1200 rub. for the photo report
We pay for photo reports on car repairs. Earnings from 10,000 rubles/month.
Write:
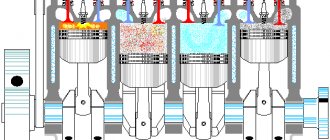
Error code P0300 indicates a violation of the ignition order , which stands for random multiple misfires of the cylinders ; in English, the diagnostic tool displays: “Random cylinder misfire detection system.” If a misfire is detected in a specific cylinder, then the last digit “P030x” will change to 1, 2, 3, 4 and so on up to 6 or even 12, depending on which particular “pot” the misfire is in. So error P0300 is derived from errors such as P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304. Most often they occur due to a lack of spark, a fuel supply failure or problems with the exhaust gases.
Let's look at the list of possible causes of misfires, why error p0301, error p0302, error p0303, error p0304 or others of this kind appears, the consequences and methods of elimination, in more detail.
Consequences of error P0300
If a misfire occurs in the engine in the exhaust pipe the level of exhaust gas toxicity increases , which, in turn, can also lead to an increase in the temperature in the catalyst, which causes its damage (the honeycombs melt because the temperature exceeds the threshold of 800 °C ). On some cars, in order to reduce the burnout of fuel in the catalytic converter and, consequently, the level of toxicity, the ECM unit monitors the frequency of misfires using crankshaft and camshaft sensors and, in addition, it registers error p0300, signaling a checkengine light can also , in which the gap was discovered. It is worth mentioning that most often, for some reason, the owners of cars such as Lacetti, Matiz, Priora and other injection VAZs, as well as Opel, Nissan, Kia cars, are interested in the reasons for the occurrence of this error.
What does P0363 mean?
To detect misfires, the PCM uses data from the crankshaft and camshaft position sensors and also takes into account the number of engine revolutions per minute. If the PCM detects that the camshaft or crankshaft position has changed and is abnormal under current conditions, or that the actual engine speed is not at the required value, it will assume that one of the engine cylinders is misfiring. In this case, the PCM will cut off fuel to that cylinder and store P0363.
When does error code P0300 pop up?
Note that error code P0300 is recorded by the control unit only when misfires are detected in several cylinders simultaneously , since a misfire in one of them is recorded after two repetitions in a row, and the rotation speed of the CV is important. At idle, the error is stored in memory after 3.5 minutes of engine operation, and at speeds above 2 thousand - a little more than one minute. threshold for registering a DTC in the ECM memory is more than 3.25% of missed flashes per 1000 revolutions. If misfires are detected only in a certain cylinder, then not error P0300 is generated, but another one, with the serial number of the combustion chamber of the internal combustion engine.
When is misfire possible?
There are many reasons for misfire. They can be roughly classified into three groups:
- no spark;
- unbalanced fuel mixture;
- low compression.
- Lack of spark may be due to low or no voltage at the spark plug, damaged high-voltage cable, broken distributor cap, worn or severely clogged spark plugs, or a faulty ignition coil or module. In the latter case, there will be not only a misfire in cylinder 1, but also in all others.
- An unbalanced mixture does not ignite well, which can lead to misfire. Violation of the quality of the combustible mixture mainly occurs when the carburetor is incorrectly adjusted, filters or jets are clogged, the pump fails, and so on.
- Insufficient compression most often manifests itself when the head gasket burns out, or the exhaust valve wears out or burns out. In this case, the combustible mixture will not ignite in the cylinder. Sometimes there may be no spark in two adjacent cylinders at once. If, for example, a misfire is detected in cylinder 2 and at the same time in cylinder 1 or 3, most likely the gasket between them has burned out.
Error p0300, p0301, p0302, p0303 and p0304 causes
Unfortunately, the diagnostic tool has not learned to determine the specific cause of the failure and, in this case, misfire in the engine cylinder, but, fortunately, the most likely malfunctions can develop in two directions - either there is nothing to burn , or it is impossible to ignite . Although it is still too early to rejoice at the possible quick search for the cause of error p0300, since it could be:
Cylinder misfires. How to diagnose the cause.
- In the ignition system
- spark plug failure;
- breakdown of a high-voltage wire;
- faulty ignition coil (or module);
- other reasons related to wiring and connectors in the ignition system.
