One of the most important elements of the front suspension is the ball joint. True, they used to be used on the rear axle, but these were isolated cases when the rear wheels were able to steer in time with the front ones (nowadays this design is practically not used). The support, as a support bearing itself, allows your wheels to deflect (simply turn), without this design this would not be possible. In this article I will talk about the device, how it works and whether it can be repaired to make it last forever. In general, as usual, there will be a lot of useful information, so continue reading...
Why do you need a ball joint?
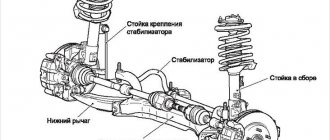
A ball joint is, structurally, nothing more than a hinge with which the wheel hub is attached to the suspension arm. Its main task is to give the wheels freedom of movement in the horizontal plane and exclude it in the vertical. In general, ball joints are used not only in hub supports - they can be found in camber arms, in the steering linkage, and even in fastening the hood gas stops.
But until a certain time, instead of movable ball joints on swivel wheels, a kingpin joint was used - heavy, requiring periodic lubrication, and most importantly, providing the wheel with only freedom of rotation along one axis, which negatively affected handling.
The designers understood that the ball joint would take every hit from the road, so the wear and tear would become colossal. There was no point in making a part with particularly durable diamond coating, so it was deliberately turned into almost a consumable. So that if something happens, you can easily unscrew a couple of bolts and a nut and replace it with a new one.
How to check a ball joint on a car yourself
Proper operation and timely maintenance help to extend the service life of ball joints. Typically, the resource of modern spherical joints in cars, depending on the brand, reaches 30-100 thousand km. mileage Vehicles that meet the following criteria may fall into the risk zone for premature breakdowns:
- the boot on the ball is torn;
- the car is often driven on poor quality roads;
- the unit has insufficient lubricant;
- the hinge pins have worn out and a gap has appeared, leading to loosening.
To check the condition of the ball joints you will need a lift or jack. After lifting the car, the wheel under test should be able to rotate freely. The driver grabs the top and bottom edges of the wheel and rocks it slightly in a vertical plane. You can ask an assistant to turn the steering wheel slightly. The wear can be heard at a certain wheel position. However, play in some cases is the result of insufficient tightening or broken wheel bearings. The gap also occurs due to damage to the silent blocks of the lever. Additional testing will be required. Using the flat part of the mount, we determine whether it is necessary to change the balls. We insert it into the gap between the lever and the pivot pin. We create a slight force on the handle and monitor the knot. If there is a working hinge, there will be no play. Negative factors will be tapping and clicking that occurs when pressing the handle.
Device
Technical progress has led to changes in the original design of ball joints, although they were not fundamental. The stamped halves of the body, connected by spot welding, were replaced by cast and dismountable supports - with a threaded cover, maintenance-free and serviceable - with grease fittings. These improvements were justified and useful. Today, the most common maintenance-free ball joint design consists of: a body with a spherical recess and a pin with a ball on one end and threads on the other. The boot, placed on the finger, prevents moisture and dirt from entering the housing filled with a special thick lubricant.
The main function of the ball joint is to ensure its fixed position in the horizontal plane during vertical movement of the wheel. The ball pin can rotate in the body, swinging at small angles. That is, in the plane of its attachment, the ball joint provides simultaneous rotational and linear (limited) movements of the finger.
All parts of the ball joint are usually made of steel. To reduce friction of contacting working surfaces, the spherical recess of the housing is covered with plastic or other polymer material. However, there are ball joints that do not include a polymer coating between the body and the pin. This applies, first of all, to outdated domestic cars. These models were equipped with collapsible ball joints, in which backlash was eliminated by tightening the cover.
There are two ways to attach the ball joint. In the first case, it is bolted to the lever. In the second, it is pressed into it. If a bolted ball joint fails, it can be replaced with a separate unit. To do this, you just need to buy and install it by bolting it to the lever. In the second case, you will have to change the suspension arm with a pre-installed, pressed-in ball joint. The cost of such repairs is much higher, since it also includes the cost of the lever.
Press-fitted ball joints are typically installed on Japanese-made vehicles. Asian manufacturers of auto parts offer consumers ball joints for such cars in the form of separate units. This is much cheaper, but you should be aware that their quality is significantly inferior to the original, and the lever will have to be remade in a “makeshift way”, turning it into a part that is not subject to warranty repair
Purpose and design
A car's ball joint is a joint with a ball at the base. It is placed in a special insert, like a joint with a human hand. Just like with the arm, the joint allows movement in different planes, the ball joint allows the wheel to turn while maintaining its position in the horizontal plane.
It is located where the suspension arm attaches to the wheel hub. In fact, the ball joint is the fastening element that connects these moving parts. In some models, this applies more to the domestic automobile industry, there are two of them per wheel. In foreign cars - one at a time.
Consider the design of a car ball joint:
- Boot - it protects the mechanism from dust, dirt, water and other road objects.
