From our articles you will receive information on the following topics:
- Device, design of the car.
- Frame, body, chassis.
- Fuel efficiency, environmental classification.
- The structure of a car engine.
- Electronic vehicle control systems.
- Fuel system.
- Gasoline fuel injection systems.
- Diesel fuel injection systems.
- Engine cooling system.
- Lubrication system.
- Transmission.
- Transmission.
- Clutch.
- Cardan shaft
- Suspension.
- Steering.
- Brake system.
Materials will be added regularly. Follow our Articles section carefully. Automotive technology is developing very dynamically. If the genius (pioneer of mass-produced cars) in the automotive industry, Henry Ford, had been shown modern transport, the mechanisms would definitely have surprised him. However, you don’t even need to be Henry Ford. You could simply have been born in the second half of the last century or at the beginning of this one, and now be amazed at the real miracles that are everywhere. Among these miracles:
- Mechatronic systems (engine fuel efficiency regulation, transmission control, power control of an attachment, control of a gearbox and dry friction clutch, vehicle anti-lock brakes - ABS).
- Hydraulic systems (hydraulic braking system is a must have, Trimble Autopilot hydraulic steering system).
- Navigation systems, including both vehicle position determination systems and remote cargo tracking systems.
It is also unthinkable to imagine modern transport without electronics and network exchange technologies.
In addition, the approach to transport itself is changing. If previously it was important to simply create an efficient means of transportation, effectively using fuel energy, the modern manufacturer aims to achieve the cleanest possible emissions. For this reason, special attention is paid to the modernization of control systems for ignition and fuel combustion processes. Automotive engineers, mechatronics, and mechanics have much to strive for when improving the design of a car. It is really possible to make good money in the field of transport technologies, but what is important is a continuous desire to improve (learn) and a good starting base. Yes, any mechatronics, electrical, or mechanical engineer is always honed by practice, but a specialist is formed, first of all, by a confident knowledge of automotive fundamentals, the design, structure of a car, its components and assemblies.
To gain such knowledge, the main thing is to have a quality source of learning at hand. Imagine a room in which there are 4,000 books specifically on transport topics, and they are updated almost every day and there is no need to scour the Internet for the necessary content. And in practice, such a “room” can easily appear.
This is the ELECTUDE online platform. Moreover, this is not just a comprehensive knowledge base on auto mechanics, auto electrical, diagnostics, but also a platform from which you will look at distance learning in a completely new way. This is not just a fashionable (and this year, forced for many) format of training. This is a real opportunity to step-by-step eliminate your gaps and hone your skills using the virtual simulator built into the system.
Car design: from terminology to smooth operation
The concept “car” combines two words:
- Autos means independence in Greek.
- Mobile (translated from French as movement).
The combination that best reflects the essence of the concept. At the same time, “independence” and the ability to “move” require special control over safety and reliability.
For this, it is important to have a deep understanding of all the relationships in the operation of automotive mechanisms and systems. The task of manufacturers and specialists in the field of repair is to ensure that the components are in good working order and operate smoothly. This is a huge responsibility, which requires not only readiness to make decisions, but also quick orientation in physical laws and technical features.
Helpful advice
You cannot learn automotive mechanics, electrical engineering, and mechatronics once and for all. You need to study every day. The only thing: you have a choice - you can chaotically watch individual television programs, videos on the Internet, read new textbooks and publications, or you can learn step by step (modularly), for example, using LMS ELECTUDE. First, for example, you get maximum “pumping” in the basics of internal combustion engines, then you “study” gasoline engines, then you undergo separate training to hone specific skills on the built-in simulator (it is an important part of the ELECTUDE platform).
General structure of the car
The design of the car is not as complicated as it might seem at first glance. Absolutely any vehicle consists of five main parts - engine, chassis, transmission, body, electrical equipment and control system.
Motor
The engine is the heart of the car, whose task is to convert thermal energy (burnt fuel) into mechanical energy. After which it is transmitted through the transmission to the wheels.
Chassis
Multiple components and assemblies that make the car move are classified as the chassis - axles, wheels and suspension (rear and front).
Transmission
Main components of the transmission:
- main bridge;
- gearbox (gearbox);
- CV joints;
- clutch.
The task of the transmission is to transmit torque to the wheels of the car from the engine shaft.
Electrical equipment and control system
Electrical components:
- battery (battery);
- wiring;
- generator.
