Description of the device and its purpose
The RTD is a diaphragm valve installed in the fuel rail. So, on the one hand, gasoline pressure is applied to it, and on the other, springs, as well as air from the intake manifold.
When the engine suddenly stops, the valve is completely inoperative and in this situation the fuel is not discharged into the tank, as a result of which the pressure in the fuel system increases. This figure is 3-5 kg/cm² instead of the required 2.
And 5 kg/cm² affects the size of the fuel that enters the combustion chamber through the nozzles.
In this case, gasoline will not burn completely, since the composition of a complete combustible mixture should include one part of fuel, as well as 14.7 parts of air.
If the valve does not hold, then fuel circulates freely through the fuel system, which results in a decrease in pressure, and when the engine requires a large amount of fuel when the speed increases, there is not enough of it. In this case, the lack of fuel significantly affects the power; it is impossible to spin it to full capacity.
When the engine stops, the pressure in the system should remain constant, but since the check valve cannot hold it, when starting, you need to turn the starter for a long time to create the optimal fuel pressure for starting the engine.
Types and symptoms of regulator malfunction
The types of RTD malfunctions are as follows. The valve does not hold - fuel begins to circulate freely throughout the fuel system, the pressure in which decreases because of this. As a result, the engine does not have enough fuel when the speed increases, and its power decreases; The pressure in the system should not change after stopping the engine, but since the valve is not able to hold it, when starting the engine, you have to work with the starter for a long time to create the required pressure.
A completely inoperative valve means fuel is not discharged into the tank, and because of this, the pressure in the system increases. As a result, the amount of fuel supplied to the combustion chambers through the injectors increases - there is overconsumption and incomplete combustion of gasoline.
Signs of a faulty RTD are the following engine operation:
- unstable;
- stalls at idle;
- insufficient pickup;
- cannot develop full power;
- the crankshaft rotates at idle speed with a reduced or increased frequency;
- dips and jerks while the machine is moving;
- difficult starting - not always;
- the content of CO and CH in the exhaust gases significantly exceeds the permissible standards;
- excessive consumption of gasoline.
Possible signs of failure
If the fuel pressure regulator for some reason does not perform certain functions, this can be determined by the following signs:
- Unstable engine operation, it may stall when idling, although the fuel level seems to be sufficient and all systems are in working order.
- Increased or decreased crankshaft speed;
- The engine “loses throttle response.”
- The occurrence of dips and jerks in a running engine while driving.
- Increased gasoline consumption compared to what it was before;
- Increased CO and CH content in the exhaust.
- Starting the engine is carried out with great difficulty, but this property is not always clearly manifested.
If the regulator has become completely unusable, then the fuel pressure increases. So, instead of the norm for a VAZ-2110 car, which is 2.5-3.3 kg/cm², it reaches 4-5 or more. A short but very informative video about how this type of regulator works.
Thus, the fuel pump begins to supply more gasoline in volume, which does not burn completely, and overconsumption is guaranteed. Of course, such a regulator requires replacement and as soon as possible.
If the fuel pressure regulator does not provide the required level of influence or does not hold, then the lack of the required level of fuel pressure leads to the fact that normal fuel supply does not occur, and the VAZ-2110 begins to “choke” when it is necessary to increase the speed.
In addition, the starter is not able to quickly spin the engine; it has to be turned on many times. It is quite clear that excessive consumption of gasoline can be seen from the sensor readings.
But sometimes these readings begin to lie, and then it is no longer possible to know the true consumption. A situation is possible when there is half a tank of gasoline, but the indicators say that the fuel is almost zero.
Thus, the flow sensor may confuse you; before rushing to replace the regulator, you need to make sure that the device indicating the fuel level is working properly. It must be remembered that the VAZ-2110 has problems with this very often.
If you find that it is lying, you may need to adjust or completely replace the fuel sensor.
Symptoms of a problem
There are quite a lot of signs of RTD malfunctions and it is quite easy to confuse them with other problems, so before you start replacing, you need to check it, but this is discussed below.
One of the main and most obvious signs of a regulator malfunction is its jamming in the open position. For this reason, engine power drops noticeably. The engine may idle well, but the engine will not be able to develop high speeds due to lack of fuel pressure.
When starting the engine, whether cold or hot, you have to rotate the starter for a long time.
