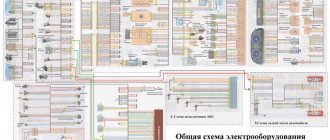
Many cars produced at Zavolzhsky Motor Plant OJSC are equipped with a 4-cylinder ZMZ-405 engine. The transmission of torque is carried out by a chain transmission. Indications for replacing the timing chain are its stretching or the “mileage” of the engine is more than 200-250 thousand km.
ZMZ-405 is a reliable, well-proven engine. It is important to closely monitor his condition. Especially with high mileage. A broken circuit can cause serious problems and require major repairs. Its cost can be several tens of thousands of rubles. It is worth purchasing replacement parts in well-established stores.
The owner always has a choice:
- original;
- analogue
Each option has its advantages and disadvantages. Analog is usually an order of magnitude cheaper.
Analogs
There are analogues on sale from various manufacturers - domestic and Chinese. It is possible to purchase a replacement chain separately or as a complete set. The price depends on the origin of the parts and the place of purchase. It is advisable to give preference to well-established auto shops.
| Name | vendor code | Price |
| Olmi | 406.1006040-20 | From 1,300 rubles |
| Miles | 040900100011801 | From 1,150 rubles |
| Ditton | 509105011801 | From 1 117 |
Maintenance and Prevention
The operating principle of an injection engine is based on controlling the fuel supply using electronics. Due to this, the engine requires preventive maintenance approximately every 12 thousand kilometers (according to the manufacturer’s recommendation). At the same time, the oil and filter are replaced.
If the Gazelle-405 (injector engine) operates in intensive mode, it is recommended to service the engine every 8-10 thousand kilometers, since under heavy loads the oil changes its chemical composition faster and loses its properties.
It is recommended to adjust the valves with the installation of appropriate washers every 15 thousand. In addition, it is necessary to check the gas distribution mechanism, since a broken belt can lead to deformation of the valves, which can lead to costly repairs or even replacement of the cylinder head.
Source
How to spot a fake
The total cost of the chain set and all other parts required for replacement can reach 7 thousand rubles. There are often fake kits on sale. It is worthwhile to carefully and in advance familiarize yourself with all the features of such products. You should refuse to purchase if:
- there is no hologram;
- the name on the box is hard to read;
- the packaging is of poor quality;
- The print is hard to read.
It is important to carefully examine the part itself.
How does an injection engine work?
The principle of operation is to supply fuel through injectors controlled by an electronic control unit (ECU). The controller monitors the state parameters of the power plant, calculates the need for supply and quantity of fuel, and provides adjustments to the fuel supply using the pulse duration.
The ECU is able to evaluate the results of calculations and commands, as well as remember previously performed manipulations, coordinating further actions with it. The process of intellectual development of the unit occurs continuously and lasts throughout the entire period of operation of the car. Fuel supply in the Gazelle-405 car (engine injector) can be carried out in two ways:
The first method is preferable. Asynchronously, fuel is usually supplied when the power unit starts. The injectors are operated in pairs or alternately.
What is needed for replacement
Replacing a chain is a complex process that requires preliminary preparation. You must purchase the following list in advance:
- engine oil;
- oil filter;
- gasket (made of cork);
- high-temperature sealant (preferably gray ABRA marked 999);
- kerosene and a metal brush - for washing the engine.
After replacing the chain, you need to fill in fresh oil (the filter is also changed with it). The valve cover has a “habit” of constantly leaking. Therefore, it is advisable to purchase it in advance and replace it along with the chain. Cork is the best option. Thanks to high natural adhesion and elasticity, high tightness is created.
The keys you will need are: a set of sockets and open-ends, reinforced by 36, a hexagon by 6. An equally important point is a lot of rags. Most engines squeeze oil out through the oil seals as well as the valve cover. A good solution is to immediately purchase a set of parts to replace the timing chain. It is identical for engines marked 405, 406, 409.
Such a kit usually includes the following main components:
- a pair of conventional tensioners and two of their hydraulic counterparts;
- drive chains – 2 pcs. (for ZMZ-405 – 72 and 92 links);
- 3 tranquilizers;
- upper, lower cover gaskets;
- pump gaskets;
- 2 soundproofing pads;
- 3 sprockets for shafts (intermediate, crankshaft, camshaft).
It wouldn't hurt to purchase a driven sprocket.
