Types of faults in manual transmissions of cars
The internal structure of the mechanical gear shift mechanism has its own characteristics, and its malfunctions can be divided into both breakdowns of the box itself and malfunctions of the transmission mechanism.
In order to be able to restore the car’s operation if any type of malfunction occurs, you should detect them in time and know the basic techniques for eliminating them. This is especially important if the breakdown occurred on the highway, on the road - then it will be important to resume the operation of the car until a visit to a repair specialist.
Let us list the main manifestations of malfunctions.
How to detect a malfunction?
The most common manifestations of malfunctions in the operation of manual transmissions include the following:
- The occurrence of extraneous noise when the handle is positioned in neutral;
- Noises when turned on, as well as when starting work;
- Difficulty when changing gears;
- The gear is switched off without affecting the shift lever;
- There is oil leakage from the transmission.
Manual transmission: causes of major malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
Let's study in more detail the main types of malfunctions of both the box itself and the transmission mechanism, as well as providing an ambulance to the car in these cases.
Noise when the shift lever is in the neutral position of the gear selector. The reason for its appearance is most often due to increased wear of the bearings located in the drive shaft of the vehicle, as well as due to a critically low oil level in the gearbox itself. Also, the oil in the transmission may already be of too low a quality level.
This manifestation can be eliminated by checking the oil level and then replacing the worn bearing. If the transmission oil really hasn’t been changed for a long time, you should drain the old one, then replace it with a new one that will match the car. It is recommended to check old oil for the presence of metallic foreign particles and water, which is unacceptable.
If extraneous noise is heard when switching gears, then this may also be due to one of the reasons listed above, or deformation and increased wear of the locking element, as well as insufficient stability of the threaded connections, malfunction of the synchronizers and incomplete disengagement of the clutch.
Elimination of extraneous noise when gears are engaged:
- You should first check that the clutch is in full working order;
- If the synchronizers are faulty, measure the gap between the gears and the blocking ring located here, and also check the gears for damage;
Measuring the gap between gear and ring
When noise is heard during operation of the gearbox, the cause may be high wear of gears, synchronizer couplings, bearings, as well as insufficient oil level in the transmission.
Elimination of noise can occur when adding oil if its level is below critical. This can be detected by the presence of traces of oil leakage from the transmission, and as a preventive measure the oil in a car of any modification should be changed every 10,000 km. It is also necessary to check the condition of the couplings for worn synchronizers and, if necessary, replace them.
This is what a worn gear with synchronizer looks like
If gear shifting is difficult, the drive cable may be loose or damaged, the clutch may not be completely disengaged, or the gear shift rod may be damaged or severely worn.
For better gear shifting in a manual transmission, you should first check whether the clutch is completely disengaged, check the oil level and its quality (if it is unsuitable for further use, replace it with a new one), and also check whether the gears are jamming and carry out a thorough inspection for damage in the system gear shift levers.
Don't forget to check the oil level
The gear shift lever is difficult to change position; you have to make some effort to change gears. The reason here is primarily the insufficient oil level in the transmission, because it is largely responsible for the smoothness of all movements associated with the transmission.
To eliminate this malfunction, you should check the oil level in the transmission and, if necessary, add it to the specified level.
In the case when the gears switch spontaneously, it is possible that the strength of the threaded connection in the fastening of the box itself has decreased, the drive cable has become stuck, or the wear of the gears has increased excessively, the wear of the synchronizer couplings, as well as the splined connections, rod or gear shift fork has reached the limit.
Cable-actuated gear selector
To eliminate this malfunction, it is necessary to clean the distance between the engine housing and the clutch lever located here from dirt, carefully inspect the threaded connections of the transmission, tighten them if necessary, and also, if the synchronizers or splined connections are excessively worn, completely replace them.
When oil begins to leak in the gearbox mechanism, it is visible even to the naked eye. The cause of leakage may be insufficient connection of the transmission itself or worn out seals. If necessary, the oil seals must be replaced, and the threaded connections must be checked and tightened.
The recommendations listed above for troubleshooting both the gearbox itself and the transmission mechanism do not exclude, but rather oblige the owner to show his car to a specialist and carry out the necessary repair work in a workshop.