When the RTD is jammed in the closed position, excess pressure occurs, which can cause the fuel pump to fail. Excess pressure in the system leads to increased fuel consumption and incomplete combustion in the combustion chamber. The exhaust gases will have a distinct smell of gasoline with characteristic black smoke.
There are also other less noticeable signs of its malfunction:
- The internal combustion engine operates unevenly at idle and stalls;
- The required internal combustion engine power does not develop;
- The car jerks when driving;
You can learn more about the fuel system in our article.
Carrying out an RTD check
So, if everything is fine with the sensor, but there is excessive fuel consumption and other problems that indicate that the regulator is malfunctioning, then you need to check it.
This is done as follows:
- The fitting plug, which is responsible for controlling the fuel pressure, is unscrewed. If the seal ring is torn or it is no longer elastic, it (and possibly the entire plug) will need to be replaced.
- Next, the spool is unscrewed from the fitting; this is done as in any tire.
- Using a tire pressure gauge, which is secured with a clamp to the fitting, the level of impact is measured while the engine is running. It must be in accordance with the norm.
- When the regulator vacuum hose is disconnected, the pressure usually increases slightly. If this is not the case, then there is only one way out for the VAZ-2110 car - the RTD needs to be replaced. The price of a standard RTD ranges on average from 300 rubles, while an analogue RTD costs around 600 rubles.
You can find out how to clean the throttle valve on our website.
Here, the operating principle of a diesel engine turbine is described in detail.
We recommend reading this article, from which you will learn how to reupholster the interior with leather with your own hands.
Replacing the fuel pressure regulator for a VAZ 2110 (and other cars)
To ensure that your car is always on the road and there are no problems with the fuel pressure regulator, you need to take the time for a thorough inspection.
1) Under the hood of the car, open the fitting plug, which is responsible for controlling the fuel pressure at the end.
2) Take a special protective metal cap and carefully unscrew the spool from the inner cavity of the fitting.
3) Then attach a hose with a pressure gauge to it. Secure it to the fitting using a clamp. After this, you should start the engine and check the pressure shown by the pressure gauge. It should not be higher than 325 kPa ( 3.25 Bar ).
4) Carefully disconnect the vacuum hose from the pressure regulator. You will immediately see how the pressure will increase on the pressure gauge. If this does not happen, you should replace the device with a new one. A device that has not been repaired cannot be repaired. But how to change the fuel pressure regulator?!
5) Now you can slightly reduce the pressure in the power system and remove the vacuum hose from the RTD. To do this, you will need to unscrew the reinforcing nut on the fuel drain pipes to the pressure regulator.
6) You need to unscrew the two bolts securing the device to the fuel rail.
7) Now you can remove the regulator from the fuel drain pipe itself. If the ring does not immediately detach and remains in the ramp, remove it. It is put on the regulator before installation. The regulator must be installed in the reverse order, observing the exact sequence.
8 ) The new regulator is also installed in this sequence. It is first checked for serviceability and only then assembled. After installation, check its operation and serviceability.
So now you know the causes of fuel pressure regulator failure and how to replace the fuel pressure regulator. The most important thing is not to rush, and follow the sequence of actions.
How to replace an RTD
The RTD is replaced in the following order:
- The pressure in the fuel system needs to be reduced; the nut securing the fuel pipe to the RTD is unscrewed.
- The bolt is unscrewed with a 10" wrench, which secures the guide tube of the direct oil level indicator, and the tube is removed.
- The bolts that secure the RDI to the ramp are unscrewed.
- The fitting is removed from the fuel rail and the RTD is removed.
- When installing a new regulator, it is recommended to lubricate the O-rings with gasoline.
VAZ fuel pressure regulator: causes of malfunctions and ways to solve them
An important element of the fuel system of any car is the fuel pressure regulator. The performance of the fuel system depends on how stable the fuel pressure regulator is.
The fuel pressure regulator in VAZ cars is a valve-membrane against which the regulator spring rests on the intake manifold side, and the fuel pressure on the other. After stopping the engine, it is the RTD that maintains pressure in the fuel system. If the pressure regulator is worn out, restarting the engine will require some time and manipulation of the ignition key.
