What does P0420 mean?
The P0420 code indicates that there is a problem with the catalytic converter. The catalytic converter is designed to break down harmful pollutants produced during the combustion cycle of a gasoline engine. By using fine platinum and gold meshes to filter exhaust gases, the catalytic converter is able to reduce emissions of harmful substances from the exhaust gases.
The catalytic converter has two oxygen sensors. One of them is located in front of the catalytic converter (at the exhaust gas inlet), and the second behind it (at the exhaust gas outlet).
If the exhaust gas inlet oxygen sensor is working properly, its readings will fluctuate depending on engine temperature and load. If the oxygen sensor installed at the exhaust gas outlet is working properly and there are no problems with the catalytic converter, its readings should be stable (without sudden fluctuations).
If the readings from both oxygen sensors are the same, this indicates that the catalytic converter is not working properly. If the downstream oxygen sensor voltage drops and fluctuates, as with the upstream exhaust oxygen sensor, the oxygen level is too high. In this case, the P0420 error will be stored in the automatic transmission control module (PCM) and the Check Engine light will light up on the vehicle's dashboard.
Under what conditions is error P0420 diagnosed?
In order for the electronic control unit to diagnose error P0420 during the system check, it must analyze information from the oxygen sensors. Over a certain period of time, information from the first and second oxygen sensors is analyzed. If, as a result of the test, it turns out that the duration of the voltage signal is not within the thresholds specified in the ECU, this is a clear sign that there are problems with the catalyst.
Please note: In order for the Check Engine light to come on, the threshold value of the difference between the amplitudes of the first and second sensors must be more than 0.7 per minute. Moreover, it should last longer than 100 seconds with a significant load on the engine (rpm from 1700). Another important characteristic for the occurrence of error P0420 is the temperature of the catalyst. It should be above 500 degrees Celsius (may vary depending on the ECU firmware).
It is worth noting that two oxygen sensors are installed on all cars of Euro 3 standard and higher. They are necessary to diagnose problems with the release of hydrocarbons into the environment above specified standards. During engine operation, the electronic control unit constantly receives information from the first and second oxygen sensors, and, based on the information received, determines the correct operation of the exhaust system and the catalyst in particular. When the exhaust system is operating properly, the oxygen sensor output signal switches gradually between two states: rich and lean. If switching occurs more often than necessary, this indicates a problem in the catalytic converter system.
Causes of error P0420
- Damage or leakage of the muffler.
- Damage or leakage of the exhaust manifold.
- Damage or leakage of the exhaust pipe.
- Misfires in engine cylinders.
- Catalyst oil contamination.
- Malfunctioning catalytic converter (most common cause).
- Engine coolant temperature sensor malfunction.
- Malfunction of the oxygen sensor installed at the exhaust gas inlet.
- Malfunction of the oxygen sensor installed at the exhaust gas outlet.
- Damage to the oxygen sensor wires.
- Poor oxygen sensor connection.
- Damage to oxygen sensor connectors
- Fuel leakage through the injector.
- High fuel pressure.
- Using the wrong type of fuel (using leaded fuel instead of unleaded fuel)
How to check the catalyst
Before making a final diagnosis, you need to know how to check the catalyst. To assess performance, you need to compare the output voltage between the upper and lower O2 sensor. To do this, you also need to view the fuel adjustment data.
Lambda probe design
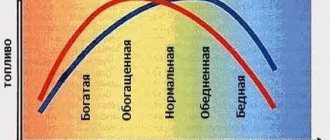
The voltage at the output of the sensors is read by the on-board computer and changes depending on how rich the air-fuel mixture is. Under normal conditions, if the mixture is rich, the voltage is about 900 mV. A voltage of 100 mV indicates that the mixture is lean. Fluctuations within these limits are quite normal.
The fuel supply adjustment ideally tends to “0”; a deviation of 10% is acceptable if the power unit has a good mileage. If the adjustment is over 25%, then this is abnormal and indicates that there are problems in mixture formation. It is worth paying attention to the presence of other errors.
Failed lambda probe and plug
What are the symptoms of a P0420 code?
The main symptoms of error P0420 are:
- Check Engine light comes on . The mechanic must read the stored error code using a diagnostic tool and determine the cause of the problem.
- Loss of power after the car warms up. The engine may run rough and may not provide enough power to accelerate the vehicle. .
- The car may not accelerate beyond 60-90 km. at one o'clock. Problems may occur when driving on highways and freeways with higher speed limits, although when driving at lower speeds in residential areas, drivers may not notice any symptoms at all .
