, at the beginning of January, at the Slobodka Airborne Forces training ground, this is the base of the Tula Airborne Forces, rig tests of the newest armored transporters entering the Russian troops since 2013 took place.
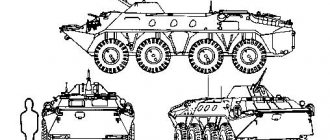
armored personnel carrier btr mdm shell
“Object 955”, also known as the MDM armored personnel carrier, was developed at VgTZ as part of the Rakushka design and development project. Design and technical specifications, multi-purpose amphibious high-speed armored airborne and air-transportable tracked vehicle for solving transport problems of amphibious assault units and airborne troops. Unlike the popular BMD-BTR-D family used by the troops, the airborne BTR-MD differs from the BMD-3 airborne combat vehicle in its slightly increased hull dimensions and the absence of a turret.
armored personnel carrier md shell
BMD-BTR-D, BTR-MD airborne armored personnel carrier
, were tested in order to ensure the timely equipping of the Airborne Forces with modern weapons. For the landing force, this type of equipment has a unique armored, super-maneuverable tracked vehicle “Minibus” for use in conditions of direct enemy influence. In addition, the vehicle commander now has the ability to fire a machine gun on the move in a 360” sector without putting his life in danger.
new armored personnel carrier shell
During controlled military operation, regular crews of units, under the control of representatives of the manufacturer, test the latest equipment in conditions close to combat. Let's watch a selection of videos from MDM Shell. This machine has recently been tested. All crews are exclusively contract military personnel. The latest examples of military equipment armored personnel carrier mdm "Rakushka" armored personnel carrier photo
come within the framework of the state defense order.
Mdm armored personnel carrier Shell photo
At the Slobodka Airborne Forces training ground, the delivery of airborne combat units and evacuation from operation sites was demonstrated, regardless of the complexity of the terrain or the combat situation on the BTR-MDM. At the same time, combat vehicles carried out automatic fire in defense from standard weapons, passed a tank route with shooting, overcame a rutted bridge, scarp, anti-tank ditch, mound, slope, mine-explosive obstacles, etc. In addition, the capability of the predecessor of the “Rakushka” - the BTR- D, which has been in service with the Airborne Forces since the 1970s.
Shell armored personnel carrier Slobodka base of the Tula Airborne Forces
Tactical and technical characteristics of the armored personnel carrier MD
Armored personnel carrier modifications
- BTR-MD - basic modification based on the BMD-4 airborne combat vehicle
- BMM-D - armored medical landing vehicle (armored ambulance transporter - BMM-D1, armored medical platoon vehicle - BMM-D2
- BTR-MDM - a modernized version based on the BMD-4M airborne combat vehicle
newest armored personnel carriers photos
At the moment, there are about 30 units of “Armored Personnel Carrier Shell Photo”
, about 10 more MDM armored personnel carriers will enter service in 2020 as part of the state defense order.
This review article will discuss two related modifications of the BTR-MD “Rakushka”
and
BTR-MDM "Rakushka-M"
.
BMD-MD
stands for armored personnel carrier, landing vehicle, respectively,
BTR-MD
M stands for armored personnel carrier, modernized landing vehicle.
the name “Shell”
because of its shape and bulletproof circular armor.
Sometimes an armored personnel carrier is not officially called BTR-D-3
or
BTRD-3
.
BTR-MDM
The development of the new BTR-4M for paratroopers began in 2008 on the basis of
the BTR-MD
"Object 955".
At one time, the technical specifications for the creation of the BTR-MD were given in 1992; the base of the famous BMD-D was taken as the basis for the new armored personnel carrier.
BTR-MDs were produced, since the sample was “raw” and was immediately followed in 2008 by the development of
the BTR-MDM.
The BTR-MDM became well known after its premiere on May 9, 2020 during the military parade on Red Square in Moscow.
It so happened that the letter M (modernized) in the name was written by different sources of information, then forgotten, and both models merged into one name “Shell”
, and then again the letter M was lost, but it should have turned out to be
BTR-MDM “Shell”
.