- In the power system
- poor quality fuel;
- clogged injectors;
- heavily contaminated fuel filter;
- low fuel pressure.
The main reasons why error P0300 occurs
Causes of misfires
There are many reasons for misfires, these include the following phenomena:
- Poor quality of the fuel mixture is often the cause of lack of ignition in the cylinders; misfires are associated with a lean or, on the contrary, excessively rich composition.
- Problems with candles. The wrong gap may be set, it may happen that the spark plug is damaged by the appearance of carbon deposits, all this leads to a weak spark formation.
- Low compression in the cylinder (determined using a pressure gauge).
- Incorrect operation of the distributor distributor element or ignition module.
- Failure of the fuel pump, and as a result low pressure in the fuel rail.
- Inoperability of one or more injectors.
Recommended: Window Button Wiring Diagram
Recommendations for checking and troubleshooting
The first thing you should check when misfiring is the explosive wires and ignition coils (module), they often turn out to have broken insulation, a break, or an oily surface. We measure the wires with a multimeter (normal resistance is about 4 - 10 kOhm), in resistance mode, but to check individual ignition coils, you just need to swap places with a known working cylinder and clear the errors again. If the code has changed to the number of another cylinder, then the coil is faulty. The ignition module is more complicated; it needs to be checked with a tester.
The second in line are the spark plugs - a damaged electrode, incorrect gap, or oil deposits lead to failure or unstable operation of the spark plug.
Having unscrewed the spark plug for inspection, then what else can be done - measure the compression in the cylinder . Reduced or absent compression leads to insufficient compression, and therefore creates problems with ignition of the mixture.
Clogged fuel injectors provoke interruptions in the supply of fuel to the combustion chamber, but, unfortunately, without a stand it will not be possible to quickly check them. And the only thing that can be recommended in such a situation is to refuel with fuel with a higher octane number, and drive the car for some time at high speeds (4-5 thousand/rev).
A fuel filter that has not been changed for a long time or bad gasoline very often becomes the culprit for the unstable operation of the injectors. Therefore, remember the last time the filter was changed, and at what gas station you filled it with fuel.
A stuck EGR valve or leaks through the intake manifold gasket , which can also cause random misfires, can be difficult to determine on your own, so when doing computer diagnostics, pay attention to such a parameter as long-term fuel correction . It will show how much the ECU compensates for the imbalance in the air/fuel ratio. When this parameter on a particular cylinder differs by more than 10%, this may indicate a vacuum leak or air leak.
FakeHeader
Comments 20
THANKS TO ALL ! I hope I figured it out. In short, I changed the filter and mesh in the tank. Then I wanted to remove the injectors. And I thought that people wrote here that there might be a problem with the wire. I look and I have a female folder at the beginning without fastening. I tied them and pulled them with wire. And voila it seems to whisper. I hope that's all)))
I had this kind of garbage on my Opel, after the engine overheated the gasket leaked and the 3rd cylinder failed
I changed the ignition coil and that’s it) well, there’s such a thing from the wire to the spark plug that goes, this is most likely the reason
Changed everything and it still works? Check the compression first, then decide what to do next. If everything is normal, check the tightness of the injector; the injector may not fit tightly on cylinder 2.
It's most likely a coil, change it from another cylinder. If the error is on the cylinder on which you put it from the second, then it will definitely be
I wrote that I changed the coil and spark plug.
Did you change the coils? did the error change?
Changed it, the error remains. Exactly on the second!
Did you change the coils? did the error change?
I'll try to swap the forms. If it doesn't change, I'll check the compression.
Most likely your wire is shorted to the injector, check
Symptoms of a problem
A mixture misfire is a failure to ignite the fuel-air mixture or its untimely ignition. In any of the cases, the system counts the number of misses and delays, and, if necessary, turns off the idle cylinder or even a pair. On most cars, the first sign of a malfunction is the “check” symbol lighting up on the dashboard.
Also among the common signs can be noted:
- Smell of fuel from the exhaust pipe . Since the mixture did not ignite in the cylinder, it is discharged almost unchanged or partially neutralized.
- Shoots in the exhaust system . If a partial fire occurs, the catalytic converter is severely damaged, which can lead to popping noises.