- Unpleasant smell from the exhaust pipe. This smell occurs due to the incorrect amount of oxygen in the catalytic converter, which leads to excess sulfur in the fuel tank. .
How the car behaves (signs of error p0420)
Depending on which of the two variants of a catalyst malfunction occurs (clogged or destruction has begun), the car will exhibit their characteristic symptoms. In addition to the fact that the check engine light will light up on the instrument panel, and in some cars the catalyst overheating lamp will light up, the exhaust gases will no longer meet EURO 3-5 standards. In general, the signs that will trigger the P0420 (P0430) error may be:
Location of catalyst and oxygen sensors
- increased fuel consumption;
- decreased engine dynamics;
- changes in the smell of exhaust gases (became very unpleasant);
- rattling noise from the catalytic converter (if it crumbles);
- sometimes unstable idle;
- It may be difficult to start the engine. So, if you observe more than two of these signs at the same time, most likely the car has problems with the catalyst, and you cannot do without diagnostics to accurately find out the fault code!
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0420 code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all error codes stored in the vehicle's PCM using an OBD-II scanner.
- Check the operation of the oxygen sensor installed behind the catalytic converter (at the exhaust gas outlet). The voltage readings of this sensor should be stable.
- Will diagnose other error codes that may have caused the P0420 code to appear.
- Eliminates problems associated with misfires in engine cylinders and the fuel system.
- Check the oxygen sensor located behind the catalytic converter (at the exhaust outlet) for wear and damage.
- Will test drive the vehicle to check the operation of the oxygen sensor installed behind the catalytic converter (at the exhaust gas outlet).
- Will replace a faulty catalytic converter and update the PCM software.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0420
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0420 code is hastily replacing oxygen sensors. If another component is causing the P0420 code, replacing the oxygen sensors will not solve the problem.
What does the error mean?
The common name for the error is Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold.
In translation, we are talking about a decrease in the efficiency level of the catalytic converter system.
The error in question indicates that the performance level of the catalyst is below the maximum permissible level.
That is, here we have to talk about problems with the catalytic converter and the components associated with it. It is a mistake to believe that the problem here lies only in the breakdown of the catalyst itself. But regardless of the reasons, the latter fails to cope with its tasks. The catalyst does not have time to process and neutralize all exhaust gases passing through it.
There are several main reasons why the P0420 error appears when scanning the control unit memory. The transcript itself gives only a rough idea of the current situation. It is necessary to find out why the catalyst does not cope with its functions, by what signs this can be detected and under what conditions the error will be recorded in the ECU memory.
When 2 catalysts are installed on a car at the same time, a similar error will appear in the form of code P0430.
This is not of fundamental importance, since the symptoms and causes will still be identical. But it’s worth remembering the likelihood of having 2 codes.
How serious is the P0420 code?
Error P0420 is considered not very serious, since when it appears it is unlikely to cause serious problems with the vehicle's handling. Other than the check engine light coming on, drivers will likely not notice any obvious signs of this error occurring. However, if the problem is left unaddressed for a long time, it can cause serious damage to other components of the car.
If the cause of this error is not corrected promptly, it may also cause serious damage to the catalytic converter. If this code is detected, it is recommended that you contact a qualified technician as soon as possible to diagnose and resolve the error.
Symptoms of malfunction
The main driver symptom of P0420 is the MIL (malfunction indicator light) illumination. It is also called Check engine or simply “check light”.
- The “Check engine” warning light on the control panel will light up (the code will be stored in memory as a malfunction).
- Other related trouble codes may also be present.
- The engine stalls or has trouble starting.
- Floating speed, as well as attempts to stall at idle.
- Reduced engine power.
- Poor speed gain.
- Increased fuel consumption.
- Sometimes there may be no symptoms despite a stored DTC.
This error is considered moderate if there are no symptoms. But if there are symptoms, then it is necessary to eliminate the cause of error P0420 as quickly as possible. Failure to do so may result in severe damage to the catalytic converter.
What repairs can fix the P0420 code?
- Muffler repair or replacement.
- Exhaust manifold repair or replacement
- Exhaust pipe repair or replacement
- Replacing the catalytic converter (the most common way to resolve the error)
- Replacing the engine coolant temperature sensor
- Replacing oxygen sensors
- Repair or replacement of damaged oxygen sensor wires
- Repair or replacement of oxygen sensor connectors
- Fuel injector repair or replacement
- Troubleshooting problems related to misfires in engine cylinders.
