A modern muffler in a car, despite the apparent simplicity of its design, is a high-tech device whose task is not only to remove exhaust gases from the exhaust system, but also to reduce the noise level, which is carried out by cutting off alternating pulses of high and low pressure exhaust gases formed in result of engine operation.
From the article you will learn what types of car mufflers there are, their structure and design features. Let's talk about the design of mufflers for VAZ 2101/2107/2109/2110, Oka, UAZ, and also consider how to make the device yourself.
Where is it located and how does it work?
The muffler is installed on the underbody of the vehicle at the end of the exhaust system.
As a rule, a resonator is installed in front of it, closer to the engine, which reduces low-frequency vibrations and plays the role of an additional component in the exhaust system.
Despite the seemingly small size of the device, the sound wave travels through it for several kilometers. This is achieved by the presence of labyrinths inside the muffler, which attenuate sound waves.
The further a wave travels, the more energy it loses and the smaller the sound becomes.
To understand what a muffler consists of, you need to understand what types of devices there are and how they differ from each other.
The main purpose of the muffler in the exhaust system
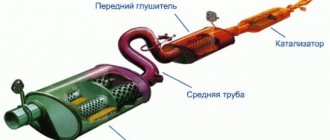
In the engine exhaust system, the muffler is installed after the catalytic converter (for gasoline cars) or the particulate filter (for diesel engines). In most cases there are two of them:
- Preliminary (muffler-resonator) - designed to sharply suppress noise and stabilize fluctuations in the flow of exhaust gases at the engine outlet. It is installed first, which is why it is often called "front". One of its main functions is the distribution of exhaust gases in the system.
- Main muffler - designed for maximum noise reduction.
In practice, the car muffler device provides the following transformations to reduce exhaust noise:
- Changing the cross section of the exhaust flow. It is carried out due to the presence of chambers of different sections in the design, which allows them to absorb high-frequency noise. The principle of the technology is simple: first, the moving flow of exhaust gases narrows, which creates a certain sound resistance, and then sharply expands, as a result of which the sound waves are dissipated.
- Redirection of exhaust gases. It is carried out by partitions and displacement of the axis of the tubes. By turning the exhaust gas flow 90 degrees or more, high-frequency noise is dampened.
- Changes in gas vibrations (interference of sound waves). This is achieved by the presence of perforations in the pipes through which the exhaust passes. This technology allows you to remove noise of different frequencies.
- "Auto-absorption" of sound waves in a Helmholtz resonator.
- Absorption of sound waves. In addition to the chambers and perforations, the muffler body contains sound-absorbing material that insulates noise.
Types of car mufflers
Modern mufflers are divided into three types: dissipative, reactive and combined.
In turn, the above types are divided into two types: direct-flow and labyrinth.
Dissipative (absorbing).
They belong to the type of direct-flow mufflers and have a simple design.
Consist of:
- Housings;
- Perforated pipe;
- Inlet and outlet pipes;
- Special heat-resistant sound-absorbing filler;
- Steel mesh;
- All this is connected by all-welded joints.
The principle of operation is simple - sound-producing exhaust gases enter a chamber from a perforated pipe where they are absorbed by heat-resistant sound-absorbing material, resulting in the energy of sound vibrations being converted into thermal energy. Mineral wool, metal shavings, and glass wool are often used as such materials.
The advantage of such a muffler is that, depending on the design, it allows you to increase engine power by 5 - 7%, because there is practically no resistance to the exhaust gases escaping.
The disadvantage is increased noise, so such products are primarily tuning and are rarely used on ordinary cars, as a rule, only on sports cars.
Structurally, absorbing silencers can be:
- Strongers or “louvered core glasspack”. They are a pipe with metal petals pressed inside. They are considered ineffective in terms of purging and are rarely used. Mistakenly installed instead of a catalyst.