- Loss of power . The engine does not work properly, causing the crankshaft to spin at a lower speed, resulting in a significant loss of power.
- Engine tripping . Failure of one or a pair of cylinders leads to the fact that the engine begins to vibrate during operation and other signs of malfunction appear.
In cars with an electronic control unit, there are several types of errors that indicate a breakdown.
- P0300 . It is a sign of multiple failures in the process of ignition of the combustible mixture in different cylinders.
- P0301 - p0304 . The last number shows which cylinder is not working properly.
Causes of misfires
Among the many reasons why the ignition does not work properly, the main ones are:
- Failure of elements of the ignition system - armored wire, spark plugs, coil or distributor-breaker (distributor in carburetor internal combustion engines). In addition, at low temperatures, condensation may form in the spark plug wells, which can cause “punching” into the block.
- Malfunctions in the fuel-air system can be associated with injection nozzles, air and fuel filters clogged with dirt and deposits. These ailments manifest themselves in the “triple” of the engine at idle, which disappears after warming up. An open circuit in an individual injector as a result of unstable power supply can also disrupt the fuel supply.
- Low compression in all cylinders or its uneven distribution indicates wear of the elements of the cylinder-piston group or problems with the gas distribution mechanism (GRM). In this case, the fuel-air mixture is compressed with less pressure, which is why ignition difficulties arise.
- Incorrectly adjusted valve clearance can lead to a violation of the tightness of the entire chamber during the compression stroke. Lack of optimal fit of the valve plate to the seat, as well as burnout of the valve, will cause misfires.
- Poor fuel quality, leakage or low supply pressure due to improper operation of the fuel pump can also cause misfires. To identify the problem, it is necessary to check the serviceability of the pressure regulator in the fuel rail. It is equally important to ensure that there are no air leaks or water entering the fuel tank.
- A malfunction of the electronic control unit results in the transmission of an incorrect signal from the sensors to turn off the injectors. Therefore, the engine begins to “trouble” and there is a misfire. In such cases, it is better to check the ECU firmware and sensors of the electronic engine management system.
Causes of misfire in injection engines
Since carburetors have a lot of shortcomings and unstable operation, injectors are mainly installed on modern cars. Stable operation, efficiency, frost resistance and environmental friendliness ensure the reliability of the motors and their durability. Injection engines are equipped with an ECU that regulates the composition of the combustible mixture and its supply.
When problems arise with fuel ignition, an error appears in the control unit, which helps to identify the faulty part of the unit.
When a breakdown is detected, it is necessary to conduct in-depth diagnostics to identify all faults. The most common reasons are the following.
Combustible mixture quality
If the air-fuel mixture has incorrect proportions, it will not ignite. Sometimes simply changing the gas station is enough, but in some cases major repairs may be needed. Low-quality fuel can clog injectors and filters. The reason for supplying the mixture in the wrong proportions may be a faulty fuel pump or pressure regulator. It is better to entrust complex diagnostics to authorized service stations, since independent examination of devices does not always allow you to detect an error.
Candles
Worn spark plugs can lead to misfires at idle and the engine constantly stalling. Sometimes you come across defective spark plugs that do not produce a spark. A change in the gap can also cause the fuel-air mixture to fail to ignite.
Armored wires
Faulty high-voltage wires do not cope with the task, which leads to misfires. Damage due to the mechanical impact of the armored wires or high resistance in them does not allow the mixture to ignite and can cause engine failure.
Cylinder deformation
If the gap between the piston and cylinder has changed, then significant changes appear in the operation of the engine. Although this reason is quite rare, it must be taken into account during a full diagnosis.
Incorrect compression
Uneven or low compression of the combustible mixture prevents it from igniting. The problem arises due to a violation of the integrity of the piston rings or wear of the CPG.
Malfunctions of the device can cause misfires on a cold engine. Due to the incorrect size of the device gaps or leaks in the hydraulic compensators, problems may arise when the mixture ignites.
The problem may also be in modules or faulty coils (
We are looking for the cause of misfire in the cylinder
Car owners whose cars are equipped with “electronic brains” are a little more fortunate in this matter, since it is possible to use an auto tester. Thanks to the “brains” and testers, you can see error codes, for example, where exactly misfires occur in cylinder 1 or 3.