- Diagnosing other error codes stored in the automatic transmission control module (PCM) memory
Additional comments for troubleshooting P0420
If problems with the ignition system, fuel system, air supply system, or engine misfire are left unaddressed for long periods of time, serious damage to the catalytic converter can occur. When replacing the catalyst and oxygen sensors, it is recommended to replace them with original high-quality spare parts.
It should be noted that replacement oxygen sensors very often fail, causing the P0420 code to reoccur. It is also recommended that you contact your vehicle's authorized dealer to determine whether the exhaust system components are covered under warranty.
Technical description and interpretation of error P0420
This diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is a generic transmission code. The P0420 code is considered a common code because it applies to all makes and models of vehicles. Although the specific repair steps may vary slightly depending on the model.
The catalytic converter is part of the exhaust system that looks like a muffler. But its operation is very different from that of a muffler. The catalytic converter works by reducing exhaust emissions.
An oxygen sensor is installed on the front and rear of the converter. When the vehicle is warming up and operating in closed loop mode. The readings of the O₂ oxygen sensor in front of it should fluctuate. The readings from the O₂ oxygen sensor located behind it should be fairly stable.
Typically the P0420 code will set and the Check Engine Light will come on if the readings from the two sensors are identical. O₂ oxygen sensors are also called lambda probes. The error also indicates that the catalyst is not working as efficiently as it should (per specifications).
Catalytic converters are usually not a "wear-resistant" type of product, meaning they need to be replaced periodically. If they fail, then you need to look for a specific reason that caused their failure.
Many nuances can lead to failure of O₂ sensors or catalysts. Before replacing parts, you must ensure that all problems have been corrected. Otherwise they may appear again.
Check with the OBD-2 scanner for other errors and correct them, as they may be the cause of the P0420 fault. Make sure your car doesn't burn oil or have other problems.
Blue smoke means oil is entering the combustion chamber. White, is water or antifreeze. Gray or black means a rich mixture.
Causes of damage to the catalytic converter
There are several causes of catalytic converter damage that can trigger the P0420 code. Here are the most common ones.
- Misfires.
- Oil consumption.
- Leaks at the outlet.
- Inlet leaks.
- Rich mixture.
- Poor mixture.
- Malfunction of the ECM/PCM control unit.
There are many reasons that lead to malfunctioning oxygen sensors or catalytic converters. You should make sure to correct these problems before you replace any part. Otherwise, they may be damaged again. Check the controller DTC memory for any other trouble codes.
Fix them first. Make sure your car is not burning oil by checking the exhaust smoke, blue smoke = oil, white = water, gray/black = rich mixture.
Known Causes of P0420 by Vehicle Model
Some vehicles are more familiar with the P0420 code than others. Here is a list of the most common reasons for each brand. These vehicles are known to have problems with the P0420 code. Please remember that these are general guidelines only and you must make a proper diagnosis before changing any parts.
Toyota Corolla
The most common cause of the P0420 code on the Toyota Corolla is a faulty catalytic converter. But, this can often be caused by oil passing through the piston rings getting stuck in the catalytic converter.
First check for leaks at the inlet and outlet. Then check to see if there is gray blue smoke coming from the exhaust pipe. If you see it, then this is a reason to contact a car service to find where the oil comes from. The usual cause may be crankcase ventilation.
If you don't see blue smoke at any engine speed, your catalytic converter is likely worn out.
Ford Focus
Ford Focus usually has an air leak. It could also be any broken solenoid that is causing the fuel/air mixture to be incorrect, activating the fault.
Check the controller memory using a diagnostic scanner to read errors related to the air-fuel mixture. If everything looks normal, check for exhaust leaks.
Replace the catalytic converter if you cannot find any trouble codes or other problems with the mixture.
Subaru / Subaru Forester
Subaru usually has the same problem as Toyota Corolla. Check for air leaks or other fuel mixture related trouble codes.
Check for exhaust leaks in front of the catalytic converter. The most common problem with Subaru engines is the catalyst itself.
Volkswagen (VW) / Skoda / Seat / Audi A4 1.8 T / V6 2.4
These VAG vehicles have some known faults that cause code P0420. Check the operation of the inlet check valves. Make sure the crankcase vent is not clogged, causing the engine to burn oil that clogs the catalytic converter.
Check for exhaust leaks around any bends in the exhaust pipe (common cause). Check for any O2 sensor trouble codes.
If no problems are found, replace the converter. This is a very common problem on both 1.8 T and V6 petrol engines. The 1.8 T catalytic converter can be quite difficult to replace if you are not experienced with it.
The V6 has two catalytic converters, so make sure you troubleshoot and replace the correct side of the catalytic converter.