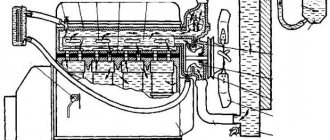
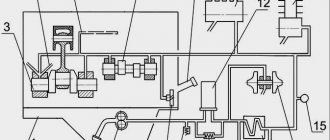
From the secondary winding of the ignition coil, a high voltage is supplied to the central electrode of the distributor, which is transmitted using a slider to the side electrodes of the distributor. The speed of rotation of the slider is equal to the speed of rotation of the camshaft and relates to crankshaft revolutions in a ratio of 1:2. The side electrodes of the distributor cover are connected to the spark plugs via high-voltage wires. The main disadvantage of this system is the difficulty in ensuring timely supply of voltage to the spark plugs at different engine speeds and operating modes. This problem was partially solved by the use of a centrifugal and vacuum ignition timing regulator, and subsequently by the use of electronic units, but did not completely solve the problem. In addition, the system has many connections and wearing contacts, which significantly reduces reliability.
Typical ignition system
Ignition system components
On the technical side, the ignition system is part of the engine electrical equipment complex.
Structurally, it consists of the following elements:
- Battery or other power source. It supplies a low voltage of 12 volts to the network.
- Switch. When you turn the key, the switch closes and low voltage flows into the energy storage device.
- Energy storage. There are two types: inductive (a transformer-type ignition coil that converts low voltage into high voltage up to 30 thousand volts) and capacitive (capacitor).
- Energy storage and distribution control unit. Depending on the type of ignition system, this may be a chopper, a transistor switch, or an ECU (electronic control unit).
- Distributor. This unit can be mechanical or electronic. It supplies certain candles with energy at a given point in time.
- High voltage circuit wires. They supply high voltage to the electrodes of the spark plugs.
- Spark plug.
The operation of the ignition system is based on the following principle: when low-voltage voltage is supplied to the network, energy is accumulated and converted, which is then distributed among the spark plugs, on the electrodes of which a spark is formed, provoking the ignition of the air-fuel mixture.
General device
As already mentioned: a car ignition system is found in any car. This is true, but not entirely. There are two fundamentally different types of operation of gasoline engines: carburetor and injection. The injector has a combined injection and ignition system, in which everything is controlled by the ECM (electronic engine control system). We are interested in a more outdated, but stably existing and not going to disappear conventional, non-combined injection and ignition system, in which everything is done separately and has its own functions.
Fundamentally, any ignition on a carburetor car consists of the following elements:
- AKB (rechargeable battery).
- Coil.
- Distributor.
- Candles.
- Switch.
- High voltage wires.
Depending on the principle of operation, elements will be added, but all of the above are required. By the way, we are talking about elements that are typical for the VAZ family of cars, but also on old foreign cars, such as, for example, the Opel Cadett, everything works extremely similarly and has no differences, even down to the identical appearance.
The principle of operation of all these systems is that electricity is taken from the battery and supplied to a coil, which transforms the 12V taken from the battery into 20 - 30 thousand volts. Next, the ignition distributor distributes the resulting electricity among the engine cylinders, where the mixture of gasoline and air ignites. It seems that everything is simple, however, let’s look at each individual type of this system.
Features of the contact system
Historically, the contact system was one of the first and today it can only be found on older car models. In such designs, the formation of high voltage occurs in a transformer coil, and its distribution to the spark plugs is carried out mechanically - by closing and opening the circuit contacts with a breaker-distributor.
Contact ignition system device
In addition to the main elements, such systems include a centrifugal ignition timing regulator, which is necessary to convert the ignition timing relative to the crankshaft speed. It consists of two weights acting on a mobile plate in contact with the cam mechanism of the breaker.
Ignition timing is a certain position of the crankshaft at which high voltage is supplied to the spark plugs. In this mode, ignition occurs until the piston reaches top dead center, which ensures the most efficient combustion of the air-fuel mixture.
Also in the contact circuits, a vacuum ignition timing regulator is used, which changes the timing angle according to the operating mode (load) of the engine. It is connected to the cavity located behind the throttle valve, and when you press the gas pedal, it changes the advance angle depending on the magnitude of the vacuum.
