The production of 2JZ engines began in 1997. The volume of the working cavity of the cylinders, regardless of modification, is 2997 cc. This 2JZ GE engine has the best power performance among JZ units. The parameters of the cylinder diameter and piston stroke are educational elements of the engine square and they are equal to 8.6 cm.
The design of the gas distribution mechanism is made according to the DOHC system. Two camshafts and 4 valves per cylinder are the formative elements of this system. Also in 1997, engine units began to be equipped with a system called VVT-i.
Cars with Toyota 2JZ GE engine
Over 16 years of assembly, the engine became legendary and popular; it was valued for its high reliability and large margin of safety. This power unit was used during the following period of time:
- From July 2001 to July 2005 on the first generation Toyota Altezza, restyling, station wagon, XE10 body.
- From July 2000 to November 2004 on the second generation Toyota Aristo, restyling, sedan, S160 body.
- From August 1997 to June 2000 on the second generation Toyota Aristo, sedan, S160 body.
- From August 1994 to July 1997 on the first generation Toyota Aristo, restyling, sedan, S140 body.
- From October 1991 to July 1994 on the first generation Toyota Aristo, sedan, S140 body.
- From August 1998 to June 2001 on the sixth generation Toyota Chaser, restyling, sedan, X100 body.
- From September 1996 to July 1998 on the sixth generation Toyota Chaser, sedan, X100 body.
- From September 1994 to August 1996 on the fifth generation Toyota Chaser, restyling, sedan, X90 body.
- From October 1992 to August 1994 on the fifth generation Toyota Chaser, sedan, X90 body.
- From August 1998 to June 2001 on the fifth generation Toyota Cresta, restyling, sedan, X100 body.
- From September 1996 to July 1998 on the fifth generation Toyota Cresta, sedan, X100 body.
- From September 1994 to August 1996 on the fourth generation Toyota Cresta, restyling, sedan, X90 body.
- From October 1992 to August 1994 on the fourth generation Toyota Cresta, sedan, X90 body.
- From August 2001 to November 2003 on the eleventh generation Toyota Crown, restyling, sedan, S170 body.
- From September 1999 to July 2001 on the eleventh generation Toyota Crown, sedan, S170 body.
- From July 1997 to July 2001 on the tenth generation Toyota Crown, restyling, sedan, S150 body.
- From July 1997 to August 1999 on the tenth generation Toyota Crown, restyling, sedan, S150 body.
- From December 1995 to June 1997 on the tenth generation Toyota Crown, sedan, S150 body
- From July 1995 to June 1997 on the tenth generation Toyota Crown, S150 sedan.
- From August 1993 to July 1995 on the ninth generation Toyota Crown, restyling, sedan, S140 body.
- From October 1991 to July 1993 on the ninth generation Toyota Crown, sedan, S 140 body.
- From October 1991 to November 1995 on the eighth generation Toyota Crown, second restyling, sedan, S130 body.
- From July 1997 to August 1999 on the second generation Toyota Crown Majesta, restyling, sedan, S150 body.
- From August 1995 to June 1997 on the second generation Toyota Crown Majesta, sedan, S150 body.
- From August 1993 to July 1995 on the first generation Toyota Crown Majesta, restyling, sedan, S140 body.
- From October 1991 to July 1993 on the first generation Toyota Crown Majesta sedan, S140 body.
- From August 1998 to September 2000 on the eighth generation Toyota Mark II, restyling, sedan, X100 body.
- From September 1996 to July 1998 on the eighth generation Toyota Mark II, sedan, X100 body.
- From September 1994 to August 1996 on the seventh generation Toyota Mark II, restyling, sedan, X90 body.
- From August 1992 to August 1994 on a seventh generation Toyota Mark II, sedan, X90 body.
- From November 2000 to April 2001 on the first generation Toyota Origin, sedan, JCG17 body.
- From May 1998 to March 2001 on the first generation Toyota Progres, sedan, G10 body.
