What does P0301 mean?
P0301 (and other P030X codes such as P0302, P0303, etc.) are simpler than you might expect. Because the ECU has already determined which cylinder has the problem, saving you the diagnostic headache.
The last digit of the P030X code indicates the number of the misfired cylinder. P0302 is a misfire on cylinder 2, P0303 is on cylinder 3, and so on.
The P0300 code indicates a random misfire. This means that several cylinders are misfiring randomly. Codes P0300 through P0308 are called misfire codes.
If you have one of these errors, you need to fix the problem as quickly as possible. If you drive your vehicle in this condition, you will damage the catalytic converter.
How does a mechanic diagnose a P0301 code?
When diagnosing this error code, a mechanic will do the following:
- Reads all data and error codes stored in the PCM memory using an OBD-II scanner
- Clear error codes from the PCM memory and test drive the vehicle to see if P0301 appears again
- Check the cylinder 1 spark plug wire for wear and damage.
- Check the cylinder 1 spark plug for wear and damage.
- Check the ignition coil for wear and damage
- Check the ignition coil wire for wear and damage.
- If necessary, replace spark plugs, ignition coils, and related wires
- If P0301 appears again after replacing the above components, check the fuel injector and related wires for damage.
- Check the ignition distributor cap and slider (if equipped) for corrosion and damage
- If there are other error codes stored in PCM memory along with P0301, it will clear all present errors.
- Test drive the vehicle to see if P0301 appears again
- If P0301 appears again, check compression in cylinder 1
- If P0301 persists, the problem may be a faulty PCM. In this case, the module may need to be replaced or reprogrammed.
Common errors when diagnosing code P0301
The most common mistake when diagnosing a P0301 code is to replace the spark plugs, ignition coils, and related wires when the problem is damaged fuel injector wires.
Another mistake is to rule out the possibility of failure of the fuel injector itself, the cylinder or the PCM.
Also, mechanics often don't look at other error codes that appear along with the P0301 code. If you do not resolve all present errors, this may cause the P0301 code to appear again.
Is it possible to drive a car with a permit?
Driving with a misfire can damage the catalytic converter, which is an expensive component of a vehicle's emissions control system.
When one of the engine's cylinders fails, unburned gasoline entering the exhaust can overheat and melt the catalytic converter.
Some manufacturers advise against driving with misfires. Others recommend driving only in a very moderate manner and getting your car checked as soon as possible. See your vehicle's owner's manual.
Algorithm for checking elements to eliminate error P0300
Since there are many possible causes for error P0300, it is necessary to adhere to a certain troubleshooting algorithm. Here is a sequence of actions to quickly detect the cause of misfires:
- Diagnostics should begin by checking the high-voltage wires. To do this, you will need to get a multimeter, set it to measure resistance (Ohm) and measure the values of the wires. If the insulation of high-voltage wires is not broken, as a result of the test the resistance will be about 4-10 kOhm;
- Next, the ignition coils (or module) are checked. To test the module, a special diagnostic stand or multimeter is used. To check the ignition coil, it is enough to move it to a 100% working cylinder, let the engine run for a while and read the errors again with the scanner. If the error code has not changed (for example, it was P0302 and remains P0302), then the problem is not in the coil;
If the problem cannot be identified, the next step is to check the spark plugs. Twist them and inspect for oil deposits or damage to the electrode. Also make sure that the spark plug has the correct gap;- The next step in finding the cause of the P0300 code is to check the cylinder compression. If the compression is too low or completely absent, it will lead to difficulties in igniting the air-fuel mixture due to low compression;
- Another common cause of the P0300 code is a clogged injector. However, if you are troubleshooting in a garage, then problems will arise with checking the injectors, since this requires a diagnostic stand. Alternatively, you can try filling your car with fuel with a higher octane number and driving it for several kilometers at high speeds;
- When troubleshooting, be sure to check the fuel filter, or better yet, replace it. A clogged fuel filter or low-quality fuel leads to problems with injectors;
- Inspect the intake manifold gasket. If it is very worn, it will need to be replaced;
- Another possible cause of P0300 is a stuck exhaust gas recirculation valve. When diagnosing a vehicle, check the long-term fuel trim value for a specific cylinder. It should differ from the ideal value (which can be found from the literature on maintenance of a specific car model) by no more than 1-3% in any direction. If the deviation is 7% or more, then there is additional air intake.
