To reduce the force applied by the driver to the steering wheel when turning the car, amplifiers are used. They perform the following functions: provide kinematic tracking action, i.e. proportionality between the angles of rotation of the steered wheels of the vehicle and the steering wheel; create a forceful tracking action - “road feeling”, i.e. they ensure proportionality between the force applied by the driver to the steering wheel and the resistance to turning the car’s steered wheels (the smaller the car’s turning radius and, therefore, the larger the steering angles, the greater the torque resistance to their rotation); allow you to drive the car when the amplifier fails; increase traffic safety, as they provide the ability to control the car if a tire breaks on the steered wheel, which is especially...
Power steering: from trucks to cars
Hydraulic power steering (Power Steering) is a unit hidden in the bowels of our cars that creates additional effort to turn the wheels, thereby helping us steer without straining our muscles.
Despite the fact that the use of these devices on passenger cars began around the end of the 50s of the last century, they were considered something exotic for many decades.
However, the history of power steering does not even go back to the 50s; it all started much earlier. Thus, the first patent for a device resembling the current power steering was received already in 1902.
The following years, marked by the rapid development of the automotive industry, determined the niche where the hydraulic booster felt best and was considered the most useful - trucks.
Pros and cons of power steering
By checking in practice how power steering works in a modern car, you can evaluate all the advantages of using this mechanism:
- Reliability. The hydraulic booster system has been tested by many years of practice on various cars, so at the moment it is installed on approximately 60% of cars produced.
- The power steering is capable of developing decent power and overcoming significant resistance from the wheels. This makes it possible to use it on vehicles of any carrying capacity and dimensions.
- Comfort for the driver is the main advantage of power steering. It was created precisely for this purpose - to make it easier for a person to control the machine.
- Improved handling. Since the steering wheel rotates easily, the driver is able to react faster to changing traffic situations.
In addition to power steering, passenger cars are equipped with new generation amplifiers that turn the front wheels using an electric motor (EUR). But such systems cannot yet compare with hydraulics in cost, and therefore fewer new vehicles are equipped with EUR.
The use of hydraulic boosters in steering mechanisms gives another bonus to car manufacturers. Since they do the physical work instead of the driver, the design can use steering mechanisms with a smaller gear ratio. For a car enthusiast, this means that the number of turns of the steering wheel from one extreme position to the other will decrease, which will increase the sharpness of control. True, if the power steering fails or the car is towed, it will be much more difficult for the driver to turn the steering wheel.
Hydraulic amplifiers have the following disadvantages:
- To avoid causing damage, the steering wheel should not be held in any extreme position for a long time, especially at high engine speeds. Due to critical pressure, oil can squeeze out the seals and leak out.
- The pump drive device is designed so that it works non-stop together with the power unit. Because of this, the pump constantly wears out, requires periodic maintenance and takes away part of the engine's energy, increasing fuel consumption.
- Other elements of the system also need to be maintained, and the level of hydraulic fluid in the reservoir must be monitored.
- In cars of the budget price category equipped with power steering, the steering wheel becomes uninformative, especially when driving at high speed.
In more expensive cars, a special device for the power steering pump is implemented, which allows the oil pressure in the system to be reduced as the speed increases . At the same time, the steering wheel “fills” with a pleasant heaviness and there is no feeling of emptiness when steering at speed.
Power steering device
Power steering is a closed, interconnected hydraulic system of components consisting of:
- Pump.
- Distribution device.
- Hydraulic cylinder.
- Backa.
- High and low pressure hoses.
Pump
The main part of the power steering design is the pump. With its help, pressure is created in the power steering and oil circulates in the system. It is fixed near the engine and driven by the crankshaft using a belt or gear drive (drive). The most common type of pump is a vane pump, usually a vane pump; it provides high wear resistance and high efficiency. However, it has a weak link, namely the bearing, which is why it has to be repaired. The pressure in this type of pump is about 150 bar, which is very high.
