Russian nuclear weapons
The history of human development has always been accompanied by wars as a way to resolve conflicts through violence. Civilization has suffered more than fifteen thousand small and large armed conflicts, the loss of human lives is estimated in the millions. In the nineties of the last century alone, more than a hundred military clashes occurred, involving ninety countries of the world.
At the same time, scientific discoveries and technological progress have made it possible to create weapons of destruction of ever greater power and sophistication of use. In the twentieth century, nuclear weapons became the peak of mass destruction and a political instrument.
Ground nuclear explosion
"Nuclear Club" of the world
The nuclear club is a symbol for several states that possess nuclear weapons. Today we have such weapons:
- in the USA (since 1945)
- in Russia (originally USSR, since 1949)
- UK (since 1952)
- France (since 1960)
- China (since 1964)
- India (since 1974)
- Pakistan (since 1998)
- DPRK (since 2006)
Israel is also considered to have nuclear weapons, although the country's leadership does not comment on its presence. In addition, US nuclear weapons are located on the territory of NATO member states (Germany, Italy, Turkey, Belgium, the Netherlands, Canada) and allies (Japan, South Korea, despite the official refusal).
Kazakhstan, Ukraine, Belarus, which owned part of the nuclear weapons after the collapse of the USSR, transferred them to Russia in the 90s, which became the sole heir to the Soviet nuclear arsenal.
Atomic weapons are the most powerful instrument of global politics, which has firmly entered the arsenal of relations between states. On the one hand, it is an effective means of deterrence, on the other hand, it is a powerful argument for preventing military conflict and strengthening peace between the powers that own these weapons. This is a symbol of an entire era in the history of mankind and international relations, which must be handled very wisely.
Video: Nuclear Weapons Museum
Atomic bomb device
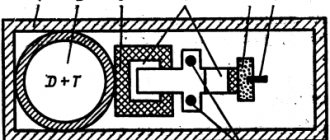
Modern nuclear bombs as means of destroying the enemy are created on the basis of advanced technical solutions, the essence of which is not widely publicized. But the main elements inherent in this type of weapon can be examined using the example of the design of a nuclear bomb codenamed “Fat Man,” dropped in 1945 on one of the cities of Japan.
See also the article Molecular bomb and its development
The power of the explosion was 22.0 kt in TNT equivalent.
It had the following design features:
- the length of the product was 3250.0 mm, with a diameter of the volumetric part - 1520.0 mm. Total weight more than 4.5 tons;
- the body is elliptical in shape. To avoid premature destruction due to anti-aircraft ammunition and other unwanted impacts, 9.5 mm armored steel was used for its manufacture;
- the body is divided into four internal parts: the nose, two halves of the ellipsoid (the main one is a compartment for the nuclear filling), and the tail.
- the bow compartment is equipped with batteries;
- the main compartment, like the nasal one, is vacuumized to prevent the entry of harmful environments, moisture, and to create comfortable conditions for the bearded man to work;
- the ellipsoid housed a plutonium core surrounded by a uranium tamper (shell). It played the role of an inertial limiter for the course of the nuclear reaction, ensuring maximum activity of weapons-grade plutonium by reflecting neutrons to the side of the active zone of the charge.
A primary source of neutrons, called an initiator or “hedgehog,” was placed inside the nucleus. It is represented by spherical beryllium with a diameter of 20.0 mm with an outer coating based on polonium - 210.
Simplified diagram of a nuclear bomb
It should be noted that the expert community has determined that this design of nuclear weapons is ineffective and unreliable in use. Neutron initiation of the uncontrolled type was not used further.
“Uranium Project” - the Germans start and lose
In September 1939, the “Uranium Project” was classified. 22 reputable research centers were invited to participate in the program, and the research was supervised by Minister of Armaments Albert Speer. The construction of an installation for separating isotopes and the production of uranium to extract the isotope from it that supports the chain reaction was entrusted to the IG Farbenindustry concern.
For two years, a group of the venerable scientist Heisenberg studied the possibility of creating a reactor using uranium and heavy water. A potential explosive (uranium-235 isotope) could be isolated from uranium ore.
But for a nuclear reactor to operate, an inhibitor is needed to slow down the reaction - graphite or heavy water. Choosing the latter option created an insurmountable problem.
