Widely used gas equipment consists of a considerable number of elements. Perhaps one of the main ones is the gearbox, which plays the role of an injector or carburetor in this equipment.
Of course, the operating principles and design of the unit are slightly different from the noted fuel distribution mechanisms, but in general they are quite similar. We will talk in more detail about the LPG reducer, methods for setting it up and other information about the part in the material presented below.
A few words about the design of the LPG gearbox
The understanding of the essence of gear systems with which gas equipment is equipped lies through consideration of its general concept. Everyone knows that gas, represented by propane or methane, is in a gas cylinder under high pressure and in a liquefied state.
In its standard form, supplying such fuel to the internal combustion engine chambers is not possible, because for its operation it is necessary to prepare a fuel-air mixture. It is the preparation of the latter that is carried out by a standard gas equipment reducer.
Please note that not all generations of gas equipment are equipped with gearbox systems. So, for example, the last two generations of gas equipment, numbers 5 and 6, do not have this equipment, because the supply of gas to them is liquefied. However, on gas equipment of 1-4 generations, the gearbox is an integral part of the system.
In many ways, the correct functioning of gas installations depends on the stable operation and configuration of gear equipment, which should not be forgotten.
Structurally, LPG gas reducers of any generation are evaporator units that convert liquefied propane or methane into evaporated gas, which is already sent to the intake tract for mixing with air, and then to the combustion chambers of the engine.
The design of the unit involves a system of several sequential chambers separated by valves. The operating principles of the GBO 2-4 and partial first generation gearbox are as follows:
- Gas in liquefied format is supplied to the inlet tract of the reducer, called the unloading valve;
- The latter produces dosage and proper distribution of fuel, which is carried out either mechanically (on vacuum gearboxes) or electronically (on gearboxes with solenoid valves and their control unit);
- After this, the gas evaporates and it enters directly into the engine through its manifold, where it is mixed with air.
Note that any gearbox, similar to a carburetor, has an idle channel through which fuel enters the internal combustion engine chambers at idle speed, as well as various adjustment elements.
In any operating mode of the engine, it does not require liquefied gas, but a fuel-air mixture, prepared in the order noted above through evaporation. To achieve the latter, special evaporation elements and their chambers are used.
Depending on the number of chambers the gas passes through until complete evaporation, there are single-stage, two-stage and three-stage LPG reducers. Regardless of the method of organizing evaporation, the pressure in the chambers invariably changes during its process, usually downward.
Today, the most popular are gear systems with two evaporation chambers, which are used on LPG from Lovato, LPG on methane and equipment.
The gearbox design, in general, is exactly the same on both second-generation and fourth-generation equipment. At the same time, it makes absolutely no difference whether propane gas is used in a car or methane gas. That is, the “carburetor” of any gas equipment is an absolutely identical unit in all its formations, which naturally involve the use of this unit.
Features of gear systems
It would seem that the structure of the LPG gearbox is quite simple, and there are no difficulties in understanding the principles of its operation. So why is this unit arousing keen interest among motorists?
Perhaps the main reason for close attention to gear systems installed on gas equipment lies in the features they have. To be more precise, there are only two of them:
- “Frozenness” of the gearbox. Probably every motorist has heard at least once that gearbox equipment for gas equipment often freezes. Is it true? And this phenomenon is connected with the fact that gas compressed to 16 or, as in the case of methane, 100-200 atmospheres, actively evaporates and loses pressure to 1.8-2 atmospheres, which is accompanied by the intake of energy (heat) from the environment. As a result, the gearbox freezes, sometimes to such an extent that it simply ceases to efficiently perform its main functions. To neutralize such a sensitive feature of gas “carburetors,” it is recommended to install them close to heating elements and, in winter, to warm up the car not on gas, but on gasoline;
- Types of equipment used. By the way, HBO gearboxes can be either vacuum, which are used on carburetor engines, or electronic, used on injection engines. How it needs to be configured depends on the configuration of the selected equipment. If, in the case of adjusting a gearbox with a vacuum operating principle, you will have to use all the skills of setting up carburetors, “shamanizing” the adjusting screws, then when using an electronic unit, it is enough to adjust its operation by using a special program on a computer connected to the LPG control unit. Of course, both tuning options are good, but the best way to adjust electronic gearboxes is definitely the best one. So, for example, on electronic systems it is possible to flexibly adjust the pressure in the chambers, which is simply unrealistic in the case of “vacuum systems”.
