To start a car engine, it is necessary to provide conditions for ignition of the air-fuel mixture. And one of these conditions is to spin the crankshaft to at least the minimum required speed so that the working processes take place in the cylinders. For turning the knees. shaft, an external source of mechanical energy is used. It is a power electric motor, called the “starter”.
The starter clicks intermittently
The battery is low
On modern cars, when the contact group brushes come out. When the ignition is turned on, the charging indicator lamp does not light up. When the engine is running, the indicator also does not light up. That is, when the ignition is turned on, the light should light up and go out while the engine is running. It's hard to pay attention to the fact that there is no generator malfunction signal. Because when you turn on the ignition, many warning lights come on.
You can only identify the charge indicator lamp if you accidentally pay attention to it. Therefore, there is still enough charge in the battery. The car starts and drives. This will last up to several days until the battery is completely discharged. As soon as this happens, the car will stall or the starter will not turn. Short knocking sounds will be heard from the starter solenoid relay.
The battery charge is enough to retract the armature of the solenoid relay. The windings will not be able to resist the spring. The anchor will be dropped. But since the key is at the start, the armature will be retracted and released. In this case, the battery will not have enough energy to crank the starter.
You can tell that the battery is dead because the lights in the lighting fixtures will dim when the starter is turned on.
There is no contact between the engine and the car body.
Or the starter mounting bolts are loose. The battery current is not enough to turn the starter due to poor contact. For this reason, the armature of the retractor relay is discarded. The force of the holding and retracting windings is not enough. To hold the armature spring in a compressed state. How the solenoid relay works is described in detail in this article. “How does the starter solenoid relay work - malfunction”
Lack of good contact is the first thing to check when such a problem occurs. That is, check the reliability and cleanliness of the contacts.
— Between the battery and the car body
— At the negative terminal of the battery.
— On the positive terminal of the battery
- between the engine and the body
— reliability of fastening of the starter bolts
— check the reliability of the connection of the positive wire going from the starter to the battery.
That is, check all connections going from the starter to the battery.
Main types of breakdowns
In general, all car starter malfunctions are divided into two categories. The first of them is mechanical. These include:
- burning of nickels;
- bearing wear;
- damage to the drive gear teeth;
- jamming of the retractor relay armature;
- destruction of the overrunning clutch;
- Bendix jamming on the shaft.
These faults are corrected by servicing and replacing confirmed items. For example, burnt coins can be cleaned and bearings can be replaced.
The second category of starter failures is electrical. These faults are considered more serious because some of them are difficult to fix. These include:
- wear of brushes and contact plates of the commutator;
- breakage of the stator windings and the solenoid relay;
- winding short circuit.
While it is easy to replace the brushes, repairing the commutator is difficult, since all its plates need to be soldered. As for breaks and short circuits, only an experienced auto electrician can fix such breakdowns. At the same time, a repaired engine often breaks down again, so sometimes it is better to replace the unit than to repair it. In case of electrical breakdowns, the relay is not repaired, but replaced.
As for gear starters, the gearbox can also fail. Its “weak point” is the ring gear, which manufacturers often make of plastic (to reduce noise and reduce the cost of production). This crown is destroyed due to loads and the gearbox stops working. To restore the starter's performance, the ring is replaced. At the same time, some car enthusiasts select and install a metal crown to prevent repeated breakdowns.
How to check the starter if it clicks but does not turn.
Reasons why the starter clicks but does not turn and does not scroll. Similar to those in which the solenoid relay is activated several times.
- The battery is discharged so much that its power is only enough to pull in the armature of the solenoid relay only once. The battery is completely discharged. Repeated retraction of the anchor does not occur. Accordingly, the starter will turn over, but it also cannot.
- Solenoid relay is faulty. It has two windings, a more powerful retractor and a holding one. Most often the pull-in winding fails. This is described in more detail in the article. How does the solenoid relay work?
The armature is pulled in only by the holding winding. His effort is only enough to retract the anchor halfway. Naturally, the nickel does not reach the terminals. No power is supplied to the motor. The starter does not rotate.
You can check this as follows.
- When you turn the key to start. Check the voltage at the terminal to which the wire from the stator winding fits. It should be missing.