- With internal diffuser. Not expensive products that have their pros and cons. In terms of noise reduction, they are more effective than other analogues, but in terms of purging, it’s the opposite. The only tangible plus here is the low price.
- With perforated cones of different lengths, treat them as a combined solution. The cones are welded into the main perforated pipe, which significantly reduces noise and at the same time the flow of gases is quite satisfactory for many.
Reactive.
The operating principle of such mufflers is based on the effect of damping reflected waves from each other, which leads to a reduction in noise.
In this design, filling material is not provided; instead, additional pipes, chambers and partitions are welded into the body, chaotically reflecting from which sound waves are damped.
But such mufflers can rarely be found on tuning and sports cars, since their design does not allow achieving good results in terms of aerodynamics, the reason being the high turbulence of the exhaust gases.
Also, in terms of design, reactive analogues are complex and therefore are mainly manufactured in factories.
Diagrams and brief characteristics of reactive mufflers are presented below.
Combined.
This form embodies design solutions from reactive and dissipative mufflers. For example, you can take devices with perforated cones (see above).
They have good efficiency in terms of noise reduction, but in terms of gas flow, the performance is low.
Muffler functions
The muffler is designed to reduce the noise level that occurs during the processing of gases and air and their release into the atmosphere. The second main function of this tool is to convert energy from processed gases, reducing their temperature and reducing their speed.
Several chambers of different sizes, separated by a partition, realize the expansion and contraction of the flow. This happens thanks to the diaphragm hole, also called a throttle.
In addition, the muffler provides for a change in the initial direction of flow of these same processed gases. This is what helps dampen high-frequency sound vibrations.
What materials are they made from?
Silencers of all types can be made from:
- Of stainless steel;
- Aluminized (alloy of aluminum and steel);
- Regular black steel.
A stainless steel product can last, during active vehicle use, from 6 to 10 years, as it is least susceptible to corrosion.
They are sold on the market in a high price range, their big advantage is that despite the high price, they are mass produced and can be matched to most car brands.
Products made from aluminized steel are sold in the middle price range, they are also quite durable, but they are difficult to match to a specific car brand, since the choice on the market is not large (only a few companies produce them).
It is problematic to make such a muffler in a garage. The main advantage is a long service life of up to 6 years, and are less susceptible to corrosion.
Products made of black steel are mass produced because they are the cheapest. They can be made in a garage for any brand of car, but they will serve for 3, maximum 5 years, then the aggressive environment and rust will do their dirty work.
Muffler device (diagram)
The design of the muffler has already been partially discussed, now let’s delve deeper into the topic.
You probably already realized that mufflers have many distinctive features; no devices have the same design; each manufacturer introduces its own innovations to improve the design of its brainchild.
The main goal is to reduce the sound as much as possible without losing engine power.
In a typical production car, the muffler takes from 5 to 7% of the power. To achieve absolute silence, you need to either increase or install an additional device with a resonator, and this will take another 5 to 7% of the power. The total is 10–15%, which no one wants to lose.
Those. It turns out that it is not so easy to make an ideal muffler so that there is little noise and no loss of power.
The design of the product is largely influenced by:
- Engine capacity;
- Tuning or regular engine installed;
- Make of the car and its purpose (sports or regular);
- Who is the manufacturer.
The classic muffler for most cars consists of:
- Inlet and outlet pipes;
- Internal pipes;
- From two or more expansion chambers;
- Internal partitions;
- Helmholtz resonator.
The sound entering the device through the inlet pipe is reflected from the walls and travels a distance of more than 1 km, constantly weakening.
The resonator serves to weaken the most powerful component of the sound wave, which a conventional labyrinth cannot cope with.
The chambers in the muffler are of different sizes because the length of the sound waves is also different.
The inlet pipe, as a rule, has holes and is considered dissipative, since sound entering it is partially dissipated in the first chamber.
The waves move chaotically in space, reflecting from the walls and constantly losing energy. This occurs due to the force of friction against air molecules.