The above are the basic steps that most often help to find the cause of the P0300 error code. When checking the above elements, pay attention to their condition - the presence of soot, traces of mechanical damage, and so on.
Other possible causes of the P0300 error must be determined depending on what other errors the scanner indicates during diagnosis. That is, if the oxygen sensor fails, then in addition to P0300, error P0134 or P0130 may occur. Try eliminating other errors that are diagnosed together with P0300, perhaps this will immediately eliminate it too.
( 414 votes, average: 4.49 out of 5)
Error P0135 – oxygen sensor heating power supply circuit open
Trouble P0012 - Excessive Camshaft Retard
Related Posts
What Can Cause Codes P0301–P0308
The most common cause of engine misfire and P030X codes in modern vehicles is a faulty ignition coil.
Other reasons include:
- The ignition coil wiring is damaged.
- Worn, cracked or dirty spark plugs.
- Cracked or shorted ignition wires.
- Carbon buildup on valves and injectors (usually in direct injection engines).
- Air leak. A vacuum leak will cause a misfire in the cylinder closest to the source of the leak. Examples of vacuum leaks include: a leaking intake manifold gasket, a broken PCV valve or hose, or open or cracked vacuum lines.
- Fuel injector malfunction.
- Leaking cylinder head gasket.
- Low compression in a damaged cylinder.
- ECU failure.
- Valves not adjusted.
Causes of Random Misfire (Code P0300)
- Malfunction of the mass air flow sensor (MAF).
- Inlet pipe rupture.
- The EGR valve or purge valve (solenoid) is stuck.
- Valve mechanism parts are worn out.
- Low fuel pressure.
- Incorrect valve timing adjustment.
- The catalytic converter is clogged.
- Problems with the crankshaft position sensor (CPS) or camshaft position sensor (CPS).
Often the P0300 random misfire code will appear along with other codes such as P0171, P0101, P0102, P0420 and P0401. In this case, the accompanying DTC must be diagnosed first.
Causes of multiple misfires
- There is no spark or the strength of the spark discharge is insufficient to ignite the fuel injection pump. The cause of interruptions in the operation of the ignition system may be spark plugs, high-voltage wires, a coil, or an ignition module.
- Loss of engine compression. Burnout of valves, breakdown of the cylinder head gasket are the most likely causes. Even wear of hydraulic compensators, incorrect valve clearance, or failure of timing marks can lead to a similar problem.
- Malfunction of the injector or its control circuit. If the injector hangs open, the control wire has a short to ground, and the fuel injection pump will be over-enriched. The fuel mixture will not burn due to either excessive leanness or an over-rich mixture. Therefore, if there are multiple misfires, the fuel pump should not be excluded from the list of causes.
- Suction of unaccounted air. For example, in the place of the gasket between the intake manifold and the cylinder head. In an unheated state, the gap at the depressurization site increases, so more unaccounted air enters the cylinders. Misfires occur due to excessive leanness of the mixture. Among the list of reasons, one should not exclude leaking injector O-rings and cracked vacuum system hoses.
Signs of misfire: the engine throttles, power decreases, fuel consumption increases. Uneven operation is clearly noticeable on 3, 4, 5-cylinder engines, but on V-shaped 6 and 8-cylinder internal combustion engines, it is more difficult to notice the shutdown of one of the cylinders.
Error codes
Self-diagnosis of a modern injection system is capable of recording misfires and determining which cylinder is the cause of uneven engine operation. Therefore, we recommend starting with diagnosing the current fault codes. When searching for the cause of a breakdown, it is important to understand in which particular engine operating mode the misfire error occurs.
Without ignition, there is no power stroke in the cylinder, which affects the crankshaft rotation speed. The engine ECU receives information from the crankshaft position sensor, so based on the moment of deceleration, the CV can calculate which cylinder is misfiring.