- Second way. Connect the terminal to which the positive wire from the battery comes and the terminal from which the wire goes to the stator windings. The voltage is transmitted through the jumper to the stator windings and the starter begins to rotate.
That is, the nickel inside the solenoid relay does not bridge the terminals.
The second malfunction in which voltage does not transfer between the terminals is that. Carbon deposits form on the coin and terminals at the contact points. Or contact burnout. As a result, one of the terminals becomes shorter and a nickel does not reach it. And even if the windings are working properly, due to the fact that there is no contact, the starter does not turn.
This can also be checked by bridging the contacts or measuring the voltage.
In case of such malfunctions, the car can still be started.
If the solenoid relay is working properly, then you can bridge the three positive terminals to the starter winding and the solenoid relay control terminal. The starter will begin to rotate and the engine will start. With this method of activating the starter, it is very important to first make sure that the car is in neutral gear with the handbrake. If the gear is engaged, the engine will start and the car will move. At best it will cause injury.
If the solenoid relay is faulty. And the bendix, like an anchor, does not reach the flywheel crown. If the terminals of the positive and stator windings are shorted more than once. The Bendix will engage the flywheel. Because it is connected to the shaft using a threaded connection. When the starter shaft rotates, it will begin to twist forward. And can connect to the flywheel crown. This may not work the first time, but after repeated attempts it will happen and the car will start.
Bendix sticking on the starter shaft
The Bendix is connected to the solenoid relay armature. It moves freely along the shaft along a screw guide. A screw connection is necessary in order to. Protect the bendix and starter from destruction. The moment the engine starts. The flywheel speed becomes higher than the starter shaft speed. That is, the flywheel will start to lie to the Bendix. Due to the fact that the bendix is on a screw connection, it will begin to move inside the starter and disengage with the flywheel.
In our case, wear may occur between the bendix and the shaft. Bendix can jam. And do not reach the engagement with the flywheel. Accordingly, the anchor will also not reach the contact between the coin and the terminals. Therefore, a click will be heard but the starter will not turn over. This kind of thing rarely happens. You can make sure that the bendix is jammed on the shaft only by removing the starter.
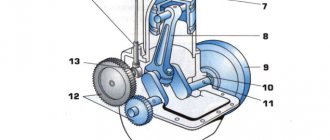
Main components
In essence, a car starter is a modified DC electric motor with a commutator-brush assembly. The design additionally includes a control mechanism that turns the electric motor on and off and an actuator whose task is to act on the crankshaft flywheel.
The control mechanism is a solenoid relay. It performs two tasks simultaneously:
- Closes the electrical circuit and supplies voltage to the electric motor.
- Engages the actuator gear with the flywheel gear sector.
The components of the solenoid relay are the winding and the armature. The latter is connected to the actuator via a fork.
The actuator used in the design of a car starter is called a bendix. Its main element is the drive gear, which transmits the rotation of the electric motor shaft to the flywheel. This gear in the classic starter design is located on the rotor shaft of the electric motor and has a splined movable connection with it. It allows the gear to move along the shaft and transmits force.
The Bendix design includes an overrunning clutch that prevents reverse transmission of force. The fact is that after starting the engine, the crankshaft rotation speed exceeds the starter rotor speed. In this case, the driver does not always have time to react and turn off the starter. As a result, due to the meshing of the gears, a reverse transfer of force occurs - from the flywheel to the starter, which leads to damage to the latter. To prevent this from happening, an overrunning clutch is used, which, if the rotor speed is exceeded, breaks its connection with the Bendix drive gear.
Two electrical circuits are used to power the starter. The first of them is direct from the battery to the electric motor. The starter consumes a large amount of electricity during operation. Therefore, to reduce losses, voltage is supplied directly to the electric motor using a large-section copper cable.
Moreover, this circuit is constantly open in the solenoid relay, which eliminates unauthorized switching on of the electric power. engine.
The second circuit is used to power the solenoid relay. It consumes little energy, so conventional wiring is used. There is also a break in this circuit - in the ignition switch.
These electrical circuits are operated in series. First, the second circuit closes, which causes the relay to operate, and it then closes the first circuit.
The starter turns but does not turn the engine
Wear of bendx rollers
When you turn the ignition key to start, the starter turns, but the engine does not move. This happens due to a broken bendix.