We recommend: Steering rod - design and malfunctions
Distributor
The distributor in the power steering is a kind of regulator that directs oil from the reservoir to the hydraulic cylinder and back. It can be installed both on the steering gear shaft and on some parts of the steering mechanism. There are two types of distributor:
- axial - if the spool makes translational movements;
- rotary - if it makes rotational movements.
Hydraulic cylinder
Or as the power cylinder is also called, it performs the function of turning the wheels. The fluid in the power steering presses against the piston under pressure and forces the rod to extend, causing the wheels to turn. In order to push the rod back, the fluid from the reverse side presses on the piston and the wheels return to their original position. The hydraulic cylinder can be located both on the steering mechanism and between the steering gear and the vehicle body.
Tank
A reservoir for working fluid, which ensures the operation and lubrication of all connecting parts of the power steering. It contains a special filter to prevent dirt from entering, since the distributor is very sensitive to this. To check the oil level there is a special dipstick and marks on it. The tank is located under the hood, usually in a visible place next to the antifreeze tank and has a cylindrical shape.
High and low pressure hoses
Of course, all fluid circulation through the power steering system is provided by hoses, which are divided into:
- high pressure hose;
- low pressure hose.
High pressure power steering hoses circulate oil between the pump, rotary or axial distributor and hydraulic cylinder. And low pressure returns this oil from the distributor to the tank, as well as from the tank to the pump. It is important to monitor the condition of the hoses to avoid fluid leaks and damage to the entire mechanism.
How does a modern power steering work?
A typical power steering kit contains:
- a pump that creates working pressure in the hydraulic booster system;
- a spool-type distribution device that supplies pressure to the hydraulic cylinder piston;
- executive cylinder with piston;
- high and low pressure hoses;
- a tank with a supply of working fluid;
- special oil for power steering.
Power steering is used with steering gears of various types, both worm and rack and pinion. Typically, its actuators are combined with the steering gear housing, and a high-pressure hose and return line are also connected to it.
Power steering operating principle
If the car is stationary, moving straight, the pump pumps idle hydraulic oil inside the system. When the steering wheel begins to move, the torsion bar begins to twist, and the spool rotates relative to the distribution sleeve. At the same time, connecting hoses open, through which oil from the tank enters a certain chamber in the power cylinder (this depends on which direction the car maneuvers under the influence of turning the steering wheel). And from another chamber, hydraulic oil simultaneously enters the tank through open ducts. The cylinder piston moves the steering rack, while simultaneously transmitting force to the steering rods that turn the wheels.
If the car maneuvers at low speed, then the efficiency of the power steering is maximum. This is achieved by increasing the number of revolutions of the pump motor. An increase in its performance contributes to an intensive flow of hydraulic fluid into the cylinder and the force applied to turning the steering wheel decreases significantly. Increasing the speed of the machine reduces the rotation speed of the electric motor, and the solenoid valve comes into action, which reduces the flow of the hydraulic system channels, and more effort has to be applied to turn the steering wheel.
Principle of operation
And now about how it all interacts with each other. The power steering is a sealed mechanism and the fluid circulates in it in a circle. But under certain modes, the amount of liquid changes, so such differences are compensated by the expansion tank (also known as the filling tank). Usually this tank is located on the pump, but it can also be remote.
In general, power steering has two operating modes:
- Rectilinear movement. In this mode, the spool connects all channels suitable to it. The liquid in the distributor is immediately supplied to the return line and returned to the pump. Also, part of it is supplied to both chambers of the power cylinder, providing equal pressure in them;
- Turn. When the steering wheel rotates, the torsion bar twists, which leads to displacement of the spool relative to the shaft. For example, consider the action of the mechanism when turning right. So, the spool has turned, which is why the supply channel and the one leading to the right chamber of the hydraulic cylinder are connected. In this case, the left chamber is connected to the return. The fluid flow in the right chamber begins to put pressure on the piston, causing the force to increase. From the left chamber, so that there is no resistance to pressure, the liquid flows through the distributor and enters the pump. Moreover, if the steering wheel is not turned all the way, but only partially and left in this position, the torsion bar will unwind. This will lead to the return of the spool to its original position - the connection of all channels and the pressure in the chambers of the power cylinder will be equalized, but taking into account the current position of the rack along with the piston.
