Exhaust system catalyst
The catalytic converter (catalyst) reduces the toxicity of exhaust products.
This is realized by converting toxic gases into harmless ones as a result of the reduction of nitrogen oxides, during which oxygen appears. In turn, oxygen is used as a catalyst for the combustion of carbon monoxide and hydrocarbons. Depending on the principle of operation, neutralizers can be reducing or oxidizing. In both cases, the catalyst is a non-separable ceramic structure in the form of a honeycomb, protected by a special coating made of a fire-resistant platinum-iridium alloy. The reliable and durable design of modern catalysts is designed for efficient operation over a range of 150 thousand kilometers.
The main reasons for premature failure of the catalyst may be destruction or damage to the carrier unit as a result of corrosion, contamination or melting. The neutralizer can melt when a certain amount of the combustible mixture burns out inside its structure due to its incomplete combustion in the combustion chamber as a result of malfunctions in the fuel supply and ignition systems.
Main elements of the exhaust system
The design of the exhaust system becomes more complex, but with each new car model it includes all the same elements.
Collector
The exhaust pipe is an intermediate link between the car engine and the converter (catalyst). The collector is responsible for the removal of gases. Since in this case there is a very strong mechanical and temperature load, which can reach up to 1000 degrees, quite strict requirements are imposed on this part of the muffler. Therefore, in the manufacture of the intake pipe, only the best alloys of cast iron and steel are used.
Also, a vibration compensator (corrugation) is sometimes installed on this part, thanks to which engine vibration is damped and does not pass further through the exhaust system.
We recommend: How to properly store tires at home?
Neutralizer
The catalytic converter (or catalyst) “afterburns” unburned fuel residues and processes carbon monoxide. This element of the exhaust system is a special chamber or tank in which a ceramic or metal element in the form of a honeycomb is located. Thanks to these honeycombs, gas mixtures are purified through chemical reactions.
Now manufacturers have begun to produce multi-section neutralizers that meet all international standards, which process a wider range of harmful substances.
Front muffler (resonator)
The resonator is, in fact, one of those parts that are commonly called mufflers. This element performs the function of reducing noise, but not cleaning exhaust gases. When gases pass through the resonator, a lot of noise is created. Therefore, the internal “filling” of the front muffler consists of numerous grilles and holes that reduce the speed of escaping gases, as well as vibration. By and large, a resonator is a tank with a perforated pipe.
Front mufflers are:
- Active. Such mufflers are made of special sound-absorbing materials, and their design is simple.
- Reactive. Silencers of this type use combinations of expansion and resonator chambers.
Do not confuse the resonator with the rear muffler, as their design is very different.
Rear muffler
When we say “muffler,” we most often mean the rear part of the exhaust system. This element provides the final absorption of noise and also carries out the final removal of gases.
Unlike the resonator, the internal “filling” of the rear muffler is heterogeneous. Several chambers with special fillers are installed inside it. Thanks to the porous structure, the system of partitions and air ducts, it is possible not only to get rid of strong noise, but to reduce the temperature in the system.
Speaking of noise reduction, we cannot ignore another type of system that reduces excessive noise in the exhaust pipe.
We recommend: “S” mode on an automatic transmission: what you need to know
Why are resonators used?
Car exhaust system: device diagram, possible malfunctions and diagnostic methods
Now more specifically regarding what resonators are needed in cars for. The name itself makes it clear that this element is responsible for resonating noise or sound streams that are formed during the operation of the motor.
If we talk in simple terms about why a resonator is in the exhaust system, then it is a damper of sound vibrations at the moment when the exhaust gases leave the combustion chamber. But this is not all the functionality of the component. In fact, resonators perform several tasks simultaneously, although the main one is considered to be resonating, or sound damping. Mainly low frequencies.
Experts say that the resonator in the design of the exhaust system serves not only to remove gas and reduce noise levels. Another point for which the device is used is to increase the useful power of the power plant. It’s not for nothing that sports cars undergo special modifications, where the standard resonator is changed to a more efficient option. In such cases, the element is placed directly behind the forward flow.
Direct exhaust system
An extremely important functional feature of the resonator is its ability to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases. This significantly extends the service life of the entire system and the muffler in particular.
As an addition, we can note the fact of reducing the level of harmful emissions due to the participation of resonators in the operation of the automobile exhaust system.
Considering the functions and purpose of this element, questions arise as to whether it is possible to remove the resonator from the car, what will happen and what consequences are possible. Some people think that removing such an element is stupid. But there is far more than one such driver who removed the structure.