In addition, using the scanner you can also determine the direction of the search itself. If the scanner showed you code P0204, and you know that this is an injector malfunction. Code P0300 indicates random misfire in all cylinders. Therefore, we can conclude that the air-fuel mixture is deteriorating, which means that the reason may lie in high air suction at the recirculation valve or in low pressure due to a faulty pump.
If a misfire occurs in a car that does not have an electronic assistant, then you will have to look for the cause using “old-fashioned methods.” They begin with checking the electrical equipment located under the hood: spark plugs, explosive wires, after which the compression in the cylinders and the condition of the fuel pump are measured.
If none of the versions are confirmed, there are two options: either continue the search on your own, or go to a service station for help, where they will help you fix the problem for money.
How to detect a malfunction yourself
We also recommend reading our expert’s article, in which he talks in detail about what a contactless ignition system is.
Be sure to read our specialist’s article, which tells you how to set the ignition correctly.
In cars with ECU
In cars with an ECU, troubleshooting is a fairly easy task. To do this, you need to connect an autotester and find the error code. If among the error codes there is an indication of a specific cylinder, then you should pay special attention to the condition of the element. Perhaps the problem is hidden in the armor wires or spark plugs that go to this cylinder. The gaskets may also need to be replaced. If a complex error (p0300) is issued, then you should pay special attention to the quality of the fuel and the filter.
Even domestic cars now have electronic units installed. If the car initially has an ECU, but its performance leaves much to be desired, then you can replace the part at a certified service station. The new “brains” must be compatible with the previous model. Thanks to the new electronic control units, you can easily find misfires in the 1st and 4th cylinders of the VAZ-2114 or on any old foreign car, as well as diagnose the operation of the 2nd and 3rd cylinders without unnecessary hassle.
Main causes of misfire
There can be many reasons for the problem; even professional mechanics spend more than one hour to identify its source.
The main reasons for misfire in cylinders 1, 2, 3, 4 can be:
- The ignition coil or module has failed;
- Inoperative fuel injector, clogged due to low-quality gasoline;
- Incorrect spark plug gap, which can lead to poor sparking;
- The spark plugs are flooded or carbon deposits have formed on them;
- Breakage of high-voltage wires, increased resistance (non-standard ones are installed), oiliness of contact points;
- A high-voltage wire has fallen off (often happens on Lada Kalina and Granta);
- On an 8-valve engine, the timing belt may jump (during replacement, an error was made due to marks or as a result of excessive wear);
- On a 16-valve engine, the hydraulic compensators are not working correctly;
- Air leak (can be anywhere);
- The compression in the engine cylinders has dropped or is different (applies to cars with high mileage);
- Low pressure in the fuel rail as a result of reduced fuel pump performance.
Causes of misfire in cylinders 1, 3 and 4. Where is the problem?
In some cases, it is useful to know the reasons for misfire in cylinders 1, 3 and 4. Until relatively recently, all passenger cars were equipped with four-cylinder power units. If one of the cylinders failed, drivers said that the engine was “troubling.” Now the number of cylinders can reach up to 12, but the failure of one or more cylinders is still called tripping. This engine condition is quite undesirable. In addition to the troubles in the form of problems with the operation of the car, there are also extremely unpleasant consequences in the form of increased wear of parts. Therefore, if possible, it is necessary to eliminate the malfunction as soon as possible. Search for a failed cylinder Causes of misfire in cylinders 1, 3 and 4. So, what does it depend on? To specifically identify the problem, you first need to identify the faulty cylinder. As soon as your car has noticeable failures in engine operation, or it begins to work like a tractor (this is especially noticeable on four-cylinder units). You need to immediately check the operation of all cylinders. In carburetor models, this is done by alternately pulling off the high-voltage wires from the spark plugs. If the engine starts to stall, then the cylinder is working. If the engine operation has not changed, then the problem area has been found. You need to pull out the wires using insulated pliers. In injectors, finding the cause is much easier. First of all, the check light will light up. After diagnostics, error P0300 is displayed on the monitor - misfire in all cylinders. If a misfire occurs in a specific cylinder, then you can see any of the errors P0301-P0304. The last digit in the error code will indicate the number of the problem cylinder. Finding the cause Misfire means a lack of fuel processing in the combustion chamber. This can happen for a variety of reasons. To determine the root of the problem, all options must be tested. Starting from the simplest to deeper problems. The search should be done in the following order:
