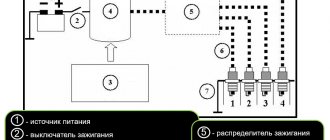
What is a distributor and what is it for?
According to its functional purpose, the distributor is a switch-distributor in the electrical system of the car. It provides regulation of the voltage supply from the battery to the spark plugs and the moment of spark formation. The specificity of multi-cylinder engines is that ignition of the fuel compressed by the piston in each cylinder occurs at different times. Therefore, it is very important to ensure the accuracy of the ignition mechanism. This function is performed by the distributor.
If we consider the operation of this device in more detail, we can highlight the following tasks:
- initiation of spark formation as a result of opening electrical contacts;
- transferring the voltage generated in the circuit to a suitable spark plug;
- adjusting the moment of sparking in accordance with the driving mode of the car and the characteristics of gasoline;
- accumulation of reserve energy reserves on a special reel.
As you can see, this module has wide functionality and is of great importance for ensuring engine performance.
Possible breaker failures and their symptoms
Repair of distributors in the automotive industry is not carried out so often, which is due to the good reliability of this unit. Of course, there is no escape from breakdowns, but few people suffer from them. It is not so difficult to identify that it was the distributor that began to “pierce” the electric charge or grabbed another “sore”. The symptoms of malfunctions of the distributor-interrupter are specific and manifest themselves in the incorrect organization of the main functions of the device.
More precisely, possible replacement or adjustment of the distributor may be necessary if the following symptoms occur:
- the spark is gone;
- the ignition operation is upset;
- the battery stopped charging while the machine was running (not on all models);
- the car began to jerk while driving;
- Unburnt gasoline drips from the exhaust pipe.
All this may indicate that one of the components of the distributor has begun to function in a clear manner and requires, at a minimum, careful adjustment. If the adjustment was useless, then you will have to think about a full repair of the distributor with the possibility of replacing it.
As for specific faults, they are often represented by the following list:
- The distributor drive (rotor) has worn out or burned out. The malfunction is diagnosed through a detailed examination of the rotor and experimental verification of its correct operation. If an element breaks, it may be necessary to either install a new drive or completely replace the distributor;
- The network has broken through. This, by the way, can happen in any component of the distributor. Most often, the high-voltage wires that extend to the spark plugs from the distributor cover are affected. Other elements of the system (small wires, connectors of distributor parts, contacts, etc.) break down noticeably less often. Checking for this malfunction is carried out using a regular “ring”;
- The seals are worn out. Perhaps this is a rather rare breakdown with characteristic symptoms. To be more precise, we are talking about a general disorder of the ignition and untimely formation of a spark. For repairs, it is necessary to replace the distributor seals, and it is worth replacing not only faulty elements, but also those that work correctly, so to speak, for prevention;
- The distributor slider or the sensor responsible for distributing the charge between the spark plugs has broken. Characteristic signs of this breakdown are the inability to correctly configure the distributor or its complete failure to operate. The malfunction is eliminated by replacing the slider or sensor;
- The ignition coil has failed. This failure is characterized by either absent or incorrect sparking. Repair is carried out by replacing the burnt coil with a new one.
Other distributor malfunctions appear much less frequently. In any case, repairing this unit is not an easy task, so not a single motorist will be able to figure it out right away. To understand the whole essence of repairing a distributor, it is important to fully understand the principle of its operation and constantly practice. If you don’t want to learn all the basics of repair work, it’s better to entrust the repair to a professional who specializes in repairing car ignition systems.
How the distributor works and how it works
This mechanism includes many components for various purposes. The main ones among them are the following:
- rotor - provides traction with the rotating camshaft gears;
- breaker - a module with a cam clutch, which is connected by special contacts to a centrifugal clutch;
- ignition coil equipped with double winding;
- a runner rotating simultaneously with the shaft, located on the distributor cover and transmitting voltage to the spark plug;
- a cover through which current-carrying wires extend to the spark plugs;
- a vacuum-type regulator that ensures the operation of the ignition advance function;
- non-contact type equipment - used on the most modern models of distributors.
In addition, many devices are equipped with an octane corrector, which changes the operating mode of the distributor in accordance with the quality of gasoline.
The operating principle of the distributor may have individual characteristics depending on the specific car model. However, the general specifics of the action of this element are almost the same in all engine models. When the crankshaft is cranked, the pistons act on the distributor cam, as a result of which its contacts open. This leads to the emergence of high voltage, which is transmitted through a special slider to one or another spark plug. This process is continuously repeated while the engine is running, only the spark plugs to which voltage is applied change.