- From August 1996 to March 2001 on the third generation Toyota Soarer, second restyling, coupe, Z30 body.
- From January 1994 to July 1996 on the third generation Toyota Soarer, restyling, coupe, Z30 body.
- From April 1996 to August 2003 on the fourth generation Toyota Supra, restyling, coupe, A80 body.
- From May 1993 to March 1996 on the fourth generation Toyota Supra, coupe, A80 body.
History of the legendary 2JZ GE engine
The power units of the JZ family are called legendary for good reason. After all, engines that were designed in the late 80s still perform successfully in international competitions. And they don’t just perform, they win them. All this is possible thanks to the large safety margin built into the design of the unit.
Start from 1JZ GE
The ancestor of the jz series motor line is 1JZGE. It went into mass production in 1990. It was a six-cylinder engine with a combustion chamber volume of 2.5 liters. The engine produced a power of 180 hp, and peak torque at 4800 rpm was 235 Nm. The gas distribution system of the engine, as well as other engines of this family, is DOHC. It consists of two camshafts and a timing belt drive. The head of the BC is aluminum, and the BC is made of cast iron.
The emergence of 2JZ GE
A year later, in 1991, the 2JZ GE engine discussed here saw the light of day. This engine is an exact copy of its older brother with a large cylinder capacity. The volume was increased by increasing the piston stroke length. To do this, the length of the connecting rods and the height of the cylinder block were changed. As a result of the changes, it was possible to obtain exactly the same engine, with a combustion chamber volume of 3000 cubic centimeters. The power of the new modification at 6000 rpm was 217 hp, and the torque at 4800 rpm was 298 Nm.
Modernization
In the second half of the 90s, the JZ family underwent a large-scale modernization. First, the first generation 1JZ GE engine received changes. The ignition system, instead of a contactless distributor, received three ignition coils. A separate coil was installed for every two spark plugs.
But the most serious changes occurred with the gas distribution mechanism. A VVTi phase regulator was installed on the intake shaft. Changes also affected the cooling system. As a result, the compression ratio and power have increased. Now the engine began to produce 20 more horses, and the power amounted to 200 hp.
A year later, in 1997, the turn of modernization came to our 2JZ GE engine. Design changes followed the same pattern. A variable valve timing system was installed on the 2jz engine and instead of a distributor, the engine received three ignition coils. As a result of modifications, the 2jz ge received 230 horses and a torque of 305 Nm.
This engine became very popular and was used in various civilian vehicles. The 2JZ GE combines high power and reliable operation. He became famous not only in Japan, but also in America, where Toyota supplied its cars en masse in those years. Serial production of the engine continued until 2007. Then it was replaced by a more environmentally friendly and economical, but not as reliable aluminum engine.
Specifications
| Construction type | In-line, six-cylinder |
| Working volume cc. | 2997 |
| Power parameter hp | 217 |
| Torque parameter Nm | 297 |
| Compression level | 11,3:1 |
| Valve system type | VVT-i, DOHC 24V |
| Fuel injection system | Straight D-4 |
| Ignition system type | Distributor/DIS-3 |
| Estimated resource | More than 1 million km, without major repairs |
The VVT-I system is a custom development of Toyota. It enables intelligent fuel injection. Its great advantage is the creation of a high crankshaft rotation speed with low thrust. The overall capabilities of the engine are enhanced by proper design of the valves, as well as their opening and closing systems.
The use of a large number of valves per cylinder is carried out using the DOHC system. This contributes to an increase in crankshaft speed and power.
The high cost of repair and maintenance, due to the large number of parts, is the main disadvantage of this system.
Technical data
2JZ GE - gasoline, six-cylinder, four-stroke engine with in-line cylinders. The placement of the internal combustion engine in the engine compartment is longitudinal. The internal combustion engine is intended for installation on rear-wheel drive and all-wheel drive vehicles. The engine works in conjunction with PP automatic transmissions only.