- They usually start with the spark plugs. This is the most common cause of cylinder failure. First you need to inspect the candle visually. In working condition, it should be light sand color. If the spark plug is black or gray, you need to clean it. To do this, it is annealed over fire and cleaned with fine sandpaper. Another equally common cause of spark plug failure is a broken gap. It can be both large and small. To eliminate the malfunction, the electrode is pressed out or, on the contrary, pressed, adjusting the gap. After all the steps, you should check the operation of the candle. The spark it creates should be white and blue. This is described in detail in the article “What should be the gap on the spark plugs”;
- Faulty injectors. Engine trouble often occurs due to problems with the condition of the injectors. Usually this malfunction is shown by computer diagnostics. The cause is often poor quality fuel. It clogs the injectors and they stop functioning normally. This can be treated by flushing the power system; in extreme cases, you will have to replace the faulty part. This problem can occur on both gasoline and diesel units;
- Low compression. This is checked by measuring this indicator. If it is less than 11 points, then measures should be taken to repair the engine;
- Incorrect timing adjustment. This usually occurs due to wear of drive parts. Sometimes the reason is a failure in the settings of the hydraulic valve compensators;
- Air entering the fuel system. This could be damage to the intake manifold or a change in the condition of the injector rings. Most often, this problem is accompanied by misfires in different cylinders. You should find the cause and remove it.
Electrical problems Problems with the ignition coil or module, distributor.
If one of the contacts on the distributor is “overgrown” with scale, its throughput will drop significantly. The check should begin with the distributor or module. The distributor should be inspected; if necessary, the contacts are cleaned; on contact ignition, the cam clearance is adjusted. The distributor cover is checked for integrity. The ignition module is checked by measuring the resistance on paired contacts (1 and 4, 2 and 3). The ignition coil is usually checked using computer diagnostics. Next, you need to check the high-voltage wires. This can be done by replacing the supposedly faulty one with another one. If the engine starts without problems, then the cause has been found. You can also start the engine in the dark. A broken high-voltage wire will glow from the discharges. You can check the resistance, it should be minimal; These are the main causes of misfire. Sometimes this phenomenon is caused by one malfunction; in some cases, engine tripping is caused by a number of reasons. Conclusion. Engine tripping is an extremely unpleasant problem. It leads to increased wear of engine parts and increased fuel consumption. Therefore, you should know all the reasons for misfire in cylinders 1, 3 and 4. This will help you quickly find and fix the problem if necessary. Which will save you time and money. AutoFlit.ru
Diagnostics using a computer
If your car is equipped with a modern control unit, then this greatly simplifies troubleshooting; otherwise, you will have to use time-tested old-fashioned methods.
By connecting the computer to the car, you can find out in which cylinder, 1, 2, 3 or 4, and for what reason there are misfires, for example, the ignition coil or one of the injectors has failed.
But in any case, before going to a car service center, you need to check the condition of the spark plugs, injectors, high-voltage wires, how the exhaust system works, and whether there is smoke from the exhaust pipe.
Many car owners cannot afford instruments for car diagnostics, these include scanners (software and portable), motor testers, oscilloscopes, gas analyzers and other devices, and you need to be able to use them, read error codes, and so on. Although if you look into it, there is nothing complicated there.
The scanner is connected to a special connector, which can be located in different places in each car model, but it has one function: diagnostics.
Next, error codes are read from the control unit and decrypted.
For example, VAZ 2110, 2114, 2115, Lada Kalina, Priora, Granta cars have the following error codes that are characteristic of misfire:
- P0300 - a large number of misfires;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires in cylinders 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- P0300 - a large number of misfires in a random order;
- P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – misfires were detected in 1, 2, 3 and 4, respectively;
- P0363 – see point 4 + fuel supply to problem cylinders is stopped;
- P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – respectively, misfires dangerous for the catalytic converter were detected in cylinders 1, 2, 3, 4;
- P0300, P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304 – detection of misfires affecting the toxicity of exhaust gases;
- P0363, P1301, P1302, P1303, P1304 – the same as in point 7, but affecting the catalyst;
- P0351, P0352, P0353, P0354 – open circuit in the ignition coil in the control circuit 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P2301 P2303 P2305 P2307 - short to on-board network in the coil in the control circuit of cylinders 1 (1-4), 2 (2-3), 3, 4;
- P0201, P0202, P0203, P0204 – respectively, open circuit for controlling injectors 1,2,3,4;
- P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270 - short circuit of the injector control wires to the body, respectively, in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th center;
- P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271 – the same as point 12, but only to the on-board network;
- P1500 – electric fuel pump relay, wire break.
