Types of DDM
Oil pressure sensors are divided into two types:
- Mechanical. They are used on cars that have become legends in the automotive industry, in particular, VAZ 2101, UAZ, Moskvich 401/407/412/, 2141 and others.
- Electronic. Installed on all modern cars, for example, domestic VAZ 2114, Kalina and other Lada models, as well as foreign cars.
Mechanical sensors
Mechanical sensors by design are divided into:
- Devices with two rods and a capillary tube.
- Devices with a rheostat.
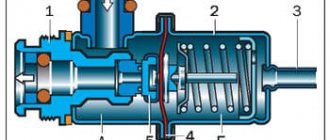
The first ones consist of a body, a membrane, two rods, and a sealed tube.
As the pressure in the lubrication system increases, the membrane bends, putting pressure on the first rod, thereby increasing the pressure in the tube. The second rod takes this pressure and transmits it to the differential pressure gauge (located on the instrument panel).
The pressure increases - the arrow of the device deviates in a larger direction, falls - the arrow goes down to the left. The principle of operation is the same as that of a pressure gauge.
The mechanical oil pressure sensor with rheostat consists of:
- Cases.
- Membranes.
- Slider.
- Nichrome winding (resistor).
The device operates on the principle of a voltmeter. The rheostat and slider play a key role here.
The rheostat changes its resistance depending on where the slider is moved. The latter, in turn, shifts in one direction or another as the membrane bends or straightens.
When there is no pressure, the membrane is not deformed and the slider does not move, the current passes freely without encountering any resistance along its path.
As the pressure increases and the membrane deforms, the slider moves along the rheostat, thereby increasing the resistance in the circuit; accordingly, the current readings change, which is displayed on the device in the driver’s cabin.
All this is recorded by the ECU, to which the sensor is connected. It is programmed in such a way that only one period of current values is equal to the standard oil pressure. Exceeding this interval is equivalent to an incorrect value.
This is clearly visible on dial analog pressure gauges, which, in fact, are ordinary voltmeters.
Electronic sensors
Electronic DDM is much simpler than its mechanical counterpart, so it is considered more reliable.
Essentially, this is an emergency sensor that does not show the pressure in the system, but only notifies the driver when it is within normal limits and when it is not.
It consists of:
- Cases.
- Membranes.
- Contacts
- Stock.
Principle of operation. When pressure is not applied to the sensor membrane, it is not deformed. The rod is in a position in which the circuit contacts are closed and current flows through them. At this moment, a lamp is lit in the cabin, which is monitored by the driver.
When the engine starts, the oil pressure in the system increases, the membrane bends, the rod moves, opening the circuit. The light goes out.
If after starting the engine the lamp does not go out within 1-2 seconds, you must immediately turn off the engine and do not start it until the cause of the malfunction is determined.
Read more here - what to do if the oil pressure light is on.
Based on the above, we can conclude that the basis for checking the oil pressure sensor on modern cars is measuring the resistor resistance with a multimeter and checking the DDM for opening and closing the circuit.
To do this, the multimeter is switched to resistance or continuity measurement mode. It depends on what type of sensor is being tested with or without a resistor.
But there are other verification methods, which we will discuss below.
Oil pressure sensor - varieties
There are two types of DDM: mechanical and electronic.
The mechanical sensor has a complex structure and consists of: a housing, a membrane, a slider, a pusher and a nichrome winding. Its operating principle is approximately the following. The fact is that information is sent to the oil pressure dial indicator on the instrument panel, depending on the position of the slider. Engine oil under pressure presses on the membrane, which in turn drives the pusher. Next, the mechanism for changing the resistance receives the changed signal, after which it transmits it to a plate with a nichrome winding, which already displays information on the instrument panel, moving the arrow along a graduated scale.
An electronic pressure sensor is also called an emergency sensor. It has a simpler design and either it works or it doesn't. Such a sensor signals problems with pressure in the oil system only in critical situations. While the mechanical DMM accurately measures the pressure in the system and transmits the data to a graduated scale located on the dashboard. Some car manufacturers use these two types of sensors at once, which improves pressure control and convenience for drivers. Technically, the sensor consists of a membrane and a pusher with contacts that are located in the housing. The electronic DDM is powered from the mains and sends data to the electronic control unit.