And the “Rakushka”
was created on the basis of the BMD-4M.
The production of the BTR-MDM
is carried out by Kurganmashzavod, the chief designer is S.S. Salnikov.
The first two Rakushki-Ms
were tested in 2013. The new armored personnel carrier should replace the BTR-D, which entered service in 1974. The characteristics of the new armored personnel carrier have almost doubled.
The difference between “Shells”
from the BMD-4M is the absence of a turret and the increased height of the cabin, due to which the number of seats has increased.
So in the BMD-4M there are 3 seats for the crew and 5 seats for paratroopers, while the BMD-MDM
accommodates 2 crew members and 13 paratroopers.
In practice, there is 1 more seat; the commander and driver need 1 extra seat in order to use it to take their regular positions. At the same time, the “Shell” is capable of fighting back and supporting paratroopers using two PKT machine guns (the paratrooper’s front-mounted one and the commander’s remote-mounted one). In essence, the “Rakushka”
is an armored bus on caterpillar tracks that can be equipped for medical, staff, and sapper tasks.
During a battle, the BTR-MDM There are 6 hatches for landing troops and crew; the landing-stern hatch, when open, makes for very convenient disembarkation and landing of troops. The landing and crew seats have a common space. The commander has the least free space, since the place is surrounded by optics, various instruments, a remote control for the PKT machine gun, and illumination spotlights. In the front of the armored personnel carrier there are 4 Cloud grenade launchers for creating smoke screens.
Inside the cabin, there are double seats in three rows on each side. The seats have seat belts. If it is necessary to transport large cargo, the seats can be folded and fastened to the sides. Securing oversized cargo is provided by special straps. Cabin "Shells"
can be quickly adapted for transporting the wounded on stretchers using special brackets.
, the Rakushka
armored personnel carrier is equipped with electric furnaces, which heat and circulate the air inside the vehicle.
For the safety of the landing party and the crew, the vehicle is equipped with a fire extinguishing system and an overpressure air system necessary during chemical or radiation hazards. In addition to air filtration, there are half masks for breathing. The armored personnel carrier has a welded cabin-type body made of aluminum alloy. The hull consists of a control compartment, an engine-transmission compartment and a troop compartment. The engine is located at the rear of the machine. The BTR-MDM
has bulletproof armor, which means it can withstand a 7.62 mm armor-piercing bullet at a distance of 50 meters.
The engine on the BTR-MDM
is an atmospheric omnivorous diesel engine UTD-29 with a power of 500 hp (on
the BTR-MD
450 hp), which is capable of “consuming” gasoline, diesel, and kerosene.
The engine works perfectly at high altitudes up to 4500 meters above sea level, which already deserves high attention. The engine is capable of accelerating the BTR-MDM
to 70 km/h.
Cruising speed over rough terrain is 40-50 km/h. The cruising range on the highway is 500 km, and on rough terrain 350 km. “Shell”
can swim at a speed of up to 10 km/h with the help of two water cannons; landing from a ship can be done at sea level 4-5. The engine is well isolated from the cockpit so that smoke and noise from the engine do not enter the cabin, plus the cabin has an additional air filtration system. The armored personnel carrier has an autonomous electric generator in the rear, behind the engine.
The driver-mechanic's position is quite comfortable, since a steering wheel and a four-speed semi-automatic transmission are used as controls instead of levers. There are two pedals: brake and gas. For ease of control while on the move, the seat can be quickly raised to poke your head into the open hatch. During the battle, the driver is guided by three periscopes, while the central periscope TNPT-1 can be equipped with a TKN-ZMB night vision device. In "Shell"
There are no analog instruments, instead there is an LCD monitor displaying all the necessary parameters.
Like the BMD-D, the Rakushka
has a variable ground clearance from 130 mm to 530 mm (the usual working ground clearance is 450 mm), which is needed to reduce the height of the armored personnel carrier so that it can be “stuffed” into the aircraft for subsequent landing.
At the moment, it is planned that the vehicle can be dropped from an airplane along with the crews and troops inside. As of 2017, the army received 30 BTR-MDM "Rakushka-M"
.