Having understood in detail each feature of the LPG gearbox, it is quite possible to avoid problems with this unit during its operation and configuration. Otherwise, you should be prepared for them.
Repair and adjustment of gearboxes
Due to the fact that the gearboxes of modern gas equipment have different principles and construction schemes, the methods for setting them up are also multifaceted. The main differences are in the methods for setting up electronic and vacuum gearboxes, which we will consider. In any case, before adjusting the gear system of your LPG, the motorist needs to:
- In the case of using vacuum equipment, prepare a slotted screwdriver; when using an electronic gearbox, prepare diagnostic equipment (GBO cable, laptop and a special program for configuration);
- Find out the necessary settings for your type of equipment;
- Check out the adjustment methods below.
When answering the question of how to adjust the gearbox to the correct mode of operation, it is worth distinguishing between the concepts of vacuum and electronic equipment, the principles of adjustment of which, we repeat, have significant differences. Electronic systems are the easiest to adjust. Setting up an LPG reducer of this format takes place in the following order:
- The motorist connects diagnostic equipment to the gas equipment control unit;
- Enables the setup program on the laptop;
- Sets the pressure indicators in correctional chambers, idle speed and similar values necessary for its gas equipment. Also at this stage it is possible to identify a malfunction of the unit or the need to drain condensate from the gearbox.
Replacing the multivalve
Often the multivalve is changed together with the cylinder, and sometimes separately. This important part has several functions.
- Test
- Shut-off
- Executive
- Safety
And it is very important that the multivalve copes well with the tasks assigned to it. There is a lot of information on the Internet: articles and photographs where, due to unprofessional installation, the cylinder simply burst from excess pressure. And just one of the functional tasks of the multivalve is to relieve excess pressure in the cylinder.
Repair of 4th generation gas reducer
A gas reducer can cause a lot of trouble for motorists if you do not monitor its operation and do not service it on time. Repair of the 4th generation LPG gearbox consists of replacing rubber seals, membranes, cleaning, and adjustments. Despite its apparent simplicity, this operation is quite difficult to carry out without the skills to repair gas equipment. And there is a possibility that the problem associated with the gearbox will worsen. And then there will be only one option left - replacement with a new one. In some cases, it is worth changing the gearbox right away, rather than spending money on repair kits and additional settings. It is necessary to change the reducer according to the installed gas equipment; the use of analogues is allowed. Only specialists can suggest the best options.
Repair of 4th generation gas injectors
Repairing gas injectors is a specific operation. Gas injectors are essentially valves that dose the amount of incoming fuel and their operating cycle is completed in a short period of time. The following symptoms of malfunction can be identified:
- Increased fuel consumption;
- Loss of acceleration characteristics of the machine;
- Unstable engine operation, internal combustion engine throttling
- A noticeable delay in response when pressing the gas pedal;
- Interruptions in the operation of various sensors;
- Clattering sound in the injectors (extraneous noise is heard);
- The car is unstable when idling.
There may be several reasons for this
- Wear of the damper rubber rings on the valve stems (this causes the injectors to knock)
- Making the seat (seat) of the valve or its locking rubber
- Wear of the rod (also called the piston, anchor) or sleeve (also called the core, cylinder, bulb)
- Armature jammed in the cylinder
- Weakening the elasticity of the piston return spring
- Failure of the electromagnetic coil (solenoid)
Violation of the integrity of electrical wiring
The listed reasons can appear either naturally or due to improper operation, as well as the use of low-quality parts, or untimely maintenance. For example, untimely replacement of filters leads to clogging of the nozzle and accelerates its wear. The quality of installation also affects the longevity of LPG injectors. Elementary neglect of the electrical supply can lead to failure of the entire injector system. To figure out what’s wrong and accurately determine the quality of operation of each injector, it is necessary to carry out a test using diagnostic equipment. What is possible only in the conditions of a dealership center. Based on the diagnostic results, a work plan is drawn up to repair or replace the entire unit or its components.
Also, in many cases, after repair or replacement of parts, computer configuration of the equipment is required. Fine-tuning the parameters can only be done using the original software of a particular manufacturer.
The design of the gas gas reducer and the principle of operation of the mechanism on different generations of gas installations
The main task of a reducer-evaporator designed to work with propane is to reduce the pressure of the mixture that comes from the cylinder. Let us remind you that propane is stored in a liquefied state in the tank.
A reducer is needed to convert the mixture into a gaseous state. To do this, the mixture is heated due to the high temperature of the engine coolant. After this, the gas, ready for operation, is supplied to the power unit.