To answer this question, you should consider what will happen when operating a car without a resonator. The following will happen:
- The sound of the exhaust system will increase significantly. Sometimes it exceeds all permissible limits and becomes extremely unpleasant and noisy. In many ways, the noise level depends on the engine power and its speed;
- The increase in noise will be especially noticeable in the low frequency range. It is the resonator that dampens low sounds;
- the temperature of the exiting exhaust gas, which passes through the vehicle muffler, will increase. This significantly reduces its service life. The muffler will have to be replaced soon;
- the normal distribution of shock waves in the gas environment will be disrupted. At the same time, the vacuum zones will change. All this leads to noticeable engine power losses;
- Fuel consumption settings will also be disrupted. This will lead to increased fuel consumption.
It is possible to completely abandon the use of a resonator only in certain situations, when a comprehensive tuning of the exhaust system is carried out with the installation of additional elements and special tuning. If you simply remove the resonator from the exhaust and continue to operate the car in this condition, this will not give anything except increased noise and accelerated wear with all the ensuing consequences.
The muffler is broken
The exhaust system of a car is the most unprotected part of the car. It is exposed to external influences and car enthusiasts often have to repair it. A breakdown of the system is not just an unpleasant knocking sound and other “delights” such as a decrease in car power, jerking of the car, but also the danger that toxic fumes coming out of the engine can leak into the cabin and poison people. In order for your exhaust system to function properly, it, in particular, and the car in general, must be systematically checked and taken for maintenance. If you neglect this, you risk getting into an accident at the most inopportune moment. Don't forget that muffler damage is on the list of ten reasons why you have to call a tow truck.
Corrosion protection
The muffler often suffers from fading of paint, which is why corrosion quickly renders it inoperable. One of the effective ways to protect the surface of the exhaust system from corrosion is to paint it. It should always be remembered that the temperature of the gases leaving the exhaust pipe is usually 420–760 °C, and the surface temperature of the exhaust pipe is 200–540 °C. Therefore, only heat-resistant, silicone varnishes and enamels are suitable for painting.
To paint the “glushak”, you need to proceed like this:
- First, remove the muffler and prepare it for painting (to do this, you need to thoroughly clean it of all dirt and oil, degrease it and dry it well).
- Inspect the dried muffler, not missing any areas where the factory coating has peeled off or oil stains.
- If you do find oil stains, take a rag soaked in gasoline and wipe them thoroughly.
With peeling factory paint, proceed as follows:
- Take a strong knife or putty knife and remove the previous coating.
- If you notice rust on the exhaust system, remove it immediately using coarse sandpaper or a special rust remover.
- After these manipulations, apply a layer of primer.
- After the primer has completely dried, paint as stated in the instructions for the paint you purchased.
- Then let the muffler dry a little, install it back under the car body and let the engine run for a few minutes so that the muffler warms up and the paint dries.
There are times when the rust has penetrated too deeply and it is impossible to get rid of it. If this is your option, then you should treat the muffler with a rust converter.
There are alternative ways to protect the exhaust system:
- First you need, as for painting, to clean the muffler and exhaust pipe from dirt, oil and rust, and then apply a thin layer of graphite lubricant. You can do it as follows:
- Let's go to the nearest computer store.
- We ask them to process the powder from the printer.
- Mix it with a small amount of grease.
- Then you need to coat the surface with the mixture, place it on stands and start drying with a hair dryer, blowing from the side of the resonator.
We recommend: The design of a manual transmission and how it works
Until the grease completely burns out, the coating will not stop emitting a pungent odor, so carry out all manipulations in a respirator and outside, or at least in a well-ventilated room (garage).
The muffler is leaking
You carried out an inspection and found no signs of corrosion on the muffler, but saw damage. Unfortunately, this happens, because the exhaust system is the most unprotected part of the car; it is affected by both mechanical influences (for example, a bouncing stone or unsuccessful parking of a car) and chemical ones, in the form of aggressive chemical compounds, salts and even the external environment. But there are also obvious reasons for the formation of a hole: perhaps the muffler is made of poor quality material.
Muffler burnout
If you are faced with such a nuisance as a muffler burning out, then do not rush to think that the problem lies inside the car. Novice car enthusiasts believe that mufflers burn out due to too intense exhaust emissions created by the internal combustion engine. But often this is not the case. Today, many car manufacturers, even well-known brands, produce cars with low-quality parts, without normal processing, which are highly susceptible to chemicals and the environment.