Diagram of the operation of a power steering system with a Servotronic valve (standard systems differ only in the absence of a limit valve and Servotronic)
When turning left, the operation of the distributor is the opposite of that described. That is, liquid under pressure is supplied to the left chamber of the cylinder. As you can see, the main work of the power steering lies with the distributor.
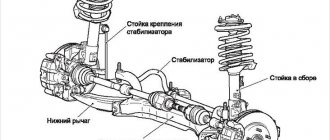
Diagram of power steering and elements
The hydraulic booster is an important steering component of a car. It consists of a pump, distributor, hydraulic cylinder, connecting hoses, working fluid, and barrel.
Let's look at each of the components in more detail.
- Pump. This device provides the entire system with the required pressure to create oil circulation. Most often, plastic pumps are used for modern cars. This is because they have a high efficiency and at the same time have an increased service life. The pump is usually located on the power unit. The drive operates via a belt drive that interacts with the crankshaft.
- Distributor. This element is designed to direct and distribute the working fluid (oil) into certain cavities of the cylinder, and also supplies it back to the barrel. There are two types of distributors: rotary and axial. It depends on how the spool moves. In the case when it has translational movements, the distributor is called axial. It is called rotary when the spool rotates. The distributor can be located both on the shaft with the steering mechanism and on the steering gear elements. This element is highly sensitive to oil contamination.
- Hydraulic cylinder. This element of the hydraulic booster system drives the pistons and rod under the influence of oil supplied under pressure. The wheels turn using levers. It can be built into the steering mechanism, and can also be seen between the drive and the car body.
- Connecting hoses. Such elements are simply necessary in a power steering system. Their main job is to ensure the smooth flow of working fluid throughout the entire mechanism. All connecting elements can be divided into two types: low and high pressure. Low pressure hoses are designed to return oil from the tank to the pump and, after working out, back to the tank. The second type of hose provides fluid supply between the cylinder, pump and distributor.
- Working fluid. This is a special oil that supplies force to the hydraulic cylinder from the pump. It also ensures lubrication of all system elements.
- Tank. A container for storing and circulating working fluid. The tank has a special filter, which helps clean the liquid supplied to the system. It also has a dipstick with special marks, which is designed to check the oil level.
We recommend: So different and so similar: liftback and hatchback, what are the differences
Diagram, power steering device
In a car everything is almost the same. The steering column is connected by a gear transmission to a rack, providing constant mechanical connection and operation in any mode. On one side of the steering wheel along the axis of the wheels there is a power cylinder, into which the fluid is supplied by a pump. The electric pump is connected to a control unit, which either reduces its speed or increases it, increasing the pressure in the system, depending on the engine speed, vehicle speed, steering wheel speed, and wheel rotation angle. While the steering wheel is set to the zero position, the fluid circulates along the circuit and is not supplied to any of the chambers of the power cylinder. As soon as you start to turn the steering wheel, a specially designed spool rotates and opens the corresponding valve - left or right. The fluid begins to be pumped into the corresponding chamber, helping you turn the steering wheel.
Now almost every modern car is equipped with hydraulic power steering. The main task of this mechanism is to create additional force on the steering elements to make it easier to turn the wheels during maneuvering.
Initially, the hydraulic booster was installed exclusively on trucks and agricultural equipment for one simple reason - without this mechanism it is very difficult to drive a truck or tractor. But over time, power steering began to appear on passenger cars.
At low speeds and when parking, the driver of a car without power steering has to make significant efforts to turn the steered wheels, but at high speeds the resistance decreases, that is, the effort on the part of the driver to perform the maneuver is reduced.