The Rakushki-M
base should become a continuation for various other modifications: anti-tank, medical, radar, etc.
By 202, the Russian army plans to receive Rakushka armored personnel carriers. TTX BTR-MDM "Rakushka-M"
| Wheel formula | Tracked chassis, traction on front stars |
| Suspension type | Hydropneumatic |
| Engine | UTD-29, diesel |
| Engine capacity | no data |
| Power | 450-500 hp 30-34 hp/t. |
| Fuel | multi-fuel |
| Volume of the tank | no data |
| checkpoint | semi-automatic, four-speed |
| Dimensions | 6085x3150x2700 mm |
| Track | no data |
| Clearance | 130 mm “during landing”, 450 mm “working”, 530 mm “maximum” |
| Base weight | 11,000 kg |
| Curb weight | 13,000 kg |
| Load capacity | 2000 kg |
| Towed trailer weight | no data |
| Crew | 2 people + 13 paratroopers |
| Speed | maximum 60 km/h, cruising 30-40 km/h, 4.5 for pilaf |
| Power reserve | 350 km cross-country and 500 km highway |
| Fuel consumption | no data |
| Obstacle to be overcome | rise-35 degrees, wall 0.8 meters, ditch 1.5 meters, floats |
| Armor | bulletproof |
| Armament | remote machine gun PKT-1000 rounds + 1000 rounds course machine gun PKT, 4 smoke grenade launchers "Tucha" |
New airborne armored personnel carrier "Object 955"
was created on the theme
“Shell”
based on the chassis
of the BMD-4
.
In various sources it has unofficial designations: BTR-D-3
,
BTRD-3
or
BTR-MD
.
In the future, this armored personnel carrier should replace the BTR-D
. It is a multi-purpose, high-speed armored amphibious airborne and air-transportable tracked vehicle for solving the transport tasks of units and units of the airborne troops and amphibious assault forces. It has increased efficiency and performance characteristics, and the design meets all modern requirements for air transport, airborne landing and landing from naval landing ships, as well as quickly overcoming large water obstacles. The dimensions of the hull in terms of length and width are chosen to ensure the characteristics of the vehicle in terms of high mobility and cross-country ability, as well as transportability, and in height to ensure the requirements for maximum buoyancy reserve and the required carrying capacity.
BTR-MD
It has a cabin-type hull with high side plates and a flat roof, occupying the front and middle parts up to the engine bulkhead. It is made in cross section with a widened upper part having internal fender niches. At the rear of the cabin there is a longitudinal opening with an inclined hatch for the crew to exit. The body has devices for attaching landing gear. The lengths of the control compartments, the middle compartment and the logistics department are in the ratio 2.1:2:1.9.
In the bow of the car in the center there is a driver's seat with controls (including an adjustable steering column), and to the right and left of it there are two universal seats (all seats are placed on an elevated floor), and in the roof there are three upper ones hatch. The driver's middle hatch has three periscope observation devices; the central one can be replaced with a night vision device. In front of the right hatch there is a sight-observation device for conducting aimed fire from a directional machine gun mount (7.62 mm). On the roof of the hull on the left, on the running device, there is a turret with an autonomous closed machine gun mount with a 7.62 mm machine gun, with an external power supply system, sighting and instrument systems and a light source. It has a lifting mechanism, as well as a universal commander-operator seat connected to the upper shoulder strap and an upper hatch.
In the middle compartment along the sides of the car in the lower part there are double side seats that recline towards the side, three per side. There are brackets and removable devices for installing and securing multi-tiered stretchers with wounded along both sides of the vehicle, as well as devices for securing various cargo (boxes with ammunition, containers with liquid substances, etc.) using seat belts with locks. At the top in the central part there are two longitudinal rectangular hatches with covers. In the aft part, on the left there is a compartment with an autonomous power unit, on the right there is an air duct with a retractable air intake pipe, to which a pipe can be connected to ensure air intake in conditions of roughness of the water surface up to three points. The external air purification system with a filter and ventilation unit is located on the starboard side. Each side of the troop compartment has one lockable loophole with a ball mount for firing personal weapons.