Malfunctions of any of the systems or individual components can occur in any machine. However, to prevent their occurrence, you should follow simple but quite effective rules regarding the operation of the car. Their simplicity does not mean ineffectiveness, because the rule that any disease is easier and faster to prevent than to treat later applies here.
Regarding the car, we can say that it is easier and also simpler to carry out a preventive inspection than to carry out expensive repairs later.
So, here are the basic tips for preventing major car malfunctions.
How to avoid problems?
It must be said that the causes of automatic transmission malfunction can be both objective in nature, caused by physical wear, and can be caused by improper operation of this unit. Many car owners neglect the need to regularly change transmission oil, which leads to problems with lubrication and constant overheating of the automatic transmission. As a result, the moving elements of the box quickly fail and require expensive repairs.
READ ALSO Which automatic transmission is the most reliable? How to properly warm up an automatic transmission in winter?
It is also necessary to properly warm up the transmission in the winter, which will eliminate problems with lubrication of the moving elements of the transmission. Low-quality oil damages solenoids, the replacement of which is difficult and expensive. It should also be remembered that automatic transmissions are extremely critical to aggressive driving style. When the engine operates for a long time at maximum speed, the clutches of the automatic transmission can quickly burn out and wear down. That is why it is not recommended to constantly practice an aggressive driving style in a car with an automatic transmission.
The difficulty of repairing automatic transmissions is due to the fact that the failure can only be determined by opening the transmission. To do this, it must be removed from the car, which will allow us to determine the nature of the breakdown. It is not possible for most ordinary motorists to carry out high-quality repairs of an automatic transmission on their own, so it is necessary to contact specialized service centers. Repair work consists of replacing damaged elements, which allows you to restore the functionality of the entire automatic transmission. It should be noted that due to the structural complexity, automatic transmission repair is labor-intensive and high-cost.
How to determine the condition of the automatic transmission yourself - Video
Car service technicians distinguish
3 levels of diagnostics:
1. Quick diagnostics - “Hear”
From the driver’s confused, hasty story, symptoms of a mild malfunction appeared like: “clean the oil from the sensor” or “check the cable that powers the ECU and solenoids” - this is, as a rule, a free diagnosis. But there may be a more serious problem, threatening major repairs and disassembly, but this is a different level...
Self-medication here can be a regular oil change in the automatic transmission or setting the optimal oil level. This happens with four-speed engines that have traveled about 200,000 km.
2. Tactile level - “Touch”
At this level, a routine circuit check may help. This is a matter of a few minutes. A more serious problem can be identified by removing the pan. This is all inexpensive automatic transmission diagnostics.
Also, without dismantling, specialists can make a diagnosis using: a table test, checking the pressure on the line, checking the serviceability of the electrical wiring and reading fault codes.
Self-medication here is the same as in the first case - topping up or completely changing the oil.
3. "Disassemble"
If the automatic emergency mode (permanent 3rd gear) or any other fault listed below is obvious, then disassembly is necessary for a more accurate diagnosis. This is typical for boxes that have traveled more than 200,000 km. This mileage is approaching the time to replace the gas turbine clutch.
Troubleshooting with 100% accuracy will only be achieved by “opening” the automatic transmission.
Tips for Keeping Your Manual Transmission Healthy
For both novice car owners and those with extensive driving experience, the rules listed below will help you avoid serious mechanical failures for as long as possible and be confident in the reliability of your car.
- Be careful with the box. This point is fundamental, since the safety of the transmission largely depends on the method of its operation. Smooth gear shifting, without jerking or tension - all this will make the operation of the box more uniform and the movement of the car calmer.
- Periodically check that there are no leaks of transmission oil and maintain its required level. The easiest way to do this is to regularly change the oil in the transmission. This rule is also important, since an oil leak that is invisible at first glance can cause serious damage and huge financial costs.
- If, nevertheless, transmission repair becomes necessary, it is recommended to use parts that have a quality guarantee and are suitable specifically for the make of your car. Both the quality of its operation and the duration of its operation depend on what components such an important element as the gearbox consists of.
By taking care of the condition of your car, you will always be happy to travel, without worrying about unexpected troubles and being confident in your safety and the safety of your loved ones.