A clear relationship with the crankshaft and pistons ensures high precision of the distributor, which, in turn, increases the efficiency of the entire car engine.
Distributor repair
Repairing a distributor is a rather complicated procedure, requiring the repairman to know the structure of the unit and the electronics in general. The complexity of the distributor design, the difficult connection diagram and the lack of electrician training among motorists reduce the possibility of its own repair to almost zero. It is based on this that garage technicians often prefer to completely replace a faulty distributor.
Often this approach is completely justified, as it significantly saves motorists’ time. However, when deciding to replace the distributor, you need:
- firstly, try to diagnose the exact malfunction of the device (for example, incorrect operation of high-voltage wires does not require a complete replacement of the distributor, because it is much easier and cheaper to simply change the wiring);
- secondly, consult with a specialist in the field of repairing ignition systems and make sure that it will be cheaper to replace the distributor rather than have it repaired by an electrician.
Let's say the need to install a new distributor is confirmed. In such a situation, it is quite advisable to save some money and carry out the replacement yourself. To organize the repair you will need:
- set of wrenches;
- spark plug key;
- screwdriver;
- rags;
- new distributor.
The repair procedure is as follows:
- First of all, you need to unscrew the spark plug of the first cylinder and determine where the distributor is located specifically on your model;
- Next, we proceed to align the motor shafts in the desired position. For this:
- jack up the front wheel on the right;
- close the spark plug hole with your finger;
- turn the wheel until air begins to press on your finger;
- Next, we gain access to the timing belt, remove the crankshaft flywheel plug and align the marks of the shaft pulley and the engine block.
- We remove the distributor. This is where it is extremely important to remember the connection diagram for high-voltage wires. It's best to take a couple of photos of the attached distributor and label each attached spark plug wire accordingly for identification. After the connection order has been successfully fixed, you can remove the part. To do this, there is a distributor cover, the spark plug wires and fasteners are unscrewed from it, after which the unit is successfully removed;
- Then the most important part begins - installing the distributor. The node is connected in the following order:
- the distributor is installed in the vehicle structure in the same way as the old unit;
- the gaps of the mechanical slider located under the distributor cover are set (if required, how to adjust the distributor - we’ll talk below);
- spark plug wires are mounted to it;
- low voltage wire is connected;
- the ignition timing is adjusted (again, if required).
Note! If for some reason you have forgotten the location of the high-voltage wires, then they are connected in the order of operation of the cylinders (1-3-4-2). The corresponding connection diagram marks are on the distributor cover.
In general, there are no particular difficulties in installing a new distributor. It is much more difficult to understand how to check the distributor for a particular malfunction, because this requires much more knowledge than is required to implement the process described above.
Important characteristics of the distributor
The concepts of UZSK and UOZ help to more accurately understand the operating principle of the distributor.
UZSK is the angle of the closed state of contacts. It characterizes the closing time of the contacts included in the distributor design. In other words, the UZSK value determines the energy that is accumulated on the ignition coil after the spark is formed. In addition, this parameter determines how much electricity will be supplied to generate a spark on the spark plug.
If the distance between the contacts is too small, a sufficient amount of energy will not accumulate, causing the motor to operate unstably. If the defect is not eliminated, the rupture time will constantly decrease and the engine efficiency will decrease.
To configure the UZSK, in some cases the distributor is adjusted. This is due to the fact that for each motor the angle of the closed state of the contacts is determined individually.
UOS is the ignition timing angle. The moment of ignition of the fuel mixture in the cylinders directly depends on this value. The essence of ignition timing is that for efficient engine operation, gasoline ignites earlier than the piston reaches the top position - this is necessary due to the fact that the fuel assembly does not burn out at once. Depending on the operating mode of the engine and driving style, the OZ changes - accordingly, voltage must be supplied to the spark plugs at different times. And this opportunity is precisely what the distributor provides - its design has a special centrifugal-type regulator, which is responsible for optimizing the period of time during which the fuel-air mixture is burned.
Ignition distributor device
The non-contact type distributor device includes a set of certain elements:
1. Rotor or so-called distributor drive. Which is often represented by a splined shaft that engages with a camshaft gear or a shaft. The difference depends on the design of the motor.
2. Ignition coil, which has a double factory winding.
3. There is also a breaker; there is a cam clutch, as well as a centrifugal clutch and a contact group.
4. A slider that is attached directly to the clutch shaft and rotates when working with it. There is also a distributor cap. It is from this that the high-voltage wiring goes to all the spark plugs.