In the engine-transmission compartment there is a turbocharged boxer diesel engine located along the axis of the machine, with an ejector-fan cooling system and in the same block with it a central gear and rotation mechanism, which has a reversible hydromechanical twin-shaft gearbox. Water-jet propulsors with an impeller with a diameter of 340 mm are made with spring-loaded dampers and on-board ejection pumping devices. The drive to the water cannons is carried out from the reversible shaft of the gearbox.
Chassis BTR-MD
with a rear drive wheel, consists (on board) of five single-pitch support rollers and four support rollers. The air springs of the suspension, located inside the body, have a hydraulic device for steplessly changing the vehicle's ground clearance with fixed clearance positions: minimum, working, maximum. Each air spring has a hydraulic shock absorber built into it. The caterpillar is small-linked, with sequential rubber-metal hinges.
Left front view of the BTR-MD in the stowed position (top) and left front view of the body of the armored personnel carrier:
1, 3, 4 – landing hatches in the roof; 2 – antenna; 5.9 – ejectors of the engine cooling system; 6, 7 – spare parts boxes; 8 – devices for attaching landing equipment; 10 – drive wheel; 11 – caterpillar; 12 – support roller; 13 – support roller; 14 – on-board ball valve; 15 – viewing device; 16 – guide wheel; 17 – commander’s cupola hatch; 18 – commander’s cupola on a ball bearing; 19 – machine gun mount searchlight; 20 – remote machine gun installation; 21 – driver’s hatch; 22 – wave-reflective shield; 23 – bracket for installing a forward machine gun; 25 – roof sheet; 26 – aft hatch opening; 27 – cover of the air intake compartment; 28 – tank-roof; 29 – removable roof sheet; 30 – back sheet; 31 – hole for installing a fan; 32 – hole for water flow pipe; 33 – hole for final drive; 34 – cover of the electrical unit compartment; 35 – middle side top sheet; 36 – side bevel of the bottom (redan); 37 – lower side sheet.
a1, a2, a3, a4
– angles of inclination of the lower sheets of the body to the horizon;
L
– body length;
Vk
– body width;
Hk
– body height;
H
– body height in MTO.
The armored vehicles of Russia and the world, photos, videos, watch online, were significantly different from all their predecessors. To provide a large reserve of buoyancy, the height of the hull was noticeably increased, and to improve stability, its cross section was given a trapezoidal shape. The required bullet resistance to the hull was provided by rolled cemented armor with an additionally hardened outer layer of the KO brand (“Kulebaki-OGPU”). In the manufacture of the hull, armor plates were welded on the inner soft side, and special stocks were used to facilitate assembly. To simplify the installation of units, the upper armor plates of the hull were made removable with a seal on fabric gaskets lubricated with red lead.
Armored vehicles of the Second World War in which the crew of two people was located near the longitudinal axis at the back of each other's heads, but the turret with weapons was shifted 250 mm to the left side. The power unit is shifted to the starboard side in such a way that access for engine repairs was possible from inside the tank's fighting compartment after removing the safety partition. At the rear of the tank, along the sides, there were two gas tanks with a capacity of 100 liters each, and directly behind the engine there was a radiator and a heat exchanger, washed by sea water when moving afloat. At the stern, in a special niche, there was a propeller with navigable rudders. The balance of the tank was chosen in such a way that when afloat it had a slight trim to the stern. The propeller was driven by a cardan shaft from a power take-off mounted on the gearbox housing.
Armored vehicles of the USSR in January 1938, at the request of the head of the ABTU D. Pavlov, the tank’s armament was to be strengthened by installing a 45-mm semi-automatic gun or a 37-mm automatic gun, and in the case of installing a semi-automatic gun, the crew was to be increased to three people. The tank's ammunition was supposed to consist of 61 rounds for the 45 mm cannon and 1,300 rounds for the machine gun. Design Bureau of Plant No. 185 completed two projects on the “Castle” theme, the prototype of which was the Swedish Landsverk-30 tank.