When the motor is not running, the sensor membrane is straightened and the contacts are closed. When the engine starts, the light on the dashboard comes on because the oil pressure is insufficient. After a few seconds of operation of the motor, the correct pressure is generated, it acts on the membrane, which in turn moves the pusher, which opens the contacts, as a result the light goes out. The motor stops and the pressure light comes on again as the pressure in the system drops and the contacts close. There are indeed other reasons when the oil pressure light may come on: firstly, problems in the oil system, and secondly, a malfunction of the sensor itself.
Sensor diagnostics
Electronic and mechanical oil pressure sensors are checked in different ways, so we will consider each of them separately.
But before you start checking, it is important to make sure that it is the DDM that is the root cause of the warning light that does not go out.
First, make sure that the oil is in good condition and that its level in the engine is within normal limits. Is the filter clogged because the fluid in the system was changed a long time ago? Make sure the pump is working properly.
IMPORTANT: check the wiring from the sensor to the ECU, the condition and integrity of the contacts.
Next, find and remove the sensor itself. This must be done with the engine turned off. Preferably cooled. On different cars the unit may be located in different places.
How does the oil pressure sensor work?
Inside the sensor there is a membrane sensitive to changes in pressure in the system. When the ignition is turned on, there is no pressure in the oil system, so the contacts located inside the sensor are in a closed state. The contacts are closed, therefore the emergency oil pressure light will be on. After starting the engine, oil pressure arises, the membrane is deformed and presses on the pusher, which opens the contacts, as a result of which the oil pressure alarm indicator goes out. In the event of problems in the engine or when the oil pressure drops, the membrane immediately returns to its original position along with the pusher, resulting in the contacts closing. This causes the oil pressure light to come on, thereby signaling to you that the pressure in the oil system has dropped.
In order to check the oil pressure sensor you need to have:
- Multimeter.
- Pump with pressure gauge.
Where is the sensor located
The most common places where it is found are near the oil filter, in the upper part of the engine near the camshaft block, or pump.
Let's look at specific models:
- VAZ 2108/09/099. Located on the top right side of the engine (when viewed in the direction of travel) next to the timing belt cover. There is only one wire coming from it. This arrangement is also typical for 8-valve engines on the VAZ 2110/11.
- VAZ 2110/11 16 valve engine. Located on the left side of the engine (when viewed in the direction of travel) on the driver's side on the camshaft block between the air filter, ignition module and oil filler neck.
- VAZ 2112, 16-valve engine. It is located on the top left side (look along the way). To find it you need to remove the air filter.
- VAZ 2114. Located on the right inner side of the engine on the cylinder head next to the timing belt. You can clearly see it from above
. To dismantle it, remove the protective cap, the terminal and turn it out with a 21 key. - Lada Kalina. Located on the right rear of the engine near the timing belt, one wire comes from it
. To get to it you need to remove the plastic cover of the cylinder block. - Lada Priora. Located on the left (when viewed along the way) on top of the cylinder block under the intake air manifold. To dismantle it, you must first remove the protective plastic cover of the engine, move the air manifold and unscrew it with a 21 mm socket wrench. It sits very tight.
- Lada Granta 8 and 16 valve engine. Located on the top right side of the engine near the timing belt cover
. To remove it, you can use a spark plug wrench or a 21 open-end wrench. - GAZ "Gazelle" (engine ZMZ-405). Located on the BC, top right. There is only one wire coming from it.
The most common wrench size for removing the sensor is 21. You can use a spark plug wrench. But it all depends on the specific brand of car.
After the pressure sensor has been removed, the seat is tightly covered with a clean rag so that dirt does not get there and oil does not leak out during possible engine operation.
It would be a good idea to measure the oil pressure in the system at idle, medium and high speeds. To do this, use a pressure gauge, which is screwed in instead of the DDM. To take accurate readings, it is important to ensure a tight connection.
For each car model, the values may differ. These can be found in the instruction manual.
For example, for a VAZ 2112 there are 16 valves, the standard engine oil pressure is:
- at idle speed 2 BAR.
- at 5 thousand revolutions from 4.5 to 6.5 BAR.
If all the readings are normal and the light is constantly on, then the information does not reach the ECU or gets distorted. This may be due to the sensor, which needs to be checked.
