas flow while the intake valve is still open during the rise of the piston. And at low engine speeds, a large delay in closing the intake valve causes partial displacement of the fresh working mixture that has filled it from the cylinder, which leads to a significant decrease in engine torque.
Description of the phase regulator device using the example of Renault F4P
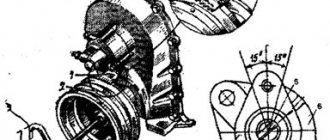
Let's look at the design and principle of operation of the phase regulator using the example of the Renault F4P engine (1.8 l.)
Phase regulator for Renault F4P engine
1. Impeller 2. Vane 3. camshaft 4. Cylinder with chambers 5. Toothed pulley 6. Locking plunger 7. Hole for lifting the plunger
The Renault F4P engine is equipped with one phase regulator installed in the intake camshaft timing pulley.
The pulley consists of two parts: an impeller with blades (attached to the camshaft) and a cylinder with chambers (mounted to the camshaft toothed pulley). Under certain conditions, the electronic control unit (ECU) commands the solenoid valve. An open valve allows oil to flow under pressure through the central channel of the camshaft.
Oil enters through the central hole of the impeller and the hole for lifting the plunger. Under the influence of oil pressure, the plunger moves upward and releases the impeller, as a result of which, under the influence of oil pressure, the impeller blades and the phase regulator rotate in the direction of the maximum delay in closing the intake valves.
When the control voltage on the solenoid valve is removed, the impeller blades return to their original position under the influence of engine rotation, after which the plunger blocks the entire system in the position of minimal lag of the intake valves.
Solenoid control valves provide pressurized oil to the camshaft phase adjusters. When the control voltage supply to the electromagnetic valves from the computer is crossed, the phase regulators return the camshafts to the position of minimum retardation of the intake valves, providing maximum torque effect at low speeds.
On models with an F4P engine, the camshaft phase control operates subject to the following conditions:
– crankshaft speed above 1500 rpm – pressure in the intake manifold above 500 mbar – antifreeze temperature above 30 degrees
The valve overlap phases are controlled by the ECU based on signals from the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors, coolant temperature and vehicle speed. The range of regulation of the camshaft rotation angle in idle mode lies in the range from +5 to -5, and in the mode of sharp increase in speed - 0-30 degrees. In this case, the ratio of the on state of the phase regulator valve is 0-2% and 0-60%, respectively.
How much does a Phase Regulator cost on a Renault?
Using the Renault-Drive card you can buy spare parts at a discount in Emekh, Exist, Autodock and other partner stores.
Comparison of prices in online stores for phase regulator (at the end of March 2015)
| exist | emex | autodoc | |||||
| vendor code | retail | on the map | retail | on the map | retail | on the map | |
| Phase control gear for 1.6 K4M engine | Original Renault 7701478505 | 5856 | 5551 | 5790 | 5572 | 5820 | 5628 |
| Phase regulator gear for 2.0 F4R engine | Original Renault 8200782671 | 9650 | 9146 | 8909 | 7038 | 9680 | 9510 Diagnosis and symptoms of a faulty phase regulator The sound of a faulty phase regulator Knowing the principle of operation and the range of regulation, it is possible to diagnose the phase regulator valves using several parameters. For this you need a scanner, an oscilloscope and a vacuum meter. The computer does not always generate an error when the phase regulator valve is faulty or jammed. When the control solenoid valve is jammed in the open position or the phase regulator in the position of maximum advance of the opening of the intake valves, the engine idles unstably, the pressure in the intake manifold is too high (above 360 mbar). The oscillogram shows the dependence of the camshaft rotation angle and the duty cycle of the phase regulator valve. You can clearly see how the wedging valve plunger destabilizes the angle of rotation of the camshaft. Hence the unstable operation of the engine at idle and in variable load mode (2000-2500 rpm) In some cases, if the phase regulator valve is completely jammed, the engine will not idle at all. Practice shows that valve jamming is most often caused by the presence of contaminants in the engine lubrication system. As a recommendation, it is advisable to change the engine oil more often, especially in harsh urban conditions. Diagnosis of a faulty phase regulator at home If symptoms of a faulty phase regulator appear (sound, engine operation) After the trip, park the car on the right side on a high curb and try to start the engine after two hours. If a crackling sound appears, it is most likely a phase regulator and needs to be changed. For an accurate diagnosis, we recommend contacting the service. You can also use video camera recording to demonstrate the problem to a dealer or service center. If the car is not under warranty, then the phase regulator must be changed at your own expense. If the phase regulator is faulty, you can drive for some time, but sooner or later it will have to be changed, since the engine will no longer start. Replacing a phase regulator is a rather expensive procedure. The cost of the spare part is 5,000 – 8,000 rubles + replacement of the timing belt + possibly oil and pump. The article uses materials from Megane2.ru and in particular M. Komarov (Mozhaisk) You can calculate the cost of Renault spare parts from our partners (existence, emech.ru and others) with a discount using your Renault-Drive card If you have anything to add to the article, or would like to share your experience on this topic, please leave a comment If you are the author of a report on repairs, modifications of a Renault car, or recommend material for the Renault-Drive Knowledge Base , please let us know If you liked or helped this article, do not forget to share the link to it with your friends on social networks: |
Renault phase control valve
The solenoid valve that controls the operation of the phase regulator can cause uneven operation of the engine at idle and negatively affect the dynamics of the car and fuel consumption. Today we will look at why this happens and talk about troubleshooting problems that arise due to malfunction of the phase shifter valve on a Renault Megane 2 car.
What determines the service life of phase regulator parts?
Most owners of Renault Megane 2 cars with 16-valve K4M and F4R engines neglect the phase regulator valve seal (also called a phase shifter, or in car enthusiast slang, “phasor”). And in vain, because the cleanliness of all components of the control device, and therefore its performance and service life, depends on the condition of the oil seal.
The phase regulator solenoid valve is located in the front of the Renault engine, and in addition, it is installed in a recess - in the place where dirt first accumulates. If the oil seal dries out or is damaged, dust and sand mixed with engine oil enter the valve channels and the working cavity of the rotary assembly. This is fraught with jamming of the electromagnetic device and accelerated wear of the chambers and blades of the phase regulator itself. In this case, excessive clearance may appear, or even damage to individual parts of the device, which is responsible for changing the valve timing.
As a result, instead of replacing the phase regulator oil seal at a cost of several hundred rubles, you have to buy parts with a total cost of more than 20 thousand rubles. For this reason, experts recommend periodically inspecting the condition of the seal and replacing it at the slightest suspicion.
Cleaning the timing valve Hyundai Elantra 4 (HD)
Good day! At the request of readers, I decided to write a short article about cleaning the timing valve on a Hyundai Elantra HD (J4). Where is this phase change valve located and what does it serve?
Just some, including me,