The Wehrmacht armored vehicles did not escape troubles with engine boost. To what has been said, we can only add that this crisis was actually overcome only in 1938, for which the tank received not only a forced engine. To strengthen the suspension, thicker leaf springs were used. Rubber tires made of neoprene, a domestic synthetic rubber, were introduced, the production of tracks from Hartfield steel by hot stamping began, and high-frequency-hardened fingers were introduced. But all these changes to the tank were not introduced simultaneously. The tank hull with inclined armor plates could not be manufactured on time. However, the conical turret with improved protection was submitted on time, and the tank with the same hull, reinforced suspension (due to the installation of thicker leaf springs), a forced engine and a new turret entered testing at the NIBT test site.
Modern armored vehicles went under the code T-51. It retained the process of transition from tracks to wheels, like the prototype, by lowering special levers with wheels without a person leaving. However, after adjusting the requirements for the tank, making it a three-seater (it was decided to retain backup control for the loader), and strengthening its armament to the BT level, it was no longer possible to implement the Landsverk-type wheel drive. In addition, the tank's wheel drive transmission was overly complex. Therefore, soon work on the “Castle” theme was carried out on the T-116 tank, in which “change of shoes” was carried out according to the BT type - by removing the track chains.
To participate in hostilities, she was born some time after its creation. Back in 1897 in Russia, the inventor Dvinitsky proved the possibility of installing a rapid-fire small-caliber gun on a vehicle. Despite the fact that this was later confirmed by successful tests, the commission from the Artillery Committee did not recommend the construction of even a prototype of a new combat vehicle. How and when did the first armored vehicles appear? What were the early car models and what are they like today? More on this later in the article.
Historical facts
The first combat-ready armored vehicle was the “military motor car.” It was demonstrated in London in 1902, on April 4th, by an engineer from England, Simms. This project was developed by the summer of 1898. The car was protected by a six-millimeter open-type armored hull, and three machine guns were covered with shields. The power of the four-cylinder engine, running on heavy fuel, reached 16 hp. With. However, the British War Ministry was as short-sighted as the Russian one in rejecting Simms' idea. But in the same year, 1989, a French company built a batch of semi-armored armed trucks.
BTR-MDM
The BTR-MDM is adapted for operation in all conditions of combat use, in a wide variety of climatic conditions. The vehicle is intended for transportation in airborne units and air assault formations of the naval marines:
- personnel (landing force),
- ammunition,
- spare parts.
In 2008, in accordance with the tactical and technical specifications approved by the head of the GABTU of the Russian Defense Ministry and the commander of the Airborne Forces, the development of the BTR-MDM began as part of the Rakushka-M program. In a short time, design documentation was developed, and a prototype armored personnel carrier was manufactured for preliminary tests. All work was carried out at the own expense of the machine-building and industrial group “Tractor Plants”.
The basic product in the development of the BTR-MDM was the BTR-MD armored personnel carrier produced by the Volgograd Machine-Building Company.
Spoiler: About the BTR-MD Shell
BTR-MD "Shell"
Sometimes unofficially called BTR-D-3, BTRD-3.
BTR-MD "Rakushka" (GBTU Index - Object 955) is a Russian airborne armored personnel carrier.
Created in the design bureau of the Volgograd Tractor Plant. The armored personnel carrier is based on the BMD-3 airborne combat vehicle. The main purpose of the vehicle is to replace the BTR-D in the troops. The dimensions and weight of the vehicle ensure air transportability and rapid overcoming of water obstacles. Main tactical and technical characteristics of the BTR-MD “Rakushka”
| Weight, no more, t | 13,2 |
| Crew, people | 2 (commander and driver) |
| Load capacity, t | 2 |
| Number of seats, pcs. | 13 |
| Specific power, kW/t (hp/t) | 22,3 (30,3) |
| Maximum engine power, kW (hp) | 331 (450) |
| Average speed on dry dirt road, km/h | 45-50 |
| Maximum speed, km/h | |
| on the highway, no less | 71 |
| afloat, no less | 10 |
| Airborne landing: | |
| airplanes, type | IL-76(M, MD), AN-124 |
| helicopter, type | MI-26 (on external sling) |
The armored personnel carrier is the basis for numerous upgrades both now and in the future.