When the contacts are closed, a low voltage is applied to the primary winding of the coil, where energy is accumulated and at the moment the contact opens, a high voltage is formed on the secondary winding. The energy then goes to the ignition distributor and then to the corresponding spark plug.
If the load on the power unit increases, the rotation speed of the chopper-distributor shaft increases, and the weights of the centrifugal regulator diverge, changing the position of the plate. This promotes earlier opening of contacts, which increases the advance angle. When the load on the engine decreases, the reverse process occurs. What are the differences between a contact-transistor ignition system? The next generation of the ignition system was a contact-transistor one, which involves installing a transistor switch coil in the primary circuit. It allows you to reduce the current in the low voltage winding, which increases the service life of the contacts.
Armored wires
The contact ignition system and other types of ignition systems are equipped with armored wires that can pass high-voltage voltage through them without damage or loss. In particular, it is an electrical flexible wire with one copper core and multilayer insulation.
In this case, the contact wire is made in the form of a spiral, which eliminates radio interference. As a rule, these wires are installed on spark plugs. With prolonged use, the insulation of the wires may develop microcracks, through which high-value pulses can be lost.
Contact-transistor ignition system
The next generation of the ignition system was a contact-transistor one, which involved installing a transistor switch coil in the primary circuit. It allows you to reduce the current in the low voltage winding, which increases the service life of the contacts.
ignition distribution systems appeared , that is, not moving. This became possible thanks to the switching of high-voltage coils by electronic units. This system completely adjusts the moment of spark formation depending on the speed and load on the engine. There are several schemes for implementing static distribution. In the first option, there are two cylinders with ignition timing shifted by 360 degrees. the crankshaft simultaneously receives high voltage from the ignition coil. In this case, sparking occurs simultaneously in two cylinders. Since the spark plugs are connected in series to the secondary winding of the ignition coil, the spark discharge on the spark plugs will be the same discharge in the series-connected spark gaps, and will flow in the same direction. Consequently, if on one spark plug of a pair the spark discharge arc is directed from the central electrode to the side electrode, then on the other spark plug, on the contrary, from the side to the central one. At the same time, the spark energy will be different. This is due to the environment in which the spark was generated. When one spark plug is in the cylinder where the compression stroke occurs, the other is in the cylinder where the end of the exhaust stroke occurs. High pressure is applied to one of the spark plugs and it ignites the mixture; the spark on the other spark plug jumps to idle. The energy of a spark discharge that does not ignite the mixture is the same as the total loss of current in the spark gaps between the rotor and the side contacts with high-voltage ignition distribution. The picture changes to the opposite after one beat. This method uses one coil in a two-cylinder engine and two coils in a four-cylinder engine, working in pairs 1 - 4 and 2 - 3 cylinders. The coils are controlled by a two-channel switch at the command of the controller. Often the coil control key is built into the controller.
Contact-transistor ignition system
Due to the installation of a transistor, the voltage supplied to the spark plugs is 30% greater than in a classic contact system. The gap between the electrodes and, as a consequence, the length of the spark is also larger, which means that the contact area with the air-fuel mixture also increases, which contributes to its complete combustion. In a contact-transistor ignition system, the breaker acts not on the coil, but on the switch.
When you turn the key, two types of currents begin to pass through the transistor:
- management;
- main current of the primary winding.
When the contacts open, the control circuit current disappears and the transistor turns off, preventing primary current from flowing. At this moment, the magnetic field forms a high voltage on the secondary winding. To speed up the turn-off of the transistor, a pulse transformer can be installed in a contact ignition system of this type.
Operating principle of the contactless system
An evolutionary continuation of the transistor-contact system is contactless ignition. In such designs, a special pulse sensor is installed instead of a breaker. This makes it possible to increase the service life of the ignition system due to the absence of malfunctions associated with the breaker contacts.
The sensor generates low voltage electrical pulses. It comes in three types:
- Hall Sensor . The design of such a sensor includes a permanent magnet and a semiconductor wafer equipped with a microcircuit.
- Inductive . The principle of its operation is based on changing the induction value of the sensing element depending on the size of the gap between the sensor and a moving plate rotor acting on the magnetic field.
- Optical . It consists of an LED, a phototransistor and a matching chip. When light from the diode hits the phototransistor, the sensor supplies ground (minus power) to the switch. Blocking the flow of light provokes the disappearance of the current in the coil and contributes to the further formation of a spark.