Example of a burned out muffler
Obviously, the main reason for system burnout is various types of environmental influences on the part. If you treat your car irresponsibly, it is stored in rain, snow or scorching sun, then you should not be surprised that part of the exhaust system quickly burns out, because this is facilitated by a natural chemical process in this case - metal oxidation.
Another common reason for part damage is idling the car and driving short distances. Do not forget that sudden temperature changes are detrimental to the muffler. At low temperatures, condensation forms in the muffler, which has a destructive effect on all metal except stainless steel.
Checking the resonator
Where is the Chevrolet Niva exhaust system located?
When identifying the problems listed above, every motorist should know how to check the resonator. This will not only normalize the operation of the engine and exhaust system, but also increase the comfort of using the car, including for the people around you.
To check, you will need an inspection hole (if you don’t have one, you can jack up the car). Diagnosis is made using visual inspection. During the process, it is necessary to carefully examine the integrity of both the device itself and the pipes connected to it (especially at their joints).
When working in an inspection pit and when lifting the machine on a jack, always be careful and follow safety rules.
A clear sign of a problem is the formation of condensation in the cooling resonator, after which it begins to drip to the ground. This means that its body has lost its tightness and must be repaired, or better yet, replaced. You can check for condensation after a while, when you turn off the engine (to allow the resonator body to cool)
Note! Some car enthusiasts, when making resonators on their own, specially drill a hole in its body to remove moisture. Therefore, if you bought a car with a similar resonator, then this testing method will not work for you
Also, the integrity of the resonator body can be determined by the presence of exhaust gases leaving it. This also indicates depressurization and the need to replace it. This fact can be checked with the car engine running by looking under the bottom. To be sure, you can ask an assistant to “turn on the gas” at the same time so that more exhaust gases pass through the system. Also, suspicion of depressurization is caused by the appearance of smoke from under the bottom of the car while driving or when parked with the engine running.
As practice shows, it is better not to repair the resonator, but to replace it. This is especially true for cars with significant mileage (more than 100 thousand kilometers).
Resonator
It is made in the shape of a cylindrical can. It is in the resonator that the first separation of the exhaust gas flow occurs. Also, by increasing the diameter, the exhaust speed decreases.
Gases gradually dissipate in this chamber. Thanks to this, vibrations and partly sound are dampened. Just like the “pants,” the resonator is made of fire-resistant metal.
Catalytic converter for exhaust gases in the exhaust system
Exhaust system VAZ 2114 injector 8 valves
The catalytic converter consists of an inlet funnel, an outlet funnel and a monolith (see figure "Catalytic Converter with Ceramic Monolith"). The monolith contains a large number of very thin, parallel channels coated with an active catalyst. The channel density ranges from 60 to 190 cells per square meter. see. The operating principle of the active catalytic layer is described below (see “Catalytic exhaust gas purification”).
The monolith can be a metal or ceramic material.
Metal monolithic block
The monolithic metal block is made of corrugated metal foil 0.05 mm thick, which is wound and soldered with hard solder at high temperatures. Thanks to the very thin walls between the channels, the monolithic metal block offers extremely low resistance to the exhaust gases. This property is often used on cars with high-power engines. A monolithic metal block can be welded directly to the funnels.
Ceramic monolithic block
The ceramic monolithic block is made on the basis of cordierite. Depending on the cell density, the wall thickness between the channels ranges from 0.05 mm (at a density of 190 cells/sq. cm) to 0.16 mm (at a density of 60 cells/sq. cm).
Ceramic monolithic blocks are extremely resistant to high temperatures and thermal shock. However, they cannot be installed directly in a metal housing and require special fastenings. These fasteners are necessary to compensate for the different coefficients of thermal expansion of steel and ceramic, and protect the sensitive monolithic block from impact
Extreme care and attention is required during the production process, especially with thin-walled monolithic blocks (The mounting mat is made of ceramic fiber. It has high elasticity, which is necessary to minimize mechanical stress on the monolithic block
The mounting mat also serves as a heat insulator.
One catalytic converter can contain several monolithic blocks with different coatings. To ensure uniform passage of exhaust gases through the monolithic block, special attention should be paid to the shape of the inlet funnel. The external shape of the ceramic monolithic
The block depends on the space under the car body and can be triangular, oval or round.
