In 2005, the EURO-4 environmental standard came into force in Russia, which seriously influenced car manufacturers. From now on, all vehicles intended for use in the Russian Federation must be equipped with special components that reduce the amount of harmful emissions into the atmosphere. Almost all modern cars with diesel engines are equipped with anti-particulate (or simply “particulate”) filters, which trap incompletely burned fuel components. It would seem that this is a very worthwhile thing, but many people bring their car to a service center to have it removed. For what?
How does a particle filter work?
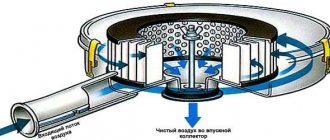
It is a metal cylinder filled with ceramic material. This material has a cellular structure - small soot particles are retained in the voids. When too much of it accumulates, a special unit in the engine activates the regeneration process and the filter is cleaned.
There is passive and active regeneration. In the first case, the soot burns out while driving due to a natural increase in temperature in the filter. To start the passive process, you need to drive at high speed and over a long distance.
Active regeneration is triggered if the unit cannot get rid of debris in the standard way (for example, when you drive only around town and slowly). In this case, additional fuel is supplied to the cylinder, which is mixed with soot and released into the catalyst. There the mixture burns, and black smoke comes out of the exhaust pipe. This does not go unnoticed - fuel consumption increases, idle speed increases.
This is what the filter looks like after a long drive on high-quality fuel.
Differences between a catalyst and a particulate filter
Presented in the table below:
| Characteristic | Catalytic converter | Particulate filter |
| engine's type | Suitable for cars with a gasoline engine or running on gas (propane, butane) | Used in diesel fueled vehicles |
| Cleans exhaust gases | From soot, carcinogenic substances | From soot. Some models have cells with a titanium catalyst that neutralizes harmful chemical compounds |
| Internal structure | It is represented by small cells, honeycombs, which accumulate the combustion products of gasoline and gas. They are made of metal or ceramic. | Like a labyrinth with many passages and pockets for collecting soot. |
| Operating principle | The surface of the cell is covered with a layer of catalyst (palladium, platinum), which at high temperatures converts carcinogenic combustion products into harmless ones using chemical reactions. This is where fumes and soot from smoke settle. | Accumulates solid combustion products of diesel fuel in pockets. In the presence of a catalyst, it converts combustion products harmful to humans into safe ones. |
| Width of internal cells, passages | Narrower | Wider |
| Life time | Depends on many indicators, but also on the material of manufacture. Iron - durable, resistant to temperature changes. Mileage – up to 200,000 km. But they are being replaced by ceramic ones, which are cheaper, fragile, and more compliant with exhaust gas cleaning standards. Mileage – 50,000-70,000 km. | It also depends on the operating conditions of the vehicle and varies from 50,000 to 120,000 km. |
| Cleaning the part | If the catalyst honeycombs are slightly clogged, cleaning without dismantling is possible using chemical liquids that are added to the fuel. If there is significant contamination, the part is dismantled, washed several times with special liquids, and cleaned with brushes. | Passive or active regeneration is used without removing the part from the exhaust manifold. The corresponding indicator will inform the driver about a filter malfunction. It can also be dismantled and washed with cleaning fluid. |
Why delete: pros and cons, consequences
Here are the undoubted advantages of removing the particulate filter:
- fuel consumption is reduced;
- you will no longer have to trigger regeneration by increasing the speed;
- the overall operating temperature of the engine decreases, which reduces the load on it;
- a clogged filter means a risk of power unit breakdown, no filter means no risk;
- there is no need to spend money on replacing this component in the future.
Note: there is an opinion that removing it gives an increase in engine power. Yes, this is true, but the difference is insignificant. The effect is achieved by accelerating the release of exhaust gases, which no longer have to overcome the resistance of the filter.
But here are the significant disadvantages:
- the car is void of warranty (if any);
- in some cases the amount of black smoke from the exhaust pipe increases;
- the load on the turbine increases, which somewhat reduces its service life;
- the car will not be able to be used in EU countries and other countries with strict emission quality requirements;
- procedures should only be performed by professionals - if a mistake is made, serious problems may arise that require expensive repairs.