How to set timing marks Gazelle 405
On ZMZ 405 engines, the timing belt assembly is carried out in the reverse order of disassembly. If you have already dealt with disassembling an engine and replacing a chain, then you already know how to reassemble the timing belt in reverse order.
Now let's talk about how to correctly set timing marks. Since many car owners do this at random, which leads to disastrous results.
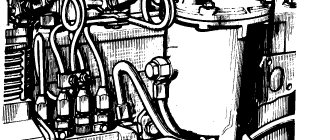
Where is the chain located
The timing chain is located on the ZMZ 405 closer to the front of the engine. But some companies, such as Volkswagen, install it behind. In our case, it will be easier to get to it.
Signs of breakdown of the gas distribution mechanism
After disassembling the gas distribution mechanism, you will be able to see signs of its breakdown or signs of unstable engine operation. Such signs may be the eaten ends of the crankshaft sprockets. It is better to immediately replace them with new ones.
The chain itself may be full of cracks. Or it sags if the timing belt tensioners are faulty. Due to the slack chain, the car owner heard knocking and noises at idle speed of the engine.
Gazelle installation of camshafts by marks
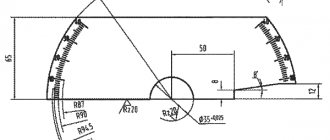
Now let's talk about how to correctly set the marks on the camshafts. It is necessary to use a protractor while working on setting timing marks.
Similar article Engine oil for UAZ Patriot ZMZ 409
- Rotate the exhaust camshaft until the timing mark is at 19 degrees on the protractor.
- The belt is put on the sprocket. And an additional hole is installed in front of the camshaft pin.
- To install the sprocket, turn it with a key.
- Then the leading branch of the chain is pulled counterclockwise.
- Now the intake camshaft is rotated until the marks converge at the protractor mark of 20 degrees.
- Using the principle of the exhaust camshaft, the sprocket and timing marks are installed.
- Then tighten the sprocket fastenings. Don't forget to install the fuel pump drive eccentric.
Then they assemble the hydraulic tensioner and proceed to checking the correct timing distribution.
Ideal phase
The ideal operating phase of the engine timing belt will be observed only if, when checking, the template arrow on the intake cam shows 20 degrees, and on the exhaust cam 19 degrees on the protractor.
Timing marks and tightening
The timing marks must be set strictly according to the diagram specified in the manual. All bolts are tightened using a torque wrench. The pressure force should not exceed or be less than that indicated in the engine operating manual.
Practice
Why can’t the mark on the crankshaft pulley be considered true? For two reasons.
- When we look at the marks on the crankshaft pulley and on the front chain cover, we do so at a minimum of a 45 degree angle. Let's assume that these marks are quite clearly visible on the Volga. But if in front of us is a UAZ “loaf” or “patriot”, then the marks can be seen, practically from one point, and only if you know where to look. There is no need to talk about the accuracy of their combination.
- The crankshaft pulley has a damper. That is, it consists of two parts, between which there is a rubber layer. I can’t say how the pulleys are assembled at the factory, I haven’t seen it. But from experience working with these engines, I can say that if the displacement of the virtual mark relative to the true one is half a tooth, you just got the perfect pulley.
Differences between ZMZ 405 and 406 engines
The power plants ZMZ 405 and ZMZ 406 are in-line, 4-cylinder, 16-valve gasoline internal combustion engines, the development and production of which was carried out by the Zavolzhsky Motor Plant. The family was widely used on cars of the Gorky plant, such as Gazelle, Sobol, Volga. Both the 405 and 406 have different design features, although the 405 engine is a worthy successor to the 406 engine.
Power plant ZMZ 406
The unit was released in 1997, after numerous tests and improvements. It was a gasoline engine on which the designers of the Zavolzhsky plant first used fuel injection. Due to its high reliability, efficiency, and technical performance, the engine was very popular among consumers and for quite a long time was the main power plant in many GAZ cars. There were also disadvantages, including:
- Noise from the timing chain due to failure of the hydraulic tensioner.
- Increased oil consumption due to rapid wear of oil scraper rings and valve seals.
- Problems with hydraulic valve compensators, piston pins, pistons, liners, connecting rods, etc.
The developers understood that the engine needed modernization and refinement, so it was soon replaced by the 405 engine.