- P0300 – multiple misfires. This means that burning problems are not limited to just one cylinder;
- P03001, P03002, P03003, P03004, P0300n... - misfires in a specific cylinder. Where N is the serial number of the combustion chamber in which the malfunction occurs.
You can determine error codes by connecting to the OBD II connector using a simple diagnostic tool like ELM 327. It is important that the software version allows you to connect to the engine control unit on your car model.
How to identify a cylinder
If the engine is misfiring, but you do not know which cylinder is causing the problem, with the engine running, remove the high-voltage wires one by one or disconnect the connectors of the ignition modules and fuel injectors. The shutdown of the working cylinders will be noticeable by a drop in speed. The problems will be in that “pot” that does not react in any way to disconnecting the GDP/connector. We have identified the inoperative cylinder, so we move on to finding the cause of the misfire.
Ignition system diagnostics
We will not consider diagnostics of the secondary ignition circuit, which requires an oscilloscope and basic skills in working with sensor signals. Let's look at the basic verification methods that you can do yourself.
Remove the spark plug. Measure the air gap, assess the condition of the electrodes, insulator and the amount of carbon deposits. We described the diagnostic process in more detail in the article “Symptoms of faulty spark plugs.”
If the spark plug is wet and there is a strong smell of gasoline, it means that fuel is being supplied to the cylinder and the power system should be the last thing to complain about.
The best way to independently determine the cause of a misfire in a cylinder is to first swap the spark plugs, then the GDP and ignition modules. Before starting after changing elements, erase all error codes. You can determine a non-working “boiler” by reading current errors or using the method described above.
Causes of misfires
Ignition coils
Bad ignition coils are a common problem on many vehicles, including BMW, Ford, Hyundai, Mazda, Nissan, Volkswagen and GM. A faulty ignition coil needs to be replaced.
Candles
If the spark plugs have not been changed for more than 15 thousand km, replacing them would be a good idea. Worn spark plugs require higher voltage to produce a spark, which puts more stress on the ignition coils.
Some car manufacturers update ignition coils during vehicle production. If one of the ignition coils has failed and the manufacturer has updated the part, then the auto mechanic may recommend replacing all ignition coils with updated ones as a precaution.
Carbon on valves
In many modern vehicles, especially those with direct fuel injection, carbon buildup on the intake valves and injectors can cause misfire.
Some mechanics may recommend cleaning the valves with a special spray or foam, as this is cheaper and sometimes helps. A more effective option is to clean the intake valves manually.
Watch the video on how to clean the valves:
Clogged fuel injectors also need to be cleaned or replaced. This repair is expensive because it requires more labor. It is necessary to remove the intake manifold and some other parts.
Air leak
Vacuum leaks, as well as a stuck EGR valve or purge valve, can cause misfires that mostly occur at idle but go away at higher rpms.
Read more here: How to find air leaks at home?
Adjustment of valves
In some older Honda vehicles, misfire can be caused by improperly adjusted valves. The misfire may be more noticeable when the engine is idling after a cold start.
As valve system parts wear, valve clearances change. To compensate for this, the valves in many Honda engines must be adjusted at recommended intervals.
Timing belt
Sometimes an engine may misfire if the timing belt or chain were not correctly aligned when replacing the timing belt. If the problem occurs after replacing the timing belt or chain, the first step is to check the timing marks.
Oil leak
In many high mileage vehicles, oil leaking into the combustion chamber due to worn valve seals and oil rings can foul the spark plugs and cause a misfire.
Often, misfires appear at idle, but disappear after increasing the speed. Blue smoke is another symptom of oil leakage into the combustion chambers.
Water
In many older vehicles, cleaning the engine compartment or driving through deep puddles can cause the engine to misfire as water gets into the ignition parts and causes short circuits.
Replacing the spark plugs and ignition wires often solves the problem. Ignition coils that have cracks or signs of sparking should also be replaced. In older vehicles with an ignition distributor (distributor), the distributor cap and rotor are also replaced.
Misfires: why they happen, how to diagnose, and how to fix
What it is?
Let's briefly recall what the symptoms of misfire may be and what can cause them.