Diagnostics of VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115, Kalina, Priora, Granta
Let's look at misfires using the example of the VAZ 2109, 2110, 2114, 2115, Kalina, Priora, Granta models.
The computer generated error P0303 (misfire in 3rd crank).
First you need to understand how the ignition coil works. It consists of two small coils, pins 1 and 4 are connected to the first, and pins 2 and 3 to the second.
Those. during operation, voltage is simultaneously supplied to the first and fourth cylinders or to the second and third.
We have misfires in cylinder 3. Remove the wires from 2 and 3 and swap them.
Start the engine and see if the error has moved to cylinder 2, then the problem is most likely in the high-voltage wires or in the coil itself, and they need to be checked first.
High-voltage wires are tested by checking their resistance. To do this you need a regular multimeter.
Set the resistance measurement mode to 20 kOhm.
In our case, we check the third wire. If the device shows numbers within the range of 3.5 - 10 kOhm, then the wire resistance is considered normal, otherwise it changes.
Next we check the coil. For this you also need a multimeter.
We measure the resistance between 1 and 4 and 2 and 3 coil terminals. Readings of 10 kOhm, or around this figure, are considered standard.
Important. During testing, the tester should not show 1. This means that there is an open circuit in the circuit and the coil is faulty.
Causes of multiple misfires
- There is no spark or the strength of the spark discharge is insufficient to ignite the fuel injection pump. The cause of interruptions in the operation of the ignition system may be spark plugs, high-voltage wires, a coil, or an ignition module.
- Loss of engine compression. Burnout of valves, breakdown of the cylinder head gasket are the most likely causes. Even wear of hydraulic compensators, incorrect valve clearance, or failure of timing marks can lead to a similar problem.
- Malfunction of the injector or its control circuit. If the injector hangs open, the control wire has a short to ground, and the fuel injection pump will be over-enriched. The fuel mixture will not burn due to either excessive leanness or an over-rich mixture. Therefore, if there are multiple misfires, the fuel pump should not be excluded from the list of causes.
- Suction of unaccounted air. For example, in the place of the gasket between the intake manifold and the cylinder head. In an unheated state, the gap at the depressurization site increases, so more unaccounted air enters the cylinders. Misfires occur due to excessive leanness of the mixture. Among the list of reasons, one should not exclude leaking injector O-rings and cracked vacuum system hoses.
Signs of misfire: the engine throttles, power decreases, fuel consumption increases. Uneven operation is clearly noticeable on 3, 4, 5-cylinder engines, but on V-shaped 6 and 8-cylinder internal combustion engines, it is more difficult to notice the shutdown of one of the cylinders.
Error codes
Self-diagnosis of a modern injection system is capable of recording misfires and determining which cylinder is the cause of uneven engine operation. Therefore, we recommend starting with diagnosing the current fault codes. When searching for the cause of a breakdown, it is important to understand in which particular engine operating mode the misfire error occurs.
Without ignition, there is no power stroke in the cylinder, which affects the crankshaft rotation speed. The engine ECU receives information from the crankshaft position sensor, so based on the moment of deceleration, the CV can calculate which cylinder is misfiring.
- P0300 – multiple misfires. This means that burning problems are not limited to just one cylinder;
- P03001, P03002, P03003, P03004, P0300n... - misfires in a specific cylinder. Where N is the serial number of the combustion chamber in which the malfunction occurs.
You can determine error codes by connecting to the OBD II connector using a simple diagnostic tool like ELM 327. It is important that the software version allows you to connect to the engine control unit on your car model.