The RTD is located either in the fuel tank itself, or, if the fuel system has a recirculation system (increasingly popular), then it moves to the fuel rail. The main task of the RTD is to maintain the difference between the pressure in the tank and the combustion chamber, the injector and the intake manifold. It is thanks to the operation of the fuel pressure regulator that control over the operation of the fuel injectors, the level of pressure in the fuel system is ensured, and excess volumes of fuel are returned to the tank through the return system.
Signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator
Over time, the spring in the regulator may sag without creating the necessary force. The fuel will begin to return back to the tank. This will cause a decrease in pressure in the fuel rail. Such a breakdown will lead to a lack of fuel and loss of power in the engine.
If the valve is jammed, the pressure level in the fuel frame will change differently each time. In this case, the engine will not operate regularly, and the car will twitch during acceleration.
The main symptoms of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator :
- Uneven engine operation;
- Stopping the engine at idle;
- A sharp increase or strong drop in the crankshaft speed at idle;
- Loss of motor power;
- Poor vehicle acceleration when shifting gears;
- Poor response to the gas pedal;
- Car choking when driving, frequent jerking;
- A sharp increase in consumption.
If you detect at least one of the above symptoms, you should immediately check the device.
The first sign of RTD malfunction
The first sign of a faulty fuel pressure regulator is increased fuel consumption. The reason for this is simple - due to problems with the RTD, excess gasoline or diesel fuel from the internal combustion chamber does not return to the tank. This leads to an increase in pressure throughout the entire fuel system; Moreover, this increase can be significant - twice or even three times higher than the norm. If the norm is 2 kilograms per square centimeter, then with a faulty RTD this figure can reach 5 and 6 kilograms per square centimeter. This situation cannot take place for a long time, since all the “weak points” of the fuel system are very quickly discovered, and one or another breakdown occurs. In turn, a malfunction in the fuel system is fraught, firstly, with breakdowns, which, in turn, will require major repairs or even a complete replacement of the engine, and, secondly, with serious situations on the road, which are no longer fraught with costs, but with a threat to health and the lives of you and your loved ones.
It should be noted that malfunctions of the VAZ 2110 RTD after five years of operation are a regularity. It is necessary to begin monitoring the condition of the regulator after three to four years of active operation. If your car is already of advanced age, and at about the same age, the fuel pressure regulator should be monitored especially carefully for signs of malfunction.
If the power decreases and the dynamics of the engine deteriorate, the turbocharger may have stopped working altogether. This means that the fuel is not supplied to the internal combustion chamber under pressure, but gets there naturally, so to speak, by gravity. In this case, the engine at high speeds cannot cope with the fuel shortage, which can lead to rapid breakdowns.
Symptoms of failure
Signs of a malfunction of the VAZ 2110 fuel pressure regulator may be the following:
- Instability in the operation of the power unit;
- inability to continue to function at idle;
- lack of power (insufficiency);
- short-term loss of speed while driving;
- excessive consumption of fuel;
- exceeding the norm for the presence of CO and CH in the exhaust.
Also, the RTD must maintain the gasoline pressure in working order in the system even after the car has been turned off. If the car, after standing for a while, does not start immediately (long rotation through the starter), then this means a loss of performance due to low pressure. If these symptoms are present, it is necessary to check the VAZ 2110 fuel pressure regulator.
Problems and their causes
- Fuel consumption has increased. The cause may be excess pressure in the fuel system due to a faulty fuel pressure regulator.
- The engine power has decreased, the dynamic performance of the car has deteriorated and continues to deteriorate. The reason is often that the RTD has stopped holding pressure (for example, due to a high level of spring wear).
- Problems with starting the engine: in order to start the engine, you have to repeatedly “torment” the starter. The reason is difficulty in the movement of fuel in the fuel system due to a faulty (for example, jammed) fuel pressure regulator.
- The car periodically stalls, and unexpected and unmotivated jerks are possible while driving. The reason is the jamming (permanent or periodic) of the fuel pressure regulator. It is to pressure surges in the network that you owe all of the above “joys”. Such manifestations are extremely dangerous, especially when driving around the city, with a minimum distance between vehicles.
The most common fuel regulator malfunctions
- The pressure is gone . This is why gasoline is pumped back into the gas tank and the car does not start.