Design and key operating principle
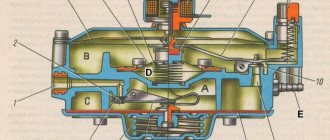
A gas reducer is a combination of several chambers, between which special valves are installed. One of the main functions is performed by a valve installed at the output of the gearbox. Manufacturers can use different options for such devices - mechanical and electrical. Some of them can also be used to prevent popping.
Principle of operation
Lovato and Tomasetto LPG gearboxes are considered to be quite popular among domestic car enthusiasts. They can often be seen on cars with carburetor engines.
The advantages of such products are affordable cost and ease of setup. No less important for lovers of economical driving is the availability of repair kits in stores. Many car enthusiasts have also chosen Atiker and Alaska gearboxes, which have good performance characteristics.
After heating the gas mixture and its transition to a gaseous state, it passes through the outlet valve and is supplied to the intake manifold (depending on the type of gas equipment, the connection method may be different).
In the manifold, gas is mixed with air, after which it is supplied to the engine. In fact, the gearbox of gas-cylinder equipment, according to the principle of its operation, resembles a conventional refrigerator. This means that during operation its temperature drops noticeably.
To avoid various troubles, it is recommended to follow the manufacturers' recommendations for connecting the gearbox to the vehicle's cooling system. A very important parameter is the temperature of the gearbox.
If mistakes were made when connecting it and the gearbox does not warm up well, you can only dream of stable operation of the engine. Also, due to the need to warm up this unit, experts do not recommend starting the engine on gas.
The best option is an initial warm-up on gasoline and subsequent switching to propane or methane. Sometimes the mechanism freezes so much that the surface of the gearbox becomes covered with frost. This is a sign that the system is not working correctly and needs to be configured or connected in another way.
Note that when purchasing a gearbox, it is very important to choose the right performance. Buying a model that is too weak will result in the unit not being able to warm up properly while operating at maximum power. This usually ends with a visit to a specialized service for gas equipment repair.
Electronic and vacuum components
In the first generations of automotive gas equipment, a vacuum-type mechanical gearbox was used. The reaction of the membrane depended on the vacuum in the intake manifold, which was connected to the reducer by a separate tube.
When the engine started, the carburetor began to consume fuel, and as a result of a drop in pressure, the vacuum valve opened to supply gas. When the engine is stopped, the pressure returns to normal, after which the gas supply stops.
Adjustment of the 2nd generation GBO reducer is carried out very simply - by rotating the so-called “greed screw”, which regulates the volume of supply of the gas mixture.
The following advantages of a vacuum reducer can be highlighted:
- ease of setup;
- no problems with maintenance (repair kit replacement);
- affordable price;
- high quality workmanship.
2nd generation
Electronic gearboxes have already appeared in the 2nd generation HBO. These mechanisms are equipped with an exhaust solenoid valve, which is controlled by an elementary power unit. The presence of electronics helps to automatically turn on the fuel supply when the engine starts.
3rd and 4th generation
The 4th generation HBO gearbox has a simplified design, since some processes occur directly in the intake manifold. The same principle applies to 3rd generation gearboxes. These mechanisms have only two stages and a solenoid valve. At the same time, the number of sensors in the gearbox has increased. Manufacturers also installed a multi-level filter for gas purification.
Connection and installation
Connecting a gearbox is a very responsible procedure. The main principle for choosing a place under the hood is that the gearbox must be installed parallel to the movement of the vehicle , while ensuring reliable attachment to the body.
Malfunctions. Repair.
If you decide to carry out repairs or adjustments yourself, make sure you have the necessary qualifications. Poor repair of gas equipment can cause a fire, explosion or poisoning. After completing the work and assembly, make sure that the device is tight and operates correctly. The tightness is checked by applying a soap solution to all joints. No bubbling indicates there is no leak. But you shouldn’t delude yourself. The tightness will need to be checked several more times (after a day, three days, a week of operation), and then checked regularly, since a leak may occur some time after the start of operation.