The country of manufacture of the motor in question is Japan. Plant produced by Tahara Plant. Years of production from 1991 to 2007.
The cylinder block is made of cast iron alloy. The BC head is made of aluminum. Fuel supply system - injector. It has electronic and sequential injection. When the crankshaft moves, a specific injector corresponding to a certain phase of the crankshaft is activated. The engine cylinders operate in this order: 1, 4, 3, 2.
The gas distribution system of the engine in question is DOHC. Two overhead shafts and 24 valves. In 1997, the intake received a VVTi system.
The piston stroke length is equal to the cylinder diameter of 86 mm. People say about such engines that the motor is square. With such parameters, internal combustion engines are characterized by high reliability and a long service life of the power unit.
The exact volume of the cylinders is 2997 cm3, cubic meters. Power at 6000 rpm is from 217 to 230 hp. Maximum torque at 4800 rpm, from 290 to 305 Nm. The compression ratio of the combustion chambers is 10.5:1.
The ignition system of the first version of the engine is non-contact, distributor. After modernization in 1997, reel-to-reel, DIS3. Three coils for six cylinders.
Compliance with European standards for emissions of pollutants Euro 2 and Euro 3.
The fuel used is AI 92 and AI 95. Gasoline consumption during city driving is 14.5 liters per 100 km, mileage. On the highway 8.6 liters. Total consumption is 10.8 liters per 100 km, mileage.
Oil consumption
The permissible consumption of motor lubricant is about 1 liter per 1000 km, mileage. Types of oil used: 0w30, 10w30, 5w30. The oil must be changed together with the oil filter no later than after 10 thousand km.
Resource
The service life of 2JZGE according to the manufacturer’s requests is 300 thousand km. The real resource, with good care and careful operation, exceeds 500 thousand km.
Technical characteristics of the 2JZ engine
The design features of the base 2jz ge unit are inherent to other modifications; engine characteristics change due to changes in order to increase power, torque or fuel efficiency of the engine.
2jz engine characteristics:
| Explanation | Index |
| Manufacturer | Toyota Tahara Plant |
| Release period | 1991-2007 |
| Fuel | Gasoline AI 95 |
| Unit power supply | injector |
| How many bars | 4 |
| Assembly block alloy | cast iron |
| Positive displacement chamber (pcs.) | 6 |
| Placement of unit chambers | row |
| Valve, total (pieces) | 24 |
| Unit volume (cm3) | 2997 |
| Operating procedure of the unit | 1,5,3,6,2,4 |
| Volumetric displacement chamber, diameter, millimeters | 86 |
| Distance between the extreme positions of the piston, millimeters | 86 |
| Ratio of space above the piston: top/bottom | 8,5/10,5/11,3 |
| Unit power, horsepower | 220-325 |
| Torque (Nm) | 294-440 |
| Environmental Compliance | 2-3 Euro |
| Engine weight 2jz gte /ge/fse(kg.) | 270/230/220 |
| Fuel consumption city/highway/mixed (liters per hundred) | 18/10/12,5 |
| Unit service life (km.) | 400000 |
| Lubricating fluid | 0W-30, 5W-20, 10W-30 |
| Lubricant volume, liters | 3.9 – 5.4 |
| Lubricant change period required/desirable, kilometers | 10000/5000 |
Modifications 2jz ge
The family of three liter engines of the second generation of the JZ series was in production for 16 years: from 1991 to 2007. The first base engine was the 2JZ GE, but besides it, other modifications were created:
2JZ GE
2JZ GE is the main, base power unit. This is an atmospheric version with a compression ratio and power from 217 to 230 hp, forces, at 6 thousand, rpm min. And the peak torque at 4800 rpm, from 290 to 305 Nm. The difference in readings depends on the version and year of manufacture. The first version had contactless ignition with a distributor. Later in 1997, the engine received three coils, instead of a distributor, and a phase regulator at the inlet. Accordingly, new electronic software was required.