- The valve becomes clogged and gasoline is difficult to flow through. As a result, gasoline begins to leak from almost everywhere. This is the most important malfunction of the pressure regulator. As soon as gasoline consumption increases sharply, you can immediately change the regulator.
- This reason is a development of the second. The valve becomes completely clogged and gasoline does not enter the fuel supply system.
- Uneven pressure . Usually caused by a stuck valve. Because of this, the car moves unevenly: it jerks or even stalls.
However, not all faults point to the valve, therefore, it is necessary, first of all, to learn how to check the pressure regulator, and then draw the appropriate conclusions.
How to check the fuel pressure regulator
If you have any suspicions about the RDT, its performance should be checked as soon as possible. It’s quite easy to do this even at home, just follow a few simple instructions.
We unscrew the fitting responsible for the fuel pressure and inspect the o-ring. Its condition is of great importance, so if this element is old or damaged, you will have to purchase a new ring. The next step is to unscrew the spool valve from the fitting.
At this point you will need a pressure gauge to measure the pressure while the engine is running. And if the pressure is less than what is specified by the manufacturer for the VAZ model you own and the installed engine, the fuel pressure regulator needs to be changed. Moreover, it is inexpensive, the operation itself is very simple, and you can evaluate the result on your first trip.
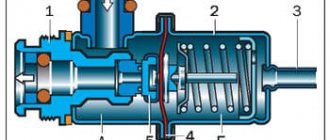
Operating principle of the fuel pressure regulator
To understand how a fuel pressure tester works, you need to know how it works. It consists of the following parts:
- Fuel pump;
- Pressure regulator;
- Electronic control unit pump;
- Fuel lines;
- Baka;
- Fuel filter;
- Injectors;
- Inertia switch.
Thanks to its design, the regulator controls and maintains the same fuel pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. Where is the fuel pressure regulator installed? Install it in the fuel tank.
Features of the device for monitoring fuel pressure in a system with fuel recirculation
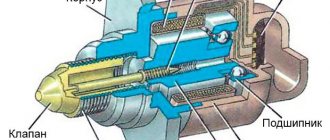
The RTD is divided by a membrane into two chambers:
- Fuel;
- Spring.
The valve holder itself is connected to the membrane and presses the valve to the seat.
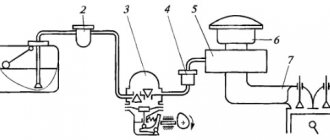
The fuel pressure, which is supplied to the chamber through special inlet passages, acts on the membrane from below. The pressure of the spring and the intake manifold acts from above. Sometimes the pressure can exceed the spring force. In this case, the valve is opened slightly, allowing gasoline to flow into the return pipeline. In this case, the pressure in the intake manifold must be taken into account. During operation of the fuel pump, fuel leaves the tank, heading towards the filter. There it is cleaned and goes to the regulator. The regulator maintains the effective pressure in the system without stopping. The main thing is that all actions must occur correctly.
The device itself is located inside a steel case. It must also be able to withstand high pressure. The device mechanism itself consists of a diaphragm and also has a check valve. It prevents the fuel, which is under pressure, from returning to the line.
VAZ 2110 fuel pressure regulator
Lada VAZ-2110 (2111, 2112). Malfunctions of the engine fuel pressure regulator
When operating a gasoline or diesel engine, the driver may encounter the fact that when pressing the gas, the engine does not gain speed. Note that after installing an LPG on a car, such a problem often occurs.
Problems in the engine power system can vary. For this reason, during diagnosis it is necessary to look for certain signs of a malfunctioning fuel pressure regulator. Most often, the main symptoms are considered to be when the engine does not pick up speed and does not develop full power, and also stalls in different operating modes. In the list of main signs, experts note:
Malfunctions
Worn rings
If the sensor begins to malfunction, this can be determined by characteristic signs indicating the presence of a breakdown:
- The engine starts to run unstably;
- The engine cannot idle;
- Power disappears, its lack is felt;
- While driving, the speed disappears for a while;
- Fuel consumption increases significantly;
- The level of emissions from the exhaust system increases;
- A car that has been parked for some time is difficult to start, and the starter rotates for a long time.
All this tells the car owner that something has happened to the fuel pressure regulator; it is necessary to urgently intervene in the situation and solve the problem as quickly as possible.