Signs of manual transmission problems
Sometimes, it is important to understand why, when operating a car with a manual transmission, problems arise when shifting gears or unusual noises are heard from the manual transmission while driving. If you do not pay special attention to this, then over time the box may fail, and you will spend a lot of money on its repair. This article will discuss typical malfunctions of a manual transmission, which most often arise either due to improper operation or manufacturer defects.
Breakage of the clutch basket and wear of the pressure plate
To select gears in a manual transmission vehicle, the driver must disengage the engine and transmission using the clutch. When you press the pedal, a special bearing presses on the elastic petals of the clutch basket, resulting in mechanical separation of the engine and transmission. When the clutch disc is closed, torque is constantly transmitted to the input shaft of the gearbox - it spins idle in the gearbox housing. When the petals wear critically, they break off and do not allow the pressure disk to open. The pressure plate clutches also wear out and begin to slip over time, preventing all the torque from being transferred to the wheels of the car. The car stops driving normally, and the engine speed increases when driving at a relatively low speed. Do not forget that clutch parts during normal operation require periodic replacement on average every 100–160 thousand km.
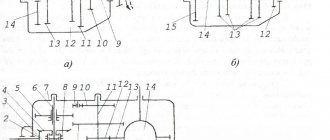
Design and principle of operation of a manual gearbox
- drive shaft
- bearing cap
- reverse light switch
- drive shaft cuff
- rear drive shaft bearing
- intermediate shaft drive gear
- breather
- 3rd gear gear
- front crankcase
- 1st gear gear
- reverse gear
- gear shift rods
- retainer ball
- spring
- shift lever
- protective seal
- lever cap
- shift lever housing
- rear housing
- driven shaft
- rear crankcase extension cuffs
- sleeve
- speedometer drive gear
- speedometer drive
- rear intermediate shaft bearing
- 5th gear
- reverse idler gear axle mounting bolts
- reverse idler gear
- intermediate shaft
- oil filler plug
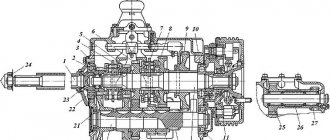
A manual transmission is designed to vary torque and transfer it from the engine to the wheels. It ensures separation of the engine and the drive wheels for an unlimited period. Before we deal with the malfunctions, let's briefly look at the gearbox design. A manual transmission is a type of gearbox, i.e. the torque in it varies in steps. A gear (or gear) is a pair of interacting gears. Each stage provides rotation at a certain angular speed or, in other words, has its own gear ratio.
And so, a manual transmission consists of a gear shift mechanism that interacts with the input, drive and intermediate shafts. Each shaft has gears with a different number of teeth. As the driver moves the gearshift lever, the gears move along the shafts and engage, depending on which gear has been selected. From this we can conclude that the gearbox consists of a gear shift mechanism and, in fact, a mechanism for driving the entire vehicle transmission. Therefore, we will consider separately the malfunctions of the speed switching mechanism and the drive.
Gear shift mechanism. Malfunctions
- loose fastening, jamming or damage to the drive cable (rod) - the gear shift lever dangles, the gears are difficult to engage or do not engage at all;
- wear or damage to the gear shift rod - it is impossible to switch the speed; wear or deformation of the locking device - after turning on the speed and starting to move, the lever moves to the neutral position;
- The gear shift fork is worn out - the speed does not turn on.
The occurrence of the above malfunctions directly affects both the operation of the entire manual transmission and the inclusion of speed.
The gearbox makes a sharp noise
Transmission problems can also be identified by a grinding sound.
Crush noise can come from chattering gears. A collision may occur due to clutch problems such as wear or needing adjustment.
Other potential sources could be a worn or damaged synchronizer, shift fork, or rail and bearing shafts.
If you only hear gear chatter when downshifting, the problem may be with the synchromesh (too much play at the end of the output shaft).
However, noise can also come from the clutch.
Shift lever problems can cause your transmission to fail.
Causes of malfunctions of the manual transmission gear shift mechanism
- violation of operating rules (using low-quality oil, operating a car with a faulty clutch);
- low quality of components;
- maximum service life of the gearbox;
- unskilled performance of maintenance and repair work on the transmission
Signs of a faulty transmission
- gearbox noise;
- Difficulty shifting gears;
- spontaneous switching off of gears;
- oil leakage.