2JZ GTE
2JZ GTE is a sports version of the base engine. To increase power, two CT20A turbines and a charge air cooler were installed on the engine. The use of such a system required major changes in the design of the piston group and gas distribution mechanism. The connecting rods were taken from GE; other, more powerful pistons were developed by Toyota employees. The timing camshafts received greater lift and more room for the intake of the combustible mixture. This made it possible to obtain a power of 280 hp, forces and a torque of 432 Nm. There are many doubts about power. The fact is that a similar engine of the first generation, with a smaller volume, 1jz gte, has the same power of 280 hp. Apparently the producers decided to cheat. At that time there was a restriction on the production of engines in terms of power, up to 280 hp. In reality, the 2JZ GE at 6000 rpm produces no less than 300 hp.
In 1997, the sports version also received a phase regulator at the inlet. The manufacturer is silent about the increase in power, but the torque has increased significantly to 451 Nm.
2JZ FSE
The 2JZ FSE is an exact copy of the base engine with VVTi and a new high-pressure direct injection system. This modification is highly economical and environmentally friendly. But it has its drawbacks. First of all, this is the low operating life of the fuel injection pump, due to the low quality of domestic gasoline. But what can you do, such a price to pay for savings and the environment.
Tuning the 2JZ engine
The features of the engine are such that the unit is suitable for modification and this is known. The power plant is so popular in terms of conversion that it is used for installation on imported equipment and vehicles developed by our designers.
From a rational point of view, it is not advisable to modify the basic modification of the 2JZ GE. In terms of the ratio of invested funds and obtained characteristics, it is economically profitable to modify the 2jz gte modification. In a unit with a safety margin, there is potential for improvement. Technical indicators increase by one and a half times without serious intervention in the design.
- A simple way is to increase the charge air pressure. For these purposes, an improved model of the air intercooler is used, the cooler is enlarged, and oil cooling is used. They also install a higher-capacity fuel pump, a three-inch improved intake mechanism, 550 cc nozzles, a boost control device, and change the program. These manipulations increase the pressure to 1.3 bar. Since the power unit is popular for such applications and has been studied to the smallest detail, it is not difficult to find common operating patterns and programs. Thus, a ready-made circuit and firmware is simply purchased and installed. Such changes will make it possible to increase the parameters of the unit by one and a half times and achieve a power of 450 horsepower.
AEM Infinity Configurable Unit Control:
- Option to replace the turbine. These steps involve purchasing and installing a larger turbine compressor. In this case, there is no interference with the cylinder head, and the power indicator will be at the level of 750 horsepower. Such an improvement will require the installation of a high-performance fuel pump capable of delivering 400 liters per hour. They use improved 1000cc nozzles, new camshafts to achieve a phase indicator of 264, install reinforced springs on the valves and a new program.
Brian Crower Camshafts:
- Major design changes will be required to achieve the next level of power rating. Replace the piston group with forged parts. The cylinder head is being modified. Camshafts with changed phases 280 are purchased. A turbine and fuel mechanism components are selected. Actions are capable of achieving power of 1500 and even 2000 horsepower.
Greddy Turbo kit for modifying the unit:
Explanation of the name 2JZ GE
The marking of each engine carries encoded information about it. Knowing certain rules and encryption symbols, you can learn a lot about the power unit just by its name.
The general scheme looks like this: * ** ***. Numbers always take first place. It determines the generation of a certain family of motors. Next comes the paired designation of the family or series of internal combustion engines. The following symbols provide information about the design and characteristic features of the power unit. If we substitute all these definitions into the name diagram of our 2JZ GE engine, we get: the second generation of the power unit of the JZ family, with a DOHS type gas distribution system, which has extended valve timing and an electronically controlled injection power system.