The amplifier provides the same force that the driver must apply, both at low and high speeds. Therefore, parking and maneuvering when starting to move with power steering is much easier.
The hydraulic booster not only increases travel comfort, but also additionally, since it allows you to keep the car on the road if a tire breaks at speed.
Also, the presence of power steering on the steering mechanism allows you to reduce the gear ratio. That is, the number of steering wheel revolutions decreases.
Power steering design
Any hydraulic power steering, no matter what its design, consists of a number of main components:
- pump;
- Switchgear;
- actuating mechanism;
- pipelines;
- fluid reservoir;
All components of the power steering are connected via pipelines into a closed system through which fluid circulates under pressure. It is this that is the main working element of the system.
Power steering pump design
A pump is included in the circuit to create fluid pressure. It can be driven either by a belt drive or by an electric motor. Pressure regulation is carried out by a bypass valve included in the system.
The distribution device ensures the redistribution of fluid flows supplied from the pump. Its main element is the spool, which, when moved, opens and closes the necessary channels.
If , then the spool connects a high-pressure pipeline through which liquid is supplied to the return pipe. That is, liquid from the pump is supplied to the distributor and immediately returned back to it without performing any actions. But when the wheel turns, the spool moves, opening and closing the required channels, and the fluid is directed to the actuator.
This mechanism is a double-acting hydraulic cylinder. It has a piston that divides the cylinder into two cavities. During rotation, the distributor supplies fluid to the required cavity, which, due to pressure, forces it to move in the required direction. In this case, the piston is connected to, so when moving it transmits force to the mechanism.
Power steering device
Main components of power steering
Power steering is installed on any type of steering mechanism. For passenger cars, the rack and pinion mechanism is most widespread. In this case, the power steering scheme is as follows:
- tank for working fluid;
- oil pump;
- spool valve;
- hydraulic cylinder;
- connecting hoses.
Power steering reservoir
Power steering reservoir
A filter element and a dipstick are installed in the tank or reservoir for the working fluid to monitor the oil level. Oil lubricates the rubbing pairs of mechanisms and transmits force from the pump to the hydraulic cylinder. A mesh in the tank serves as a filter from dirt and metal shavings that arise during operation.
The liquid level inside the tank can be checked visually if the tank is made of translucent plastic. If the plastic is opaque or a metal reservoir is used, the fluid level is checked using a dipstick.
In some cars, the fluid level can only be checked after briefly running the engine or by turning the steering wheel several times in different directions while the car is idling.
Special notches are made on the probes or reservoirs, both for a “cold” engine and for a “hot” one that has already been running for some time. Also, the required liquid level can be determined using o and “Min”.
Operating principle of the power steering system, power steering pump, power steering
- Articles and reviews
- Steering
- Power steering pump - design and operation features
Power steering
Driving vehicles, especially heavy trucks and tractors, using the driver's muscle power is often simply impossible. To reduce the amount of muscle effort when driving a machine, as well as to create comfortable working conditions for the driver and reduce his fatigue, cars and tractors are equipped with power steering.
Classification of amplifiers by wire type:
— mechanical — due to an increase in the gear ratio (compared to the usual one);
— pneumatic — now practically not used;
— hydraulic;
- electric;
— electrohydraulic.
The most widely used systems today are hydraulic and electro-hydraulic power steering. Both types have much in common and differ, by and large, only in the drive of the hydraulic pump, that is, we can say that the electric power steering (EGPS) is just a type of power steering (GUR).
Power steering device
Power steering is an isolated hydraulic system consisting of the following components (Fig. 1):
Rice. 1. Schematic diagram of power steering
- pump;
— pressure regulator;
— compensation tank for working fluid;
— distributor;
— power hydraulic cylinder.
The hydraulic cylinder is double acting (transmits force in two directions). It is integrated into the steering rack and transmits force to the steering rods.
