1200 rub. for the photo report
We pay for photo reports on car repairs. Earnings from 10,000 rubles/month.
Write:
The density of the electrolyte in the battery is a very important parameter for all acid batteries, and every car owner should know: what the density should be, how to check it, and most importantly, how to properly increase the battery density (specific gravity of the acid) in each of the cans with lead plates filled with a solution H2SO4.
Checking the density is one of the points in the battery maintenance process, which also includes checking the electrolyte level and measuring the battery voltage. In lead batteries, density is measured in g/cm3 . It is proportional to the concentration of the solution , and inversely dependent on the temperature of the liquid (the higher the temperature, the lower the density).
The density of the electrolyte can determine the condition of the battery. So if the battery does not hold a charge , then you should check the condition of its liquid in each of its jars.
The density of the electrolyte affects the battery capacity and its service life.
It is checked with a densimeter (hydrometer) at a temperature of +25°C. If the temperature differs from the required one, corrections are made to the readings, as shown in the table.
So, we figured out a little what it is, and that you need to check it regularly. What numbers should we focus on, how much is good and how much is bad, what should be the density of the battery electrolyte?
What density should the battery have?
Maintaining the optimal electrolyte density is very important for the battery and it is worth knowing that the required values depend on the climate zone. Therefore, the battery density must be set based on the totality of requirements and operating conditions. For example, in a temperate climate, the electrolyte density should be at the level of 1.25-1.27 g/cm3 ±0.01 g/cm3. In the cold zone, with winters down to -30 degrees, it is 0.01 g/cm3 more, and in the hot subtropical zone it is 0.01 g/cm3 less . In those regions where winter is especially harsh (up to -50 ° C), in order to prevent the battery from freezing, it is necessary to increase the density from 1.27 to 1.29 g/cm3 .
Many car owners ask the question: “What should be the density of the electrolyte in the battery in winter and what in summer, or is there no difference, and should the indicators be kept at the same level all year round?” Therefore, let’s look at the issue in more detail, and a table of the density of the electrolyte in the battery , divided into climatic zones, will help to do this.
You also need to remember that, as a rule, the battery, while in the car, is charged to no more than 80-90% of its nominal capacity, so the density of the electrolyte will be slightly lower than when fully charged. So, the required value is selected a little higher than that indicated in the density table, so that when the air temperature drops to the maximum level, the battery is guaranteed to remain operational and not freeze in the winter. But, regarding the summer season, increased density may threaten boiling.
Battery electrolyte density table
The density table is compiled relative to the average monthly temperature in the month of January, so that climatic zones with cold air up to -30 ° C and moderate ones with temperatures not lower than -15 do not require a decrease or increase in acid concentration. All year round ( winter and summer ) the density of the electrolyte in the battery should not be changed , but only checked and ensure that it does not deviate from the nominal value , but in very cold areas, where the thermometer is often below -30 degrees (up to -50), adjustments are allowed.
Electrolyte density in the battery in winter
The density of the electrolyte in the battery in winter should be 1.27 (for regions with winter temperatures below -35, at least 1.28 g/cm3). If the value is lower, this leads to a decrease in electromotive force and difficulty starting the engine in cold weather, up to freezing of the electrolyte.
When the density in the battery is reduced in winter, you should not immediately run for a correction solution in order to raise it; it is much better to take care of something else - high-quality charging of the battery using a charger.
Half-hour trips from home to work and back do not allow the electrolyte to warm up and, therefore, to charge well, because the battery only accepts a charge after warming up. So the rarefaction increases day by day, and as a result the density also decreases.
For a new and serviceable battery, the normal range of changes in electrolyte density (full discharge - full charge) is 0.15-0.16 g/cm3.
Remember that operating a discharged battery at sub-zero temperatures leads to freezing of the electrolyte and destruction of the lead plates!
Using the table of the dependence of the freezing temperature of the electrolyte on its density, you can find out the minus threshold of the thermometer at which ice forms in your battery.