5. Vacuum-type ignition timing advance regulator. A capacitor is also included in its circuit. It functions as a “lightning rod”, since it is it that takes on a little charge, protecting the group of contacts from melting under the influence of high voltage.
6. Depending on the type of distributor, an octane corrector can also be installed in the lower part of the structure, which controls the speed of revolutions, depending on the brand of gasoline. Have you ever heard of the concept of octane number? This is what it is, only in the classic versions its correction is done with your own hands.
Common distributor malfunctions
The complex design and abundance of small elements cause a wide variety of problems that can arise in the operation of the distributor. Let's look at the most common of them:
- damage to the cover - manifested by instability of the engine, its jerking, drops in speed, and in wet weather - a stalling engine. Problems can be mechanical (cracks, chips, moisture getting inside the cover) or chemical (oxidation of contacts hidden under the cover);
- burnout of the slider fuse - as a result, it becomes impossible to transfer electricity to the ignition coil;
- failure of the capacitor, leading to the supply of excess voltage to the spark plugs;
- violation of the rotation geometry of the shaft, its jamming or deflection, damage to the distributor body are the result of serious mechanical damage and require complete replacement of the failed part.
- vacuum ignition regulator - becomes unusable when the diaphragm ruptures or becomes dirty.
Please note that these are only the most common faults - in practice, you may encounter other problems that only a specialist can identify.
Subtleties of work
Among other things, it is worth knowing important subtleties in the work that the distributor provides. So, for example, it is very important to take into account the fact that the vacuum regulator is inextricably linked with the intake manifold and tube, the so-called throttle space.
This means that it is sensitive to the mode of air supply to the engine and changes the ignition timing itself. The spark is supplied to the cylinder a little earlier and ahead of schedule. In this case, detonation will occur at the moment of gasoline injection into the combustion chamber, thereby pushing the piston down. Of course, Uzbek indicators will change.
Coil comparison
When it comes to the differences between a coil of a contact ignition system and a contactless one, everyone immediately pays attention to the markings. Indeed, from it you can immediately find out for which system the coil is used. However, we are interested in the external and technical differences of the coils, so we will present the differences in these parameters:
- The coil in the contact ignition system has a larger number of turns in the primary winding. This change directly affects the resistance and the amount of current passing. In addition, limiting the current on the contacts is related to safety (so that the contacts do not burn).
- The coil breaker contacts in a contactless ignition system do not become dirty or burn. This reliability allows for one important advantage: setting the ignition timing does not take much time.
- The coil in a contactless ignition system is more powerful and reliable. This advantage is directly related to the fact that the most contactless ignition system is a more reliable option. Therefore, in such a system, the coil provides greater engine power.
The combustible mixture supplied to the engine cylinders is ignited by a spark that jumps at the right moment between the electrodes of the spark plug. Such a powerful spark discharge is created by a high voltage electrical pulse. To understand how this is implemented in a car, it is worth studying the design and operating principle of the ignition coil, which plays a major role in this process.
Design and principle of operation
The structure of the ignition system element in question looks like this:
- the metal core is connected to the main contact connected to the central electrode of the spark plug through a high-voltage wire;
- a secondary winding is made around the core, consisting of a large number of turns of a thin copper conductor with insulation;
- on top of the secondary winding there is a layer of dielectric and a small number of turns of thick copper wire - the primary winding;
- the core with windings is placed inside a sealed plastic case filled with transformer oil;
- the windings are connected in a series circuit, 2 connected ends are connected to one external terminal, the other two are connected to separate contacts.
Note. The characteristics of the windings - the thickness of the wire and the number of turns differ depending on the make and model of the car. The number of turns of the primary winding rarely exceeds 150, the secondary - 30 thousand.
A high-voltage wire is connected to the central terminal of the coil, going to the ignition distributor or directly to the spark plug. The remaining contacts are connected to the negative terminal of the battery (ground) and the positive wire of the low voltage circuit.
The operating principle of a boost coil is based on the effect of electromagnetic induction - creating a constant field around the core. How sparking is implemented in practice:
- After turning on the ignition, a voltage of 12 V from the battery is supplied to the primary winding. An electromagnetic field appears, amplified by the iron core.
- When the starter cranks the crankshaft and any piston reaches TDC, the electronics, through a relay, breaks the low-voltage power circuit.
- A circuit break provokes the formation of a short-term pulse inside the second multi-turn winding. At this moment, the voltage on the ignition coil reaches 20 thousand volts or more.
- The current is transmitted to the spark plug, a spark discharge occurs and the fuel mixture is ignited. The engine starts.