And now in detail about the above mentioned gearbox malfunctions.
As a rule, the noise that occurs in the gearbox during engine operation has its own diagnostic character.
Signs of a gearbox malfunction
The main signs of automatic transmission damage include the following:
The appearance of shocks and vibrations when changing one gear to another. This is observed when switching to maximum and minimum gears. This kind of malfunction is steadily progressing. With a minor degree of damage, such shocks can hardly be noticed. But over time they intensify and the breakdown becomes critical. The cost of repairs in this case directly depends on the time of seeking help - the sooner, the cheaper.
Gearbox failure and transition to emergency mode. It is impossible to change speeds. Under such conditions, the vehicle is unable to start moving.
Leaking fluid used in the automatic transmission. The occurrence of this damage can be recognized by the characteristic accumulations of red liquid under the car.
Crunching or rustling noise from the gearbox, which can sometimes be replaced by a knocking sound.
When the car accelerates, the dependence of the dynamic factor on the speed of movement is lost. Such problems may indicate problems in the operation of the engine and other transport mechanisms.
The appearance of metal shavings on the pallet. This can only be detected when changing the oil, when the pan is removed.
Activating the warning light on the instrument console. A system malfunction can occur as a result of various reasons, in particular damage to the power unit or transmission.
Slipping of transmission gears in the gearbox in all modes before warming up. Once the required temperature is reached, the mechanism resumes normal operation.
Refusal to accelerate after the start of braking. When using first gear, acceleration is very slow before shifting to second. The change in speed per unit of time and movement after that proceed as normal.
Transition from one mode to another with delays. When vehicles are moving, gears are switched with a delay of 1-2 seconds.
When changing from one speed to another, the speed increases. The clutch block does not slip.
Reduced oil pressure to protect transmission parts from normal. At the same time, the desired indicator on the control panel lights up.
Engine operation without load with metallic noise.
Inability to start the engine with the key.
The lever intended for performing step shifts does not occupy the P position.
Driving in neutral and first gear is the same.
The occurrence of slipping on a long climb at maximum speed.
Loss of transmission fluid from the torque converter housing.
The first symptoms of a manual transmission failure
The first symptoms of a manual transmission failure
Quite often, due to ignorance, car enthusiasts do not distinguish between the signs of a manual transmission failure and a clutch failure. The manual transmission is less demanding to maintain than others. But even the most reliable devices are subject to wear and tear during operation - they make noise at idle and when driving, and also change gears poorly. Reasons that can cause manual transmission failure:
- violation of operating rules;
- low quality parts;
- maximum gearbox service life;
- incompetent repair and maintenance of the gearbox.
Symptom No. 1.
Noise in the transmission in neutral and howling sounds at speed.
Low transmission fluid level in the gearbox is the main reason.
If there is not enough oil in the gearbox, this will inevitably lead to poor lubrication of the rubbing pairs. The howling sound during movement provokes thermal expansion and friction of degreased surfaces. If the vehicle's mileage is more than one hundred kilometers, then slight noise when operating in neutral gear should not cause fear. In this case, it will be enough to change the oil in the manual transmission.
The reason is abrasion of gear teeth.
Replacing old parts completely eliminates howling sounds and other noise. Worn bearings on one of the shafts. Causes of abraded fragments, scuffing and intermittent production:
- oil hunger;
- excessive loads;
- increased torque due to strengthening of the internal combustion engine or natural shock absorption on the rolling elements and bearing races.
Development of differential components for front-wheel drive vehicles.
In such situations, it is quite common to experience jitter as the speed increases. Some VAZ models deserve a separate line, in which manual transmissions are noisy, and also make howling sounds and trembling at relatively low mileage. Experts suggest that this failure is associated with structural defects and poor quality of stamping of transmission elements; this guess makes the possibility of repair controversial.
Symptom No. 2.
Poor gear shifting with crunching sound
Signs of malfunctions in the operation of manual transmission synchronizers:
- complicated gear shifting;
- the sound of metal rubbing at the moment of switching. But before removing the gearbox for repair work, you should inspect the gear selection mechanism and clutch.