The only plant for the production of heavy water, which was located in Norway, was disabled by local resistance fighters after the occupation, and small reserves of valuable raw materials were exported to France.
The rapid implementation of the nuclear program was also hindered by the explosion of an experimental nuclear reactor in Leipzig.
Hitler supported the uranium project as long as he hoped to obtain a super-powerful weapon that could influence the outcome of the war he started. After government funding was cut, the work programs continued for some time.
In 1944, Heisenberg managed to create cast uranium plates, and a special bunker was built for the reactor plant in Berlin.
It was planned to complete the experiment to achieve a chain reaction in January 1945, but a month later the equipment was urgently transported to the Swiss border, where it was deployed only a month later. The nuclear reactor contained 664 cubes of uranium weighing 1525 kg. It was surrounded by a graphite neutron reflector weighing 10 tons, and one and a half tons of heavy water were additionally loaded into the core.
On March 23, the reactor finally started working, but the report to Berlin was premature: the reactor did not reach a critical point, and the chain reaction did not occur. Additional calculations showed that the mass of uranium must be increased by at least 750 kg, proportionally adding the amount of heavy water.
But supplies of strategic raw materials were at their limit, as was the fate of the Third Reich. On April 23, the Americans entered the village of Haigerloch, where the tests were carried out. The military dismantled the reactor and transported it to the United States.
Operating principle
The process of fission of the nuclei of uranium 235 (233) and plutonium 239 (this is what a nuclear bomb is made of) with a huge release of energy while limiting the volume is called a nuclear explosion. The atomic structure of radioactive metals has an unstable form - they are constantly divided into other elements.
The process is accompanied by the detachment of neurons, some of which fall on neighboring atoms and initiate a further reaction, accompanied by the release of energy.
The principle is as follows: shortening the decay time leads to greater intensity of the process, and the concentration of neurons on bombarding the nuclei leads to a chain reaction. When two elements are combined to a critical mass, a supercritical mass is created, leading to an explosion.
Principle of nuclear reaction
In everyday conditions, it is impossible to provoke an active reaction - high speeds of approach of the elements are needed - at least 2.5 km/s. Achieving this speed in a bomb is possible by using combining types of explosives (fast and slow), balancing the density of the supercritical mass producing an atomic explosion.
See also the article What is a hydrogen bomb and how does it work?
Nuclear explosions are attributed to the results of human activity on the planet or its orbit. Natural processes of this kind are possible only on some stars in outer space.
What are thermonuclear weapons
One type of nuclear weapon is a thermonuclear weapon , which many of us are better known as a hydrogen bomb . Such a bomb has a huge destructive effect. The operating principle of this type of weapon is based on the release of a huge amount of energy during the synthesis of light chemical elements into heavier ones. Today, thermonuclear weapons come in the form of cruise missile warheads, ballistic missile warheads, and aircraft bombs.
Damaging factors
Atomic bombs are rightfully considered the most powerful and destructive weapons of mass destruction. Tactical use solves the problem of destroying strategic, military targets on the ground, as well as deep-based ones, defeating a significant accumulation of enemy equipment and manpower.
It can be applied globally only with the goal of complete destruction of the population and infrastructure in large areas.
See also the article Bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki
To achieve certain goals and perform tactical and strategic tasks, explosions of atomic weapons can be carried out by:
- at critical and low altitudes (above and below 30.0 km);
- in direct contact with the earth's crust (water);
- underground (or underwater explosion).
A nuclear explosion is characterized by the instantaneous release of enormous energy.
undefined
Leading to damage to objects and people as follows:
- Shock wave. When an explosion occurs above or on the earth's crust (water) it is called an air wave; underground (water) it is called a seismic explosion wave. An air wave is formed after critical compression of air masses and propagates in a circle until attenuation at a speed exceeding sound. Leads to both direct damage to manpower and indirect damage (interaction with fragments of destroyed objects). The action of excess pressure makes the equipment non-functional by moving and hitting the ground;
- Light radiation. The source is the light part formed by the evaporation of the product with air masses; for ground use, it is soil vapor. The effect occurs in the ultraviolet and infrared spectrum. Its absorption by objects and people provokes charring, melting and burning. The degree of damage depends on the distance of the epicenter;
- Penetrating radiation is neutrons and gamma rays moving from the rupture site. Exposure to biological tissue leads to ionization of cell molecules, leading to radiation sickness in the body. Damage to property is associated with fission reactions of molecules in the damaging elements of ammunition.
