The stability of any vehicle depends on the operating conditions and technical characteristics of the internal combustion engine. An indicator such as engine operating temperature depends not only on environmental conditions, but also on many operational factors. If this parameter corresponds to the calculated value, i.e. is within the acceptable range, the power unit provides maximum energy output for a long time. Optimal operating conditions of the internal combustion engine create the best conditions for the functioning of all vehicle systems.
What should be the operating temperature of the engine?
When fuel mixtures burn in the engine cylinders, a huge amount of heat is released. In the combustion chambers the temperature reaches more than 2000°C. The design of the power units includes a cooling system, the elements of which remove heat from the working units. Thanks to the efficient operation of the internal combustion engine cooling system elements, the thermal regime is maintained within optimal limits from +80 to 90°C. There are certain types of motors for which the standards have been extended to 110°C, most often these are air-cooled mechanisms.
When the engine operates at optimal temperature conditions, the best conditions are created for:
- Complete filling of cylinders with air-fuel mixtures.
- Stable operation of the power unit while driving.
- Reliable operation of vehicle mechanisms and systems.
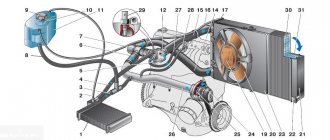
Brief description of the operating principle of the cooling system
This system includes the following operating elements:
- Expansion tank.
- Cooling radiator.
- Top and bottom pipes.
- Cylinder block cooling jackets.
- Connecting hoses.
- Coolant pump.
- Thermostat.
- Interior heater radiator.
- Coolant.
Scheme of operation of the power unit cooling system:
As can be seen from the diagram, the following processes occur in the cooling system:
- The coolant, under the influence of the pump, is forced to pass through hoses, tubes and other lines.
- It effectively washes every cylinder of the internal combustion engine.
- Cylinders, in particular combustion chambers, are the source of the main heat generated by the power unit.
- Around each cylinder there are special technological cavities called “cooling jackets”.
- The cooling jackets communicate with each other through prepared channels. Coolant circulates through these cavities in a constant mode.
- Thanks to the movement of the coolant, thermal energy is transferred from the internal combustion engine to the radiator through the upper pipe.
- Passing through the labyrinths of thin radiator tubes, the liquid is cooled using natural airflow or air currents created by a fan.
- Next, the coolant continues its circular motion through the lower pipe of the cooling radiator.
Deviations from the norm in temperature conditions of power units
Temperature readings inside the engine can be seen on a device located in the interior of any modern car.
What does exceeding the normal operating temperature in the engine cause? At ultra-high temperatures, the technological thermal clearances of metal elements are violated. This causes the following negative changes in the operation of the power unit:
- accelerated wear of working units and parts;
- deformations and breakdowns of mechanisms;
- reduction in engine power;
- occurrence of detonation;
- unauthorized ignition of fuel.
What does the concept of low engine temperature mean? If, while the car is moving, the gauge needle is below the recommended temperature level, there are good reasons for alarm. The unheated fuel-air mixture condenses and settles on the cylinder walls. When condensation enters the oil pan, the engine oil dilutes. The technical properties and characteristics of the lubricant deteriorate sharply. During prolonged operation in low thermal conditions, the components and parts of the power unit quickly wear out and become unusable.
Gasoline engine operating temperature
The operation of each internal combustion engine is accompanied by the release of heat. The working elements of the motor operate under high temperature conditions.
When lowering the piston to the lowest point, a large amount of energy is expended, and at the same time heat is released. Elements of power units are made of metal. As you know, when heated, this material expands. In the manufacture of engine components and parts, special thermal gaps are provided, designed to heat the products to optimal values. To prevent jamming, the engine design includes an engine cooling system.
What is the optimal operating temperature for a gasoline engine? The operating temperature of gasoline power units, both carburetor and injection, should not exceed +90°C. The coolant's job is to maintain a constant engine temperature at the proper level.
Interesting: There is a concept of “dangerous engine temperature”. For gasoline-type internal combustion engines it is 130°C. After reaching the limit values, jamming of the power unit elements may occur.
Important: After turning on the engine and further moving the vehicle, the operator constantly monitors the operating temperature of the internal combustion engine. Deviations indicate problems in the cooling system:
- An increase in temperature in a gasoline engine leads to boiling and rapid evaporation of the coolant.
- As its quantity decreases, the engine temperature will rapidly increase.
- Under the influence of high temperatures, the metal will begin to deform and expand in volume.
- The dimensions of the parts will be greatly changed.
- As a result, the motor will jam.
To restore the performance of such an engine will require an expensive overhaul of the vehicle.
avtoexperts.ru
Many car enthusiasts wonder what the optimal operating temperature of the engine should be. The question is far from clear and much depends on its design features. So for any person, the normal temperature is 36.6 degrees, providing its owner with a healthy existence, when all life processes proceed without any deviations. Likewise, for automobile engines there is a design temperature at which they are able to operate stably, with full power output, in economical mode for a long time.
Why is the operating heating range considered optimal?
The process of combustion of the air-fuel mixture in the cylinders is accompanied by the release of a large amount of heat, since the temperature in the combustion chamber is about 2000 degrees and higher. The task of the cooling system is to maintain optimal thermal conditions in the range of 80-90 degrees. For some types of power plants, temperatures up to 110 degrees can be normal, more often on air-cooled engines.
At optimal temperature conditions, there is better filling of the cylinders, stable starting and reliable operation of the vehicle.
Heat
Structurally, the engine provides thermal clearances when its parts heat up and are subject to expansion. When heated above the permissible value, the gaps are violated, which causes intense wear, scuffing and various types of breakdowns. In addition, there is a decrease in power due to deterioration in cylinder filling, as well as the appearance of detonation and self-ignition of the fuel.