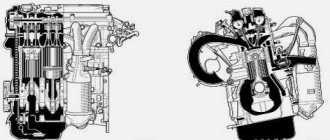
Description of the 2JZ GE design
The power unit in question is very similar to its brother of the first generation of JZ series engines. The 2JZ GE is the base unit of the second generation JZ engine family. The six cylinders of the engine are placed in one row and have a volume of 3000 cubic centimeters.
The motor housing, which is the cylinder block, is made of durable cast iron. Inside the block there are seven supports designed to install the crankshaft. The supports are closed with covers processed together with the supports. Therefore, they cannot be swapped. The crankshaft design consists of seven main and six connecting rod journals. At the toe of the crankshaft there is a pulley necessary to drive attachments.
The internal combustion engine oil system consists of:
- trochoid pump;
- pressure reducing valve;
- cleaning filters;
- electronics elements;
- filler neck and other small parts.
If you use motor lubricant recommended by the manufacturer and replace it in a timely manner, then the lubrication system performs its functions adequately and does not cause any problems to its owners.
Cooling system
Cooling system with forced circulation, closed type. The coolant circulates using an oil pump, also known as a pump. The pump is driven by one common belt.
ICE power system - injector. It consists of an electronic and mechanical part. The electronic part consists of sensors, wires and an ECU.
Mechanical, mostly represented by executive bodies, such as:
- injectors and fuel rail;
- fuel filters, tank and fuel lines;
- pressure regulator;
- The mechanical part is based on an electric fuel pump.
Electronics collects and processes information about the operation of the internal combustion engine, and also transmits control impulses to the executive bodies of the mechanical part.
cylinder head
The BC head is made of durable aluminum. It is common for all engine cylinders. In its upper part, camshafts are located. One shaft is responsible for the intake of the combustible mixture, the second for the exhaust gases. Each timing shaft has 12 valves; they do not have hydraulic compensators, so manual adjustment of the valves is periodically required.
This power unit was produced in two versions, the first version was produced from 1991 to 1996. In 1997, the 2JZ GE received a VVTi phase regulator and a DIS3 ignition system. Previously, this internal combustion engine used a contactless ignition system with a distributor.
Timing system
The timing system is driven by a toothed belt with a roller tensioner. In addition to the timing drive, the belt drives all attachments. Therefore he is very overloaded. Failure of the tensioner bearing can lead to premature belt breakage. The only good thing here is that the engine does not bend the valves.
The intake design on the engine has a variable geometry, also called a two-stage manifold.
As can be seen from the above, 2jz has many similar parts and mechanisms. What was said at the beginning of the chapter. If we look at the design of both engines in more detail, it becomes clear that the 2JZ was obtained by increasing the engine capacity to 3 liters. This was achieved by increasing the piston stroke. The result was a square engine. The cylinder diameter and piston stroke are the same and equal to 86 mm. Motors with such parameters are highly reliable and have a long service life. As a result of the change in the piston stroke length, the height of the block and the length of the connecting rod increased. Due to the greater length of the connecting rod, the load on the cylinder walls and piston group was reduced, which contributed to an increase in the service life of the internal combustion engine.
2JZ engine types
The 2JZ engine was produced in several modifications
- The 2JZ FSE series engine is an analogue of the previous 1JZ series engine. Produced from the beginning of the century until 2007. It has a power of 217 horses and a compression ratio of 11.3. Fuel is supplied to the cylinders by direct injection under pressure. This method of fuel supply practically does not improve technical characteristics, but has a positive effect on reducing fuel consumption and the content of harmful substances in the exhaust. The power of this modification is 217 horses. The 2JZ series engine was always equipped with an automatic transmission. It was installed on Toyota Brevis, Progres, Crown
- TOYOTA engine 2JZ GE series - the largest quantity of this modification was produced. It produces 220 horsepower at 6,000 rpm and 298 lb-ft of torque at 4,800 rpm. The injection of the fuel mixture is phased (sequential), that is, when the crankshaft is rotated 180°, a specific injector corresponding to the injection phase is activated. The classic order of operation of the TOYOTA engine cylinders of the 2JZ GE model is 1-4-3-2. The cylinder block is cast iron, the head is aluminum. At first, it was equipped with a standard DOHC timing system, with two camshafts and 4 valves per cylinder.