- Radioactive contamination. During a ground explosion, soil vapors, dust, and other things rise. A cloud appears, moving in the direction of the movement of air masses. Sources of damage are represented by fission products of the active part of a nuclear weapon, isotopes, and undestroyed parts of the charge. When a radioactive cloud moves, continuous radiation contamination of the area occurs;
- Electromagnetic pulse. The explosion is accompanied by the appearance of electromagnetic fields (from 1.0 to 1000 m) in the form of a pulse. They lead to failure of electrical devices, controls and communications.
See also the article Biological weapons and their technical characteristics
The combination of factors of a nuclear explosion causes varying levels of damage to enemy personnel, equipment and infrastructure, and the fatality of the consequences is associated only with the distance from its epicenter.
Damaging factors
Testing of thermonuclear weapons
The first tests of thermonuclear weapons were carried out by the United States of America on November 1, 1952. The charge was detonated on Eniwetak Atoll in the Pacific Ocean. It was not a bomb, but a laboratory sample that looked like some kind of structure. But the first ready-made hydrogen bomb was tested - the RDS-6 bomb, made in the USSR. Tests of the ready-to-use device were carried out at the test site in Semipalatinsk on August 12, 1953.
The largest hydrogen bomb that was tested was a 50-megaton hydrogen bomb, called the Tsar Bomba . Its test was carried out at a test site located on the Novaya Zemlya archipelago on October 30, 1961. Initially, it was planned to test a 100-megaton bomb, but then it was decided to halve the power of the weapon being tested. The bomb was detonated at an altitude of 4 kilometers, after which the blast wave circled the globe three times. The tests were successful, but the weapon was not put into service, but these tests made it clear to America that the Soviet Union could create thermonuclear bombs of any megatonnage.
History of the creation of nuclear weapons
The creation of weapons using nuclear reactions was accompanied by a number of scientific discoveries, theoretical and practical research, including:
- 1905 - the theory of relativity was created, stating that a small amount of matter corresponds to a significant release of energy according to the formula E = mc2, where “c” represents the speed of light (author A. Einstein);
- 1938 - German scientists conducted an experiment on dividing an atom into parts by attacking uranium with neutrons, which ended successfully (O. Hann and F. Strassmann), and a physicist from Great Britain explained the fact of the release of energy (R. Frisch);
- 1939 - scientists from France that when carrying out a chain of reactions of uranium molecules, energy will be released that can produce an explosion of enormous force (Joliot-Curie).
The latter became the starting point for the invention of atomic weapons. Parallel development was carried out by Germany, Great Britain, the USA, and Japan. The main problem was the extraction of uranium in the required volumes for conducting experiments in this area.
The problem was solved faster in the USA by purchasing raw materials from Belgium in 1940.
As part of the project, called Manhattan, from 1939 to 1945, a uranium purification plant was built, a center for the study of nuclear processes was created, and the best specialists - physicists from all over Western Europe - were recruited to work there.
Great Britain, which carried out its own developments, was forced, after the German bombing, to voluntarily transfer the developments on its project to the US military.
It is believed that the Americans were the first to invent the atomic bomb. Tests of the first nuclear charge were carried out in the state of New Mexico in July 1945. The flash from the explosion darkened the sky and the sandy landscape turned to glass. After a short period of time, nuclear charges called “Baby” and “Fat Man” were created.
Atomic bomb "Baby"
Interesting facts about thermonuclear weapons
In 1958, over the coast of Georgia (USA), an F-86 fighter collided with a B-47 bomber. The latter had to make an emergency release of the MARK 15 hydrogen bomb into the ocean. The bomb has still not been found.
Over Spain on January 17, 1966, a tanker plane collided with a B-52 bomber carrying five hydrogen bombs. Three bombs were found immediately after the accident, and two only after two months of searching.
