Main functions of the suspension
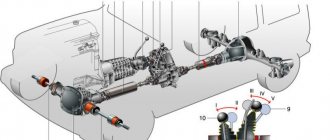
Suspension device
The suspension of any modern car is designed to perform several basic functions:
- Connection of axles and wheels with the main supporting system - frame and body.
- Transmission of torque from the engine and the main load-bearing force.
- Ensuring the necessary smoothness.
- Smoothing out road imperfections.
All manufacturers are working to improve the efficiency, reliability and strength of the suspension by introducing more advanced solutions.
Types of pendants
Let's look at the most common types of car suspensions.
Dependent type suspension
The oldest type of suspension, dependent suspension is still used today, and its main distinguishing feature invariably remains a fairly rigid connection of the wheel axles through a simple beam or axle housing. Initially, springs were used as guides and elastic elements, but in modern cars the cross member connecting the wheels is fixed by two longitudinal arms and a transverse rod, which absorbs lateral forces. Used on the rear axle of front-wheel drive budget cars, as well as many SUVs.
It is generally accepted that, apart from low cost and ease of use, the dependent suspension of a car has no advantages - this is absolutely not the case. Its advantages are light weight if we are talking about the driven axle, a fairly high roll center and, most importantly, constant camber and track. Regardless of roll and sway on a flat road, the angle of inclination of the wheels to the road surface does not change, which means that in any mode the car has the best grip on the surface. I would like to say that no other pendant can boast of similar properties.
Unfortunately, the situation worsens on poor road surfaces - the failure of a wheel in a hole causes a change in the camber of the other, and this reduces traction properties. When driving straight this is not very noticeable, but when turning it can lead to an unexpected skid.
There are also significant problems with the car's handling. Multidirectional wheel travel occurs with the rotation of the axle beam, which provokes poor steering and a complete lack of stability on a straight line. Also here the Panhard rod jerks the axle left and right, which worsens the situation.
Fortunately, this is fixable. In order for the cross member to stop unfolding, instead of one trailing arm on each side, you can use two, located according to the Watt mechanism system. The problem of axial displacement can be eliminated by installing a trailing arm that holds the beam in the center instead of a Panhard rod. But in practice it becomes clear that such a change is pointless - the design becomes noticeably more complicated and requires more space in height. But the main area of application of dependent type suspension is budget cars.
A typical representative of this design could be a rear suspension with coil springs as elastic elements. As an example, we can consider the design of the rear suspensions of classic Zhiguli models. Here, with the help of two coil springs, the rear axle beam is “suspended” and is also additionally attached to the car body thanks to four trailing arms. In addition, a reactive sway bar is installed to improve ride quality, improve handling and reduce body roll when cornering.
Front suspension device
All elements that are used to create a pendant can be divided into the following classes:
- Providing elasticity.
- For smoothing out uneven road surfaces.
- To distribute the direction of forces.
- To stabilize the car and improve its stability on the road.
The following elements can be distinguished that provide elasticity:
- Springs are used on all passenger cars to create the front suspension. Despite the simplicity of the design of the element in question, it comes in two types: with constant and variable stiffness. These performance qualities are achieved by changing the thickness of the coils. There is a bumper in the center, which is necessary to absorb the shock if the spring is compressed to its maximum.
- The pneumohydraulic or pneumatic system operates using compressed air or a special fluid. Such a system is used quite rarely, but its operating features make it possible to ensure comfortable movement even with poor quality road surfaces. It is also worth noting that the system in question allows you to adjust the suspension parameters: stiffness, ground clearance and other indicators.
- Torsion bars are a special metal tube with a rod installed inside. Before installation, it is screwed on; unwinding is limited to levers, shock absorbers and other structural elements.
Useful: Fuel injection nozzles. Types of nozzles.
The elements that serve to distribute force can be called various types of levers. They determine the correct location of the wheels and a certain transfer of force from the wheels to the body.
Dampening design elements are designed to increase the comfort of the driver and passengers while driving. They create a counter force against the springs. Often a shock absorber is used as a damping device. It can be pneumatic or hydraulic (oil is used as the working fluid).
Independent suspension
It has an independent connection between the wheels and a more complex design. An example is a trailing arm suspension. The wheel is attached to the lever and is hinged to the body. At the same time, a fairly strong trailing arm with a wide support base ensures clear parallelism of the wheels. Bushings reduce impacts, cornering occurs simultaneously with the body, and the roll center is level with the road. The car is stable to drive on a straight road, but when turning, the speed must be reduced.
Five Signs It's Time to Check Your Suspension
Increased stiffness while driving
If, while driving, you begin to feel that every small impact on the road causes a hard jolt to the body, this means that there are problems with the shock absorbers.
The car “pulls” when turning
There is something wrong with the suspension if you feel that the car is “pulling” when cornering. This means that the shock absorbers can no longer maintain vehicle stability during the centrifugal forces generated when cornering. This increases the risk of loss of control and rollover.