Bendix consists of two parts.
- The first is connected to the starter shaft
- The second is a gear that meshes with the flywheel ring.
They are connected to each other using spring-loaded cylindrical rollers. The cavity in which these rollers are located is at an angle in the direction of rotation of the bendix. That is, the rollers do not create an obstacle in one direction of rotation. In the other direction, the rollers, due to the frictional force and the location of the movement of the rollers, become a wedge. Between two surfaces.
During operation, the rollers wear out and become thinner. The working surfaces also wear out. The rollers stop clamping. As a result, the bendix rotates and does not transmit rotation from the starter shaft to the flywheel.
If this happens on the road, there is a chance that the engine will still start. To do this, you need to drive the starter several times. Friction surfaces heat up. Thermal expansion of the bendix elements occurs. At some point it will work and the engine will start. As a rule, such a malfunction appears gradually. At first the Bendix slipped once. Then more and more often. It's better to replace it immediately. There will come a time when the Bendix completely fails.
Damage to bendix teeth and flywheel ring
There is one point in which a working starter does not rotate the engine. This happens due to the destruction of the bendix teeth and flywheel crown. That is, Bendis comes out completely. The contacts of the retractor relay are connected through a nickel. The starter is turning. But the engine does not turn over.
The Bendix feed was not initially adjusted. Or the bendix jammed on the starter shaft.
The contact patch of the Bendix gears and the flywheel crown is adjusted using the screw on which the Bendix fork is attached. The surface of the bolt is offset along its axis. Thanks to this, it is possible to adjust the bendix output up or down.
If the bendix teeth do not create a complete contact patch. Partially or half-engaged. Rotation occurs along the edge of the teeth. As a result, the teeth grind down or break off. It is difficult to check the starter as if the teeth are broken or the bendix is faulty.
Most likely, sounds that are not characteristic of the starter will appear. Grinding and sparking.
Principle of operation
When turning the key, the driver closes the power supply circuit for the retractor relay. Electrical energy is supplied to the relay winding, which leads to the formation of a magnetic field. This field acts on the armature, and it is pulled into the relay. As it moves, it pulls the fork behind it and moves the bendix along the rotor shaft, the drive gear engages the flywheel teeth.
The solenoid relay also opens the first circuit - power supply to the electric motor. On the outside there are two terminals for connecting the cable coming from the battery and the bus through which voltage is supplied to the electric motor. On the inside of the relay body, contacts called nickels are connected to these terminals. These two terminals, not in contact with each other, are a break in the motor power supply circuit.
When the relay is triggered, the armature, after being retracted, closes the coins, voltage is supplied to the engine, and it turns on. In this case, the Bendix gear is already engaged.
After starting the power plant, when the crankshaft speed exceeds the rotor speed, the overrunning clutch is activated, disconnecting the bendix from the shaft, they begin to rotate separately.
Video: How the starter works
After releasing the ignition key, the power supply circuit of the solenoid relay is interrupted. The magnetic field disappears and the spring installed in the relay returns the armature to its place, opening the coins and disengaging the bendix - the starter is turned off.
When I turn the key to start, the starter does not respond at all.
- The first thing you need to check is how the starter works. To do this, make sure that the gearbox is in neutral and put the car on the handbrake. Using a jumper. Bridge the control terminal of the solenoid relay and the terminal that receives the positive from the battery. If the starter began to rotate the engine, and it started. This means the starter is OK. Most likely the problem is in the starter relay or ignition switch.
- Check the presence or absence of voltage at the control terminal. To do this, measure the voltage at the control terminal with a multimeter. Turn the key to start. If voltage does not appear, the starter relay is faulty.
- The starter relay is an electromagnetic coil that receives voltage from the ignition switch. As soon as voltage is applied to the coil. It attracts the plate with the contact. Which connects to another contact. As a result, voltage is transferred to the control terminal of the solenoid relay. A starter relay is used so that the current generated when the retractor relay is turned on cannot burn the ignition switch contacts.
Starter device
Structurally, the starter is an electric motor and is designed to convert electrical energy into mechanical energy. The principle of its operation is that, according to Ampere's law, a current-carrying frame located in a constant magnetic field begins to rotate. Let's look at the main components of the starter.