Spoiler: About the BTR-MD Shell
Options for loading the usable area of the BTR-MD
| Landing | Wounded |
| Ammunition, property | Fuels and lubricants |
| Volgograd Machine-Building LLC. |
The modernization, which included unification of the chassis components with the BMP-3M and BMD-4M, was carried out in order to improve the main tactical and technical characteristics and reliability. The following borrowed from the BMP-3M are installed on the vehicle:
|
|
“The design of the BTR-MDM makes it possible to equip it with various interchangeable equipment, which is why it is intended to become the basic vehicle on the basis of which in the near future a whole family of military equipment for the Airborne Forces will be developed - command and staff vehicles, communications and control vehicles, medical, logistics support and others,” reports TASS, citing its source.
Video: Military tests of BMD-4M in low temperatures
https://youtube.com/watch?v=ClH64fR-aGQ
In the Ryazan region, airborne troops mastered a new combat vehicle
Video: Military operational tests of the modernized Rakushka armored personnel carrier
https://youtube.com/watch?v=4s4iOkqY4eA
The modernized Rakushka armored personnel carrier is undergoing military operational tests. Tula paratroopers are mastering the latest armored personnel carrier. Conditions are as close as possible to combat conditions. The machine is tested for strength to identify all possible defects.
- — In 2020, paratroopers will receive two battalion sets of BMD-4M and the Rakushka armored personnel carrier;
- — Adjustment of technical requirements for the production of BMD-4M;
- — Vladimir Shamanov personally took the helm of the BMD-4M;
- — Planned re-equipment with the BMD-4M will begin in 2020.
| Next > |
Description
The main characteristics of the vehicle and its design ensure the performance of the functions assigned to the BTR-MD. Its dimensions are perfect for possible air transportation and landing, the power plant provides a high degree of maneuverability and speed, the BTR-MD can accommodate 13 paratroopers and two crew members. The Rakushka can also transport ammunition, spare parts, equipment, evacuate wounded soldiers from the battlefield, and, in addition, after a slight modernization, it can serve as a headquarters vehicle, communications vehicle and logistics support vehicle.
The vehicle's armor protects against small arms fire and shrapnel.
The BTR-MD is a multi-purpose vehicle and its main task is transport. The armored personnel carrier must deliver the maximum number of paratroopers to the desired point at maximum speed. And its technical characteristics allow it to cope brilliantly with this task. It differs from the base vehicle in its large hull dimensions and the absence of a turret.
300w" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: bottom; max-width: 100%; height: auto;" width=”600″ />
The “shell” is made according to a “tank” layout: its engine and power compartment are located at the rear, and the control compartment is in the front of the vehicle. The tower is missing. In the middle part of the vehicle there is space for troops and crew. In the control compartment there is a seat for the driver, measuring instruments and controls for the vehicle, as well as two more seats: for the commander of the vehicle and one of the paratroopers.
In the front of the vehicle, on the top, on the left side, there is a small turret in which a PKT machine gun with observation and aiming devices is mounted. Another PKT machine gun is located on the right side of the front of the hull. In the front part of the hull there are three hatches through which the crew and troops can be evacuated.
In the middle part of the hull there are embrasures with ball mounts and observation devices that can be used for firing from personal weapons.
300w, 84w" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: bottom; max-width: 100%; height: auto;" width=”650″ />
In the middle part of the BTR-MD there are places for landing, two rows of double seats under each side. The paratroopers sit facing the direction of travel of the armored personnel carrier.
There are also mounts available for stretchers with wounded people. The seats have a special design that increases protection when the vehicle is blown up by a landmine or mine. There are electric heaters in the middle part of the car, which create very comfortable conditions in the car. This fact is especially important when using BTR-MD for transporting the wounded. An armored personnel carrier can very quickly be converted into an ambulance or a vehicle for transporting goods. It can very quickly install medical equipment, stretchers, or securely secure cargo.