The main reasons for the increase in the temperature of the power plant:
• Thermostat valve jammed in the closed position;
• The electric radiator cooling fan does not work (the electric motor of the fan is faulty, the fuse is blown, the fan power circuit is faulty, the temperature sensor or fluid coupling is faulty);
• The cooling radiator is clogged;
• The valves in the expansion tank cap are faulty;
• Block gasket breakdown;
• The tension of the drive belt for additional mechanisms is loose or broken;
• Depressurization of the cooling system.
Operating temperature does not reach
Incomplete warming up is also undesirable. The surface of the cylinders is not heated and the fuel, in contact with the cold walls, condenses and enters the crankcase, diluting the oil located there, which leads to intense wear of both the CPG and all friction pairs. The main thing is the crankshaft journals and bearings, as well as the camshaft bed and the shaft itself, as well as the intermediate (pig) and balancer shafts, etc.
Plus, when working on an unheated engine, this is especially true in winter (a large amount of condensation on the internal surfaces of the CPG) when traveling short distances, the additives in the oil practically do not work, and do not act as protection.
In addition, unheated oil is thicker and is no longer fully supplied to the friction pairs, causing wear on the cylinder walls, plus fuel consumption increases and, accordingly, the power of the power plant decreases.
Causes of low temperature:
• Sticking of the thermostat valve in the open position;
• Frequent trips over short distances;
• The thermostat or temperature sensor is colder than specified by the manufacturer.
Operating thermal conditions
When the thermal regime is in a given operating range, then all processes proceed without any deviations, nothing threatens the motor and only its natural wear occurs.
Engine types and temperature conditions
There are low and high boost, as well as “cold” and “hot” types of power units, where the working processes of fuel combustion proceed according to different laws.
The temperature at which the thermostat valve operates, when the coolant is able to circulate in a large circle (for cooling after removing the temperature from the water jacket), will actually be the optimal temperature.
In this case, the heating parameters will be different, which directly depends on the calibration of the factory thermostat and the temperature sensor for triggering the electric fan, that is, what the manufacturer installed on the conveyor.
So for gasoline engines even of the same brand of car, for example, a VAZ model, where the operating heating of the coolant is different for carburetor and injection models. Here again, everything depends on the calibration of the thermostat provided by the developers and on the type of cooling system.
Features of cooling systems and their impact on temperature conditions
Liquid cooling systems are divided into two types:
• Open; • Closed (sealed).
An open-type system communicates directly with outside air, that is, air can constantly enter the system and leave it in the form of steam. The boiling point of the coolant is 100 degrees.
The closed system is connected to the atmosphere through special valves mounted in the radiator cap or expansion tank cap. The release of hot air and steam occurs only with a strong increase in pressure in the system.
In a closed type system, the pressure and boiling point of antifreeze are significantly higher, which is about 110-120 degrees Celsius.
The disadvantage of a closed system is a sharp increase in engine heating in the event of depressurization of the system and failure of the valves in the expansion tank cap. This is due to the fact that the system is under high pressure and in the event of depressurization, most of the liquid will immediately be thrown out.
If the valves in the tank cap malfunction, the liquid begins to boil, which also leads to critical overheating of the engine, followed by complex and expensive repairs.
Ecology and engine life
When, to please environmental standards, they began to raise the thermal regime of the engine for complete combustion of fuel, it turned out that other oils were needed, since the existing oil simply could not provide full protection at high temperatures. This had a negative impact on the service life of power plants, which were not designed to operate in such temperature conditions.
What causes engine overcooling?
The phenomenon of hypothermia also negatively affects the quality of operation of the power unit. Most often this happens in winter or when operating a vehicle in difficult climatic conditions of the far north.
The operating temperature of the engine in winter can be sharply reduced while the car is moving. At the same time, flows of cooled air blow over the radiator and the entire power unit. As a result, the coolant sharply lowers the engine temperature, even if it is running at full load.
Diesel engine operating temperature
Maintaining the operating temperature of a diesel engine is a necessary condition for the optimal functioning of vehicle mechanisms and systems. The operating principle of a diesel engine is fundamentally different from a gasoline engine. Here the fuel mixture is not prepared in advance. Air enters the chamber first. With strong compression, the air mass heats up to +700°C. At the moment of fuel injection, an explosion occurs, followed by uniform combustion of the resulting mixture. As a result, the piston moves to bottom dead center.
Diesel temperature depends on the following factors:
- motor type;
- ignition delay period of the air-fuel mixture;
- quality, uniformity of fuel combustion.
It is believed that the optimal operating temperature of the engine should be in the range of 70 – 90°C. The permissible maximum for diesel power units operating under heavy loads is +97°C, no more.
Advice: If the diesel engine is in good condition, it is recommended to warm up the coolant to a temperature of at least +40°C before driving. In severe frosts outside the car, the engine may begin to warm up only when driving. At first, it is recommended to engage a lower gear. In the future, the load on the engine should increase gradually, only after the temperature rises to at least 80°C.
What can the owner do?
And even in extreme heat, you can adjust your driving style to reduce the thermal stress of the engine. Accelerate more calmly, and the temperature will not exceed the calculated values. If you have a manual transmission, then use the “engine braking” technique more often. In this case, combustion of the air-fuel mixture does not occur in the engine, and the pump continues to intensively pump coolant. So the engine temperature decreases.
The higher operating temperature of modern engines is due to design features that have appeared recently. As a result, a modern engine is easier to overheat. It is a fact. Therefore, more attention should be paid to the maintenance of the machine to prevent trouble. Read - additional expenses for repairing or replacing the engine.
Is there a conspiracy among the automakers in this? Depends on your worldview.
Photo: companies-, depositphotos
Source