As you can see, if the battery is 100% charged, it will freeze at -70 °C. At 40% charge it freezes already at -25 °C. 10% will not only make it impossible to start the engine on a frosty day, but it will also completely freeze in 10 degree frost.
When the density of the electrolyte is not known, the degree of discharge of the battery is checked with a load fork. The voltage difference in the elements of one battery should not exceed 0.2V.
Load plug voltmeter readings, B
Battery discharge level, %
If the battery is discharged by more than 50% in winter and more than 25% in summer, it must be recharged.
Density of electrolyte in the battery in summer
In summer, the battery suffers from dehydration , so given that increased density has a bad effect on lead plates, it is better if it is 0.02 g/cm3 below the required value (especially for the southern regions).
In the summer, the temperature under the hood, where the battery is often located, is significantly increased. Such conditions promote the evaporation of water from the acid and the activity of electrochemical processes in the battery, ensuring high current output even at the minimum permissible electrolyte density (1.22 g/cm3 for a warm, humid climate zone). So, when the electrolyte level gradually drops , its density increases , which accelerates the process of corrosive destruction of the electrodes. This is why it is so important to monitor the fluid level in the battery and if it drops, add distilled water, and if this is not done, then overcharging and sulfation threatens.
If the battery is discharged due to the driver’s carelessness or other reasons, you should try to return it to its working condition using a charger. But before charging the battery, they look at the level and, if necessary, add distilled water that may have evaporated during operation.
How to increase electrolyte density
You can lower or increase the density of the electrolyte in the battery by pumping out a certain amount of it and replacing it with distilled water or an electrolyte with a higher density (correction). This procedure requires a lot of time, since the pumping-topping cycle can be repeated several times until the required value is reached. After each adjustment, you need to charge the battery (at least 30 minutes), and then let it stand (0.5-2 hours). These actions are necessary to better mix the electrolyte and equalize the density in the jars.
In the process of increasing (or decreasing) the density of the electrolyte, do not forget about monitoring its level. It is carried out by a glass tube with two holes at the edges. One edge is immersed in the electrolyte until it hits the safety mesh. Next, the upper end is closed with a finger, and the tube itself is carefully lifted along with the column of liquid inside. The height of this column indicates the distance from the top edge of the plates to the surface of the poured electrolyte. It should be 10-15 mm. If the battery has an indicator (tube) or a transparent case with minimum and maximum marks, then monitoring the level is much easier.
Do not forget that all operations with electrolyte must be performed carefully, using protective gloves and goggles.
How to check battery density
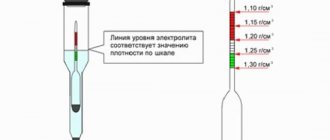
To ensure proper operation of the battery, the density of the electrolyte should be checked every 15-20 thousand kilometers . Measuring the density in a battery is carried out using a device such as a densimeter. The device of this device consists of a glass tube, inside of which is a hydrometer, and at the ends there is a rubber tip on one side and a bulb on the other. To check, you will need to: open the cap of the battery can, immerse it in the solution, and use a bulb to draw in a small amount of electrolyte. A floating hydrometer with a scale will show all the necessary information. We will look in more detail at how to properly check the battery density below, since there is also a type of battery called maintenance-free, and the procedure for them is somewhat different - you do not need absolutely any devices.
Density indicator on a maintenance-free battery
The density of a maintenance-free battery is displayed by a color indicator in a special window. The green indicator indicates that everything is normal (the degree of charge is within 65 - 100%), if the density has dropped and recharging is required , then the indicator will be black . When a white or red light , an urgent addition of distilled water . But, however, the exact information about the meaning of a particular color in the window is on the battery sticker.
Now we continue to further understand how to check the electrolyte density of a conventional acid battery at home.
Checking the electrolyte density in the battery
So, in order to be able to correctly check the density of the electrolyte in the battery, first of all we check the level and, if necessary, adjust it. Then we charge the battery and only then start checking, but not immediately, but after a couple of hours of rest, since immediately after charging or adding water there will be unreliable data.