Similarities between catalyst and particulate filter
Defined by the following characteristics:
- Designed to collect and neutralize combustion products of automobile fuel, both solid particles and carcinogenic exhaust gases (carbon oxides, nitrogen oxides, lead, etc.). More than 90% of these substances are converted into chemical compounds that are safe for humans (carbon dioxide, water, nitrogen).
- Protect the atmosphere from harmful substances contained in vehicle exhaust gases.
- They are part of the vehicle's exhaust manifold.
- According to modern European standards, all cars must be equipped with these parts, depending on the engine type.
- They have the shape of a cylinder or rectangular parallelepiped with inlet and outlet pipes. The top of the case is made of metal, but the internal filling is different.
- As the car is used, they become contaminated with fumes and soot . Require regular regeneration or complete replacement if necessary.
- Modern cars are equipped with special sensors that monitor the degree of contamination of the catalyst or filter.
Removal process: physical and software stages
The procedure consists of two stages - physical and software.
Physical is not difficult. Experts find the jar containing the filter and catalyst and cut it out. In some car models, you will have to remove the exhaust pipe to do this. You need to put something in place of the filter - these can be either ordinary metal plugs or flame arresters. Installing a flame arrester will slightly increase the life of the muffler. If the component is equipped with temperature sensors and carbon dioxide probes, they may need to be removed and installed in a blank to help avoid software errors.
Appearance of the removed particulate filter
Then you need to reprogram the engine block. If this is not done, the sensors will assume that the filter is constantly clogged. The result is a display of fault codes, and in some cases the emergency mode is even activated.
This part of the procedure is performed exclusively by service center experts. There are three ways to achieve this result.
- Install the firmware from the version of the car that does not have a particulate filter by default. The method is fraught with a decrease in functionality - for example, cruise control is disabled on a Honda CRV.
- Install firmware created by enthusiasts. It's a kind of lottery - you might get lucky, maybe you won't. The quality of firmware varies greatly.
- Install firmware from the vehicle manufacturer. The best option that carries virtually no risk.
In some Nissan, Toyota, Mazda and Ford models it is impossible to perform a standard flashing - you have to resort to emulation. A decoy device is installed that makes the unit think that the filter is in its place. The controller receives the signals and does not notice the removal of the component. However, this option has a drawback - the regeneration mode will still be activated, so fuel consumption will not decrease.
Easy breathing: why and how to remove the particulate filter
What is a particulate filter and how does it work?
In general, everything is clear from the name of this device: it is just a filter that retains soot.
It was invented for the sake of the environment, and therefore initially against the interests of car enthusiasts. Although it would be stupid to say that this is a completely useless thing. Of course this is not true. If you see a new diesel car, put your nose to the exhaust pipe. The absence of a black coating on your face interested in the experiment and a sour smell instead of the stench of burnt diesel fuel is the merit of the particulate filter. In general, this is where his merits end. It doesn’t add one hundred (or even five hundred) horsepower to the engine, and while it’s fresh, it doesn’t take it away. Problems begin when the filter becomes clogged with soot. But more on that later. First, let's see what it is from a technical point of view. Before us is a particulate filter of a Volkswagen Transporter T5. By the way, T5 is one of the leaders in terms of service traffic with the need to do something with the particulate filter. So, the filter has already been dismantled and lies in front of us. To the untrained eye it may seem like some kind of piece of hardware with wires. This is partly true, but let's look at its structure.
The catalyst and particulate filter are combined in one housing. If you look from the beginning of the release, then the catalyst will be the first on the path of exhaust gases, but inside a can with a larger diameter there is a particulate filter. But look: there are still some tubes and wires here! What it is?
Let's put the first wire aside: this is the oxygen sensor connector, which has nothing to do with the soot. But everything else is directly related to the filter. One of the connectors is a temperature sensor connector. There are two of them in total, one before the filter, the other after (we still have it on the outlet behind the filter, and its connector is not shown in the photo). Two more tubes belong to the differential pressure sensor. As is already clear from the name, it measures not just pressure, but the difference in pressure before and after the filter. In general, there is nothing more interesting in the filter. But let's see how it works.