ZMZ 406 installation characteristics:
- Production period: 1997-2008;
- Cylinder block, material: cast iron;
- Power supply - from an injector or carburetor;
- Type - in-line;
- Cylinders, quantity, pieces - 4;
- Valves, quantity, pieces - 16;
- Piston, stroke, mm - 86;
- Cylinder, diameter, mm - 92;
- Compression - 9.3;
- Volume, cm3 - 2286;
- Power, hp - 145;
- Torque, Nm - 201;
- Fuel - gasoline, AI-92;
- Compliance with environmental standards - Euro 3;
- Engine weight, kg. - 187;
- Fuel consumption, liters per hundred (city) - 13.5;
- Engine resource, km. - 150000.
The cylinder block of the power plant has channels for coolant, which is pumped by the pump. The pump drive is located in the front of the engine; in addition, the drives for the hydraulic power steering pump and generator are also located here.
The cylinder head is aluminum, with pressed cast iron seats and valve guides. The valves do not require adjustment because the engine is equipped with hydraulic pushers.
The camshafts operate from a chain, the tension of which occurs automatically; transmission is carried out through the intermediate shaft sprocket.
Power plant ZMZ 405
The motor replaced the ZMZ 406 model and became its worthy replacement. The appearance on the market occurred in 2000; the unit was equipped with equipment from the Gorky plant. New modifications of the installation were constantly being released, the engine was improved, and shortcomings were corrected.
Due to modifications that significantly increased engine power, the 405 began to be installed not only on passenger cars, but also on minibuses. ZMZ 405 has proven itself well as a reliable, unpretentious unit that meets all requirements and expectations.
The power plant was the successor to the 406 model, so most of the shortcomings are exactly copies of the old model. As for the characteristic shortcomings, they were: a complex fuel supply system and an electronic control system. In the event of a breakdown, problems arose with maintenance and repair, since the knowledge and skills of highly qualified specialists were needed.
ZMZ 405 installation characteristics:
- Production period: 2000-present;
- Cylinder block, material: cast iron;
- Power supply - injector;
- Type - in-line;
- Cylinders, quantity, pieces - 4;
- Valves, quantity, pieces - 16;
- Piston, stroke, mm - 86;
- Cylinder, diameter, mm - 95.5;
- Compression - 9.3;
- Volume, cm3 - 2464;
- Power, hp - 152;
- Torque, Nm - 211;
- Fuel - gasoline, AI-92;
- Compliance with environmental standards - Euro 3;
- Engine weight, kg. - 193;
- Fuel consumption, liters per hundred (city/highway/mixed) - 13.5/8.8/11.0;
- Engine resource, km. - 150000.
Distinctive features of power plants
Considering that one power plant replaced another for the purpose of modernization, we can conclude: the main difference between the 405 engine and the 406 is that it is more modern and of higher quality. A clear answer to the question: “Which engine is better, 405 or 406?” no, each of them has its own characteristics. The difference between the series can be seen from the following comparison:
- The first thing you can pay attention to is that the ZMZ 405 differs from the 406 in its power supply system. So, the 406 uses a carburetor in its design, while the 405 has a better system - an injector.
- The engines differ in volume: the 406 power plant has 2.28 liters, while the 405 is slightly larger - 2.46 liters.
- The speed of both units is the same - 5200 min-1. However, the power of the 405 unit is greater - 150 hp. versus 145 hp at 406 motor;
- Thanks to the presence of an injector, engines of the 405 family start easier and have lower fuel consumption. It was the efficiency and simplicity of the plant that made this power plant popular among GAZ car users.
- Despite the higher fuel consumption, the carburetor of the 406 model had high reliability and maintainability.
- The cylinder diameters also differ: 92mm. at 406 and 95.5 mm. at 405.
In addition to all of the above, power plants have a number of differences in the design of the unit. The 405 model has characteristic transverse slots, 2 mm wide. between the cylinders in the cooling system. This was done in order to improve heat removal from the cylinder walls. In practice, this design feature leads to a decrease in the rigidity of the top plate of the block.
As a result, when the head bolts are tightened, the cylinder wall becomes deformed. The 406 series had special ducts made using casting. The large size of the jumper: 406 - 14 mm, 405 - 10.5 mm made it possible to avoid such a problem.
To the question: “Which engine is reliable?” it is impossible to clearly identify a leader. Both models deserve praise for their simplicity and reliability of design. Unfortunately, these days, the 406 series of engines is no longer installed on GAZ and UAZ cars; the car manufacturer has given preference to a more modern unit.