The key point in engine operation is the flash in the combustion chamber of the cylinder. Since today our test car was a Cadillac Escalade with a gasoline engine, we will talk about gasoline engines. On cars with a four-cylinder engine, misfires manifest themselves in what is most often called “triple”: the engine begins to shake, vibration appears, and often it even stalls at idle. That is, at this moment it runs on only three cylinders (if we are talking about multiple misfires). The Escalade has a V8 under the hood, so the word “triple” in relation to it would be downright an insult, and saying “seven” is somehow not accepted. But the symptoms are the same: periodic failure of one cylinder and the associated loss of traction, shaking, and a flashing Check Engine light. At idle, of course, the car does not stall: the remaining seven cylinders are quite capable of turning the crankshaft.
Why does this happen?
There can be many reasons for missing. A classic of the genre in the ignition system is a breakdown of high-voltage wires, an ignition coil (or coils), or failure of a spark plug. In the power supply system, the fuel injector may be to blame (we are, of course, talking about an injection engine; a carburetor is no longer fashionable). And finally, the last reason is mechanical faults in the motor. Since ignition of the fuel-air mixture in a cylinder requires not only the mixture itself and a spark at the right moment, but also compression, all malfunctions leading to the loss of the latter will lead to misfire in a particular cylinder.
And there are many such malfunctions: critical wear or breakage of the piston ring, burnout of the valve, its freezing, loose fit of the valve plate due to the formation of a large amount of carbon deposits or malfunction or wear of the hydraulic compensator, pusher, camshaft cam or valve spring...
In a word, the field for diagnostics is vast - walk around it as much as you like.
There is, of course, an old, proven way to find such a malfunction: garage, beer, roach, alternately replacing wires, coils and spark plugs. It didn’t help - advice from friends, dancing with a tambourine, reading forums (this is when it’s already really hard).
You can, of course, do the same with Escalade, but, for example, the cost of one coil is seven thousand. The wires are also not cheap, and iridium spark plugs for eight cylinders are much more expensive than the Brisk kit for a “cheap”. And access to the fifth and sixth cylinders is difficult, and the seventh and eighth are generally for octopuses with tentacles. Therefore, it is better to go in a more civilized way - conduct computer diagnostics, find out which cylinder has the problem, and try to better learn about its causes. Just? If!
Microscope on a nail
Articles / Practice Dealerships, multi-brand brands, clones: what is the difference between different diagnostic scanners Quite recently, we talked about how computer diagnostics work, but did not say a word about how it is carried out. Therefore, today we will talk about them – scanners. And we don’t… 15292 9 0 01/23/2017
Everything would be completely boring if the malfunction always appeared. But here the situation is more interesting: the problem appears only under load and at speeds above 120 km/h. There are no skips at idle or in city mode. You can, of course, connect a scanner, go out of town (in our case, onto the St. Petersburg roundabout), break the rules and get the necessary information.
The inconveniences are obvious: driving at a speed of 120 km/h in winter, and even with a scanner connected, at the risk of getting a fine, is below average pleasure. Moreover, it may take a long time to drive: there is nothing more exciting and unpredictable in life than searching for a floating fault.
Therefore, we will choose another method, refined and intelligent, like Brodsky’s poetry: we will drive the car onto a dynamometer stand. We have a drum brake, with an inertial mass of 1.7 tons. It’s also all-wheel drive, so it’s easy to recreate driving under load at high speed. At the same time, we learn that the stand is needed not only for measuring power, but also as an effective diagnostic tool.
True, first the car must be changed to summer tires: you cannot drive into the stand on studs. Let's leave this work to the professionals, because I am not allowed to lift anything heavier than a pen, a notepad and a camera according to my job description, and 22-inch wheels are not an easy thing.
Stand, OBD II, first surprises
Before entering the stand, we fix the drums. For this purpose, there is a pneumatic braking system, just like on many trucks. As soon as our enemy luxury bus with its 409 American horses is on the stand, we fix it with slings to prevent it from escaping from the stand into the wall. Then we connect the scanner through the OBD II connector, accelerate the car, simulating road conditions, and begin diagnostics. The first results are 346 misfires in the sixth cylinder and two in the second. And, of course, the accompanying error p0300 is multiple misfires.