The exhaust gases through the catalyst (in this model through the catalyst, but it happens that there is a filter, but there is no catalyst) enter the filter. The particulate filter itself consists of a large number of crypts - blind perforated gas channels. Passing through these channels, unburned carbon particles settle on their walls. It is the filter's job to retain these soot particles. The question arises: why do we need temperature sensors and a differential pressure sensor? These devices monitor the condition of the filter. The control unit contains the parameters of temperature and pressure difference at the inlet and outlet of the filter. If, for example, the inlet temperature is very high and the outlet temperature is too low, the ECU “understands” that something is wrong with the filter. It's the same with pressure. If it is too high at the inlet and too low at the outlet, the filter is clogged. Since a filter clogged with soot is no longer able to pass gases normally, the engine has a hard time. And in this case, the situation must be corrected. Here we come to the next issue, which cannot be skipped - regeneration of the particulate filter.
What is regeneration?
Regeneration is a filter self-cleaning procedure. It is performed differently, depending on the type of filter and directly on the algorithm for starting regeneration.
There are two types of particulate filters: DPF (such as on our experimental Transporter, these are usually found on German cars) and FAP (developed by the PSA concern, found on Peugeot, Citroen, can be found on Ford, Volvo and some other brands). The differences between DPF and FAP are small.
Let's look at how regeneration occurs in DPF filters.
The self-cleaning method is simple: everything that has settled in the filter channels is burned out. For this purpose, fuel is used, supplied either additionally through the engine injectors or through a separate special injector. At a temperature of 600-800 degrees, the soot in the filter burns out (though not always). FAP is distinguished by the presence of a special liquid, which is poured into a separate tank. This liquid is called Eolys, it acts as a catalyst that allows you to reduce the temperature of soot burning. In this system, regeneration takes place at 400-450 degrees.
Regeneration can be spontaneous or forced. In the first case, it is launched by the ECU based on the readings of the temperature and differential pressure sensors. In addition, the control unit can sometimes have a fuel consumption meter, and then regeneration can be started when the amount of fuel burned specified in the ECU is reached. All this is spontaneous regeneration. Forced, as the name suggests, is started manually to clean the filter, for example, in a service center.
Normally, regeneration, depending on the make of the car and its operating conditions, can take place every 1,500 - 5,000 kilometers. If it starts to run more often, then the filter will soon be finished: the procedure cannot ensure that the temperature and pressure difference parameters are within the norm. Most likely, the deposits in the filter have reached a stage where they can no longer be burned.
Articles / Practice Don't be so green: how to properly disable EGR While bourgeois courts are dealing with bourgeois engineers who do not want to make the car sufficiently environmentally friendly, our fellow citizens in orderly rows go to services to disable the system… 76675 3 9 08/14/2017
Services don’t really like to enable forced regeneration. Firstly, it can be simply dangerous: the temperature rises strongly, the car should be kept far from combustible and flammable materials. Secondly, if spontaneous regeneration does not help, then forced regeneration is also unlikely to give anything.
However, the ECU cannot always start regeneration. This procedure requires certain conditions: sufficiently long straight-line movement of the car at a relatively uniform high speed. In urban environments, sometimes such conditions simply do not exist. It is also highly recommended not to interrupt the regeneration that has begun. This is a big inconvenience. We arrived at work - and then regeneration was in progress. Sit and wait 10-15 minutes, or better yet, drive along the highway. And if you forcefully turn off the engine, regeneration will not complete. Therefore, after the subsequent launch and warm-up, the request will appear again and again until the procedure is completed correctly. And this is fuel consumption, up to 3-4 times more at idle and in heavy traffic. This is an increase in oil level. With all that it entails: from squeezing out the seals to tearing them apart. And always - a decrease in the lubricity of the oil. In especially severe cases, when regeneration does not proceed successfully and is not completed, errors on exceeding the limit of regeneration attempts or “regeneration is impossible, forced is required.” Or similar errors - they are different for different brands.
Perhaps this is all the main thing we need to know about regeneration. Let's move on to the next question: why the particulate filter fails.
What affects the life of the particulate filter?
Obviously, excess soot in the exhaust gases quickly “kills” the filter. There are only two reasons for the increase in soot amount: excess fuel and lack of air. The first is possible if there is a malfunction of the fuel equipment - for example, if an injector is leaking.