It should be remembered that density directly depends on air temperature, so check the correction table discussed above. After taking liquid from the battery can, hold the device at eye level - the hydrometer should be at rest, floating in the liquid without touching the walls. Measurements are taken in each compartment, and all indicators are recorded.
Table for determining battery charge based on electrolyte density.
The electrolyte is prepared by diluting battery sulfuric acid with a density of 1.83. 1.84 (GOST 667-73) in distilled water with acceptable impurities.
The chemical purity of the electrolyte has a significant impact on the performance and service life of batteries. Contamination of the electrolyte with harmful impurities such as iron, manganese, chlorine and others leads to increased self-discharge of batteries, a decrease in the output capacity, destruction of the electrodes and premature failure of the battery. Therefore, it is prohibited to use technical sulfuric acid and contaminated (undistilled) water to prepare the electrolyte. When preparing electrolyte, putting batteries into working condition and maintaining batteries in operation, you must use only clean utensils and maintain cleanliness.
In exceptional cases, in the absence of distilled water, snow or rain water may be used to prepare the electrolyte, pre-filtered through a clean cloth to remove mechanical impurities. You cannot collect water from iron roofs or in iron vessels.
The electrolyte should be prepared in sulfuric acid-resistant containers (ebonite, earthenware, ceramic), while observing special caution and safety rules. The use of iron, copper, zinc or glass utensils is strictly prohibited .
Batteries, depending on the climate zone, are filled with electrolyte having a density indicated in column 5 of Table 3. The electrolyte of the required density can be prepared directly from acid with a density of 1.83. 1.84 g/cm 3 and water. However, with the continuous pouring of acid into water, the solution becomes very hot (80-90 °C) and a long time is required for it to cool. Therefore, to prepare an electrolyte of the required density, it is more convenient to use an acid solution of intermediate density 1.40 g/cm 3, since in this case the cooling time of the electrolyte is significantly reduced.
Table 3. Electrolyte density when bringing batteries into working condition
| Climatic zones and regions (GOST 16035-70) | Average monthly temperature in January, °C | Numbers of zones and districts according to the map diagram | Season | Electrolyte density, normalized to 25 °C, g/cm3 | Note |
| poured | fully charged battery | ||||
| Cold, climatic region is very cold | from -50 to -30 | 1a | winter |
all year round
Table 4. The amount of distilled water, acid or its solution with a density of 1.40 g/cm 3 required to prepare 1 liter of electrolyte of the required density (at 25 °C)
| 1.28 | for car batteries for car batteries for tank batteries | |||||
| Cold, climatic region cold | from -30 to -15 | 1b | all year round | 1.26 | 1.28 | for all batteries |
| Moderate | from -15 to -4 | 2 | all year round | 1.24 | 1.26 | for all batteries |
| Warm wet | from 4 to 6 | 3 | all year round | 1.20 | 1.22 | for all batteries |
| Hot | from -15 to 4 | 4 | all year round | 1.22 | 1.24 | for all batteries |
| Required electrolyte density, g/cm 3 | Quantity of water, l | The amount of sulfuric acid with a density of 1.83 g/cm 3 | Quantity of water, l | The amount of sulfuric acid solution with a density of 1.40 g/cm 3, l | |
| l | kg | ||||
| 1,20 | 0,859 | 0,200 | 0,365 | 0,547 | 0,476 |
| 1,21 | 0,849 | 0,211 | 0,385 | 0,519 | 0,500 |
| 1,22 | 0,839 | 0,221 | 0,405 | 0,491 | 0,524 |
| 1,23 | 0,829 | 0,231 | 0,424 | 0,465 | 0,549 |
| 1,24 | 0,819 | 0,242 | 0,444 | 0,438 | 0,572 |
| 1,25 | 0,809 | 0,253 | 0,464 | 0,410 | 0,601 |
| 1,26 | 0,800 | 0,263 | 0,484 | 0,382 | 0,624 |
| 1,27 | 0,791 | 0,274 | 0,503 | 0,357 | 0,652 |
| 1,28 | 0,781 | 0,285 | 0,523 | 0,329 | 0,679 |
| 1,29 | 0,772 | 0,295 | 0,541 | 0,302 | 0,705 |
| 1,31 | 0,749 | 0,319 | 0,585 | 0,246 | 0,760 |
| 1,40 | 0,650 | 0,423 | 0,776 | – | – |
A solution of sulfuric acid with a density of 1.40 g/cm3, reduced to 25 °C, must be prepared in advance and, after cooling, stored in a glass or polyethylene container.