Reasons for difficult gear shifting:
- gap in the gear shift lever;
- unclear cable operation;
- incorrectly adjusted speed selection mechanism.
The cause of the crunching sound and grinding sound is insufficient release of the clutch after pressing the pedal. Movement with such a defect quickly leads to the breakdown of synchronizers. If a vehicle shifts into second or third gear with a crunching sound, then in 99% this is due to the synchronizers. The depreciation of the conical friction part causes the locking ring to slip, and the clutch's engagement with the gear teeth becomes rigid. When disassembling the gearbox, you should be careful when inspecting the gears, as well as the gear clutches and their forks.
Symptom No. 3.
There are teeth of a certain shape on the synchronizer blocking ring and gears; the clutch comes into contact with them when changing speeds. When grinding the coupling spline, teeth on the ring and gear during load, releasing the gas pedal, involuntary gear engagement will occur. Changing synchronizers alone will not work; you also need to change the broken transmission gear and gear shift clutch.
Causes of manual transmission breakdowns:
- shock absorption of the rod, gear shift fork;
- cable jamming;
- damping of the intermediate shaft bearing;
- wear of the manual transmission cushion;
- reducing the pressure of the bolts securing the gearbox housing.
Symptom No. 4.
Transmission fluid leak
- wear of the drive shaft oil seal;
- violation of the integrity of the boot of the internal constant velocity joint;
- leaky compression of the manual transmission pan, decreased fixation of the inspection hole bolt.
A small oil consumption can be caused by the oil seal of the speed selector rod having exhausted its service life. If oil leakage is noticed, it is necessary to inspect the transmission breather. If this element is clogged, then excessive pressure inside the gearbox housing will inevitably cause the seals to dislodge and oil leakage. At the bottom of many components there is a control hole to check the amount of transmission oil. The norm is that the oil level is equal to the control hole or approximately 10 mm lower. If the manual transmission makes noise due to insufficient oil volume, then the deficiency can be compensated through the breather. In case of limited access to the top cover of the box or the breather, you can use a special syringe and add the missing liquid through the control hole.
Tips for operating manual transmission
Long-term and high-quality operation of the transmission largely depends on the method of operation of the gearbox and clutch. Increasing the “life” of the checkpoint is quite simple - you need to follow basic tips:
- 1. Smooth gear shifting with the clutch pedal fully depressed. It is strictly forbidden to shift gears with the clutch engaged not all the way, as this is the main reason for rapid wear of the gears and increases the risk of their breakage.
- 2. Move to a gear corresponding to the current speed.
- 3. Reducing the speed of the vehicle when switching to a lower gear.
- 4. It is strictly forbidden to shift into reverse gear even at minimum forward speed.
- 5. If the first gear does not engage on the first try, then initially you need to depress the clutch, and then only engage the gear again.
Damage to manual transmissions can be varied. This device is a very complex design, but with timely detection and elimination of minor breakdowns, the transmission can last for quite a long time.
Transmission malfunctions, symptoms
The more components a transmission has, the higher the likelihood of it breaking. And in each of the components there are many faults.
Clutch
On all of these cars, the clutch has an almost identical design - it is single-plate, “dry”.
Without a clutch, it would be impossible to start moving smoothly during a trip and change the gear ratio at the gearbox, since this requires disconnecting the engine from the transmission.
Since the clutch is structurally the same, the faults on all of the listed cars are identical. The only difference is the types of drives.
Thus, the VAZ-2106, 2107, as well as the VAZ Niva, Niva Chevrolet, and UAZ Patriot use a hydraulic drive, while the VAZ-2109 uses a mechanical cable drive.
If we consider the clutch itself, its main faults are:
- Wear of the driven disk (friction linings, splines, dampers);
- Wear of the working surfaces of the flywheel and drive disk;
- Damage to dampers, diaphragm release spring;
- Wear of the release bearing and damage to its drive fork;
- Incorrect adjustment.
Signs of a clutch malfunction are quite clearly visible, and they manifest themselves in the form of “slipping,” “driving,” increased noise under certain operating conditions, and jerking when starting to move.
In most cases, to eliminate problems with the clutch, it is necessary to disassemble it, troubleshoot it, and replace damaged and worn elements.