The lack of air can be caused by the owners themselves. The service specialists recalled a case when a car arrived at their place with a clogged air filter that had already begun to curl up inside the air duct. I don’t know how it’s possible not to love your car, but it turns out that this happens.
Sometimes there is not enough air due to charge air leaks or improper operation of the turbine.
And, of course, the quality of the fuel affects the smokiness.
However, even if everything is in order with the motor, over time the filter will fail due to natural wear and tear (critical clogging at high mileage). And even if the owner takes good care of the car, short winter trips from home to work or to the store also reduce the resource: the engine sometimes does not have time to warm up, and there is simply no time for regeneration to start. And the filter gradually becomes clogged with soot. Here the question arises: what to do with it?
What is good and what is bad
There are several ways to solve the problem, but only one is good.
- The first method is to replace the filter with a new one. OK, seems good. Only the original filter sometimes costs a hundred thousand rubles. So it’s a good solution, but only for Rockefeller’s son-in-law. Well, or for Rockefeller himself. In general, this is not for us.
- The second method is to install an analogue. This is one of the most unfortunate solutions to the issue. The fact is that the original filter is expensive for a reason; it uses precious metals, so its cost cannot be low. Those analogs or universal filters are not only useless, but also dangerous. You remember about regeneration, right? So, not all of them are able to survive this operation, and enough cases of fire have been recorded to give up the idea of installing some dubious nonsense instead of a filter. By the way, sometimes they suggest filling a jar with metal filings instead of a removed filter - they say it will be the same as the filter, but cheaper. This also applies to “dubious nonsense.” Such a home-made filter will not ensure that the filter sensors are within acceptable limits, and errors will occur again and again. And it’s better not to even imagine what could happen with such a packing and with the rest of the release when trying to regenerate.
- And finally, the third method is to physically remove the particulate filter and programmatically remove it from the system. This is the best way to get rid of the problem once and for all. There will be no fatal consequences, except that that same sourness in the exhaust smell will disappear. But I don’t think it’s scary.
How is the filter removed?
So, first it is removed from the car. In our case, this has already been done, and the filter is ready to survive all subsequent procedures. More precisely, it won’t survive, because now it will have to be removed from the jar.
To do this, cut the jar with a grinder. Now, on the one hand, we have a catalyst left, which we will not touch, and on the other, the filter itself. The latter is removed in two ways: pressed out entirely or hollowed out in pieces. Here we see the implementation of the second method in all its glory.
1 / 3
2 / 3
3 / 3
Let's take a look at the extracted fragment. You can see from the color that it was clogged at the beginning: closer to the start of production it is already almost black. However, soot, which can be collected with your finger both from the inner surface of the can itself and from the surface of the filter, speaks of the same thing.
1 / 5
2 / 5
3 / 5
4 / 5
5 / 5
Now the empty jar is brewed. This can be done with argon welding, or with a regular “semi-automatic”. The first method is more suitable for wealthy aesthetes, because it is long and expensive, but the seam turns out beautiful. But there is no need to weld with argon; semi-automatic welding is quite sufficient here. The main thing is to then treat the seam with an anti-corrosion agent.
1 / 3
2 / 3
3 / 3
That's it, the bank is collected. Some people prefer to install a downpipe instead - they say that an empty can will make unpleasant sounds. In fact, due to the design of the diesel engine, the sound of operation will not change, it will not become louder. Although, of course, if the client wants, then why not.
Now all that remains is to install the can in place and... start programming.
Articles / Practice I want to know everything: what is computer diagnostics and how it is carried out Many motorists know that computer diagnostics allows you to find out some parameters of the engine, find out what is wrong with it, and sometimes even correct the operation of the engine... 61082 14 5 01/16/2017
As we remember, there is a set of sensors that monitor the operation of the filter. Physically removing the filter will change their readings, which can confuse the ECU. For example, the absence of a difference in temperature or pressure at the inlet and outlet will make him doubt the correct operation of the sensors or filter. And then the error will appear again, and perhaps emergency mode too.