The amount of water, acid or its solution with a density of 1.40 g/cm 3 required to prepare 1 liter of electrolyte is indicated in the table. 4. The approximate amount of electrolyte required to fill one battery is given in table. 1. Using tables 1 and 4, you can calculate the amount of electrolyte of a given density for filling both one and several batteries of any type.
The calculation is carried out in the following sequence: from table. 1 determines the total volume of electrolyte to fill the required number of batteries, then according to the table. 4, the amount of distilled water and an acid solution with a density of 1.40 g/cm 3 (or strong acid) required to prepare an electrolyte of a given density to fill all batteries is calculated.
Requirements for different climate zones
Before adjusting the electrolyte density in the battery, you need to understand why this is being done. In winter, this parameter must be increased so that the battery does not freeze at low temperatures. In summer it decreases, which extends battery life. Experienced specialists are able to increase the density by adding a corrective electrolyte for batteries, and if necessary, it can be lowered using distilled water. At the same time, car enthusiasts recommend not using this method unless absolutely necessary, since the battery may be damaged due to failure to maintain the correct proportions. Many use average density, which allows you to use the battery at any time of the year without unnecessary manipulation. The table summarizes the most common density parameters: If abnormal cold is expected in the central or southern region, it is recommended to take the battery into a warm room, check the charge level and bring it to 100% if necessary. A fully discharged battery has a low density (1.10 g/cm 3 ), which contributes to its freezing even at -5°C.
A few words about acid electrolyte
Acid electrolyte is one of the components of many rechargeable batteries (AB). This substance is a mixture of two main elements:
- acid, which is often sulfuric acid;
- and distilled water.
A similar solution is often used to refill lead-acid batteries, which have been actively used in the automotive industry for about 170 years. Note that in this case the electrolyte is in a liquid state and requires constant topping up. Noticeably less often when using cars, gel batteries are used, which are based on the same solution with the composition noted above, but there it is no longer in a liquid state, but in a more or less thickened state.
In the usual version, the liquid electrolyte requires periodic filling, because during operation it partially evaporates and goes through the gas outlet sections of the battery. Also, depending on the season, the solution should be either less or more dense. It is by correctly maintaining the amount and density of the acid electrolyte from the battery used that the highest efficiency can be achieved. In fact, only these two indicators of a mixture of acid and distilled water require proper monitoring and appropriate adjustment.
Life time
It is important to understand that an acid electrolyte is precisely a solution that does not have an expiration date. The latter for a mixture of this kind is determined based on how well it is able to perform the functions assigned to it. The main indicators affecting the current use of the battery include:
- electrolyte density;
- temperature regime of its operation;
- battery charge level.
Monitoring of these indicators must be carried out in accordance with special technical literature and some GOST standards. It’s probably not worth going into details of the normal parameters, because not a single motorist will fully comply with them. It’s better to pay attention to the basic rules necessary to comply with the correct operating mode of acid batteries. To be more precise, their list includes:
- Maintaining normal electrolyte density. A normal indicator of this parameter is considered to be anywhere from 1.07-1.3 grams per milliliter (approximate sulfuric acid content is 30-40%). It is officially recommended to adhere to an electrolyte density of 1.21-1.24 g/ml in warm seasons, and 1.27-1.30 in cold seasons. This battery parameter is checked using special instruments - analyzers or hydrometers. A decrease or increase in density occurs by adding distilled water or correction electrolyte;
- Battery charge monitoring. Note that when the battery is discharged, the density of the electrolyte drops, so it is advisable that the battery is always charged to 60-100%. It is better to avoid complete battery discharge or, if it occurs, completely change the electrolytic solution and restore the battery in the mode recommended by the manufacturer;
- The battery is always fully charged. This, again, is necessary to maintain good electrolyte density;
- Maintaining a normal electrolyte level in the separator. Here it is worth considering the indicators recommended by the manufacturer. That is, fill in the electrolyte according to existing standards;
- Avoiding overloading the battery by operating too vigorously or operating in high temperature conditions at frequent intervals. These phenomena, which is not surprising in principle, negatively affect the condition of any electrolyte, including an acid solution.