The spool (distributor) is mounted on the steering column and reacts to steering wheel turns.
The pump is driven by a car engine or an electric motor.
The pressure regulator is a bypass valve. It drains excess working fluid, bypassing the spool.
Power steering pump - device, principle of operation
The purpose of the power steering pump is to ensure circulation and maintain pressure of the working fluid in the hydraulic system.
The pump is driven from the crankshaft of the vehicle's power plant via a belt or gear (on trucks and tractors) transmission. Thus, the hydraulic drive functions while the engine is running.
The hydraulic steering drive uses two types of pumps:
— gear;
- plate (blade or gate).
Vane pumps have high performance, are reliable and easy to maintain. Therefore they have become widespread.
Let us consider the design and principle of operation of a vane pump.
The pump consists of the following main parts (see Fig. 2):
- frame;
— rotor;
- sealing ring.
Rice. 2. Design of a power steering vane pump
A belt pulley is attached to the outer end of the shaft, supported by rolling bearings. At the opposite, splined end of the shaft, a rotor is mounted, in the grooves of which plates (blades) are freely installed.
A stator having an internal surface of complex shape is attached to the housing.
When the rotor rotates, due to centrifugal force, the plates move out of the grooves and form closed chambers.
In the suction section, where the volume of the chambers increases as the rotor rotates, working fluid enters them from the line, which in the discharge section, when the volume of the chambers decreases and the pressure increases, is discharged into the pressure line through the outlet pipe. This ensures a continuous, pulsation-free flow of working fluid.
This can be illustrated by the diagram in Fig. 3.
Rice. 3. Operation of the power steering vane pump
If the pressure in the system exceeds the permissible value, the bypass valve discharges excess working fluid into the compensation tank.
There are two types of pumps used on cars:
— single-circuit;
- double-circuit.
Single-circuit pumps operate exclusively on power steering. They are less powerful than dual-circuit ones, their design is simpler, and they are cheaper.
Double-circuit pumps also serve the hydraulic suspension. They are much more expensive and more productive.
The compensation tank can be installed directly on the pump, or separately. More often the tank is located in the engine compartment, using the engine compartment. This greatly simplifies power steering maintenance.
Features of power steering operation
While the vehicle's power plant is running, the power steering pump is also running. When the machine moves in a straight line, the working fluid circulates from the pump to the spool, and from it to the compensation tank. That is, the pump operates with minimal load. When you turn the steering wheel, the spool directs the flow of working fluid into the hydraulic cylinder, turning the wheels.
Thus, the parts of the power steering pump wear out even at idle. Despite the good lubricating properties of the working fluid and the high reliability of the entire structure, wear makes itself felt over time, and the pump has to be replaced.
EGUR system
Electrodynamic power steering differs from conventional power steering by the presence of an electric pump powered by the vehicle's on-board electrical system.
Rice. 4. Electric power steering
The power steering system includes motion sensors. It is their readings that indicate the need to turn the pump on or off at the right moments. Thus, the pump resource is consumed much more economically. Another advantage is compactness due to the absence of a bulky belt drive. The disadvantage is the higher price.
EPS pump
The pump for electric power steering is made in the form of a pump unit - a compact unit that combines a pump, an electric motor and a compensation tank. The pump unit is equipped with an electronic control unit.
Rice. 5. Pump for power steering
The advantages of an electro-hydraulic pump are the absence of a belt drive, as well as less wear of parts - because its pure operating time is less than that of a conventional hydraulic pump. There are also disadvantages - high price and dependence on the operation of the on-board power supply system.
Possible power steering malfunctions
Problems in the power steering system manifest themselves in different ways. The main signs are:
— reverse shocks on the steering wheel;
— difficulty turning the steering wheel in one or both directions;
— vibration;
— extraneous noise during operation;
— unclear operation of the steering wheel.