Subsequently, they began to install a system for regulating the gas distribution phases, DIS ignition, in which one ignition coil was intended for each pair of cylinders. This modification was designated 2JZ GTE VVTi.
Compared to 2JZ GE non VVT-i configurations, engines equipped with a variable valve timing system have improved traction performance at low speeds. The phases are controlled using a special clutch mounted on the camshaft.
As the engine speed of the 2JZ GTE increases, the VVT-i valve opens and the camshaft changes position in relation to the drive pulley and, accordingly, changing the position of the pushers, and they open the valves earlier and close later. The power of the 2JZ GE VVTi remains the same, but the torque increases as the speed increases.
The engine of the 2JZ GE model was equipped with TOYOTA Altezza, Aristo, Crown, MarkII, Chaser, Cresta, Progress, Soarer, SupraMKIV, Lexus 300 series IS, GS, SC cars. Currently, when converting cars, in some car service centers they install 2JZ on UAZ and GAZelle.
- The 2JZ engine of the GTE modification is perhaps the most advanced engine in the 2JZ line. In the nineties of the last century, TOYOTA Supra MK4 began to come off the assembly line, on which they began to install the 2JZ GTE engine with VVTi.
Typical malfunctions of 2JZ GE
The motor in question is very reliable, but, like any technology, it has weaknesses:
- The first place for problems should be attributed to electronic glitches. A large number of sensors and electronic devices lead to periodic engine malfunctions. What’s sad is the inability to figure it out on your own, without the necessary knowledge and equipment. For any electronic problems, contact a service center.
- The engine is afraid of frost and moisture, it is advisable to always have a set of spare spark plugs with you.
- A common problem is when the engine stalls or the speed fluctuates. The engine malfunctions due to the failure of the ignition coil, and the speed fluctuates due to a dirty throttle valve or a malfunction of the sensor responsible for idling the engine.
- After a decent mileage, the oil starts to bother me. This problem is standard for most engines. The fault may be caused by either stuck oil scraper rings or worn oil scraper seals.
- The VVTi system causes a lot of trouble. It is very demanding on the quality of motor lubrication. The design of the system is not reliable and rarely runs more than 150 thousand km.
- The tensioner belt bearing is often a source of concern. With excessive wear and increased play of the roller, the belt may burst prematurely. Therefore, the tensioner pulley must be changed together with the timing belt no later than after 100 thousand km.
- Malfunctions of the cooling system occur due to the fault of the water pump. Its design is not reliable and its service life is no more than 100 thousand km. Therefore, at the first signs of wear, it must be replaced.
Operational Maintenance
The 2JZ GE engine is considered more reliable than its older brother 1JZ GE. But all this is true with proper and timely maintenance.
Oil
First of all, an important step is to replace the engine lubricant. It must be carried out simultaneously with the oil filter. The manufacturer recommends performing this activity after 10 thousand km. But the engine breaks down less and runs longer if this period is halved.
Filters
The next important step is to replace the fuel and air filters. They can be replaced after 20 thousand kilometers.
timing belt
The manufacturer guarantees a service life of the timing belt of 100 thousand, km, mileage. But here you need to take into account its load. After all, it is common to all attachments. Therefore, it is better to install a new one after 60 thousand km. The tensioner pulley also needs to be replaced.
water pump
Also, after 60 thousand km, the coolant and pump should be updated. Its declared resource is 100 thousand km. But this does not always correspond to reality.
Adjustment of valves
Every 100 thousand km, the thermal clearance in the valves needs to be adjusted. This need arises due to the lack of hydraulic compensators.