Sealing elements
So, we have listed the main components of the exhaust system and their design. However, we haven't talked about how they connect to each other. Fastening is done using bolts and clamps. The exhaust pipe is connected to the exhaust manifold and the resonator using two gaskets. Depending on the type of car, the gasket can be made of pressed corrugated foil or solid metal. Additionally, a washer can be used. As for the muffler itself, it is connected to the resonator thanks to an overlapping clamp. Some cars may use a ring (for example, the domestic G8). For better sealing, experts recommend using heat-resistant sealant (up to 1100 degrees). It perfectly seals all gaps and prevents gases under pressure from escaping prematurely.
Traffic fumes
During operation, various vehicle systems (internal combustion engine, fuel, ventilation, and chassis) emit harmful substances in the form of gas and fine dust. Some of them are non-toxic compounds that are found in ordinary air. The other part is poisonous, toxic and carcinogenic substances, which not only negatively affect the environment, but also destroy human health.
Main pollutants:
- CO
(also known as carbon monoxide, or carbon monoxide) is colorless and odorless, but leads to pathology of the central nervous system, depression of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and in a concentration of 0.3% of the volume of air is fatal. It occurs as a result of incomplete combustion of fuel. - CH
(hydrocarbons) are a large group of compounds with a common structure that arise when fuel is burned incompletely or not quickly enough. These include paraffin, olefin, aldehyde, formaldehyde, benzene, toluene, xylene and other polycyclic compounds. These mutagens and carcinogens destroy the respiratory system and promote the growth and development of cancer cells, including blood cancer - leukemia. - NOx
(nitrogen oxides) is the main cause of acid rain, since when combined with water, nitric and nitrous acids are formed. It is one of the serious carcinogens that causes cancer. The toxic gas destroys the respiratory system and accumulates in the blood. Formed during fuel combustion. - SOx
(sulfur oxides) is similar to the previous chemical element. On contact with water they form sulfuric and sulfurous acids. In a gas state it causes pathologies of the organs of vision and breathing. - H2S
(hydrogen sulfide) - causes general poisoning of the body, occurs when using low-quality fuel with a high sulfur content. - NH3
– ammonia – causes blindness and burns of the upper respiratory tract. - Soot particles are a product of incomplete combustion of fuel and oil.
Basically, the problem of carcinogen occurrence is typical for diesel engines. - Fine dust particles of hydrocarbons, sulfur, and heavy metals
are less dangerous, since they can be filtered directly by the body. - Blue or white smoke
is a product of evaporation of diesel engine oil. - CO2
- carbon dioxide - causes depression of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system and respiratory organs, and when contained in the atmosphere at 6% of the total air volume, it leads to death. - Other, minor, but no less dangerous components of exhaust gases
: methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride.
In modern legislation, the problem of ecology and the standards of maximum permissible exhaust gases for motor vehicles are regulated by the technical regulations of the Customs Union TR CU 018/2011 as amended on July 11, 2016. However, from November 11, 2021, amendments will be made to it, but for now the following limit values are allowed: CO - 85 g/kWh, HC - 5 g/kWh, NO - 17 g/kWh.
And mandatory vehicle components include exhaust gas aftertreatment systems, including replacement catalytic converters (with the exception of urea-based aftertreatment systems).
Traffic fumes
Main pollutants:
- CO
(also known as carbon monoxide, or carbon monoxide) is colorless and odorless, but leads to pathology of the central nervous system, depression of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and in a concentration of 0.3% of the volume of air is fatal. It occurs as a result of incomplete combustion of fuel. - CH
(hydrocarbons) are a large group of compounds with a common structure that arise when fuel is burned incompletely or not quickly enough. These include paraffin, olefin, aldehyde, formaldehyde, benzene, toluene, xylene and other polycyclic compounds. These mutagens and carcinogens destroy the respiratory system and promote the growth and development of cancer cells, including blood cancer - leukemia. - NOx
(nitrogen oxides) is the main cause of acid rain, since when combined with water, nitric and nitrous acids are formed. It is one of the serious carcinogens that causes cancer. The toxic gas destroys the respiratory system and accumulates in the blood. Formed during fuel combustion. - SOx
(sulfur oxides) is similar to the previous chemical element. On contact with water they form sulfuric and sulfurous acids. In a gas state it causes pathologies of the organs of vision and breathing. - H2S
(hydrogen sulfide) - causes general poisoning of the body, occurs when using low-quality fuel with a high sulfur content. - NH3
– ammonia – causes blindness and burns of the upper respiratory tract. - Soot particles are a product of incomplete combustion of fuel and oil.