Main malfunctions: the gas pressure at the outlet does not correspond to the nominal value (reason: the spring is broken or deformed), gas leakage (reasons: the membrane is damaged, the tightness of the connection between the membrane and the housing is broken, the float valve is leaking)
Here is a selection of materials:
IN
Everything you need to know about heating and climate control Features of the selection and maintenance of boilers and burners. Comparison of fuels (gas, diesel, oil, coal, wood, electricity). Do-it-yourself ovens. Coolant, radiators, pipes, heated floors, circulation pumps. Chimney cleaning. Conditioning
If the float bypass valve leaks, then the leak may not occur in the reducer itself, but somewhere further, for example, in a gas stove, since in this case, in zero consumption mode (when the stove or some other consumer is turned off), at the outlet reducer and gas pipes, the pressure can reach the inlet pressure. Gas gradually leaks through the valve, and there is nowhere for it to go. If there is a gas cylinder at the inlet, the pressure can reach 15 bar, which is 500 times higher than the nominal one. Such pressure will definitely lead to leakage. At the same time, it is difficult to detect this malfunction, since when the stove is turned on, the pressure normalizes. There is no sign of overpressure (flame blowout). The fault can only be identified by measuring the outlet pressure in zero consumption mode. It can be no more than 20% more than nominal.
To repair, the gearbox must be disassembled. Only a dismountable gearbox with a spring can be repaired. Sealed gearboxes are not suitable for repair.
In the picture, the membrane is with the bottom side up.
An inspection will show if there are defects in the membrane or a broken spring. A torn membrane can be replaced. But it’s not worth it, it’s better to buy a new gearbox, since it’s quite difficult to hermetically connect the new membrane with the washers. A broken spring can be replaced. Most often, the spring does not break, but simply compresses a little over time. As a result, the outlet pressure becomes lower than nominal. This malfunction can be easily corrected by placing a gasket between the housing and the spring. Read about this below in the section on transferring to another pressure.
Membrane - top view.
If you have diagnosed problems with the bypass valve, then you need to inspect it. It is a tube with a thin hole. A piece of hard rubber mounted on a rocker arm is pressed against the end of the tube. The valve may not close for the following reasons: Firstly
, the mobility of the rocker arm is impaired.
Move it with your hands, make sure it moves freely. If there are problems, grind or replace the hinges. Secondly
, a piece of rubber was worn out and torn.
It can be removed with a sharp knife and replaced by gluing another one of the appropriate size in its place. Thirdly
, the end of the inlet tube may not be smooth, with damage and roughness. This prevents a tight seal. The end can be sanded with fine sandpaper.
Gas reducer
When considering the question of how the LPG gas reducer functions, what its features are and how it affects the overall operation of gas-cylinder equipment, motorists are faced with a lack of information regarding the components of gas equipment. This article provides a brief analysis of the device and the basic principles of its operation, as well as a classification of gearboxes of various generations
Operation of the gearbox in different generations of gas equipment
When examining in detail the principles of the operation of gas equipment, many people have a question about how liquefied gas (methane or propane), under high pressure, turns into a vaporous gas-air mixture that can be injected into the engine. In different generations of HBO, the process can be organized in completely different ways.
Thus, in the most innovative injection systems of the 5th and 6th generations, this issue is not relevant, since direct-flow injection occurs from the liquid phase. However, the bulk of gas equipment on the market belong to the 1st-4th generation, and a reducer is used to convert gas into fuel in such systems.
The normal functioning of the vehicle directly depends on its adjustment and quality of work.
The design and key operating principle of the gas reducer
A gas reducer is a mechanism that consists of a number of chambers connected in series, separated by valves. The main thing is the unloading valve at the outlet, which also plays the role of a kind of injection dispenser. This valve can be either electromagnetic or mechanical, and also have additional protection against possible popping.
To properly adjust the LPG gearbox in the event of a malfunction, it is also necessary to have a repair kit, which includes seals, gaskets and rubber wear rings. The gearbox, regardless of generation, always has an evaporative element and an idle channel.
Principle of operation
Liquefied propane or methane passing through the line enters the first stage of the reducer and evaporates with expansion, simultaneously reducing the pressure in the system. Depending on what type the gearbox belongs to, the generation and the manufacturer, there may be one or several stages.
Examples include the Lavato LPG gas reducer or Tomasetto LPG reducers, which are aimed at carburetor cars with a two-stage evaporation system, and at the same time are distinguished by a reasonable price, ease of further maintenance and the availability of repair kits at affordable prices.
The exhaust valve passes gas ready for use through a special line into the manifold, then the gas is mixed with air to a certain proportion and enters the engine.
During evaporation, the gas expands; if propane is compressed to 16 atmospheres, and methane to 200, then the pressure drops to 1.8 atmospheres. This kind of process, according to thermodynamics, occurs with the rapid absorption of heat and energy from the external environment.