There can be many reasons for such problems. These include a worn or loose pump drive belt, airing of the hydraulic system, loss of tightness and an associated drop in the level of the working fluid, and low-quality or deteriorated working fluid. If the pump fails, the verdict is clear - replacement. And the sooner the better, since operating a hydraulic system with a faulty pump is fraught with failure of other elements.
How to extend the life of a pump?
The power steering pump is a reliable and durable unit; it does not require complex maintenance. Even if the pump completely fails, you can continue driving the vehicle. True, you will have to put in more effort to control the car.
To ensure that the power steering pump does not fail and lasts as long as possible, you should follow a number of recommendations from experts:
1. Check the condition and tension of the drive belt. The appearance of steering wheel beating, especially at the beginning of movement, is the first sign of insufficient belt tension.
2. Maintain the required level of working fluid in the compensation tank. Choose only the liquid recommended by the manufacturer.
3. Regularly check the condition of the power steering hydraulic system units. Promptly repair leaks in places where working fluid is leaking. In the hydraulic system, it performs, among other things, the function of lubricating rubbing joints. A decrease in the working fluid level below the maximum permissible level can lead to accelerated wear of pump parts and rapid failure.
4. Monitor the condition of the anthers and seals that protect the system from dirt. Contaminated working fluid causes irreparable damage to the connections of the pump and other units.
5. Inspect the hose, fittings and their connections regularly. Twisting of the hoses, excessive sagging, delamination of the braid, and oxidation of fittings and clamps are not allowed.
Pros and cons of power steering
The indisputable advantage of power steering and its main property is to make the work of your hands easier when maneuvering during parking. But the amplifier has another useful property - it softens the force on the steering wheel from impacts on uneven roads.
The disadvantage of power steering is the absence or low reaction force on the steering wheel. The hydraulic booster assists the driver too much, eliminating the return force that provides the “feeling of the car.” And when developing and adjusting the chassis, designers need to achieve excellent information content of the steering drive and at the same time not make the steering wheel too tight. There are many factors to consider: pump efficiency, rear and front suspension geometry, wheel mounting angles, overall tire characteristics, and even body torsional rigidity!
Therefore, good cars in this regard are extremely rare. Still, many companies deliberately abandon information content in favor of comfort, knowing the sympathy of their clientele. A striking example of this is Toyota cars. Although in Europe the opposite is true.
The fruits of the designers' labor are delightful. Another task for them is to make sure that at low speeds the steering wheel remains light, and at high speeds it becomes elastic and informative. There are different ways out of the situation. An electrohydraulic pressure modulator has been added to the circuits of German hydraulic boosters from the well-known company ZF (all models of Jaguar, Audi A6 & A8, BMW 5 and 7 series). As the speed increases, it holds back the pressure in the working circuit, which is why the assistance of the hydraulic booster is equal to zero.
We recommend: How to determine the polarity of a battery: forward or reverse?
There is another way to solve the problem - to drive the power steering pump from an electric motor instead of the crankshaft. By changing the rotation speed of the electric drive using electronics, it is possible to vary the efficiency of the pump as desired.
And the power steering needs attention
In conclusion, a few words about caring for your car's power steering. Like any other mechanism, it requires some attention. In fact, there are few rules, and by following them, you will definitely extend the life of your car. Here are the main ones:
• control and replacement of oil in the power steering reservoir (at least once every two years);
• regular replacement of the filter in the tank;
• if you find a leak in the hydraulic booster, immediately contact the service center;
• regularly check the tension of the power steering pump drive belt.
Maintenance
The steering mechanism and hydraulic booster are reliable mechanisms in a car. For this reason, they do not require frequent and expensive maintenance. The most important thing is to follow the regulations for changing the oil in the system, which are determined by the manufacturer.
As part of power steering maintenance, it is necessary to periodically check the fluid level in the reservoir. If the level drops noticeably after adding the next portion of liquid, you should check whether oil is leaking at the hose connections or at the pump seal.