The more of the wave remains in the first chamber, the more the wave attenuates.
The remaining waves pass into the second scattering chamber; however, it is not easy for them to pass from a narrow pipe into open space since, according to the law of acoustics, a sound wave seems to collide with a wall of air.
Part of the wave is not able to enter the second chamber and is reflected back from the interface and partially absorbs the oncoming flow.
The same waves that were able to get into the second chamber are randomly reflected from the walls, absorbing each other and losing energy during friction with the air.
But the main component of the sound wave passes further and enters the Helmholtz resonator.
The sound wave again has to leave the narrow space into the free chamber, and it seems to press on the air in the resonator, creating air vibrations.
This creates a reverse sound wave that has the same frequency as the original one. They collide and destroy each other.
Some of the waves remaining in the second chamber enter another pipe and are transported to the third chamber.
There again, sound loss occurs due to friction with the air, and only after this the weakened wave enters the output pipe, and from there out.
Where is the element located and what does it look like?
The main source of noise is the combustion chambers of a running engine. The sound waves generated there cannot penetrate through solid metal walls and tend to exit along the path of least resistance - through the exhaust pipe along with the exhaust gases. There a muffler is installed in the form of a metal barrel of a round or oval shape.
The operating diagram of a car exhaust system looks like this:
- A vibration-isolating corrugation is installed first behind the exhaust manifold. Its task is to smooth out the vibrations transmitted to the pipe from the motor.
- After passing through the corrugation, smoke and sound waves enter the catalytic converter. Its task is to burn off the remaining flammable gases so as not to release them into the atmosphere. Inside the part there are small ceramic honeycombs that partially absorb and disperse sound.
- After the neutralizer, the exhaust passes into the resonator tank. This is the first stage of noise reduction.
- The last in the chain is a muffler, which finally dampens sound vibrations.
In fact, a resonator is also a muffler; you will learn its structure and principle of operation in the next section.
The resonator tank always stands along the axis of the car, and the muffler can be installed transversely (at the rear of the car). There are options when both elements are combined in a single housing in order to save space. On cars with high-power V-engines, a distributed exhaust system with 2 pipes is installed. Accordingly, the number of all parts doubles.
Muffler design for VAZ 2101/2107/2109/2110/2015
Despite the fact that the principle of operation of all VAZ muffler classics and later models is the same, they still have design distinctive features.
For example, consider the muffler design on a VAZ 2101.
The product has three cameras, the general structure is presented below:
- Upper half-body;
- Thermal insulation;
- casing;
- Partitions of the right and left chambers;
- Inlet pipe;
- Front partition;
- Perforated exhaust pipe;
- Perforated pipe internal;
- Perforated intake pipe casing;
- Rear partition;
- Semi-hull lower;
- Exhaust pipe;
- Front exhaust pipe;
- Main muffler;
- Suspension strap;
- Pillow suspension;
- Grazing pipe.
Muffler design of late models using the example of a VAZ 2110.
- Reception pipe;
- Bracket;
- Clamps;
- Resonator;
- Suspension cushions;
- Main muffler;
- Exhaust pipe;
- Perforated rear resonator tube;
- Posterior partition;
- Front partition;
- Perforated front resonator tube;
- Frame;
- Front perforated pipe;
- Inlet pipe;
- Outlet pipe;
- Frame;
- Posterior partition;
- Middle partition;
- Rear perforated pipe;
- Front partition.
Making a VAZ muffler with your own hands
You can often come across a car that can scare even a lion with its roar. This does not mean that the car is living its last days. This can only mean that a gap has formed in the exhaust system through which gases are escaping. Let's start by determining where the noise comes from. The fact is that in the combustion chamber and exhaust manifold the gas temperature is very high, about 700 degrees. In the exhaust pipe it drops a little, but the pressure remains enormous.