Functionally, the reducer is little different from a standard refrigerator, and therefore the gas reducer freezes during operation.
The mechanism may freeze to such a stage that it begins to become covered with ice or frost and becomes unsuitable for further operation, since due to the swollen valve, the installation allows liquefied gas to pass further (in this case, a repair kit and new adjustment of the LPG reducer will be needed).
To prevent this phenomenon, the device is connected to the cooling system and installed closer to the heating elements of the car. The temperature of the LPG reducer is the most important indicator; it is precisely because of the peculiarities of the gearbox operation that in cold weather it is impossible to start the engine on gas; first it needs to be warmed up on gasoline, and only then switch to methane or propane.
Each gearbox has its own performance, and if the wrong choice is made, the gas supply may be insufficient, the gearbox will work more intensely and cool down more. Ultimately, this can lead to the shutdown of the gas installation and the need for subsequent repairs.
Classification of different types of gas reducers
Device components may vary depending on generation. The methods of locking the unloading chamber and the adjustment methods also vary. In earlier generations there was a vacuum mechanical reducer; the membrane responded to the vacuum level in the intake manifold, to which there was an additional tube.
When the engine started, the carburetor began to suck in fuel, and the falling pressure opened a vacuum valve to the gas flow. If the engine stops, the pressure returns to normal and blocks the flow of propane. To adjust the LPG reducer, simply rotate the gas supply metering screw (greed screw).
Gas reducers for gas cylinder, price and types
Let's try to choose a reducer for gas cylinders, from those popular types that are in greatest demand among consumers. Let’s take a look at the gas appliance market and find out what the price for a gas reducer for a cylinder was at the end of 2017.
Household gas reducer RDSG for propane stabilization
The leading position in the market, and among consumers in the country, is occupied by the RDSG-1-1.2 “Frog” device with a threaded fastening. The RDSG-2 Baltika gearbox equipped with a threadless connection is not inferior in popularity. Both leaders represent the simplest design. As a result, they can offer the lowest possible cost. Specifications: — inlet pressure from 0.7 to 15.7 Bar; — the output pressure lies in the adjustment range from 30 to 32 mBar; — device weight 310 g; — permissible operation in the range from -30 to +45 ±3 °C; — gas throughput characteristic — 1.2 m3/hour. You can buy a gearbox RDSG 2-1.2 Baltika or RDSG 1-1.2 Frog for up to 350 rubles.
Source: https://teplogalaxy.ru/reduktor-na-gazovyj-ballon/
The principle of operation of a gas reducer on a car
Each element of gas equipment performs a specific function. Fuel consumption and the operation of the vehicle engine in general depend on the coherence of the entire system. The key role in this complex scheme is played by the gas reducer.
How does a gas reducer work, why is it so important to maintain it in perfect working order? The answers to these questions will help car owners navigate the choice of this device and recognize gas equipment problems in a timely manner.
What is a gas reducer?
The principle of operation of the gas reducer in household gas cylinders, in the main gas pipeline network, where pressure adjustment is required, in the gas equipment of cars, is similar. This device is designed to reduce the pressure of gas fuel and maintain this pressure at an optimal level.
If the device does not cope with its functions, the safety and performance of the gas system will be at risk. In all cases, the task is the same: to ensure that the gas pressure is always at a given operating level.
To understand the principle of operation, the device can be divided into series-connected zones separated by valves. The most important of them, the unloading one, additionally performs the function of an injection dispenser. The device contains an evaporator, as well as an idle channel.
On a note! In innovative gas equipment kits of the 5th and 6th generations, installation of a gearbox is not required: gas injection occurs in a liquid state.
On what principle does the device work?
The temperature of the antifreeze should rise to 40. The operation of the gas reducer is possible only after the car has warmed up well. How does a gas reducer work on a car?
The following happens:
- Liquid gas from the reservoir enters the filter and is purified. There it remains while the solenoid valve is closed.
- The fuel then passes through the 1st stage valve seat and turns into steam. The membrane, under its pressure, pulls back the valve rocker arm, it lowers onto the seat and the gas flow stops. This gives a working pressure of 0.4 atm. It is adjusted by a spring mechanism.
- Automotive gas fuel moves further to the 2nd stage valve seat. The fuel then goes through the outlet fitting to the engine.
Idling
The fuel supply to the 2nd stage is controlled by the valve load. The adjustment screw rotates through a spring mechanism. The elastic membrane “freezes” in equilibrium. In this case, the vacuum from the internal combustion engine at idle is compensated by the load of the spring mechanism. This is the principle of operation of the LPG gearbox at idle speed.