By adhering to only the 5 rules noted above for the operation of acid batteries and corresponding electrolytes, it is quite possible to extend their service life by 2 or even 3 times. Remember this.
Preparation
So, if, as a result of checking with a hydrometer, a low density of the electrolyte in the battery is discovered, it needs to be raised. But before doing this, you need to make sure that some conditions are met:
- The battery is charged;
- the temperature of the electrolyte in the jars is within 20-25 °C;
- in all jars the liquid level is normal;
- the battery is intact. On batteries, cracks often appear near the current terminals due to loosening of the contacts. Therefore, there is no need to knock or use excessive force to remove the terminal on the battery. It's better to spend a little more time and do it carefully.
If the car battery is discharged, it is charged, and then the density is measured. Why is that? The fact is that with a low charge, the concentration of acid in the jars decreases.
If you pour the correction solution into an uncharged battery, the concentration of sulfuric acid can be increased to such an extent that the plates in the jars will fall off.
It is also necessary to take into account the fact that a car generator charges the battery only 85-90%. Therefore, before taking measurements, the battery must be charged.
Corrective battery charging
Sometimes, a situation may arise that after a full charge, the density of the electrolyte in the banks turns out to be different. In general, the difference in density is allowed no more than 0.01 kg/cm3. Otherwise, it needs to be leveled.
To do this, you can perform corrective charging of the battery. The current strength is reduced by 2-3 times (compared to the nominal value) and the battery is charged in 1-2 hours. If this does not help level the electrolyte density, more radical measures will be required.
Correction electrolyte
Corrective is called an electrolyte with a density of 1.40 kg/cm3. Remember, under no circumstances should you just pour it into the battery. Those. first, you need to check the battery and find out the reason for the drop in the liquid level, and then raise it.
There is often a situation where novice car enthusiasts misinterpret the name “corrective”. For example, when the water evaporated from the cans. Those. you need to raise the liquid level, and here is the corrective solution. The logic is simple:
- The battery is filled with electrolyte and its level has dropped;
- correction solution, which means it is intended to adjust the liquid level.
Unfortunately, this point of view is fundamentally wrong. In most cases, distilled water is poured into the battery to level the level.
And the corrective electrolyte is poured in the following cases:
- if liquid has leaked from the cans;
- if you poured too much distillate into the battery and reduced the density.
The procedure for filling and topping up acid electrolyte in the battery
From the information presented above, it is clear that it is important to maintain the acid electrolyte of any battery at the proper level and condition. The use of low-quality or small quantities of solution is a factor that can significantly reduce the service life of the battery.
During operation of acid batteries, it may be necessary to either completely change the electrolyte or top it up. Any of these processes should be carried out when the following signs appear:
- the battery has stopped holding a charge or is doing so extremely poorly;
- electrodes, separators and their plates are intact;
- The battery was charging, but there was no result or it was, but extremely weak.
Do you observe these moments specifically in your situation? Then changing or partially topping up the acid electrolyte is simply necessary, because perhaps it is they that will revive the battery.
If motorists do not have any particular difficulties with changing the solution, many cannot cope with refilling it. In fact, there is nothing complicated in carrying out this procedure and the procedure for its implementation is as follows:
- Remove the battery from the car;
- Take the battery to the place where it is topped up, which must be protected from third parties, current, fire and water;
- Prepare a protective suit and some tools to top up the electrolyte;
- After this, carefully remove the separator covers and use an analyzer to check the density of the electrolyte, as well as its filling level. If the density is higher than normal, dilute the electrolyte with distilled water; if it is lower, add correction electrolyte. It is advisable to add the solution to the level recommended by the battery manufacturer, but a slight deviation from it while maintaining the normal density of the electrolyte, checked by the analyzer, is also acceptable;
- Then all that remains is to assemble the battery to its original form and return it to the car structure.