Basically, the problem of carcinogen occurrence is typical for diesel engines. - Fine dust particles of hydrocarbons, sulfur, and heavy metals
are less dangerous, since they can be filtered directly by the body. - Blue or white smoke
is a product of evaporation of diesel engine oil. - CO2
- carbon dioxide - causes depression of the central nervous system, cardiovascular system and respiratory organs, and when contained in the atmosphere at 6% of the total air volume, it leads to death. - Other, minor, but no less dangerous components of exhaust gases
: methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons, sulfur hexafluoride.
Homemade muffler with a pleasant sound
I don’t know how it is now, but many people used to know that an old car fire extinguisher is an excellent preparation for direct flow.
The story is simple: what I didn’t do with the original muffler can on the pita was of little use. I changed the muffler stuffing, made a flute like a Yamaha one, but still the sound was disgusting, rattling and loud, in general - a barrel organ.
It is possible to install a full-fledged direct flow from the pit, but you need to shorten it, digest the fasteners, but you understand: there was no particular desire to buy a barrel for 5 rubles and still digest it all, but the desire to get rid of the original muffler still did not leave.
And so back to the fire extinguisher. One was lying gathering dust in the garage a long time ago, but to make a direct flow you need two... And so, one fine May morning, on a small river, among the snags on the surface, the desired second fire extinguisher was spotted. Exactly the same as the first one, and now there were two of them. Well, you yourself understand what this led to.
In general, let's go)))
We take the most attractive tool in the garage, affectionately called “Binder,” and saw the bottoms of the fire extinguishers evenly.
Next, take a forty pipe, cut the gas distribution slots with a grinder, or, if you’re not too lazy, drill a billion holes. Then we weld one end of the pipe to the part of the muffler where the outlet will be.
You don’t even need to do anything with the outlet hole: the mounting location for the fire extinguisher spray is just perfect and the diameter is just right.
Now we stomp into the kitchen and tear open the casing of the ZIL refrigerator, tearing out the glass wool from there. Just wear thick clothing and gloves when working with glass wool, otherwise you will itch for two days, and if during these two days you want to relieve yourself, then... yes, it will itch there too... In general, we take glass wool and stuff the outlet part of the jar as tightly as possible.
Then we proceed to the entrance part. The thread in it needs to be cut so that the magpie pipe passes through, and, of course, we also fill it with glass wool, the denser the better.
Well, well, the only thing left to do is weld both parts together and weld the pipe to fit it with the standard muffler.
I didn’t bother with the fastenings to the frame, and why should I? I made two points of attachment to the luggage frames (it couldn’t be stronger): this fastening withstood a revolution on the asphalt and the can became a junk)))
The end of the jar is at your own discretion. I made pipes of a smaller diameter, and it looks quite good)
The sound, let me tell you, turned out surprisingly great! Even though it’s forward flow! At idle you can’t hear it at all, even the electronics are louder, but when driving it’s just the most beautiful sound - a soft growl without a dull metallic rumble and yelling.
Well, here’s the final look) The plastic doesn’t burn, the sound is pleasant, nothing was done to the original pipe. What else does?)))
Muffler functions
The muffler is designed to reduce the noise level that occurs during the processing of gases and air and their release into the atmosphere. The second main function of this tool is to convert energy from processed gases, reducing their temperature and reducing their speed.
Several chambers of different sizes, separated by a partition, realize the expansion and contraction of the flow. This happens thanks to the diaphragm hole, also called a throttle.
In addition, the muffler provides for a change in the initial direction of flow of these same processed gases. This is what helps dampen high-frequency sound vibrations.
Causes of muffler failure:
- High temperature conditions inside the system, about 600 °C. Temperature promotes metal burning;
- As a result of active exposure to the external environment (water, dirt, temperature changes);
We recommend: When should you change brake pads and what are the signs of wear?
Exhaust fumes and road surfaces are two of the exhaust pipe's worst enemies.
- The main enemy of a car muffler is low quality fuel, which contains many different impurities. This contributes not only to rapid burnout, but also to contamination of the catalyst, which cleans the exhaust gases of impurities.
- Incorrectly configured ignition system parameters (high CO content).
Devices that set the acoustic parameters of mufflers
Used to reduce individual spectral components of unwanted frequencies in exhaust noise. These components can be used to effectively attenuate sound in certain frequency ranges.