In the USA, on August 29, 2007, an incident occurred - 6 cruise missiles with thermonuclear heads were mistakenly loaded into a B-52H bomber and transported from North Dakota to Louisiana.
The accidental transfer became known only 36 hours later, and all this time the weapon was unguarded. The situation caused a loud scandal and serious changes in the country's Air Force. Thermonuclear weapons
Nuclear weapons in the USSR - dates and events
The emergence of the USSR as a nuclear power was preceded by long work by individual scientists and government institutions. Key periods and significant dates of events are presented as follows:
- 1920 is considered the beginning of the work of Soviet scientists on atomic fission;
- Since the thirties, the direction of nuclear physics has become a priority;
- October 1940 - an initiative group of physicists came up with a proposal to use atomic developments for military purposes;
- In the summer of 1941, due to the war, nuclear energy institutes were transferred to the rear;
- In the fall of 1941, Soviet intelligence informed the country's leadership about the start of nuclear programs in Britain and America;
- September 1942 - atomic research began to be carried out in full, work on uranium continued;
- February 1943 - a special research laboratory was created under the leadership of I. Kurchatov, and general management was entrusted to V. Molotov;
The project was led by V. Molotov.
- August 1945 - in connection with the nuclear bombing in Japan, the high importance of developments for the USSR, a Special Committee was created under the leadership of L. Beria;
- April 1946 - KB-11 was created, which began to develop samples of Soviet nuclear weapons in two versions (using plutonium and uranium);
- Mid-1948 - work on uranium was stopped due to low efficiency at high costs;
- August 1949 - when the atomic bomb was invented in the USSR, the first Soviet nuclear bomb was tested.
The reduction in product development time was facilitated by the high-quality work of intelligence agencies, who were able to obtain information on American nuclear developments. Among those who first created the atomic bomb in the USSR was a team of scientists led by Academician A. Sakharov. They have developed more promising technical solutions than those used by the Americans.
Atomic bomb "RDS-1"
In 2020, Russia made a breakthrough in improving nuclear weapons and their delivery systems, thereby declaring a state capable of repelling any aggression.
Between 1940 and 1996, the United States spent $8.8 trillion on its nuclear program.
The United States is the undisputed leader in the cost of developing nuclear weapons. It is roughly estimated that $8.8 trillion. The US spent on the nuclear program until 1996.
Where do these amounts come from?
In fact, no more than a billion was spent on the development of the weapons themselves, and the lion's share of the costs is associated with the development and production of delivery systems.
What's happening today?
Of course, countries spend enormous amounts of money on nuclear weapons even today. Modernizing existing weapons and developing new delivery systems requires considerable funds. Countries are reluctant to share budgets in this area, so we can build on the data that is freely available.
According to some reports, in 2010 the nuclear budget of countries was approximately as follows:
- USA - $61.3 billion,
- China - $14.8 billion,
- Russian Federation - $7.6 billion,
- France - $6 billion,
- Great Britain - $5.5 billion,
- India - $4.9 billion,
- Pakistan - $2.2 billion,
- Israel - $1.9 billion,
- North Korea - $0.7 billion
9
First atomic bomb tests
After testing an experimental nuclear bomb in New Mexico in the summer of 1945, the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki were bombed on August 6 and 9, respectively.
1949
The development of the atomic bomb was completed this year
In 1949, under conditions of increased secrecy, Soviet designers of KB-11 and scientists completed the development of an atomic bomb called RDS-1 (jet engine “C”). On August 29, the first Soviet nuclear device was tested at the Semipalatinsk test site. The Russian atomic bomb - RDS-1 was a “drop-shaped” product, weighing 4.6 tons, with a volumetric diameter of 1.5 m, and a length of 3.7 meters.
The active part included a plutonium block, which made it possible to achieve an explosion power of 20.0 kilotons, commensurate with TNT. The testing site covered a radius of twenty kilometers. The specifics of the test detonation conditions have not been made public to date.
See also the article History of creation, description and properties of TNT
On September 3 of the same year, American aviation intelligence established the presence in the air masses of Kamchatka of traces of isotopes indicating the testing of a nuclear charge. On the twenty-third, the top US official publicly announced that the USSR had succeeded in testing an atomic bomb.