What happens after the valve opens?
The throttle valve opens and the ejection process occurs. The 2nd stage diaphragm plate deflects in proportion to the load experienced by the motor. It pulls the valve rocker, opening the seat and increasing the intensity of the fuel supply. Such actions automatically increase engine speed.
Operating principles of gearboxes in various generations of gas equipment
Despite the fact that the principle of operation of the GBO gearbox of generations 1, 2, 3 and 4 is subordinated to a single task, the equipment of the device varies depending on the generation. The unloading compartment locking methods and settings are also different.
1st generation gearbox
In the 1st generation there was a vacuum device of a mechanical type. The membrane plate responded to the vacuum in the intake manifold, to which an additional line was extended.
When the engine started, the carburetor began to draw in fuel, the pressure dropped, and the vacuum valve opened the way for fuel. The engine was turned off, the pressure returned to normal and the fuel inlet was blocked. The device was adjusted simply: by mechanical rotation of the greed screw.
These are the main differences in the operating principles of the gas reducer of the 1st and 2nd generations.
2nd generation gearbox
The operating principle of the 2nd generation gas reducer has evolved. Now this is not a vacuum, electronic device. An important addition: it is equipped with a solenoid intake valve controlled by the power unit.
This ensured an automatic response of the device to starting the car engine. The solenoid valve supplies gas based on impulses from the oxygen sensor. This is the main advantage of an electronic type device, since older carburetor engines do not always have enough vacuum for the membrane to work.
Gearbox 3rd and 4th generations
In the 3rd and 4th generations of HBO, this device is simplified in design. Some options have been transferred to the collector. There is no need for a large number of membrane partitions. For a split injection system, 2 stages and one solenoid valve are enough.
The number of sensors has become larger in number. A complex design filter device was added to ensure gas purification.
The mechanism has become more convenient to configure. The electronic control unit is connected to the laptop. A special program is launched that performs configuration and diagnostics. Devices from the brands Tomasetto and Lovato are easy to adjust.
The operating principle of the gas pressure reducer must be taken into account when choosing this device. Pay attention to what generation it belongs to, whether it has dust and moisture protection. Power characteristics should be with reserve. But the dimensions must correspond to the area that can be allocated to the device in the engine compartment.
LPG malfunctions
Regardless of the classification of the gas system, the symptoms of component failure are similar for all generations. Let's briefly describe them.
- smell of gas in the cabin
- smell of gas from the exhaust pipe
- loss of traction when running on gas
- unstable operation at idle
- car stalls when switching to gas
- The car experiences jerks when driving
All these signs indicate that it is necessary to look for and eliminate the cause of the malfunctioning equipment.
The principle of operation of the gas water heater reducer
By opening the water tap, water enters the reducer, resting against the constricted Venturi nozzle, creating pressure that puts pressure on the membrane.
Water passes at the bottom of the membrane, the pressure is less at the top. The pressure difference bends the membrane upward, which acts on the plate, the plate presses on the rod. The steel rod sends a signal to supply gas and lights the burner. Shutting off the water, the membrane bends down, the rod lowers, the water pressure in the reducer is equalized, and the burner turns off.
The retarder ball is responsible for the gas supply rate. The pressure created by the membrane pushes the ball to the side. Moving along the channel, the ball creates a smooth activation of the burner. When turning off the water, the ball moves to the side without interfering with the passage of water. The rapid outflow of water quickly turns off the gas.
The smoothness of gas activation is additionally regulated by a screw installed inside the plug. By rotating the adjusting screw you can adjust the speed of turning on the gas. Removing the retarder or incorrect manual adjustment will result in the gas suddenly turning on with a pop.
Gearbox adjustment
After the car gearbox has been repaired, it needs to be adjusted, which may vary slightly for different models. For do-it-yourself adjustment, there are two screws on the gearbox - for regulating the idle speed and a sensitivity screw (gas amount).
To adjust the LPG gas reducer, start the car engine using regular fuel - gasoline - and wait until it warms up to operating temperature. The dispenser on the cylinder should be fully open, the sensitivity screw should be fully tightened, and the idle adjustment screw should be unscrewed five turns.
Switch the car engine to run on LPG. While maintaining the speed with the gas pedal or choke handle so that the engine does not stall, turn the adjustment screw from idle until it operates at maximum speed. Now, when tightening the screw, you need to set the engine speed to the same speed as when running on gasoline.