Read on the topic - what to do if the oil pressure in the engine is lost.
Checking the electric oil pressure sensor with a multimeter and a light bulb
The method is suitable for all modern Lada cars, in particular VAZ 2114, and foreign cars. Where there is only an emergency warning about low oil pressure.
In such cars, a sensor is installed that works on the principle of opening a circuit. The pressure is normal - the circuit is open, not normal - it is closed, the light is on.
To check with a light bulb you will need:
- The control itself is 12 V.
- An electric car pump or compressor, preferably with a pressure gauge. If they are not there, then use a regular foot pump.
- 12 Volt power supply. You can use a car battery or a computer power supply.
Connect the negative wire of the battery to the ground of the sensor, and the positive wire to a similar wire, but through the control. The light should light up. If not, then the sensor is faulty.
Start the pump or compressor and supply air to the sensor inlet. If the latter is working properly, then the light should go out.
Adjust the pressure using the pressure gauge; it should not exceed 1.5 atmospheres, otherwise the membrane may be damaged. Optimal limits are from 0.5 to 1.5.
When checking with a multimeter you will need:
- The device itself is switched to the “dialing” mode.
- Electric pump or other air blower.
Connect the multimeter to the sensor, minus to the body, plus to the center wire. The circuit will close and a signal should appear.
Turn on the pump and apply pressurized air to the sensor inlet. Monitor the pressure on the pressure gauge.
The circuit should open and the sound coming from the multimeter should disappear.
Checking the electrical oil pressure sensor
Checking the sensor with a multimeter
Electronic oil pressure sensors, used both on foreign and domestic cars, in particular on VAZ-2114 cars and other modern Ladas, are easy to check. Their design is similar to that of a rheostat, but they simply open the circuit at a certain pressure. Accordingly, its verification is even simpler. To do this you need:
- Set the multimeter to the “continuity” (break) mode of the electrical circuit.
- Ensure a tight connection between the air pump and the inlet (sensitive) hole where air is supplied. Here, similarly, it is necessary to ensure high-quality sealing, since the result of the experiment directly depends on this.
- Place one multimeter probe on the central output contact of the sensor, and the second on its body, “ground”.
- At the same time, use a pump to apply air pressure of about 1...1.5 atmospheres to the sensor. There is no need to blow hard so as not to damage the membrane. If the sensor is working properly, the electrical circuit will open almost immediately, under the mechanical action of the rod, which is in rigid connection with the bending sensitive membrane of the oil pressure sensor.
As is clear from the operating diagram of the sensor, if the circuit is open (detected with a multimeter), then the sensor is working. Otherwise, no. In rare cases, instead of the sensor, the problem why the oil light is on must be looked for in faulty (broken or damaged insulation) wiring.
You can also check the performance of the oil pressure sensor using another method. So, you need to remove the power wire from the sensor and short it to ground. If the sensor is working properly, the warning light on the dashboard should not light up. Otherwise the sensor is faulty.
Checking two sensors
On some modern machines, two pressure sensors of the same type (“new”) are installed. The first is designed for an absolute pressure value in the range of about 0.15...0.45 atmospheres, and is designed to open the warning lamp after starting the engine. Its verification is similar and follows the procedure described above. That is, the connection is the same. Its circuit should open when pressure is pumped into it in the specified range.
The second sensor is designed to monitor oil pressure while the engine is running. It is similar in type to the first, but its difference is to control the upper limit of the oil (in order to prevent it from increasing to a critical value). The upper value may vary and differs for specific car models. However, in most cases it is around 1.8 atmospheres. When this pressure level is reached or higher, the contact circuit should close and the engine oil pressure warning light should be activated on the instrument panel.
We recommend: How to change the alternator belt yourself correctly and quickly?
Checking the pressure sensor using a light bulb
To check the electric (new) oil pressure sensor, instead of a multimeter, you can use a light bulb designed to operate under 12 V DC voltage, as well as a power supply (battery) and a compressor (preferably with a pressure gauge). The verification algorithm is as follows:
Connection diagram
- Two wires must be connected to the contacts of the light bulb.
- Connect one end of the wire going to the light bulb to the output contact of the pressure sensor.
- Connect the ground from the power supply (or minus from the battery) to the housing (ground) of the sensor.