As for the drive, there are not so many breakdowns in the VAZ-2109 and they usually come down to problems with the cable - its breaking or biting. Everything can be “cured” with the usual replacement.
But there are more faults in the hydraulic drive. In such a drive, depressurization of the system may occur, damage to the main and working cylinders.
Restoring functionality depends on the component in which the problem occurred. If the system leaks, it is eliminated by replacing the pipeline and then pumping it.
The cylinders are either repaired using repair kits, or simply replaced.
Transmission
The gearbox is one of the main components of the transmission, and it has the most complex design among all components. That's why it has more breakdowns.
The VAZ of the classic family (2106, 2107), Sputnik (VAZ-2109, 21099), Niva 21213 and Chevrolet Niva, as well as the UAZ Patriot, use three-shaft manual transmissions with constant mesh gears.
And although the gearboxes are structurally different (especially the VAZ-2109 compared to the others), the principle of operation is the same for all of them.
Therefore, the malfunctions of these transmission units on all of the listed cars are essentially identical, as well as their symptoms.
If there are problems at the checkpoint, this will definitely manifest itself, and in different ways. Signs of damage to the box are:
- Increased operating noise (in different modes). Often this problem occurs due to wear on the shaft bearings or synchronizer couplings. But such a malfunction can also appear due to damage to the locking device, loosening of the gearbox, low level of lubrication in the gearbox, malfunction of the clutch;
- Reduced clarity of gearbox shifting, difficult gear shifting. Such signs occur in case of severe wear of synchronizers or gears, damage to the switching slides, misadjustment or damage to the elements of the switching mechanism;
- Knocking out speed. This problem arises due to wear and damage to a number of components of the box (the same synchronizers, gears, shift mechanism, etc.);
- Oil leaks occur when the gearbox seals wear out and the fastening elements of the covers become loose;
- Crunching sound when changing gears. This result is produced by damaged or heavily worn gears and synchronizers, as well as severe backlash in the shafts;
As you can see, most of the malfunctions are associated with wear and tear on the component elements of the box.
But it is possible to accurately identify the cause only after dismantling the unit and disassembling it. It is possible to restore the functionality of the gearbox by replacing worn components.
There are also more specific breakdowns, although they are much less common. These include destruction of the housing, loosening of fasteners with subsequent getting between gears, etc.
Cardan shafts
The next element of the transmission is the driveshafts, which are used to transmit rotation to the VAZ-2106, 2107, as well as Niva 21213, Chevrolet Niva and UAZ Patriot.
But in the case of the first two cars, they have only one shaft in their design, but in SUVs there are two cardans (to transmit force to two drive axles); in Nivas there is also an intermediate shaft connecting the gearbox to the transfer case.
The components of these shafts are also damaged and worn out during operation, which leads to a number of malfunctions that manifest themselves in the form of:
- Knocks when accelerating. This indicates a malfunction of the joint cross or its bearings, as well as loosening of the shaft fasteners;
- Creaks (constant or periodic). Usually this result is caused by jamming in the hinge;
- Vibrations when moving. It appears as a result of strong backlash in the hinges, imbalance or bending of the shaft itself;
Problems with driveshafts are eliminated by checking the condition of their hinges and replacing them if critical wear is detected, and balancing. But often car enthusiasts simply change the shaft assembly.
Main bridge
Main gears with differentials in VAZ 2106, Niva, Niva Chevrolet, UAZ Patriot cars are an integral unit and are located in the drive axles (in passenger cars it is the rear axle, in SUVs it is both).
The task of these components of the transmission is to distribute rotation to the wheels.
Although this unit is relatively simple in design and consists of a small number of elements, it can still have faults.
Signs of problems in the operation of the drive axle are as follows:
- Increased noise from the bridge. An increase in noise can occur due to wear of bearings, deformation of the bridge beam or axle shafts, wear of spline joints, misadjustment of clearances and the appearance of backlash in the main gear and differential, jamming of satellites and axle shaft gears;
- Knocks when starting to move. It appears as a result of the appearance of increased gaps in the splined joints or the meshing of the main gear gears;
- Lubricant leak. Here the fault is due to the oil seals used in the bridge structure;
Troubleshooting the bridge is carried out by disassembling, troubleshooting, replacing worn and damaged elements, followed by adjusting the engagement gaps.