- Housing with a steel core (shoe), with a conductive winding. Four cores are installed and bolted into the body. The result is a stator winding, which is also called the field winding. The input to the winding is supplied from the side of the housing, and the output is to two copper-graphite brushes. The result is a standard electromagnet. The design of the starter in modern cars is simpler - here the cores are replaced with permanent magnets, which allows the devices to be made more compact.
- An anchor is a steel shaft onto which a core is mounted. It is made from thin sheets of special electrical steel to eliminate the influence of eddy currents. Conducting frames are placed in the grooves of the core, leading to a copper collector. The stator winding brushes with a positive charge and the negative brushes connected to the ground of the device go to it.
- The back cover has special brush holders that hold the brushes in place and spring them to improve the quality of contact with the commutator. A support sleeve is installed in the center to support the armature.
How to check the starter if the starter relay is faulty
If you do not hear any knocking or clicking noises when you turn the starter key, there is most likely a problem with the starter relay. You need to find the deck on which the starter relay is installed. This can be done by following the indicators on the covers covering the fuse and relay boxes. And check the serviceability of the relay or determine whether the plus is suitable for it or whether there is an open circuit.
- On the block where pin No. 87 fits, check for voltage using a multimeter. If it is missing, check the integrity of the fuse through which the plus goes to the relay. This plus comes to the control terminal of the solenoid relay.
- If there is a plus. With the ignition on. You can briefly bridge the contacts on the block where relay contacts No. 87 and No. 30 are inserted. In this case, it is necessary to make sure. That the car's transmission is in neutral gear. If the car starts, there is a problem with the starter relay or ignition switch.
- When you turn the key to start, you should hear a click in the starter relay. This indicates that the coil is working properly. What if the starter doesn't turn? The problem is most likely with the contacts. They burned out or carbon deposits formed.
- If the click is not heard. The coil winding has burned out or the relay does not receive voltage from the ignition switch. You can check this by checking for the presence of voltage at the terminal of the block where relay contact No. 85 is inserted.
- If the voltage from the ignition switch does not reach the starter relay block, then there is a malfunction either in the ignition switch, or it is necessary to check the integrity of the wiring.
In all cases, you can check how the starter works. Start the car and drive. Or by briefly bridging the control terminal with the battery positive terminal. Or also briefly while starting the engine by bridging the contacts on the starter relay block. The most extreme case is a tug, of course, if the gearbox is not automatic.
How to check the starter if the malfunction cannot be detected by external signs is described in detail in the article The starter turns poorly when the battery is charged
Possible starter problems
It is quite natural that the starter – we have already discussed the device and principle of operation – experiences much less load compared to other components and assemblies of a modern car. After all, when fully operational, it is activated only for a few seconds. However, this does not mean that starter breakdowns are impossible. Among the most possible problems, experts identify the following.
The starter does not start. There are many reasons for this, and mostly they are directly related to the “stuffing” of the device - winding, contacts, relay malfunction, etc.
Insufficient crankshaft speed. Most often, this failure occurs for several reasons: oxidation of contacts, excessive viscosity of the lubricating fluid, discharged battery.
The starter runs longer than expected. Professionals claim that this defect is caused by the ignition switch (it gets stuck), incorrect operation of the contact connectors and a failure in the winding.
The design and operation of the starter does not lead to rotation of the crankshaft. Most likely, something is preventing the free movement of the advance clutch along the shaft.
Gear grinding. In most cases, behind it lies an incorrectly set contact closure or a scuff on the crown of the car engine flywheel. In addition, sometimes the gears disengage with a delay. Also, the cause of grinding, albeit infrequently, is the drive spring - over the period of operation it loses the ability to fully expand.
Of course, the car owner’s thorough knowledge of the car’s starter device allows for possible problems to be prevented in a timely manner. In addition, many problems in the operation of the device can be compensated for by competent repairs. However, often knowing the basics of the starter design is not enough to troubleshoot problems, since you also need to understand the technical characteristics of the starter. And this is the current strength, voltage and power, the amount of torque, etc. Therefore, very often car owners are faced with a dilemma: what is more rational, to buy a new starter or to send the old one to specialists for repair?