How to identify a cylinder
If the engine is misfiring, but you do not know which cylinder is causing the problem, with the engine running, remove the high-voltage wires one by one or disconnect the connectors of the ignition modules and fuel injectors. The shutdown of the working cylinders will be noticeable by a drop in speed. The problems will be in that “pot” that does not react in any way to disconnecting the GDP/connector. We have identified the inoperative cylinder, so we move on to finding the cause of the misfire.
Ignition system diagnostics
We will not consider diagnostics of the secondary ignition circuit, which requires an oscilloscope and basic skills in working with sensor signals. Let's look at the basic verification methods that you can do yourself.
Remove the spark plug. Measure the air gap, assess the condition of the electrodes, insulator and the amount of carbon deposits. We described the diagnostic process in more detail in the article “Symptoms of faulty spark plugs.”
If the spark plug is wet and there is a strong smell of gasoline, it means that fuel is being supplied to the cylinder and the power system should be the last thing to complain about.
The best way to independently determine the cause of a misfire in a cylinder is to first swap the spark plugs, then the GDP and ignition modules. Before starting after changing elements, erase all error codes. You can determine a non-working “boiler” by reading current errors or using the method described above.
Screw the spark plug from the cylinder that has ignition problems into a working “pot”. If the problem moves to a previously good cylinder, then the cause of the misfire is in the spark plug. Do the same with GDP and individual ignition coils.
On cars with a DIS system, the design of which involves one coil for 2 cylinders, a malfunction of the ignition coil will manifest itself as misfire in 2 “boilers” at once.
Checking high voltage wires
- Measure GDP resistance. If you know how to use a multimeter, you can test the high-voltage wires yourself and compare the values obtained with the nominal values. Infinite resistance indicates a break - such a high-voltage wire should be replaced.
- Definition of breakdown. Spray the GDP with water, start the engine. Connect one control contact to an unpainted metal part in contact with the body. Run the second contact along each wire. There should be no spark breakdown between serviceable high-voltage wires and the control panel.
Attention! The contact must be connected to ground, and not to the negative terminal of the battery! Otherwise, if there is a breakdown, there is a risk of the battery exploding. The control should have an incandescent lamp, not an LED.
Possible faults
At the beginning of the article, the main reasons were described, but there are also some more rare malfunctions.
- Worn contact of the resistive throttle position sensor. The ECU cannot adequately calculate the amount of air and the desired load.
- A stretched timing chain, which causes the valve timing to shift.
- Failure of the DPKV crown damper. Wear leads to uneven rotation of the crown, which can be interpreted by the ECU as a problem with the combustion of the working mixture.
Don't get caught
On some vehicles, the ECU, after registering a misfire in a cylinder, forcibly turns off the fuel and spark supply. This is how the catalytic converter protection system works, preventing unburned gasoline from reaching the catalyst cells.
Diagnostics without a computer
If you do not have a scanner, and most likely this is the case, and there is no desire to contact a car service, then the causes of misfire can be identified using the so-called old-fashioned methods.
They need to be checked first; they must be dry without soot and oil.
If the spark plug is flooded, then ignition will not occur in this cylinder, and if it does, it will be misfired. The spark plug gap must be correct.
A common situation is that the wire just fell off. Also, the wires may be broken, damaged, or oily.
Remove the cap and conduct an external inspection of the wires, especially their contacts, to see if they are oxidized.
Check the resistance of the wires; read how to do this above. The resistance should be no higher than 10 kOhm and no lower than 3.5 kOhm. Replace the wires if necessary.
Ignition module or coil.
Everything is done simply with the car running; one by one, remove the high-voltage wire from the coil and observe what happens to the engine.
If nothing changes, then most likely the problem is not her. Also check the coil resistance as described above.
Also remove them one by one and check for clogging, clean if necessary. Check the resistance, read above how to do this, we won’t repeat it.
When replacing it, a mistake could have been made by several marks; also check its condition; due to stretching, the belt could have jumped several teeth.
This could also be the cause of a misfire. You need to check everything from the air filter to the injectors.
On the injectors, pay attention to the rubber seals, which dry out over time and begin to leak air. Check the manifold gasket.
Other reasons, impaired compression, valve condition, etc. described above.
But I would like to note that using a scanner or oscilloscope significantly speeds up the search for the cause of a misfire, and in some cases it is impossible to do without these devices.
Write your opinions in the comments. And finally, the video is Nissan Altima 2.5S.
«>