The vehicle control mechanism is represented by a steering wheel connected to the front wheels. The steering wheel is used to determine the turning angle and direction of movement of the vehicle. Brakes are another important component of the vehicle control system, responsible for reducing its speed and stopping it completely.
Body
Almost all units and components are attached to the load-bearing part of the car - the body.
Body components:
- spars;
- vehicle roof;
- bottom;
- engine compartment;
- other attachments.
This division is very arbitrary, since all the parts in the car are, one way or another, interconnected.
The design of the vehicle is constantly being improved, increasingly filled with electronics and automation. Manufacturers are working to improve vehicle operating safety, fuel efficiency, and reduce noise levels and exhaust toxicity.
Main components and assemblies of the car
A car enthusiast can superficially study these diagrams with descriptions without going deeper.
Internal combustion engine
The engine is the main part of any car. It is the internal combustion engine that has been popular for many years and is still installed today.
There are two types of motors:
- diesel;
Diesel internal combustion engine
- petrol.
Gasoline internal combustion engine
In the first engine, combustion occurs due to the high temperature in the cylinder. The mixture is compressed, which leads to ignition. Diesel fuel is used to power such engines. The units have low consumption and high torque, but less power. Good for trucks.
The gasoline engine appeared much earlier and is still the most numerous. It has a number of advantages and disadvantages, for example, it is more powerful than a diesel engine, but not as economical. It is used on cars and trucks, but is more widely used in motorsports.
Body
The body is the basis of the car. The chassis, seats, and electrical equipment are installed on it. The car cabin provides protection for the driver and passengers from the weather and collisions with other cars. The body of a passenger car is the load-bearing part, since it is on it that the suspension and engine are mounted. Such a design is always made of metal, but history knows many cars when plastic and wood were used.
Car body elements
Steering
Steering appeared along with the first methods of transportation. From primitive mechanisms, the steering became a separate independent part of the car.
Car steering device
In simple words, this is a set of parts that convert human muscular force into mechanical force and change the rotation of the wheels. To simplify this effort, two types of amplifiers have been invented:
- electric;
- mechanical;
Electric power steering helps turn the shaft using an electric motor, and power steering acts on the pistons that push the steering rods.
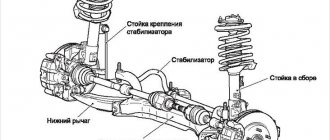
Suspension
Car suspension comes from the word “to hang” the wheels. It is impossible to secure them rigidly to the body: all vibrations and shocks from the holes will be transferred to the driver and passengers, which is not very pleasant. The car should be comfortable.
The suspension affects not only the comfort in the cabin. This is an important part of the car's handling. The type of suspension determines the purpose of the machine. There are two types:
- dependent - for SUVs and trucks;
- independent - for cars;
Each of the schemes is implemented in its own way and can be multi-link or MacPherson-type suspension. The first type is the most expensive and is now used on prestigious cars. It is soft and comfortable. The second is called the European type of suspension of most modern cars. The cheapest, simplest and most common.
Transmission
To climb a mountain using maximum torque, and then quickly accelerate down the mountain and gain maximum speed, car manufacturers came up with a gearbox (gearbox). One of the most common gearboxes is considered to be a manual one, where the car owner himself chooses the gear depending on the speed, speed and load. Shifting gears is a complex process that takes some time to learn.
But mechanics are gradually being replaced by automatic transmissions or automatic transmissions. In such a box, all switching actions are automated. There are several varieties:
- classic automatic - with torque converter;
Gearbox with torque converter
- variable speed drive;
CVT gearbox design
- robotic transmission;
Robotic gearbox
Automatic transmissions are less suitable for off-road use, but they are much more convenient in traffic jams. The mechanics are much more reliable, but it is inconvenient to move around the city.
Brake system
The brakes of all modern passenger cars are hydraulic.
Diagram of the car brake system
Operating principle:
- The driver presses the brake pedal, acting on the master cylinder.
- The brake cylinder compresses the fluid inside the system, and it transmits force to the wheel brake wheel cylinder.
- The pads expand or compress and stop the drum or special brake disc.
Independent of the main part of the brakes - the “handbrake” or handbrake - fixes the car while parking or even stops it when the main brakes fail.
Electrical equipment
Full electrification of cars is just around the corner. Most of the units in the car are controlled, diagnosed and operate electronically: gearbox, brakes, engine. The main direction in the development of electrics in cars was, is and will be the creation of electric motors.