Read on the topic: causes of knocking when turning the steering wheel.
Drive shafts
As for the VAZ-2109, it does not have a drive axle, and rotation from the main gear (part of the gearbox design) is transmitted to the wheels through drive shafts with CV joints.
Note that such drive shafts are used on the front axle in Niva 21213 and Niva Chevrolet. Also, the CV joint on Nivas is installed on the intermediate shaft.
Regarding the UAZ Patriot, this SUV has a slightly different design of the front axle - axle shafts are present, but unlike the rear axle, CV joints are installed at their ends.
In such a drive, the “weak link” is precisely the constant velocity joint. This unit is very sensitive to dirt and damage to the boot always leads to gradual destruction of the element.
It is not difficult to identify problems with the joint, since if dirt gets inside it, a distinct crunch will be heard when you turn the steering wheel.
In this case, the CV joint cannot be restored and when a sign of wear appears, it is replaced.
Gear box
The gearbox is designed to change the traction forces on the drive wheels and vehicle speeds by increasing or decreasing the gear ratio.
Depending on the nature of the change in gear ratio, boxes are distinguished:
- stepped
- stepless
- combined
Based on the nature of the connection between the drive and driven shafts, gearboxes are divided into:
- Mechanical
- Hydraulic
- Electrical
- Combined
According to the control method:
- Automatic
- Semi-automatic
- Non-automatic
Gearboxes
- the most stable part of the car. Transmission failures are much less common than other parts of the car. The main factor in maintaining the gearbox in good condition is the good condition of the oil in the box.
All gearboxes are very similar in their performance. Front-wheel drive vehicles with cylindrical final drives located directly in the gearbox housing allow the same oil to be used in the vehicle's transmission as is used in the engine.
Gearboxes of rear-wheel drive cars are filled with special gear oil.
Manual transmissions are simpler in design, do not require special hydraulic fluids to operate the torque converter, and are less prone to failure.
Automatic transmissions benefit from ease of use; their repair is well mastered at service stations. An automatic transmission on a used foreign car is a necessary element of risk. Such a transmission imposes increased obligations on the driver to comply with operating rules.
Howling and humming
A worn-out manual transmission manifests itself with all sorts of extraneous sounds, which manifest themselves in the form of a characteristic howl, clicking or hum. These sounds come from collapsing bearings and heavily worn friction pairs. In this case, the nature of the sounds changes depending on the selected gear, engine speed and driving mode. It is dangerous to ignore such noises. They manifest themselves especially strongly when the oil level is insufficient or it is contaminated. Transmission noise can indirectly determine the mileage of a car. However, some gearboxes (for example, domestically developed ones) are noisy even from the factory due to weak design and extremely low workmanship.
Basic faults in the gearbox and their elimination
| Cause of failure | Elimination or prevention |
| Gearbox noise | |
| Wear of bearings, gear teeth and synchronizers or their breakdown | Replace worn parts |
| Insufficient oil level in the gearbox | Add oil. Check and, if necessary, eliminate the causes of oil leakage |
| Poor quality gearbox oil | Change oil |
| Axial movement of shafts | If necessary, replace the parts that retain the bearings or the bearings themselves. |
| Wear of the reverse spline shaft axis bushings | Replace spline shaft bushings |
| Difficulty shifting gears | |
| Incomplete clutch disengagement | Clutch check and repair |
| Ball joint surface jamming | Remove the lever and clean the mating surfaces of the spherical joint |
| Gear shift lever deformation | Remove the lever, eliminate deformation or replace the lever |
| Stiff movement of fork rods (burrs, contamination, jamming of locking blocks) | Disassemble, identify the cause, if necessary, repair or replace worn parts |
| Synchronizer malfunction | Replace worn parts or synchronizer assembly |
| The crankcase is filled with the wrong brand of oil | Drain the oil, flush the gearbox and fill with oil or substitute oil recommended by the manufacturer |
| Deformation of the switch drive forks | Straighten the forks, replace if necessary |
| Loosening or unscrewing the screws of the shift mechanism heads | Tighten and secure the screws |
| The holes for the pins in the neck of the shift mechanism are broken | Replace the shift mechanism cover or repair it by boring the holes and pressing in the stepped pins. |
| Spontaneous shutdown or unclear gear shifting | |
| Incorrect gear shift | With the clutch pedal depressed, move the shift lever all the way |
| Wear of the balls or loss of elasticity of the springs of the gear shift rod clamps | Remove the cover of the clamps and inspect the parts; replace if necessary |
| Worn or incorrectly positioned shift rod locking nuts | Disassemble and replace worn parts, ensuring correct assembly |
| Wear of synchronizer blocking rings | Replace worn synchronizer rings |
| Broken synchronizer springs | Replace springs |
| Worn synchronizer clutch or gear synchronizer teeth | Replace clutch or gears |
| Loosening the nuts securing the gearbox to the clutch housing or the nuts securing the extension to the transmission housing | Tighten the nuts |
| Worn shift control bearings or worn rubber parts in the gear shift levers | Replace worn parts |
Checking the technical condition of the transmission
So, it is important to understand that diagnostics of the gearbox and transmission as a whole should be performed regularly. Moreover, even if the owner does not notice any signs of malfunction, it is necessary to check the technical condition of the transmission. The fact is that professional diagnostics allows you to promptly identify possible problems at an early stage, which significantly reduces the cost of repairing units and components, and also increases comfort and safety.