At the rear of the vehicle there is a landing hatch, as well as a power compartment with an engine. “Rakushka” is equipped with a turbocharged diesel engine. This allows the car to reach speeds of more than 70 km/h on the highway. Very good for a tracked armored personnel carrier. The BTR-MD is a floating vehicle. On water it can reach speeds of more than 10 km/h. The movement is carried out by water-jet engines, which are installed in the rear of the vehicle. The average speed over rough terrain can reach 50 km/h.
The car has a very decent reserve of buoyancy. This allows her not only to cross water obstacles, but also to land from ships and even overcome the surf. The wave-reflective shield is located in the front part of the housing.
The car can change the ground clearance. It has three standard positions: maximum, working and minimum.
Modifications of BTR-MD
This machine became the basis for numerous modifications. On its basis, machines were created that perform special functions. MRD-U is used to create tactical air defense systems. MRU-D performs the functions of a battery command post. On the basis of this BTR-MD, the BMM-D1 and BMM-D2 medical armored personnel carriers (can transport up to six wounded), as well as the VDVBMM-DZ medical vehicle, were created.
300w" style="margin: 0px; padding: 0px; vertical-align: bottom; max-width: 100%; height: auto;" width=”600″ />
Goals and objectives for application
Rakushka armored personnel carriers are designed as a landing vehicle, the main purpose of which is to support units in any combat conditions.
The tasks of an armored personnel carrier include:
- support for infantry formations, cover;
- transportation of goods, supply of units;
- removal of the wounded, conversion into an ambulance;
- organization of a command center or radio communication center.
The key tasks of the armored personnel carrier remain the delivery of troops to specified positions. The new vehicle allows you to transport soldiers under your own power, to land from the air, as well as to force water obstacles and land from the sea overcoming the surf line. The last factor makes it a full-fledged amphibian.
The first armored personnel carriers of Russia
The construction of these machines from the First World War was led by Dobzhansky. They were designed at the Russian-Baltic Plant. The carrying capacity of the vehicles reached two tons. The Colonel was familiar with the French armored truck manufacturing process. Moreover, Dobzhansky even participated in their design. In Russia, armament and armoring of vehicles was carried out at that time near St. Petersburg, in Kolpino, at the Izhora plant. Due to the fact that the front needed protected vehicles, the chassis of serial trucks was simply sheathed with chromium-nickel rolled sheet steel, which could not be penetrated by a pointed bullet from two hundred steps. The protection was attached to the body with rivets. During construction, the rotating tower had to be abandoned. Three Maxim machine guns were used as weapons. They were installed in the embrasures of the frontal sheet and sides.
Post-war technology
The experience of the 1944-1945 offensives showed that support for armored units was needed in the form of additional motorized infantry units. The best solution was the use of all-terrain vehicles, which had light armor that protected soldiers from shrapnel and small arms bullets. The development of the first such car was carried out under the leadership of Rubtsov, the leading designer at that time. The development of the first domestic armored vehicle, the index of which was “object 141,” was carried out in the design bureau of the Gorky Automobile Plant on the basis of the GAZ-63. The two-axle model with all wheelbases was designed to transport eight infantrymen. The machine had an open body on top, which was welded from sheets of 6-8 millimeters. The rear wall was equipped with a door for the landing; for the crew, entrances were equipped on the sides of the vehicle.
Special purpose vehicles
The sanitary transport armored personnel carrier (armored personnel carrier) was designed at the Izhora plant in 1939. It was intended to transport troops, wounded and various cargo. It never went into mass production. It was created on the basis of a GAZ-AA truck with a “box-shaped” body welded from six-millimeter armor plates. For boarding the crew, which consisted of troops and two people, there were two doors on the sides of the hull and one in the rear wall. The total weight of the car was 5.24 tons. The engine power of the car was 40 hp. s., and the speed reached forty kilometers per hour. Increased cross-country ability was ensured by removable large-link chains. When driving on good roads, they were attached above the rear wheelbase along the body. The car was equipped with a radio station. The capacity of its fuel tanks is more than one hundred liters. This volume provided a highway traffic reserve of 250 kilometers.