Source: https://avtodvigateli.com/marki/otlichiya-zmz-405-i-406.html
content .. 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 ..Rice. 3.1. Cylinder block and piston | Hole | Shaft | Landing | |
| 1 | Piston - oil ring | 3,050,01 | 3 0,0050,030 | Gap 0.0900.045 |
| 2 | Piston - lower compression ring | 1,80,01 | 1,75 0,0050,030 | Gap 0.0900.045 |
| 3 | Piston - upper compression ring | 1,550,01 | 1,5 0,0050,030 | Gap 0.0900.045 |
| 4 | Block cylinder - piston skirt | Ø95.5 0.072 0.036(three groups through 0.012 mm) | Ø95.5 0.024 0.012(three groups through 0.012 mm) | Gap 0.0600.036(selection) |
| 5 | Connecting rod bolt - connecting rod | Ø10.15 0.0080.019 | Ø10.15 0.015 | Gap 0.023 Preload 0.019 |
| 5 | Connecting Rod Bolt - Connecting Rod Cap | Ø10.3 0.043 | Ø10.15 0.015 | Gap 0.2080.150 |
| 6 | Cylinder block - bearing cap | 130 0,0140,064 | 130-0,018 | Preload 0.064 Gap 0.004 |
Rice. 3.2. crank mechanism
| Resistance no. | Mating Parts | Hole | Shaft | Landing |
| 1 | Chain cover - oil seal | Ø70 0.070 | 0.4Ø70 0.2 | 0.47 Preload 0.20 |
| 2 | Crankshaft - Bushing | Ø38 0.0300.005 | Ø38 0.0200.003 | Gap 0.027 Preload 0.015 |
| 3 | Sprocket - crankshaft | Ø40+0.027 | Ø40 0.0270.009 | Gap 0.018 Preload 0.027 |
| 4 | Connecting rod - piston pin | Ø22 0.0070.003 (4 groups every 0.0025mm) | Ø22 0.0050.015 (2 groups every 0.005mm) | Gap 0.0170.007(selection) |
| 5 | Piston - piston pin | Ø22 0.0050.005 (2 groups every 0.005 mm) | Ø22 0.0050.015 (2 groups every 0.005mm) | Gap 0.0150.005(selection) |
| 6 | Pulley - pulley key | 8 0,030 | 8 0,050 | Gap 0.030 Preload 0.050 |
| 7 | Crankshaft - Pulley Key | 8 0,0060,016 | 8+0,050 | Gap 0.006 Preload 0.066 |
| 8 | Crankshaft - sprocket key | 6 0,0100,055 | 6-0,030 | Gap 0.020 Preload 0.055 |
| 9 | Crankshaft sprocket - sprocket key | 6 0,0650,015 | 6 0,030 | Gap 0.0950.015 |
| Resistance no. | Mating Parts | Hole | Shaft | Landing |
| 10 | Flywheel - crankshaft | Ø40 0.0140.035 | Ø40 0.0350.050 | Gap0.036 |
| Crankshaft - pin | Ø10 0.0050.010 | Ø10 0.0150.006 | Preload 0.0250.001 | |
| 11 | Flywheel (pin hole) - pin | Ø10 0.0760.040 | Ø10 0.0150.006 | Gap 0.0700.025 |
| 12 | Toothed rim - flywheel | Ø292+0.15 | Ø292 0.640.54 | Preload 0.640.39 |
| 13 | Flywheel - gearbox drive shaft bearing | Ø40 0.0140.035 | Ø40-0.009 | Preload 0.0350.005 |
| 14 | Flywheel - spacer | Ø40 0.0140.035 | Ø40 0.10.5 | Gap 0.4860.065 |
| 15 | Oil seal holder - oil seal | Ø100 0.087 | 0.5Ø100 0.3 | 0.587 Preload 0.300 |
| 16 | Crankshaft (3rd main bearing) - cylinder block + thrust bearing washers | 34+0,05 | 29 0,0120,060+2(2,5-0,05) | Gap 0.270.06 |
| 17 | Crankshaft - connecting rod (width) | 26+0,1 | 26 0,250,35 | Gap 0.450.25 |
| 18 | Connecting rod, bearings - crankshaft | Ø60+0.019––2(2+0.008) | Ø56 0.0250.044 | Gap 0.0630.009 |
| 19 | Block, main bearings - crankshaft | Ø67+0.019––2(2.5+0.008) | Ø62 0.0350.054 | Gap 0.0730.019 |
| 20 | Damper pulley - crankshaft | Ø38 0.050 0.025 | Ø38 0.0200.003 | Gap 0.0470.005 |