- Pin - a metal rod that secures the wheel hub to the hinge
- The ball and the finger are one whole. Allows the wheel to move freely in the desired direction. The ball rotates freely in the liner cage
- Plastic liner. It “envelops” the hinge ball, fixes it, eliminating play and free movement in the support body.
- Frame. It contains the internal part of the structure: a cage with a ball. This part of the joint is bolted to the suspension arm.
Thus, the ball joint is secured, “pressed” with a finger (metal rod) into the seat of the steering knuckle, fixed on it with a washer or cotter pin, and attached to the lever by the body. Only thanks to it the wheel is held on the suspension in a certain position, the car can easily overcome uneven roads and turn at the same time. You can clearly see what a car’s ball joint is made of and how it works in the video .
Video of what's inside the ball joint - disassembling the case and reviewing its internal components:
Diagnostics and replacement
If, when directly turning the steering wheel of a vehicle, the motorist needs to make special efforts or a characteristic creaking occurs, then most likely there are problems with the ball joint. In addition, this will also be indicated by the occurrence of a knocking sound when the car is moving at low speeds on uneven surfaces. Another sign of failure of ball bearings is wobbling and instability of the front wheels when moving directly in a straight line. Another sign of this problem is uneven wear on the vehicle's tires.
It is quite clear that a quick and high-quality replacement of the entire ball joint device will be possible only with the help and operation of professionals. However, many car enthusiasts prefer their own labor and work. In the modern world, the question of the production of ball joints finds its answer in the thesis that this is a high-tech process that allows us to achieve a high degree of reliability and durability. However, replacing this device is one of the most common types of car repairs. The situation, of course, can in no way change until the quality of our domestic roads changes.
How does it work?
As you understand, a closed “ball” can rotate in any direction, even spin. A fixed mount is attached to the cylindrical body, which is installed in the necessary suspension elements - this part is not movable. But the upper threaded pin is attached to the moving parts, thanks to which they can turn or even rotate.
In old rear-wheel drive cars, for example our VAZs, there were about 3 ball joints. Two were located in the burdocks and allowed the caliper to rotate along with the wheel. One was located in the steering rod and pushed the wheels.
The MacPherson suspension has greatly simplified the design. Here, as we know, there is a support bearing and it allows the strut and caliper to rotate, but the ball joint remains at the bottom. There are also steering links that push the calipers, causing the wheels to turn. There are only two ball joints here.
It is also worth mentioning that there are options with four supports, but they are quite rare and should not be considered.
Now there may be objections - that the ball joint and the steering tip are not the same thing. Guys, the only differences are in the mounting of the case, the essence of the work is the same.
If we summarize the work, the following comes out: you turn the steering wheel, the force passes through the steering rack to the caliper, and in order for it to turn, hinge joints are needed, this is exactly the work that the supports, steering tips and, of course, the support bearing do.
Video
This video shows in detail the design of the ball, what it is used for, etc.
Here you can clearly see how a ball joint works in motion.
How to diagnose the suspension yourself.
Diagnostics of steering tips and balls.
This video shows how to check the suspension.
Checking and replacing the ball joint on a FORD FOCUS 2 / FORD FOCUS 2 car.
0
Author of the publication
offline 1 week
Causes and consequences of ball joint failure
As mentioned above, the support was invented as a replacement for the pivot, but getting rid of it did not get rid of the forces acting on the hinge. If you ask an almost philosophical question: “So why do ball joints wear out?”, then the answer will consist of three main points (there is also a fourth - time - but it is not interesting, since it is understandable).
First: increased shock loads on the suspension when driving, for example, along tram tracks at indecent speeds or normal vehicle operation in unusual road conditions, which will not surprise us. Second: lack of lubricant where it should be (remember the grease fittings?). And finally, third: destruction of the support boot.
As for the design features of suspensions and the effect of this on wear, we can say the following: any ball joint, no matter how it is installed - on the lever or on the steering knuckle - will wear out due to shock and friction. And if you want to save money and nerves, then you need to look behind the wheel more often, and also not shout “Banzai” to yourself when you see approaching misunderstandings in the form of potholes.
Ball joint repair
There are several repair methods. Often, the ball joint is replaced with a new one. Replacing a support along with a lever on most foreign cars is a very expensive pleasure, since the price of one lever is not a small amount, and there are also cars that have complex multi-link suspensions (up to 5 on one side only). The cost of the work performed will also be quite high for the lower lever, and twice as much for the upper one. Therefore, the services of restorers who repair even those supports that are replaced in the assembly with a lever are in great demand.
Restoration is much cheaper than purchasing a new part. This is especially noticeable for supports that come complete with arms. Various technologies can be used to restore them.
- The easiest one is to convert the ball joint into a collapsible one, change the plastic inserts and polish the pin.
- A somewhat labor-intensive technology - the housing is filled with liquid polymer under pressure. Next, this polymer hardens in the gaps. The pressed supports into the levers are first removed and then replaced with non-original supports.
Remember that such savings may cause troubles on the road; to avoid this, it is recommended to use new components.