Note! When adding distilled water, we recommend purchasing the liquid not from pharmacies, but from car dealerships. The former often sell ordinary tap water, which is not recommended to be poured into the battery.
Note that when replacing or adding a large amount of electrolyte, it is advisable to additionally recharge the battery. When completely replacing the solution, the battery must be fully charged; when partially topping up, a third or a quarter of the duration of a full charge is required.
Electrolyte preparation process
Summarizing today's material, it would not be amiss to consider the process of preparing an acid electrolyte with your own hands. Of course, buying a solution is not so difficult, especially considering its low cost, but many motorists still like to “do some chemicals.” For these purposes, when preparing an acid electrolyte, it is important:
- First, prepare sulfuric acid with a density of about 1.83 g/ml and distilled water - 1.4 g/ml. At least, this is what GOST recommends for the preparation of an acid electrolyte, from which it is undesirable to deviate;
- Secondly, find a cast iron or plastic container with a tight-fitting lid, similar items for stirring the electrolyte and an analyzer (hydrometer);
- And thirdly, organize a place for preparing the solution, which must be protected from third parties, current, fire and water.
After basic preparation, you can proceed directly to preparing the acid electrolyte. The order of operation looks like this:
- Place 1-2 liters of distilled water in the prepared container;
- Then sulfuric acid is slowly added and mixed thoroughly;
- After this, the analyzer checks the density of the electrolyte and, if necessary, corrects it either by adding distilled water (to reduce the density) or by adding acid (to increase the density).
The prepared mixture should be stored in a glass container with a tightly closed rubber stopper. The storage location of the acid electrolyte should be protected from the sun and children.
Perhaps the most important information on the issue under consideration today has come to an end. We hope the material presented above was useful to you. Good luck with car repairs and on the roads!
Complete replacement of electrolyte in the battery
The electrolyte is a mixture of sulfuric acid and water in a certain proportion. The concentration of a solution is determined by the density measured by a hydrometer. The basic indicator, even hundredths, affects the ability of the electrolyte to work to store energy.
Signs of an unusable electrolyte:
- Measuring density on a charged battery with a hydrometer. The value should be 1.25 -1.27 g/cm3.
- A cloudy electrolyte is evidence that parasitic sulfation processes are taking place inside.
- The electrolyte froze, but the seal of the case was not broken.
- The solution is black or dark brown with a suspension of coal and scale.
Replacing the electrolyte in a battery will be effective when the cavities of the cans are examined, washed, and sulfate deposits are removed. If the plates are destroyed and the active substance has fallen off, the battery cannot be repaired.
At home, a complete replacement of the electrolyte in a car battery occurs in the following sequence:
- Prepare enamel or glass containers for draining the electrolyte, personal protective equipment, and a place to work, preferably outdoors.
- Remove the battery from the car, remove the plugs or drill holes in the maintenance-free battery, drain the liquid into a prepared container using a bulb or syringe.
- The battery is washed with distilled water several times until the sediment is removed. Lead sulfate may need to be removed if there is residue on the plates. You need to make sure that the active putty has not crumbled and that the coal grate is intact.
- Slowly, intermittently, pour the electrolyte of the required density into each jar 5-7 mm above the plates. Wait 2-3 hours for the bubbles to come out, measure the density of the electrolyte, bring it to normal
- After replacing the electrolyte, charge the battery with a low current of 0.1 A, avoiding boiling. After reaching half the capacity, charging is carried out cyclically.
- Seal the cans.
How long does it take to charge the battery? After replacing the electrolyte, you need to charge the battery carefully, as after a deep discharge. The operation of replacing the electrolyte with your own hands in a car battery is considered complete if it fully accepts current for a long time. Charging is carried out carefully; boiling in jars is unacceptable.
We invite you to watch a video on how to properly replace the electrolyte in a car battery.
This is interesting: Is it possible to use fog lights as daytime running lights?