1 / 4
2 / 4
3 / 4
4 / 4
Well, there are first results: we found out that the piston in the sixth cylinder is maliciously clogging up its work. Now let's try to find out what is the reason for this parasitism. Since this malfunction only appears at high speeds under load, it can be assumed that the exhaust valve is stuck: the 6.2-liter L92 engines of these cars are famous for their weak valve springs, due to which such a malfunction occurs frequently.
But just in case, we’ll sign and move the coils from the sixth and second cylinders to the fifth and seventh. We are not touching the spark plugs for now: they are iridium, they were changed only 20 thousand kilometers ago, so their service life is not even a quarter spent. And most importantly, as has already been said, it is very inconvenient to get to them, so for now we will follow the path of least resistance and maximum manufacturability. Laziness is the engine of progress, what can I say...
We start the stand again and press on the gas with all our hearts. There are 1,172 misfires in the sixth cylinder and - which is a little strange - misfires appear in the fifth and seventh cylinders. What conclusions do we draw? The coils are clearly not in the best condition (we did not change the wires), but the main problem of the sixth cylinder is definitely not in its coil. Looks like the valve springs will have to be replaced.
Bad people, strike them with thunder
You could check the compression in the cylinder the old fashioned way: chew a piece of paper, stick it in the spark plug hole and crank the crankshaft with the starter. If the piece of paper flies out, there is compression. Okay, I'm joking, of course. There is a compression gauge for this.
The method is reliable, but since we decided to carry out diagnostics in the most technologically advanced way, we will also refuse this device. It shows the average maximum pressure at the end of the compression cycle, and we like accurate numbers, and in all strokes of the engine. Therefore, let's take the MotoDoc motor tester. It can do a lot, from checking ignition timing and timing to lambda sensors. It will now show us the pressure in the sixth cylinder in the form of a continuous graph throughout the entire cycle.
To do this, you still have to find a person with long flexible arms with three elbows and a good extension cord for the spark plug wrench. Such a master was found, dived headlong under the hood, from where at first a foul sniffling sound was heard, and then a practically new Denso iridium spark plug appeared. In general, after examining it, further fuss became pointless: it had an almost completely burnt-out central electrode, which led to an increase in the gap and numerous breakdowns of the insulator. Look at the photo: the black marks on the insulator are traces of breakdowns.
What can we say? The service life of normal iridium spark plugs is 80-100 thousand kilometers. These spark plugs even lasted a little less than twenty. And although they cost like real iridium ones, there is less iridium in them than the conscience of those bad people who clandestinely rivet them for sale. Well, if the spark plug is still unscrewed, let’s connect MotoDoc.
To do this, instead of a spark plug, screw in the pressure sensor, then start the engine. The main thing is not to press on the gas pedal, the motor tester sensor does not like this, and if there are any problems with compression, this will be visible on the graph at idle speed. Let us note separately that we did not measure compression, but the pressure in the cylinder without ignition: there is a difference in this.
In general, the graph turned out to be smooth, although the peak pressure at the end of the compression stroke is slightly different. Such jumps, differing within 10%, are normal: firstly, the valve rotates during operation, and secondly, there are still minimal pressure leaks, only freshly ground valves do not have them. So there is no crime with the valves here. Maximum pressure - 5.7 atm, vacuum - 0.7 atm. For this motor these are quite working indicators. You could say they are good.
They scratched the bottom of the barrel and found the same candle. Not new, but it looks working. We put it in place of the one we unscrewed, start the engine, and accelerate on the stand. That's it, there are no errors. It's time to draw conclusions, which we will divide into two parts.
What's wrong with the car?
So, what will need to be done with this Cadillac? First, replace all spark plugs. In this case, you will need to try and find the original ones.
Secondly, two coils (of the second and sixth cylinders) will still have to be replaced, although this will cost 14 thousand. Driving with such reels can be even more expensive.
But for now you can rest assured about the mechanical part of the engine, and good compression gives confidence in this. Actually, at this point the diagnosis can be considered complete.