A 10-megaton hydrogen bomb accidentally fell from an airplane
Pictured: Mark 17 hydrogen bomb
Yes this is true. Government documents show that the 42-kiloton Mark 17 hydrogen bomb, one of the most powerful ever made, accidentally fell from a bomber near Albuquerque in 1957.
The non-nuclear explosives used to launch the nuclear weapon were reported to have detonated, but there was no nuclear explosion.
No one was injured in the incident because the bomb hit an area belonging to the University of New Mexico, creating a crater about 4 meters deep and 8 meters in diameter.
The documents indicated that minor radioactive contamination was found in the crater.
Bomber Boeing B-47E-50-LM
And this was not the only such case. In March 1958, a similar incident occurred in South Carolina when, due to the fault of the crew of a Boeing B-47E-50-LM bomber, a 30-kiloton atomic bomb was accidentally dropped on the village of Mars Bluff. But, fortunately, the nuclear filling of the bomb was stored separately on the plane, so the bomb, when falling from a height of 4,600 meters, created an explosion from non-nuclear charges, leaving a crater with a diameter of 20 meters and a depth of 10 meters.
6
"Disarming Strike"
Media playback is unsupported on your device
The main destabilizing factor from the 1960s to the present day is the fear that one of the sides, thanks to some incredible technological breakthrough, will be able to deliver a so-called disarming first strike: instantly destroy the enemy’s nuclear forces, leaving him “naked” and helpless.
Military experts and designers consider this option unrealistic. The creation and implementation of breakthrough developments takes years, and no one, as they say, sleeps.
The periodically renewed discussion of this topic serves, rather, the propaganda purposes of politicians and the very material interests of weapons manufacturers.
In particular, American missile defense projects are unlikely to be able, even in a fairly distant future, to actually depreciate the value of the Russian nuclear sword.
Any system, by definition, is not 100% reliable, and the breakthrough of even one ballistic missile with a megaton warhead is fraught with the destruction of a large city and millions of losses: as experts put it, “unacceptable damage.”
If missile defense becomes a reality, which, of course, cannot be ruled out in the context of the new Cold War, the goal will be not so much to achieve military superiority as to involve Russia in a costly arms race.
Serov Ivan Aleksandrovich - head of the bomb creation operation
Of course, the Soviet government could not ignore the successes of German nuclear physicists. After the war, a group of Soviet physicists, future academicians, were sent to Germany in the uniform of colonels of the Soviet army.
Ivan Serov, the first deputy people's commissar of internal affairs, was appointed head of the operation, this allowed scientists to open any doors.
In addition to their German colleagues, they found reserves of uranium metal. This, according to Kurchatov, shortened the development time of the Soviet bomb by at least a year. More than one ton of uranium and leading nuclear specialists were taken out of Germany by the American military.
Not only chemists and physicists were sent to the USSR, but also qualified labor - mechanics, electricians, glassblowers. Some of the employees were found in prison camps. In total, about 1,000 German specialists worked on the Soviet nuclear project.
The struggle of the world community against the nuclear threat
The total stockpile of nuclear weapons in the world is now equivalent to 1 million bombs dropped on Hiroshima. And the fact that we have so far managed to live without nuclear war is largely due to the UN and the entire world community.
Countries that own nuclear weapons are members of the so-called “Nuclear Club”. It currently has 9 members. This list is expanding.
The USSR took a very clear position in nuclear policy. In 1963, it was in Moscow that a treaty was signed banning the testing of nuclear weapons in three environments: in the atmosphere, space and under water.
A more comprehensive treaty was adopted at the UN Assembly in 1996. 131 states have already put their signatures on them.
A special commission has been created to monitor events related to nuclear tests. Despite the efforts being made, a number of states continue to conduct nuclear tests. We have witnessed how North Korea conducted six nuclear weapons tests. It uses its nuclear potential as an act of intimidation and an attempt to achieve a dominant position in the world.
The Russian Federation now ranks second in the world in terms of nuclear potential.
Russia's nuclear forces consist of ground, air and sea components. But unlike the DPRK, the military power of our country serves as a deterrent that ensures the peaceful development of the state. If this message was useful to you, I would be glad to see you in the VKontakte group. Also, thank you if you click on one of the “like” buttons: