Checking the coolant temperature sensor (CTS) is a work aimed at determining the performance of the unit and its ability to respond to changes in temperature conditions.
To complete the work, you can go in two ways: immediately dismantle the device or first carry out a check without removal.
When choosing the first option, you will need a regular wrench of the required size (usually “19”), but on some foreign cars - a 20, 21 or 22 socket.
First make sure that the DTOZh receives a voltage of 5V (from 5 to 12 on some models). If it fits, you can proceed with the rest of the test.
Below we will consider in detail all the diagnostic methods, the causes of sensor failure, features of its location and other features using the example of VAZ cars with 8 and 16 valves, Kalina, Gazelle, 2115, 2114, Renault Logan, Lada Priora and Chevrolet Niva. The methods described below are also suitable for most other brands of cars.
Design and principle of operation
The DTOZh temperature sensor is a resistor (thermistor) that reacts to the temperature of the antifreeze in the engine cooling system. Information about the resistance of this element is transmitted to the ECU, which decides to change the settings in the engine operation.
The information obtained is used by the ECU to determine the steps of the idle speed regulator to optimally adjust the required volume of the fuel mixture.
The peculiarity of DTOZH is that in the cold its resistance increases, and when heated, on the contrary, it decreases.
So, when reaching 130 degrees Celsius, the resistance parameter is 70 Ohms, and at minus 40 degrees - 100.7 kOhms.
The thermistor is controlled by applying +5 V voltage to it from the controller.
The potential passes through a classical resistor with constant resistance (R).
The antifreeze heating level is calculated based on the voltage drop across the DTOZh with variable R (Ohm). In this case, the drop will be large on a cold engine, and low on a warm engine.
What is a coolant temperature sensor (CTS)
Purpose
There are many sensors in a car. All of them control the operation of various systems of the car and its engine. If the sensors give incorrect readings, the performance of the vehicle is jeopardized. The same can be said about DTOZH.
DTOZH is designed to maintain stable operation of the internal combustion engine (hereinafter referred to as ICE). Due to DTOZH, the car warms up faster and reaches too high temperatures less often. Some people confuse the DTOZH with the coolant temperature gauge sensor. These are two completely different devices.
The DTOZH provides its readings to the electronic engine control unit, and the second sensor notifies the driver about the temperature of the working fluid in the cooling system. The failure of the second sensor does not lead to serious consequences, unlike the first.
Speaking about DTOZH, we should also mention the purpose of the engine cooling system, since the operation of these two units is inextricably linked. Most often, a liquid cooling system is used, the main task of which is to remove heat from the engine.
In addition, the system also has the functions of cooling the oil in the lubrication system, the air that circulates in the turbocharging system, exhaust gases, and the working fluid of the gearbox. It also has the function of heating air in ventilation and heating systems.
Design and principle of operation
The design of the DTOZH resembles a resistor. The design of the sensor provides for a change in its resistance to electric current when the ambient temperature fluctuates. These changes are recorded and used to issue commands to the internal combustion engine.
The predecessors of modern DTOZH were thermal relays. Thermal relays were installed in injection systems. When the contacts were in the open position, the engine became hot. If the contact closes, it means the engine has already warmed up enough (reached operating temperature).
The design of modern DTOZH is based on a thermistor, which establishes the dependence of resistance on temperature. The thermistor is based on cobalt and nickel oxides. As the temperature rises, the number of free electrons in these substances increases, due to which the resistance drops.
Some thermistors in DTOZH are characterized by a negative temperature coefficient. In this case, the thermistor produces maximum readings when the engine is cold. A voltage of about 5 volts is supplied to the sensor. After this, as the power unit warms up, the resistance decreases. The engine electronic control unit (hereinafter referred to as ECU) monitors voltage changes and calculates the fluid temperature. After the engine warms up, the ECU begins to lean the fuel mixture. A malfunction of the DTOZH can also lead to an erroneous enrichment of the fuel mixture. The result of this will be increased atmospheric pollution and premature failure of candles.
If the engine speed at startup is insufficient, the engine may stall. A floating command from the ECU to increase the speed can prevent this. To maintain drivability while the engine is starting, the recirculation valve must be closed until the engine reaches its set operating temperature.
Here, the result of a DTO malfunction will be floating engine speed. The engine may also stop. The ignition angle also depends on the functioning of the sensor, since this parameter is regulated by the system. The emission of harmful gases with this adjustment is significantly reduced. Ultimately, engine power and thrust, as well as the level of fuel consumption, directly depend on the operation of the DTOZH.
Thus, DTOZH is very important for the correct functioning of the car.
Sensor installation location
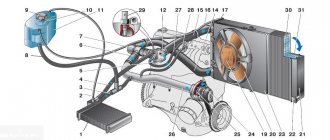
Where is the coolant temperature sensor located in a car? The location of the DTOZh installation differs for different models. Most often it is installed in the cylinder head near or on the thermostat housing. It is mandatory to locate the sensor near the outlet pipe through which the coolant flows back into the radiator. This arrangement is necessary for the accuracy of data transmission to the ECU.
Types of sensors
DTOZH are classified according to the principle of dependence on changes in resistance:
- DTOZH with negative temperature coefficient. The principle of operation of such sensors is that the internal resistance decreases as the temperature increases and vice versa.
- DTOZH with a positive temperature coefficient. The operating principle is the opposite of the previous type of sensors. In these sensors, the resistance increases as the temperature increases.
Currently, the first type of sensor is the most popular. Sometimes there are two sensors in a car: the main one and the additional one.
Where is
To check the DTOZH, you need to know its location. Please note that the location of the sensor may vary depending on the make/model of the machine.
Most often, the thermistor is mounted between the cylinder head and the thermostat or on the coolant outlet pipe.
But on some cars it is installed on the radiator pipe.
Externally, the device looks like a small element with a thread, with which the DTOZH is screwed into a special hole. In this case, the regulating element itself is located in the antifreeze and controls its temperature.
In certain cars, for example, the BMW E39, there may be two DTOZH. One controls the heating of the antifreeze and is installed at the outlet of the engine, and the second is located behind the radiator. To remove you will need a 22 key.
This type of installation allows you to control the temperature in different areas and thereby take action faster.
Note that two sensors are installed on powerful / expensive cars, where the temperature parameter is of key importance.
In this case, the control unit must have appropriate programs. For more information, please refer to your vehicle's manual.
Functionally, the sensor is very reliable and breaks down in rare cases. Most often it shows false information. Sometimes other damage is possible, for example, chafing of wires or poor contact quality.
As for the features of the location of the DTOZH on different models, we will dwell on this issue below.
What it is
A standard coolant sensor is a device that is used to measure the antifreeze present in an internal combustion engine. The recorded parameters of the sensor are returned using signals to the engine control unit, which in turn uses this data to adjust the required amount of fuel and a certain ignition angle.
In some car models, the alarm can be used to switch to an electric ventilation cooling system. Let's say this is how the car coolant temperature sensor works in the VAZ-1117 (and number 1119) Lada Kalina, Lada Priora and Granta, Lanos, Toyota Camry (Toyota).
Photo – coolant temperature sensor VAZ 2010
On many foreign cars, the device readings are also displayed on the dashboard. For example, in Volkswagen Golf, Subaru, Mazda, Opel Vectra and Passat, BMW, Ford Focus, Daewoo Nexia , Fiat (Fiat), Audi (Audi) and others.
As the sensor temperature is measured, its resistance level may change. There are two types of such sensors depending on changes in resistance:
- Sensors with a negative temperature coefficient work on the principle: internal resistance decreases as temperature increases and vice versa;
- Positive temperature coefficient sensors. As the temperature rises, they increase resistance.
Almost all cars have warning lights with a negative coefficient. Negative coolant temperature sensors are available in Gazelle, GAZ, MAZ, KamAZ, Mercedes, Nissan, Niva, Mitsubishi, OKA, Peugeot, Volvo, Renault Logan, OPEL Astra, Geely, ZMZ.
Photo – temperature sensor
Symptoms of a problem
To take measures to control the coolant temperature sensor, it is necessary to identify problems in this unit in time.
But it is worth considering that the signs discussed below may indicate other malfunctions of the power unit.
This is why additional diagnostics may be required to obtain an accurate result.
It is also important to understand what part the DTOZH takes in the operation of the engine:
- Informs the driver in real time about the coolant temperature.
- When the engine reaches a threshold temperature value, the ECU, having received information from the coolant sensor, turns on the forced cooling fan, as a rule, this is about 100 0C.
- Participates in the process of increasing idle speed by enriching the fuel-air mixture on a cold engine.
- When the car is moving, the ECU generates general information about the operation of all systems based on the data received from the sensors and, based on this data, forms the correct fuel-air mixture. The coolant temperature sensor also takes part in this process.
Primary symptoms of failure:
- The Check Engine light on the dashboard comes on. To obtain more accurate information, it is better to scan the ECU and look for errors, for example, through an ELM327 auto scanner connected to a smartphone. See error codes below.
- The engine starts and immediately stalls.
- Malfunction of the fan in the radiator. The malfunction may manifest itself as a refusal to turn on when it heats up or operation even after the motor has cooled down. When the DTOZ is turned off, the electronic control unit of the machine perceives the problem as a break and turns on the fan.
- The appearance of dark or gray-black smoke from the exhaust pipe.
- Increased "gluttony" of the car. This is due to the fact that incorrect information is supplied to the ECU. Accordingly, the “brains” of the machine cannot determine the volume of displacement required to maintain optimal temperature conditions.
- Antifreeze leaking from under the DTOZh housing. This problem can be determined by visual inspection.
- A hot engine stalls. The problem may occur when the maximum temperature is reached. In this case, the type of coolant filled does not matter.
- The power unit heating indicator on the dashboard does not work.
- Engine malfunctions. The problem may manifest itself as stopping at low speeds, difficulties starting in winter, hesitation when operating at idle, etc.
- The coolant boils, but the instrument panel displays the temperature within normal limits.
- Increased engine heating time, etc.
The problems discussed above can occur one at a time or in combination, but in most cases they indicate a malfunction of the power unit. However, the antifreeze temperature sensor is not always the main cause of the malfunction.
Operating principle of the sensor
The vehicle's control unit sends a regulated voltage (9 volts) directly to the coolant temperature gauge sensor. Depending on the drop in voltage at the contacts of the alarm, the resistance will drop, which will immediately be detected by the control unit.
In this case, the automotive computer or mechanical system will be able to calculate the engine temperature and then (using data from other devices) apply lookup tables to make adjustments to the engine drives, i.e. change the level and flow of fuel or the ignition timing.
Photo - diagram of the coolant temperature sensor
The resistance of the coolant sensor is highly dependent on external factors. This is the air temperature outside the car, various drive features. For the most correct operation of the alarm, you need to use coolant recommended for a certain time of year; it is expensive, but it prolongs the life of your car.
Video: checking the engine temperature sensor
How to check without removing it from the car
If you suspect a faulty DTOZH, it is not necessary to remove it from the car. All manipulations can be done without dismantling using a tester or diagnostic device. Let's consider each of the methods in more detail.
Pre-check
To check the temperature meter, start the car and let the engine warm up at idle to 90 - 95 0C.
Disconnect the connector from the sensor and notice how the arrow on the instrument panel behaves:
- if the arrow remains in place, then you need to check the meter itself or the electrical circuit going to the device (more on this later);
- if the arrow goes down, then check the fuse. If it is intact, and when the contact is shorted to ground, the arrow jumps, then the sensor is faulty.
Multimeter
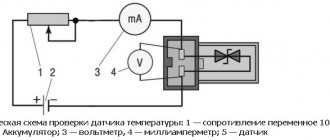
The simplest method to check the coolant temperature sensor is to use a tester.
First, we check the voltage; for this, set the multimeter to the “Measure constant voltage up to 20V” mode.
- Disconnect the connector from the meter.
- Turn on the ignition.
- Connect the positive wire of the device to the “+” connector, and short the second contact of the tester to the motor. The device should show between 4.8 and 5.2 V.
When working on a hot engine, be careful not to touch the metal surface, so as not to burn yourself and damage the measuring device.
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Discard the contacts from the sensor.
- Set the resistance measurement mode on the multimeter.
- Measure the parameter between the terminals.
- Compare them with the tabular data that can be found in your vehicle's repair and maintenance manual.
On some car models, it is very difficult to get to the sensor connectors and you will have to remove it.
To minimize antifreeze losses, unscrew the expansion tank cap to relieve pressure in the system. Then tighten the plug again.
Exact resistance specifications may vary depending on model.
As an example, we give several resistance parameters for a VAZ 2110 car.
Table 1.
| Temperature 0C | Ohm resistance |
| +100 | 177 |
| +80 | 332 |
| +60 | 677 |
| +40 | 1459 |
| +20 | 3520 |
| +10 | 5670 |
| +5 | 7280 |
If the DTOZH produces erroneous information, it may need to be removed for a more detailed check, and subsequently replaced.
Diagnostic tool
If an engine error appears on the dashboard, it is worth checking the ECU for errors related to the temperature sensor.
The most convenient option is to use an ODB2 scanner. To avoid high costs, you can use a simple model of Scan Tool Pro Black Edition or ELM327, which we wrote about above.
The general algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Inspect the DTOZH for damage to the wires or the appearance of rust.
- Connect the device and read the errors (see the link above for how to do this).
- Codes P0115, P0117. P0116 or P0118 indicate the presence of malfunctions in the functioning of the sensor.
The capabilities of the model discussed above allow you to look at the operation of the sensor online, as well as look at the functioning of other components: gearbox, transmission, ESP, ABS and others.
The device works with all diagnostic software and works without loss of communication. Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are used for communication.
Replacing the sensor
To begin repairing the coolant sensor, you need to determine its location. Most often it is installed near the thermostat or radiator; in some cases, the on-board computer uses readings from both sensors or one of them, depending on the make and model of the car. For example, this is how the sensor is located in Renault, Chevrolet, Citroen, Skoda, Chery, KIA, Subaru Impreza.
There are several ways to help you find out that the sensor needs to be replaced. If all other systems in your car are working, then the dashboard will indicate a malfunction using a light signal. If the car has computer control, then the problem can be determined by deciphering the combination on the monitor.
Photo - temperature sensor on the dashboard
Depending on the year of manufacture of the car, as well as its brand, many car enthusiasts note an increase in engine fuel costs. But at the same time, you need to understand that diesel cannot be defined this way (UAZ, PAZ and others). If you have a mechanic and not a computer control system, then here are the signals that you need to buy a new coolant temperature sensor:
- The car began to consume more fuel than usual;
- When the car starts and the engine reaches its maximum temperature, it stalls;
- There were problems starting up;
- Black smoke comes out of the muffler pipe.
Let's look at how to replace the G62 coolant temperature sensor on a Kia Sportage with a 2-liter engine. Similar instructions will also be useful when repairing Acura, BMW, Buick, Chevrolet, Ford, Toyota, Volkswagen, VAZ 2110/2112 injector, Renault Grand Scenic and others.
Photo - different coolant temperature sensors
In this model, if the coolant sensor breaks down, alarm 117 is received, which indicates that further operation of the device is impossible and it is necessary to install a new alarm. In Chevrolet the number PO118 is a high signal. The general scheme of work looks like this:
- To get to the sensor, you need to remove the air duct that cools the air filter housing and is connected to the radiator using two bolt connections and an air supply hose. Unscrew the bolts and remove the clamp, carefully remove the entire system. Disconnect the electrical wires from the sensor to correctly measure the resistance. Set the multimeter to ohmmeter mode and set the value to 1000 ohms. Connect the device pins to the positive and negative terminals. Normal resistance should be within 2700 Ohms when the motor is off. To check the sensor with the engine running, you need to move the tester away from the rotating parts of the car;
Photo - checking the sensor with a multimeter - Once you are sure that the temperature sensor needs repair, you need to disconnect it from the engine. To continue removal, you must first drain the antifreeze fluid from the radiator using the drain valve. Afterwards, check the radiator and sensor contacts again and unscrew the adjusting bolt as in the photo;
Photo - sensor removal - Assembly is done in reverse form. It must be remembered that practically the main characteristic of the coolant temperature sensor is the material of the washer. If the washer is copper, then the thread of the alarm does not need to be treated with sealant; otherwise, be sure to lubricate the device.
Photo – copper temperature sensor
Checking the removed DTOZH
For a more accurate check, it is recommended to remove the device from the vehicle. To do this, you need to let the engine cool, and then drain the coolant from the system.
To remove it, you only need a key “19” (20, 21, 22), with which you can unscrew the sensor and remove it together with the ring.
At the same stage, it is worth assessing the condition of the device itself, its threads, cleaning and lubricating it.
The same operations can be done with respect to the sensor itself. After dismantling is completed, you can proceed directly to work.
Checking with a thermometer
After dismantling, you can check with a thermometer. This option provides the most accurate information, so it is recommended for most cases.
The algorithm of actions is as follows:
- Prepare a vessel and pour water into it.
- Use a boiler to heat water.
- Prepare your multimeter for measurements.
- Immerse the sensor element in the liquid.
- Provide the ability to connect a multimeter to the contacts.
- Place a thermometer in the water to monitor the temperature. It is better to use the electronic version, which provides greater accuracy.
- Heat the water and take measurements for different temperatures, for example, from +5 degrees Celsius and above in steps of “5”.
- Fill out the table containing the resistance parameters in relation to the set temperature.
- Check with the information provided in the vehicle manual.
Of course, inaccuracies may occur during the measurement process. The error depends on several factors: operating conditions and the characteristics of a particular DTOZH. In particular, even in devices of the same model, the resistance parameter may differ.
Without thermometer
If desired, checks can be made without using a water temperature meter.
In this method, you can act according to the principle discussed above, but with minor restrictions.
The general algorithm is:
- Boil the water.
- Install the DTOZh sensitive element into it.
- Measure the resistance at the terminals.
At a temperature of about 100 degrees Celsius, the resistance should be about 177 ohms. But here you need to take into account possible errors.
In particular, at the time of measurements, the temperature may change downward.
The disadvantage of the method is that the test is performed only at one temperature point.
Performance test
To check the thermal sensor, it will have to be removed from the car. To do this, follow these steps:
- Allow the engine to cool to 40-50 °C to avoid burning your hands during operation. Partially or completely drain the antifreeze from the cooling system.
- Disconnect the battery from the on-board power supply by removing the negative cable.
- Disconnect the block with wires from the thermoelement.
- Unscrew the part using a wrench of the appropriate size.
If the device is installed at the top point of the system, then it is not necessary to empty it entirely; it is enough to drain a third of the liquid into the container. All antifreeze must be drained when the thermocouple is located at the bottom of the radiator.
To carry out the tests you will need:
- a multimeter or other device capable of measuring circuit resistance;
- a small container for water (you can use a regular glass);
- thermometer with a scale up to 100 °C.
A thermometer is essential if you want to make accurate resistance measurements by referring to the reference chart for your vehicle. When there is no table, the serviceability of the part is checked without a thermometer according to its operating principle: the hotter the water in the glass, the lower the resistance at the contacts should be.
Before checking the coolant temperature sensor under heating, test its contacts with an ohmmeter. It may happen that the device has burnt out or has a short circuit. Then further manipulations become meaningless and the element must be changed, since it cannot be repaired.
If the multimeter shows a certain resistance, then immerse the thermocouple in a glass of cold water and record the readings. Then add hot water and watch the resistance change, it should decrease. If there are no changes, purchase and install a new temperature sensor.
Features of checking for VAZ 2110
The “tens” configuration includes two types of engines – 8 and 16 valves. But the features of the DTOZH, location and replacement are identical.
On these VAZ 2110 you can use the Lusar LS 0101 temperature sensor. The car has two coolant temperature meters installed, one near the thermostat and it interacts with the computer, the second on the radiator and transmits data to the instrument panel.
The procedure for checking is the same; resistances at different temperatures are shown in Table 1.
VAZ 2114, VAZ 2115
On these cars, GM 2112-3851010-01 can be used as a DTOZH. The location of the device is between the cylinder head and the thermostat.
To check, it is recommended to dismantle the element (open-end wrench size 19). To do this, you need to wait until the engine cools down, reset the negative voltage on the battery and drain the antifreeze.
After this, you need to dismantle the device and check it by heating the liquid, a thermometer and a multimeter.
The following parameters must be present.
Table 2.
| Temperature, 0C | Resistance, Ohm | Voltage, V |
| +30 | 1350-1880 | 8 |
| +50 | 585-820 | 7,6 |
| +70 | 280-390 | 6,85 |
| +90 | 155-196 | 5,6 |
| +110 | 87-109 | 4,7 |
If there is a discrepancy in the readings, the device must be replaced.
Gazelle (engines ZMZ 406, 405, 409)
Installation location - on the power unit in the area of the thermostat or on the body of the latter.
To remove it, it is necessary to partially drain the coolant from the engine, disconnect the spring clamp of the harness block and discard the block from the sensor.
Next, using a key set to “19” you need to loosen the broach and unscrew the device.
When choosing a device, you need to focus on the engine and ECU.
406 engine and ECU Mikas 7.1, 5.4, SOATE, VS5.6
In such cases, a DTOZH is used, operating at a voltage of 5 to 12 Volts through a resistance of 9.1 kOhm.
Several types of devices are suitable for replacement: Kaluga 19.3828, Luzar LS 0306, Rikor 40.5226 or Autotrade 42.3828.
When checking, you will also need water with a boiler and variable temperature, as well as a multimeter.
To work, you need to assemble a circuit and apply 1 to 1.5 mA to it. In this case, it is necessary to measure not resistance, but voltage.
When checking, the following parameters must be present:
- -60 0С - 2.13 V;
- -40 0C - 2.33 V;
- -20 0C - 2.53 V;
- 0 0C - 2.73 V;
- +40 0С - 3.13 V;
- +80 0С - 3.53 V;
- 105 0C - 3.83 V;
- 125 0C - 3.98 V.
When the engine is running, the voltage will be 5 V.
Engine 405, 409, UMZ 4216E3, 4213 control unit Mikas 11 / 10.3, VS8, SOATE
DTOZH with catalog numbers 234.3828, 40.5215 or 421.3828 are used here.
Unlike the method discussed above, here it is necessary to measure resistance.
In this case, the dependence should be as follows:
- 128 0C - 80.8 Ohm;
- 100 0С - 177 Ohm;
- 80 0С - 332 Ohm;
- 60 0С - 667 Ohm;
- 40 0С - 1459 Ohm;
- 20 0С - 3520 Ohm;
- 0 0С - 9420 Ohm;
- -20 0С - 28680 Ohm;
- -40 0С - 100707 Ohm.
In case of significant deviations from these parameters, the device must be replaced.
Niva Chevrolet
For installation, you can use DTOZH 2112-3851010 Kaluga (23.3828). It is difficult to visually determine the location of the device, because it is covered by other parts.
After removing them, you can see that the device is located in the upper part of the thermostat in the hole in the front pipe of the water jacket (the one that goes into the cylinder block). After unscrewing it (snap on 19), antifreeze does not flow.
The check is carried out according to the same schemes as discussed above. In this case, you need to have before your eyes a table with the parameters of temperature and resistance of the DTOZH.
Table 3.
| Temperature, 0C | Resistance, Ohm |
| +100 | 177 |
| +90 | 241 |
| +80 | 332 |
| +70 | 467 |
| +60 | 667 |
| +50 | 973 |
| +45 | 1188 |
| +40 | 1459 |
| +35 | 1802 |
| +30 | 2238 |
| +25 | 2796 |
| +20 | 3520 |
| +15 | 4450 |
| +10 | 5670 |
| +5 | 7280 |
| 0 | 9420 |
| -4 | 12300 |
| -10 | 16180 |
| -15 | 21450 |
| -20 | 28680 |
| -30 | 52700 |
| -40 | 100700 |
Also on the Chevrolet Niva, in the area of the 4th spark plug, there is a DUTOZH (coolant temperature indicating sensor), which displays data on the instrument panel; it does not transmit information to the ECU and does not affect the operation of the engine.
But it can provide incorrect data to the instrument panel and mislead the driver.
You can unscrew it without draining the coolant, but before doing this, relieve the pressure in the system by unscrewing the cap of the expansion tank.
It is also checked by comparing the temperature with the readings of the multimeter.
See table below.
How can you tell if your car is overheated?
You can see if the car is overheating by looking at the coolant temperature gauge we marked in the photo above. This temperature sensor is located on the dashboard. The sensor pointer should not exceed 90-95 degrees, that is, go far beyond half the values. If the temperature gauge is above 90-95 degrees, your engine has a cooling problem and may overheat at any time.
Kalina
The official version of the DTOZH for the VAZ 2112 is 2112-3851010. But you can use analogues, for example, ERA (33026), Luzar (LS 0112), Fenox (TSN 2211207).
The location of the sensor on a car with an 8- and 16-valve engine is near the thermostat. In this case, the device is slightly closed by the filter housing.
In this case, on the Lada Kalina 1 you will have to remove the air filter to access the temperature meter.