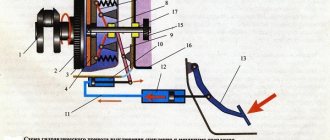
Helmholtz resonator
The Helmholtz resonator consists of a pipe located along the direction of movement of the exhaust gases and a certain volume attached to it (see Fig. “Helmholtz Resonator”). The volume of gas acts as a spring, while the gas contained in the pipe section acts as a mass. At the resonant frequency, this mass and spring system provides a very high degree of sound attenuation in a narrow frequency band. The resonant frequency/depends on the volume V, as well as on the length L and cross-sectional area A of the pipe:
f = c/2π √(A/L V)
Where:
c - speed of sound
Resonators λ/4
The λ/4 resonator includes a pipe, closed on one side, that branches off from the exhaust system. The resonant frequency f of such a resonator depends on the tap length L and is defined as:
f = c/4L
These resonators also provide a high degree of sound attenuation in a narrow frequency band around their resonant frequency.
Exhaust gas dampers
Exhaust gas dampers are most often installed in rear mufflers. Depending on the crankshaft rotation speed or the intensity of the exhaust gas flow, the damper opens or closes the muffler bypass pipe or the second exhaust pipe (see Fig. “Exhaust gas damper controlled by external vacuum”). As a result, exhaust noise levels at low engine speeds can be significantly reduced without loss of power at high engine speeds.
The dampers can be self-regulating depending on the pressure and speed of the exhaust gases or have external control. In the latter case, it is necessary to provide an interface with the engine control system. This makes the system more complex, but at the same time expands its scope.
The principle of operation of the exhaust system
Exhaust system location
In the classic version for gasoline engines, the exhaust system of a car works as follows:
- The engine exhaust valves open and exhaust gases with remaining unburned fuel are ejected from the cylinders.
- Gases from each cylinder enter the exhaust manifold, where they are combined into one stream.
- Through the exhaust pipe, exhaust gases from the exhaust manifold pass through the first lambda probe (oxygen sensor), which records the amount of oxygen in the exhaust. Based on this data, the electronic control unit adjusts the fuel supply and the composition of the air-fuel mixture.
- Next, the gases enter the catalyst, where they enter into a chemical reaction with oxidizing metals (platinum, palladium) and a reducing metal (rhodium). The operating temperature of the gases should not be lower than 300°C.
- At the outlet of the catalyst, the gases pass a second lambda probe, with the help of which the serviceability of the catalytic converter is assessed.
- Next, the purified exhaust gases enter the resonator and then into the muffler, where the exhaust flows are converted (narrowed, expanded, redirected, absorbed), which reduces the noise level.
- From the main muffler, exhaust gases already enter the atmosphere.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=sNVJ_RJ9FK4
The diesel engine exhaust system has some features:
- Coming out of the cylinders, the exhaust gases enter the exhaust manifold. The temperature of diesel engine exhaust gases varies in the range of 500-700 °C.
- Then they enter the turbocharger, which performs supercharging.
- The exhaust then passes through the oxygen sensor and enters the particulate filter, which removes harmful components.
- Finally, the exhaust passes through the car muffler and is released into the atmosphere.
The principle of operation of a car exhaust system
Timely and high-quality removal of exhaust gases plays a big role. Because if exhaust gases are not removed in time, they will remain in the combustion chambers of the cylinders and fill a certain volume, which means this will lead to loss of engine power and unstable operation.
The exhaust system consists of several sections connected to each other by mounting bolts.
Purpose of all sections:
The simple design of the exhaust system removes gases through pipes. Everyone probably knows that if a muffler or muffler pipe gets a hole, the noise of the engine increases several times.
The toxicity level is reduced by installing catalysts in the exhaust system. The operation of the catalyst is monitored by a lambda probe. Diesel units use a particulate filter to reduce emissions of harmful substances.
Some people remove this sensor themselves and install a false lambda probe.
Both gasoline and modern diesel internal combustion engines use a turbocharger, which forces a mixture of oxygen and exhaust gases, which it sucks from the exhaust manifold. A sensor is installed on the exhaust manifold housing of such machines, which regulates the supply of exhaust gases to the turbine.
How is a typical exhaust system integrated into a mid-life gasoline engine?
- Exhaust manifold - collects exhaust gases from the cylinders and directs them into one exhaust pipe
- Short pipe connecting the exhaust manifold to the three-way catalytic converter
- The first lambda probe is a sensor for the percentage of air in the exhaust gases, connected to a computer that controls engine operation.
- Three-way catalyst - catalytic reactions occur in it aimed at the oxidation of carbon oxides and hydrocarbons, as well as the reduction of toxic nitrogen oxides into oxygen and nitrogen
- The second lambda probe is the so-called adjustment
- Exhaust pipe connecting the catalyst to the middle muffler
- Middle muffler - designed to suppress exhaust noise
- Exhaust pipe connecting the middle muffler to the last muffler
- End muffler
- The exhaust pipe that releases exhaust gases from the last muffler into the atmosphere
The location may be more complex on newer vehicles. In its composition you can find more than one catalyst and two lambda probes. The latter, from 2021, also installs a GPF particle filter (Gasoline Particulate Filter).
Empy flue gas consists mainly of nitrogen (about 76 - 78% by volume), oxygen (2-18%),
steam (up to 4%), carbon dioxide (up to 10%), nitrogen oxides (up to 0.5%), hydrocarbons (up to 3%), aldehydes (up to 0.009%) and particulate matter (up to 1.1%).
More information about the design of the muffler and resonator
The resonator design includes the following elements:
- inlet and outlet chambers separated by a mesh;
- reflectors.
Reflectors, due to the presence of perforations, extinguish residual flows of combustion products due to the friction of gaseous particles moving inside the block in two different directions. This leads to what the resonator is for - reducing the volume of the exhaust sound.
Resonators function due to the presence of a large number of closed cavities, which are connected to the exhaust pipe by multiple holes. This scheme allows the formation of sound vibrations of various frequencies, which change when gases rub against the inner surface of the device.
This is a rather complex cycle, because the muffler must absorb sound, but also not deprive the engine of power. As the manufacturers assure, the car can be made almost silent by installing another resonator and increasing the volume of the muffler - but the power from the engine will be “eaten off” significantly.
DETAILS: Do-it-yourself neon lighting » AvtoNovator || Neon illumination of the underbody of a car - spectacular auto tuning
If the standard version takes away from 5 to 7%, then installing new resonators will increase this figure to 10 - 15%! Do we need it? So manufacturers work on the ideal shape so that only the “rustle” of the power unit can be heard, and the power is at the same level.
What is the cross-section of the resonator? If you imagine its cross-section, these are several perforated pipes inside a metal casing; they are not at the same level, but seem to be parallel. The “working off” flow enters the resonator, where it first meets the walls, losing its pressure and part of the sound.
At the bottom of this chamber there is a third pipe through which gases flow to the muffler. Thus, at the resonator level, 30–40% of the gas pressure and its sound (mainly low tones) are damped. But why not everyone? If you make the resonator larger, it simply won’t fit under the car in the middle - the volume will be too large, which will also steal the engine’s power.
Muffler - located at the rear, where there is most space. It is the largest of all the parts; in fact, it differs little in design from a resonator (there are also chambers and “blank” walls), only in volume. Another difference here is a chamber with a so-called absorber - from a perforated pipe, gases and sound pass into the absorber, leaving most of the energy and sound there.
The absorber chamber, as I wrote, has a perforated pipe on top (in simple terms, drilled with many holes) and an absorber lined next to it with a soft and porous material. Primarily absorbing sound vibrations.
This material can be a non-flammable substance:
- Glass fiber or other mineral wool.
- Metal shavings
- Metal wool
- Other porous non-combustible materials
It should be noted that there can be two silencers in the system! For example, for every 3 - 4 cylinders, on each side of the power unit.
Car muffler device
The design of all mufflers is approximately similar and includes the required elements:
- Expansion and contraction of the flow of exhaust gases, the so-called throttling, due to which both the speed of the exiting gases and the frequency of sound waves change
- The superposition of sound waves on top of each other, which changes their amplitude - interference
- Absorption and dispersion of sound waves - sound energy is converted into heat, resulting in a very significant reduction in the sound of the exhaust exhaust
- Repeated change in the flow of exhaust gases, the so-called labyrinth, also serves to reduce the rate of gas exit, its energy and conversion into thermal energy
Why does it fail?
The answer is quite banal, since it is made of metal and is constantly in an aggressive environment with high temperatures and water (snow) under the bottom - it simply burns out or rots. The metal begins to decompose due to the salt on the roads.