Structurally, the pulse sensor is integrated into the distributor and is regulated by the engine crankshaft rotation mode. Interruption of the current in the primary winding of the ignition coil of the contactless system is also carried out by a transistor switch, but responding to sensor signals. When the crankshaft rotates, the sensor sends voltage pulses to the switch. The latter, accordingly, generates current pulses in the low voltage winding of the coil. When no current flows, a high voltage appears on the secondary winding, which is transmitted to the distributor and then through high-voltage wires to the desired spark plug. Changing the advance angle in a contactless ignition system is also performed by centrifugal and vacuum regulators.
Malfunctions of the contactless ignition system: signs and causes
Like any other solution, a contactless ignition system has both pros and cons. Among the main disadvantages, one can highlight the fact that the reliability of some components (especially if cheap analogues are used) may be low.
Of course, malfunctions of the ignition system immediately affect the operation of the engine. It is important to pay attention to the following signs:
- Starting the engine is difficult or impossible (problems with spark plugs, explosive wires, ignition coil, etc.);
- Also, a malfunction in the ignition system is indicated by the fact that the engine is unstable at idle. This may be caused by breakdowns in the cover of the sensor-distributor, malfunctions of the transistor switch or the sensor-distributor itself;
- High gasoline consumption, drop in engine power, misfires, etc. were noted. In this case, there may be a breakdown of the centrifugal ignition timing regulator, malfunction of the vacuum ignition timing regulator, etc.
We also add that the contactless system traditionally has weaknesses. This fully applies to switches, especially old ones. The coil may also be failing.
We also recommend reading the article on how to determine whether the ignition is early or late. From this article you will learn by what signs you can understand that the ignition is earlier or later, what symptoms indicate malfunctions in the ignition system, etc.
In practice, you need to purchase a modified switch, as well as a better foreign-made product. This solution lasts longer, but its service life, unfortunately, in some cases may not be long.
In any case, malfunctions of the contactless ignition system can also be associated with the spark plugs; there are violations in the area of connections of low-voltage and high-voltage circuits, broken wires, oxidation of contacts, and poor connections. For more advanced electronic systems, you can also add problems with the ECU, failure of individual sensors.
One way or another, it is important to understand that the use of low-quality ignition system elements may well lead to problems. For example, installing unsuitable or problematic spark plugs, not replacing them in a timely manner, using cheap ignition coils or faulty high-voltage wires can affect the serviceability and condition of other elements of the system and the operation of the internal combustion engine as a whole.
It is also impossible to exclude the influence of other factors (damage, ingress of liquids, oxidation, etc.). For example, when washing an engine, the elements of the ignition system must be separately insulated; active accumulation of moisture, etc., is not allowed during vehicle operation.
Electronic and microprocessor systems
The most modern system is considered to be electronic. It has no mechanical contacts, and therefore can also be called contactless. Electronic ignition is part of the engine management system.
In this system there is practically no voltage loss, as in the previous ones, and the operation of each spark plug does not depend on the work of other spark plugs, as in the first and second variants of static ignition. In addition, in this case, the ignition timing is precisely adjusted directly in each cylinder, which allows complete combustion of fuel, thereby reducing the emission of harmful substances into the atmosphere.
Electronic ignition system
There are two types of electronic contactless ignition systems:
- With distributor . In such a circuit, a mechanical ignition distributor is used, which supplies high voltage to a given spark plug.
- Direct ignition . With this scheme, high voltage is supplied to the spark plug electrodes directly from the coil.
In addition to the basic elements, the electronic ignition system includes:
- Input sensors . They record data about the current operating mode of the motor and supply it in the form of electronic signals to the control unit.
- Electronic control unit . It processes the signals and transmits the appropriate commands to the igniter.
- Actuator , or igniter. In fact, it is a transistor board that, in open mode, provides voltage supply to the primary winding, and in closed mode, cuts off and generates high voltage on the secondary winding of the coil.
Such systems can be equipped with one common (in designs with a distributor), individual (when energy is supplied directly to the spark plug) or dual ignition coils.
A type of electronic system is a microprocessor. It uses a whole complex of sensors, the signals of which are processed by the ECU. It calculates the optimal operating mode of the system at a given point in time. The advantages of this design are reduced fuel consumption and improved dynamic characteristics of the vehicle.