Vehicle electrical system
Ignition operating principle
The set of devices responsible for the appearance of a spark at the required moment is called the ignition system and is part of the electrical equipment. Normal operation of a gasoline engine is impossible without an ignition system. There are three main types of ignition systems, similar in principle of operation, but differing in design.
Kinds:
- electronic;
- contact;
- contactless.
Ignition system design
- Power supply
When the car is started, the battery is the power source, after which this function is transferred to the generator (while the engine is running).
- Egnition lock
A device used to transmit voltage.
- Storage device
A device necessary to accumulate the necessary energy. There are induction (in the form of a coil) and capacitive storage devices.
- Energy distributor
The system consists of a block and a switch. The distributor can be electronic or mechanical. Responsible for supplying energy.
- Candle
A porcelain insulator with two electrodes placed close together. Responsible for creating the spark for ignition.
Main stages of ignition operation:
- accumulation and supply of the required charge level;
- high voltage conversion;
- moment of distribution;
- spark formation;
- fuel ignition.
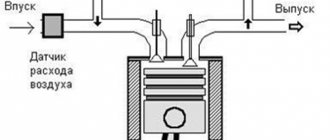
Operating principle of the engine
Engine device:
- the ignition system supplies current to the spark plug to produce a spark;
- the cooling system removes heat from the cylinder walls and heads, preventing engine overheating;
- the power system is responsible for preparing a new portion of the working mixture (fuel + air);
- the gas distribution mechanism is responsible for the timely intake of a new portion of the working mixture and the removal of exhaust gases;
- the crank mechanism converts the (reciprocating) movement of the pistons into rotational movement of the crankshaft;
- The lubrication system is responsible for supplying oil to the rubbing surfaces.
Most cars now use a four-stroke combustion system to convert fuel into energy. For the engine to operate properly, the compression in the cylinders must correspond to values from 11 to 15.
Combustion cycle:
- the fuel-air mixture is admitted (intake stroke);
- the mixture is compressed and ignites (compression stroke);
- the mixture burns and pushes the piston down (expansion stroke);
- combustion products are released (exhaust stroke).
Inside the engine cylinder there is a chamber into which a mixture with air (or separately) is introduced, where fuel combustion occurs. During combustion, thermal energy is converted into mechanical energy. Afterwards, the combustion products are removed from the cylinder, and a new portion of fuel arrives in their place. The combination of these processes is the engine operating cycle.
Clutch operating principle
The connecting link between the gearbox and the engine, connecting and disconnecting the gearbox input shaft from the crankshaft flywheel is called a clutch. On a manual transmission, gears shift only when the clutch is depressed.
Clutch assembly design:
- pressure plate or “basket”;
- release bearing drive fork;
- release bearing;
- driven disk;
- drive system;
- clutch release pedal.
According to the number of driven discs, the clutch is divided into single-disc and multi-disc.
In the single-disk version, the basket is connected to the flywheel and rotates with it. All rotation is transmitted to the gearbox, since the driven disk contains a splined clutch into which the gearbox shaft enters. To change gear, the driver presses the pedal, which triggers the following processes:
- pressure is transmitted to the clutch fork through the clutch drive system;
- the fork, in turn, moves the release bearing clutch along with it to the basket springs;
- the bearing exerts pressure on the basket legs;
- the paws temporarily disconnect the disc from the flywheel.
When the driver releases the pedal, the bearing separates from the springs and the basket engages with the flywheel.
In double-disc versions, a basket is used that has two working surfaces and two clutch discs. Restrictive bushings and a synchronous pressure adjustment system are located between the working surfaces of the drive disk. The process of disconnecting the flywheel occurs as in a single-plate clutch.
Types of clutch:
- mechanical;
- hydraulic (the most common option);
- electrical;
- single and multi-disc.
Operation of transmission parts
The clutch serves to separate the gearbox (Gearbox) from the engine, then smoothly connect them when changing gears and when driving away.
The gearbox changes the torque transmitted from the crankshaft to the cardan shaft. The gearbox unit disconnects the connection between the motor and the cardan drive to the extent necessary to move the vehicle in reverse.
The main function of the cardan transmission is to transmit torque from the gearbox to the main gear at different angles.
The primary function of the final drive is to transmit torque at a ninety-degree angle from the driveshaft through the differential to the drive shafts of the main wheels.
The differential rotates the drive wheels at different speeds when cornering and on uneven surfaces.