- Connect the plus from the power supply or battery to the other wire on the light bulb.
- If the sensor is working properly, then after turning on the power supply (or simply when contact is made from the battery), the light should light up. Otherwise, the sensor can immediately be considered faulty.
- Next, to check, you need to apply a pressure of about 0.5 atmospheres to the sensitive element of the sensor using a compressor or pump. The pressure value can be different, and it depends on what pressure the sensor is designed for. Usually it is around the already mentioned 0.5 atmosphere.
- When the pressure increases to the specified value (critical for the sensor), the light should go out, since this will open the control electrical circuit in the sensor body. If this does not happen, then the sensor can also be considered unusable.
Instead of a compressor, you can easily get by with a regular car or even bicycle pump, which will easily produce the required half-atmosphere air pressure.
Checking two sensors
Two oil pressure sensors are not uncommon on modern cars. The first one performs a standard function, signaling the presence of working pressure immediately after starting the engine.
The range of its operation (opening the circuit) is 0.15…0.45 atmospheres. It is checked in the same way as we described above.
The second sensor monitors the upper limit of oil pressure when the engine is running. It notifies via light and sound alarms of low oil pressure at high engine speeds.
It works and is tested in the same way as the first sensor, except that:
- The air must be pumped with high pressure. It may be different for each brand of car, but as a rule, it is 1.8 atmospheres. For example, on a Volkswagen Golf with a 1.8 engine it is 2.0 - 2.5 BAR. Therefore, it will not be possible to perform a check here with a conventional hand pump. And the car compressor must be connected to the sensor very tightly.
- The circuit is not permanently closed, like the first sensor, but rather open. Therefore, when checking, the light (control) should not initially light up, but light up when air is supplied.
Mechanical sensor check
On a VAZ “classic” and many other older cars, checking the mechanical oil pressure sensor can be done without a multimeter, but this does not mean that the procedure will be easier as with an electronic analogue.
You will need:
- Electric car pressure gauge.
- Manual pump or electric compressor.
Algorithm of actions:
- Remove the sensor and locate the two contacts on it. The first one is responsible for sending a signal to the oil pressure warning lamp. The second is for displaying readings on the pressure gauge.
- You need to understand the pinout of the contacts on the electric pressure gauge. Where are the plus, minus and third wire receiving the signal from the sensor.
- We take the mass from the DDM body through the cylinder block.
Let's put together a diagram. We connect the power and supply air from the pump at a pressure of 1…2 atmospheres.
If the sensor is working properly, then on the electric pressure gauge, as the pressure increases, the arrow will deviate upward. If not, the device is faulty.
The oil pressure sensor cannot be repaired and must be replaced immediately. When installing it, the seat is lubricated with heat-resistant sealant.
Also read about signs of a malfunctioning mass air flow sensor.
Oil pressure indicator on
The oil pressure gauge in your car will give you a good idea of the condition of the engine oil level. If the low oil light comes on, but you check the engine oil level and it is good, then a faulty oil pressure sensor is to blame. When this sensor fails, it will begin to give inaccurate readings. Once the readings are outside the specification, the warning light comes on. The sooner this sensor can be replaced, the less stress you will have regarding your car's oil level.
Advice from experienced
It cannot be said that one electronic emergency oil pressure sensor is convenient. The light does not go out, but it is not visible what pressure is in the lubrication system at this moment.
Also, if the oil was not changed on time, different brands were used, and after a major engine overhaul, clots may form in the system, due to which the sensor may not work on time. Oil starvation will occur, which will lead to a decrease in engine life or its wedge.
To solve this problem, experienced motorists recommend installing, in addition to the electronic sensor, a mechanical one with readings displayed on the dashboard through a pressure gauge.
To do this, automobile Kulibins use a special tee (2103-3810610), a fitting (2103-3810310), and two gaskets (10282460), with the help of which a mechanical analogue sensor and a standard electronic one are connected to the lubrication system.
A pressure gauge is mounted on the dashboard in any convenient place. You can take it from any VAZ “classic”, Moskvich or UAZ. The main thing is that the scale is convenient and understandable for you.
The wires from the DDM are placed in a hose or plastic corrugation and carefully mounted in the engine compartment. This must be done in such a way that they do not overheat and are not subject to mechanical stress.