Of course, the design of modern mufflers has been improved, other alloys have been used in the design, but it still burns out after some time. Moreover, with modern options, the partitions inside often suffer, or the porous material (often mineral wool) burns out, which is why even a muffler that is intact on the outside begins to roar.
This is the muffler device, as you can see now it is not only “muffling” the sound from the engine, but also ecology and power.
I’ll end with this, I think it was useful for you, sincerely your AUTOBLOGGER.
Similar news
- Where is the catalyst located? Detailed photos of the machine
- How to unscrew a stuck bolt (nut). Let's disassemble the muffler, call...
- Removing the catalyst. Pros and cons, consumption, firmware - revealed...
Do-it-yourself exhaust system repair
Very often, a simple muffler breakdown does not allow you to continue driving and even getting to the service becomes problematic. This happens when hooks, fasteners break or when the connecting pipe ruptures. Then the exhaust system circuit is separated, and it is no longer possible to drive such a car. Simply broken fasteners or rubber bands can be repaired using thick wire. Once the muffler is secured, you can continue driving slowly. If the connecting pipe breaks, a corrugation or a wide connecting clamp will help you. Connect the two parts together and secure.
Of course, this will not return the original sound, but you will be able to continue driving the car. A pipe rupture can be properly welded, but the welding site, as a rule, becomes unusable again under the influence of high temperatures and harmful factors, so at the first loud sound you should think about replacing the muffler. The appearance of a hole in the resonator does not prevent you from driving further, but it does indicate that it urgently needs to be replaced.
Design of the structure and purpose of its components
The parts that make up this design have different functional loads and their own designations, reflecting the stages of their work. The exhaust system diagram itself and the names of its parts look like this:
- exhaust manifold;
- exhaust pipe;
- catalyst or in other words catalytic converter;
- resonator or flame arrester;
- muffler.
The exhaust manifold is an attached type of equipment of the power unit, and is designed to receive exhaust particles and gases of the fuel mixture from the combustion chambers of each cylinder into it, and is made mainly of ceramics, cast iron or stainless steel alloys with increased heat resistance.
Exhaust system design
The downpipe, referred to by car enthusiasts as the “pants” due to its similar appearance, is designed to combine several streams of exhaust gases into one and further transport them to the catalytic converter (catalyst). The pipe is often equipped with a so-called corrugation, which dampens the vibration transmitted to the entire structure of the exhaust system by the running engine.
The catalyst is a ceramic honeycomb, the surface of which is coated with a layer of an alloy of platinum and iridium, which allows exhaust gases to enter into a chemical reaction with them, resulting in their separation into oxygen and nitrogen oxide. The released oxygen in the catalyst helps to burn the remainder of the fuel mixture more efficiently, as a result of which only a nitrogen-dioxide-carbon mixture is supplied to the muffler. The operation of the catalytic converter is monitored by a special lambda probe sensor, transmitting a signal to the control unit of the vehicle's power unit. A similar sensor is installed on the exhaust manifold to analyze the toxicity indicators of the exhaust gases entering the catalyst.
All components of the exhaust system are connected to each other through flanges using fastening bolts and heat-resistant seals, which are responsible for the tightness of this structure, without which the full operation of the engine of a modern car is impossible.
Exhaust system diagram
Car exhaust system design
The structure of the exhaust system of modern cars includes about 5 elements, each of which performs its own function. The exhaust system diagram includes:
An exhaust manifold
The exhaust manifold is used to receive exhaust gases from the combustion chambers of the cylinders. Material: cast iron or stainless steel, or ceramics.
Downpipe
The exhaust pipe, which is usually called the pants, serves to combine exhaust gases coming from different cylinders into one common manifold. The exhaust gas mixture then passes through the catalyst. In this area, corrugation is often installed to dampen vibrations, which are transmitted to the exhaust system structure by the engine through a rigid connection.
Catalyst or catalytic neutralizer
The catalyst resembles a ceramic honeycomb. The catalyst is coated on top with an alloy of iridium and platinum. Such substances allow them to enter into a chemical reaction with substances contained in exhaust gases. Here the separation into oxygen and nitric oxide occurs. The separated pure oxygen helps burn the remaining fuel-air mixture, resulting in a nitrogen-carbon dioxide mixture being supplied to the muffler. The lambda sensor probe transmits catalyst operation data to the control unit (ECU). A similar sensor is installed on the exhaust manifold to analyze the toxicity of gases that enter the catalyst.
Resonator or flame arrester
This device serves to reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases. The temperature decrease occurs due to the cellular structure.