Design and structure of the amphibian
Key differences between the basic and modified versions
The body of the Rakushka armored personnel carrier is made of welded armor plates. The machine is divided into three compartments. In the front is the control room, where the driver, commander and one of the paratroopers are located. The armored personnel carrier is made according to the design of a tank, so the engine is located in the rear.
The middle part is intended for transporting troops. Paired seats are located facing the direction of travel, three pairs on each side. There is space for cargo in the niches above the tracks. Also in the body there are loopholes for firing from the vehicle.
Surveillance and communications equipment
Surveillance of the surroundings is carried out from the driver's seat through three periscope devices. If necessary, the central one is replaced with a night vision device. Additional tracking is carried out from the airborne unit through loopholes. Internal communication and switching are provided by the R-174 system.
Taking into account the weapons, aiming is ensured from the shooter's position. The turret installation is also equipped with a TNP3VE01-01 sighting system for guidance and automatic firing from the commander’s position. Through this device he can also monitor the area.
Main weapons
The armament of the Rakushka armored personnel carrier is represented by a 7.62 mm Kalashnikov machine gun. Power is provided by two boxes of 1000 rounds of ammunition, united by a single path. The modified version has an additional machine gun on the right front side.
Armored personnel carrier armor protects soldiers from bullets and shrapnel. The undercarriage is protected to overcome mines.
Means of camouflage
Most of the equipment elements of the Rakushka armored personnel carrier are borrowed from the BMP-3. These also include means of camouflage. In addition to the camouflage color, the armored personnel carrier is equipped with “Tucha” smoke grenades.
History of the model
BTR-MDM "Rakushka"
The task of developing a new multi-purpose landing vehicle was set before the designers back in 1992. The difficult economic situation of the country and lack of funding for the army led to the freezing of the project. As a result, active work on it began only in 2008.
The key task of the new armored personnel carrier was to replace the outdated Soviet amphibious armored personnel carrier, produced back in 1974. The new vehicle had to meet the requirements of modern equipment and weapons, and also take into account the specifics of landing operations.
In 2020, armored personnel carriers began to enter service with the army, and from that moment on, their photos began to appear on the Internet. As of 2020, there were already 30 such machines. It is expected that by 2025, about 200 armored personnel carriers of this line in various modifications will enter service with the landing force. As a result, the BMD-4M and Rakushka armored personnel carriers will become the basic landing equipment.
Links
- Armored personnel carrier BTR-MD "Rakushka" (object 955) (BTRD-3) (Russian) (inaccessible link - history
). Retrieved February 18, 2012. - Armored personnel carrier BTR-MD (Russian) (inaccessible link). Volgograd Machine-Building LLC. Retrieved January 24, 2013. Archived February 3, 2013.
- Armored personnel carrier BTR-MDM (Russian). JSC SKBM. Retrieved January 29, 2014.
- BTR-MDM “Rakushka” and BMD-4M “Gardener”: why the latest vehicles of Russian paratroopers are dangerous // RIA, September 2017; participate in West 2017
Advantages and disadvantages
Armored personnel carrier "Rakushka" during exercises
The key advantage of the BTR-MD is its versatility. The vehicle is designed for almost any operating conditions, which in many ways brings it closer to an infantry fighting vehicle. At the same time, the design of the armored personnel carrier allows it to be quickly converted into any center - from an ambulance to a command headquarters.
The vehicle borrowed the most successful design solutions of previous generations of armored personnel carriers and infantry fighting vehicles. Regarding the shortcomings, no significant aspects have yet been highlighted. This is due to the short service life, which does not allow an objective assessment of the project in the long term.
Multi-purpose armored personnel carrier (landing) BTR-MD "Rakushka"
- multi-purpose, mobility
- airborne, floating
- high cross-country ability, maneuverability
- improved performance
- modernization opportunities
BTR-MD "Shell"
(GBTU index - Object 955) - Russian airborne armored personnel carrier. Created in the design bureau of the Volgograd Tractor Plant. Sometimes unofficially called BTR-D-3, BTRD-3.