When released into the atmosphere, the speed of the gases is so high that they hit the air, creating a strong bang. Thus, it turns out that the main purpose of the exhaust system is to reduce the pressure and temperature of gases, and therefore their speed. Many people have probably noticed that foreign-made cars make less noise when driving. The main difference between their exhaust system and domestic systems is the diameter of the exhaust pipe and the volume of the resonator and muffler.
Device
Let's look at the muffler of a VAZ 2107 car in cross-section. If you cut it lengthwise, you can see a kind of labyrinth in it. Through which exhaust gases travel outward.
So, here there are only two turns, while for “foreign cars” their number reaches 6. The domestically produced resonator is a simple receiver, without any partitions. I must say, it is of little use. In addition, the diameter of the exhaust pipe of a serial Japanese car reaches 65 mm, while in the VAZ 2107 it has a radius of 26 mm. All this suggests that the exhaust system of a domestic car needs serious improvement. But that’s not what our article is about.
Materials
The Soviet muffler VAZ 2107 weighed 7.5 kg, but now it weighs only 5. What do you think is the reason for this difference? It's a matter of the thickness of the metal used. Previously, 1.2 mm sheet iron was used, but now this thickness is 0.9 mm, that is, the metal is slightly thicker than on a car fender. But are their operating modes comparable? In no case.
Making a muffler with your own hands
From the above it follows that replacing the standard system is simply necessary. At least the main muffler. Let's look at its manufacture in a little more detail. For this we need a sheet of iron with a thickness of 1.1-1.4 mm, its length is approximately 0.5 m. We also need a sheet of asbestos, it will be useful for thermal insulation. You also can’t do without a grinder and a semi-automatic welding machine.
First you need to cut out three identical ovals along which the “buckle” will be curved. After this, the ovals must be placed evenly along the length of the sheet. In the central oval it is necessary to make three holes for the pipes that will be used. Thus, if we insert all three pipes, we will get a zigzag along which the movement of gases will occur. Welding parts is a technological process that does not need description.
Conclusion
In conclusion, I would like to clarify some points, such as fire safety: do not forget about the asbestos sheet (if not, you can remove it from the old muffler along with the shield). In addition, it would be better to choose stainless steel as a material, and cook everything using argon welding. Then the muffler will not only be more reliable, but also aesthetically pleasing.
VAZ 2114/2115
There are no innovations in the VAZ 2114/2115 mufflers, the same 4 chambers and three partitions, three perforated pipes and one outlet pipe with an increased diameter.
As a rule, the metal of the outlet pipe rots, and that’s where the rattling noise comes from.
UAZ
Next, let's look at the muffler design using the UAZ Patriot as an example.
First comes the upper housing casing, under which there is a layer of fiberglass.
Inside there are three chambers, separated by two partitions, two perforated pipes without narrowed sections. There are no vibration-absorbing materials.
The inner diameter of the outlet pipe is 52 mm, the inlet pipe is 53 mm. The outer diameter of the inlet pipe is 57 mm, the outlet pipe is 55 mm. Body length 50 cm.
The UAZ Patriot muffler is no longer distinguished by anything special. It makes a lot of noise and rusts inside.
OKA car
The Lada OKA muffler is located perpendicular to the car body.
Inside the device there are three chambers and two partitions, three perforated pipes. No special innovations were introduced into the design of the product, so the principle of operation remains unchanged.
Repairing the muffler yourself
To make it easier for you to inspect the muffler, you should disconnect it from the car. This will help you complete the job faster and better. If during a visual inspection you do not see any serious damage, then most likely the damage is internal.
It is very important to remind you that without sufficient experience, it is better to contact a car service, where experienced technicians will help eliminate all muffler defects.
If during a visual inspection you find damage (a hole made by a stone), then you will need a welding machine. But if burnt, rusted holes are visible, then it is not recommended to cook such a muffler, since it will soon lose weight again; the muffler needs to be replaced, preferably from high-quality material. It often happens that a breakdown occurs at the junction of the engine and the exhaust pipe. This element is called corrugation.