From a cannon to sparrows
Someone may say: you were too clever with this stand, you shot sparrows from a cannon. They would have looked at the wires, coils, spark plugs - and, of course, they would have found everything. I repeat once again: if a set of wires for a “ten” can be used anywhere for a while, you can even inexpensively replace them preventively, but with wires for a Cadillac such a trick will not work.
Firstly, it is almost impossible to find a test kit, and secondly, buying it just like that is unreasonably expensive. It's the same with coils. Unscrewing the spark plugs one by one is also not an option, because doing this is very inconvenient, and without knowing which of the cylinders is wobbling (and this can only be found out with the help of computer diagnostics), it is too long and tedious.
It turns out that in difficult cases, especially on cars with V8, it is easier to connect a scanner, stand on a stand and find out where the problem lies. True, this requires the presence of the necessary equipment and that same stand, which not everyone has. Well, and experience. You can just get enough of it, the main thing is not to screw up anything, so that later it won’t be painfully offensive.
We thank you for your help in preparing the material (St. Petersburg, Khimikov St., 2, (812) 385-50-70)
Survey
Have you ever had misfires?
Your voice
Total votes:
How to troubleshoot P0301
The cause of the misfire should be fairly easy to determine if the problem is persistent.
Check spark plugs, ignition coils, distributor
Spark plugs can tell you a lot. Signs of sparking on the ignition coil, distributor cap, or rotor may also indicate a faulty part.
A faulty spark plug coil is usually checked by replacing the coils between the cylinders. They look to see if the misfired cylinder has changed or remains the same.
Compression, marks, fuel pressure, lean mixture
Compression, timing marks and fuel pressure can also be checked. The engine may need to be checked for air leaks.
Short-term fuel control (STFT) and long-term fuel control (LTFT) must be checked using a diagnostic scanner or an ELM327 adapter with Torque software. This is necessary to make sure that the air-fuel mixture is not lean.
Often, a faulty mass air flow sensor (MAF) causes the engine to run lean, causing random misfires.
Checking the cooling system pressure can help identify a leaking head gasket.
Exhaust gas recirculation
If the misfire only occurs at idle, the EGR valve and purge valve should be checked as either one may be stuck open.
What is a cylinder misfire?
The principle of operation of internal combustion engines is clear from the name of the power plant: the source of energy for movement is the ignition of the fuel mixture in the cylinders. In gasoline engines, the fuel-air mixture is ignited by a spark produced by a spark plug at the moment of highest compression (compression); in diesel engines, as a result of compression, the fuel ignites on its own.
When the fuel does not ignite or ignites out of timing, a so-called misfire occurs. The unburned mixture enters the exhaust system, where it detonates due to the high temperature. That is why a car with an ignition malfunction can be immediately distinguished due to strong pops and “shots” from the exhaust pipe. This fuel detonation damages the catalytic converter, the most sensitive part of the exhaust system.
The main signs of a misfire include:
- difficulty starting the engine;
- stopping the engine after starting or while driving;
- uneven operation of the power plant at idle;
- engine vibration transferring to the body;
- smell of fuel from the exhaust pipe;
- increased fuel consumption;
- reduced power;
- "Check engine" lamp;
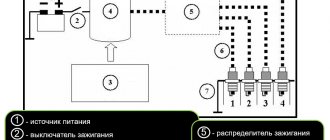
Technical description and interpretation of error P0301
The OBD II error code P0301 is a generic one that reads “Cylinder #1 misfire detected.” Set when the PCM (powertrain control module) detects a misfire in the first cylinder.
The misfire detection system uses input data that is sent to the PCM through dedicated feedback circuits. If the PCM does not receive feedback, it interprets this as a misfire.
Trouble P0301 indicates that the first cylinder is misfiring. They occur when insufficient fuel is burned in the cylinder. Efficient combustion of fuel is important. Because fuel combustion is the source of energy for engine operation.
Misfires can be caused by many reasons. Due to a faulty ignition system, fuel system or internal engine failure. Often the fault occurs due to worn spark plugs, spark plug wires or a faulty coil.