Transmission diagnostics is a comprehensive approach. A series of checks are aimed at diagnosing most of the main components, without disassembly. As a result, it is possible to fairly accurately assess the condition and performance of individual elements.
As part of diagnostics, specialists practice both visual inspection and checks using mechanical tools, and use scanners, as well as special high-precision diagnostic equipment. The use of such equipment makes it possible to detect hidden defects, read errors from electronic control units of automatic transmissions, etc.
In general terms, transmission diagnostics are carried out taking into account the strict order of work. First of all, the specialist listens to all the comments of the car owner. Next, regardless of whether there are complaints or not, the following actions are performed:
- the engine starts, the quality of its operation at idle is assessed, electrical connections, rods and throttle cables are inspected, vacuum lines are checked;
- the condition and level of technical fluids and lubricants are checked, then a visual inspection is performed of possible leakage points of engine and transmission oil (oil seals, gaskets, seals, etc.);
- diagnostics of the engine ECU and gearbox ECU (if equipped) is carried out, after which the final stage is a test drive in the car with several stops to evaluate the operation of all components and assemblies in motion and under load;
If the owner separately points out signs of breakdown, this becomes a reason for conducting in-depth diagnostics. As a rule, at the initial stage, the specialist immediately makes a test drive with the owner, who points out the malfunction (if it appears). It is more difficult to detect so-called “floating” problems, when failures, noises, knocks, vibrations and other signs do not appear constantly.
- If we talk about manual transmission diagnostics, in this case it is necessary to check the oil level in the gearbox,, if necessary, make adjustments to the rocker, assess the condition of the cables, etc. Special attention is also paid to the clutch, the clutch pedal travel is checked, etc. The technician also inspects CV joints, drives, axles, cardan shafts and other elements (depending on the type of drive and design features of the vehicle).
- In the case of automatic transmissions, automatic transmission diagnostics are complicated by the fact that such transmissions are often a complex combination of mechanics, hydraulics and electronics. This means that in addition to mechanical elements (by analogy with a manual transmission), attention must be paid to electronic and hydraulic components.
First of all, the ATF oil level in the gearbox is checked, then its condition is assessed. You may also need to measure the oil pressure in the automatic transmission. The fact is that deviations in the ATF level from the norm or contamination of the automatic transmission fluid can be the reason why characteristic signs of a large number of malfunctions appear (starting from the valve body and ending with the gas turbine engine). At the same time, adding oil or replacing it along with automatic transmission filters in some cases allows you to completely normalize the operation of the unit.
When diagnosing automatic transmissions, a specialist must make a test drive. As part of the test drive, it is necessary to use all available automatic modes, the quality of up and down shifts, etc. is assessed separately.
The operation of the gearbox is also checked when the car is stopped (engine speed at idle is taken into account when switching from D to R). The presence of shocks, vibrations and shocks when switching the automatic transmission is also excluded or confirmed. The data obtained allows us to evaluate the quality of the torque converter, indicate the condition of the freewheels, etc.