And don't forget about regeneration. Even if the ECU does not start it based on sensor readings, it is quite capable of doing this based on the fuel consumed. Since after such “regeneration” of an empty can nothing in the readings will change, the control unit can run it endlessly. In the end, this will again lead to an error at best. At worst, the release will be thoroughly “fried” at high temperatures, which is also not very good and even dangerous. Finally, do not forget that additional fuel is needed for regeneration. The easiest consequence is significantly increased fuel consumption. But it’s better not to deal with heavy things at all. It occurs when diesel fuel begins to enter the oil, as a result of which its concentration in the crankcase increases so much that the oil no longer becomes oil, but a completely suitable fuel for diesel engines. As you know, a diesel engine does not need a spark to ignite, so if the engine starts running on a mixture of oil and fuel from the crankcase, it will not be possible to stop it by turning off the ignition. And the engine will start working “in a rush”. The spectacle is terrible, and for the engine itself, this mode usually ends in exactly the same blowout.
But it is worth noting that the main reason for going into overdrive is not the removal of the particulate filter, but its malfunction, due to which frequent attempts at regeneration lead to an increase in the oil level. Spread can also occur if the filter is not removed. However, this is a topic for another discussion. For now, let’s just say that such an outcome is possible if the work is carried out incorrectly, and monitoring the oil level can reduce the risk. If it is higher than normal, this is a cause for concern, and it is better not to start the engine at all.
In a word, it is simply necessary to disable the filter in the program. It is best when it is possible to simply turn off this system. If there is no switch, then there are other methods that we will not talk about - a professional secret.
You also need to remove particulate filter errors, but not affect the entire diagnostic system. Some not-so-best “specialists” screw up all the diagnostics, after which the car owner then drives to other service stations, where innocent servicemen dance with a tambourine around the car, which says that everything is OK in its life, but at the same time does not drive .
Instead of a conclusion
As you already understand, removing the particulate filter is practically the only acceptable way to get rid of the problem with this device. And on the one hand, it is not so complicated, but on the other, the cost of an error can be very high.
And certainly removal will be cheaper than installing a new filter (we won’t talk about analogues, everything has already been said above). True, it’s unlikely that anyone will do this job well even for three kopecks, so you need to choose a service carefully. So that later it won’t be excruciatingly painful...
Another nice bonus: on engines with a particulate filter, it is necessary to use a special oil, which is called “For engines equipped with a particulate filter.” It is significantly more expensive than usual. But after removal, you can pour the usual one.
We thank you for your help in preparing the material
(St. Petersburg, Khimikov St., 2, (812) 385-50-70)
Survey
Have you already removed the particulate filter?
Your voice
Total votes:
Is it possible to remove it yourself?
Yes, you can, but it is highly not recommended! The likelihood of breaking something is very high. Remember - you act at your own peril and risk!
- First you need to disconnect the sensors and cut the exhaust pipe, which is located after the filter, with a grinder.
- Then unscrew the bolts from the engine side, cut and open the filter casing.
- Take out the device itself. It may be necessary to knock out individual segments.
- Weld the housing and install it in place. Connect the sensors.
Diesel particulate filter housing without filter itself
After this, all that remains is to download the new firmware.
Passive regeneration
I told you about the combination for a reason. WE already understood that sooner or later regeneration is needed, and it is the catalyst that contributes to this process.
The thing is that the neutralizer is capable of heating the particulate filter to high temperatures, about 300 - 500 degrees. In this case, soot particles oxidize and burn.
If we describe the process chemically, we get:
— Nitrogen compounds react with oxygen in the catalyst - nitrogen dioxide is formed
— Nitrogen dioxide reacts with soot to form nitrogen oxide and carbon monoxide
— Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide react with oxygen to form nitrogen dioxide and carbon dioxide.
Thus, the particulate filter is cleared of soot. Here's a small diagram.
However, if you do not drive enough, frequent short trips, then the particles may not burn, they simply do not have enough temperature. Then the car may require forced regeneration - there is a special function on diesel engines.
This procedure occurs at high speeds and the filter heats up to 600 - 650 degrees Celsius. All the chemical reactions that I described above take place in it, and the cells are cleaned.
The system is fully automatic and does not require human presence. The car reads information from sensors (air, exhaust gas temperature before the filter, after the filter and, most importantly, the pressure of the particulate filter). When (during cleaning) the pressure is restored, the system automatically ends - this indicates that regeneration is complete.