To unscrew, use a 19 key. There is no need to drain the antifreeze.
Check, as in the previous case, after removing the device with the key to “19”.
For temperature and resistance readings, see Table 3.
Checking the presence of operating voltage is carried out with a multimeter with the ignition on without removing the sensor between the block terminal “B” and ground (there are two terminals on the blocks “A” and “B”), standard readings are within 4.8-5.2 V.
Causes of malfunctions
DTOZh breakdown rarely bothers motorists due to its simple design. But there are still enough reasons for failure. The use of low-quality antifreeze and motor oil leads to the destruction of the surface of the DTOZH. The sensing element of the sensor may become covered with sediment in the form of crystals. The reason may also lie in a manufacturing defect. You should not buy DTOZH at flea markets and various cheap auto parts markets. DTOZH purchased on such a market will often not meet the declared parameters and the slightest damage will lead to sensor failure. An antifreeze leak can cause the gasket to wear out. A voltage surge in the on-board power supply and corrosion of contacts can also cause sensor failure.
Renault Logan
On Renault Logan you can use many types of DTOZH, for example, MEAT & DORIA 82187, JP GROUP 1293102400, Vernet WS2602 and others.
Originals:
- 12-RENAULT-7700101968 (triangle contacts) - installed on 8 valve engines until 2012.
- 12-RENAULT-226307034R – after 2012 (contacts in a row).
All of them are suitable for K4M and K7M motors, their locations vary.
So on the K4M (8 valves), the temperature meter is installed in the water distributor housing (in the cylinder block). He is alone, transmits information to the instrument panel and works in conjunction with the ECU.
On the K7M engine at the rear end of the cylinder head.
On the body of the block there are markings for the three terminals “A”, “B1” and “B2”. The operating voltage is measured, as in the case above, with the ignition on between terminal “B1” and ground. The norm is from 4.8 to 5.2 V.
If voltage is not supplied to the block, disconnect the wiring harness from the ECU and use a tester to check the wiring for an open circuit. We take measurements between “B1” and pin “13” of the ECU.
If the circuit is working, then the control unit has failed.
We switch the tester to the “Resistance measurement” mode and check for an open circuit in the “ground” circuit of the sensor between terminal “B2” and the body of the machine (engine).
Readings of less than 1 ohm indicate a healthy circuit. If the device shows infinity, then there is a break between terminals “73” of the ECU and “B2” of the block.
Next, if you don’t want to remove the coolant temperature sensor from the engine, use a tester to measure the resistance readings on a warm and cold engine between the sensor terminals “B1” and “B2”.
Normative data are shown in Table 4.
| Temperature, 0C | Resistance, Ohm |
| 120 | 105 |
| 110 | 135 |
| 90 | 240 (+/ — 30) |
| 80 | 335 (+/ — 35) |
| 50 | 810 |
| 25 | 2050 |
| 20 | 3500 (+/ — 500) |
| 4 | 7500 (+/ — 500) |
To further check the device, you can use one of the methods discussed above.
For greater reliability, it is advisable to dismantle the device; use a 21 head.
DTOZH malfunctions and their symptoms
It is generally accepted that DTOZH is quite reliable due to its simple design. However, sooner or later, almost every component of the car is subject to wear and tear. In the case of DTOZH, there is a violation of the calibration. Such a violation leads to an unplanned change in resistance and incorrect operation of the ECU.
This indicator is not considered reliable if the car has both primary and secondary sensors. In this case, the malfunction will be more accurately indicated by oxidation of the wiring or failure of the additional sensor. The main signs of a DTOZ malfunction are as follows:
- a drop in engine speed or spontaneous stopping at idle;
- longer vehicle warm-up time;
- increased frequency of the engine going beyond the optimal temperature range during operation;
- increased fuel consumption;
- decreased driver control over the car;
- smoke from the exhaust pipe takes on a black tint;
- violation of engine stability.
In addition, detonation knocking in the engine is sometimes possible. Some older car models have a special controller. When the needle of this controller goes beyond the critical zone, the vehicle must be stopped immediately. In this case, sometimes there is also a malfunction of the DTOZH. And in more modern models, the on-board computer notifies drivers of engine overheating. But such a message does not always indicate a malfunction of the sensor. This often occurs due to wiring breakage and oxidation.