When they talk about advanced weapons, they first of all mean the power of a weapon capable of inflicting a crushing defeat on the enemy. The legendary T-34 tank became the personification of the victory of the Soviet Union in World War II. But there are less significant components, for example, the V-2 tank engine, without which the legend could not exist.
Military equipment operates in the most difficult conditions. Motors are designed taking into account the use of low-quality fuel, minimal maintenance, but at the same time they must maintain their original characteristics for many years. It was this approach that was embodied in the creation of the diesel engine of the T-34 tank.
Engine prototype
In 1931, the Soviet government set a course for improving military equipment. At the same time, the Kharkov Locomotive Plant named after. The Comintern received the task of developing a new diesel engine for tanks and aircraft.
The novelty of the development had to lie in fundamentally new characteristics of the motor. The nominal crankshaft speed of diesel engines of that time was 260 rpm. Then, as in the task, it was stipulated that the new engine should produce 300 hp at a rotation speed of 1600 rpm. And this already imposed completely different requirements on the methods of developing components and assemblies. Technologies that would make it possible to create such an engine in the Soviet Union did not exist.
The design bureau was renamed Diesel, and work began. After discussing possible design options, we settled on a V-shaped 12-cylinder engine, 6 cylinders in each row. It was supposed to be started by an electric starter. At that time there was no fuel equipment that could provide fuel for such an engine. Therefore, it was decided to install a Bosch injection pump as a high-pressure fuel pump, which was subsequently planned to be replaced with a pump of our own production.
Two years passed before the creation of the first test sample. Since the engine was planned to be used not only in Soviet tank construction, but also in aircraft construction on heavy bombers, the low weight of the engine was specially stipulated.
Farm
Despite the fact that the tank is gold-dependent, it is quite possible to farm on it. Let me remind you that the price of a premium cumulative projectile is 5600 credits (14 gold), which is quite expensive.
Yes, you can drive a full gold, but then it will no longer be farming but fun, but you can load a dozen cumulative shells for especially thick-skinned tanks and shoot with armor-piercing ones. I chose the second option.
The thing is that our fragile armor is not designed for a frontal attack, therefore we must constantly maneuver to maintain our HP and fire at weakly protected areas of enemy tanks.
Penetration with a basic armor-piercing projectile is quite enough for most of the tanks we encounter in random games. So, on average, you can take out 50,000 credits or more per battle net, taking into account the premium account.
Engine modification
They tried to create the engine from materials that had not previously been used to build diesel engines. For example, the cylinder block was made of aluminum, and it, unable to withstand tests on the bench, constantly cracked. High power caused the light, unbalanced motor to vibrate violently.
The BT-5 tank, on which the diesel engine was tested, never reached the test site under its own power. Troubleshooting of the engine showed that the crankcase block and crankshaft bearings were destroyed. In order for the design embodied in paper to migrate to life, new materials were needed. The equipment used to make the parts was also unsuitable. There was not enough manufacturing precision class.
In 1935, the Kharkov Locomotive Plant was replenished with experimental workshops for the production of diesel engines. Having eliminated a number of shortcomings, the BD-2A engine was installed on the R-5 aircraft. The bomber took off, but the low reliability of the engine did not allow it to be used for its intended purpose. Moreover, by that time more acceptable options for aircraft engines had arrived.
Preparing the diesel engine for installation on the tank was difficult. The selection committee was not satisfied with the high smoke, which was a strong unmasking factor. In addition, the high fuel and oil consumption was unacceptable for military equipment, which must have a large range without refueling.
Unique: the legendary T-34 tank turns 80 years old
In 1945, journalists asked the British Prime Minister which weapon of the just ended war he considered the best. Winston Churchill answered without hesitation: “Three. English gun (obviously meant Ordnance QF 17-pounder, colloquially “17-pounder”, supposedly capable of penetrating any armor. - Author). German plane Messerschmitt. Russian T-34 tank." And he added: “However, if in the first two cases it is clear to me how it was done, then I absolutely do not understand how such a tank appeared...”
The cannon mentioned by Churchill was not adopted even by the British's closest ally, the Americans. And the life of the weapon turned out to be relatively short-lived: by the end of the 1940s it was supplanted by a more advanced one, which had absorbed the best technologies... of the defeated Third Reich.
40 T-34 tanks took part in the parade on November 7, 1941, and immediately after its completion they went to the front.
The Messerschmitt aircraft provided Germany with an advantage in the air until the summer of 1943. It was in service with 10 European states, Japan and Israel. From the first flight on May 28, 1935 to complete decommissioning, 23 years passed, from the start of operation in 1937 - a little more than 20 years.
A completely different picture with the T-34 tank. In the armored forces of the country that created it, it remained in service for about 50 years, without losing its combat effectiveness until it was withdrawn from service in September 1997. More T-34 tanks with modifications were produced than any other tanks anywhere: 65,909 (including licensed ones). It was in service in 46 countries around the world, located in all time zones; used in all climatic zones - from the Arctic to equatorial Africa; in some African, Asian and other countries (in Cuba, for example), it is still stored in tank parks, and it is still ready to carry out combat missions. And these are far from the only achievements in the list of records of the T-34 tank.
Experimental tanks A-32 (left) and A-20, predecessors of the T-34.
He is a champion in the field of military strategy, because the German political and military leadership did not have reliable intelligence information about him at the beginning of the war, although on June 22, 1941, the Red Army had 1066 T-34 tanks in service. They received their baptism of fire in the battles of Alytus and Grodno (June 22-23 and 24-25, 1941, respectively). Having learned about the existence of such combat vehicles, Hitler allegedly said to his high command: “If I had known about such tanks from the Russians, perhaps I would not have started this war.”
For the time being, the Wehrmacht command did not share the Fuhrer’s pessimism. The commander of the 2nd Panzer Group, Colonel General Heinz Guderian, was at first skeptical about the new product - until 300 of his tanks fought in a duel with 50 thirty-fours of the 4th Tank Brigade of Colonel M.E. Katukov in the battles near Mtsensk, where they showed complete superiority in weapons, armor and maneuverability. For this victory, the colonel became a general and was awarded the Order of Lenin. The brigade was the first in the tank units of the Red Army to be awarded the title of Guards. And three and a half years later, in May 1945, the guards of Marshal Katukov would be the first to break into the lair of the beast, almost defeated Berlin.
Commanders of tank formations H.V. Guderian and M.E. Katukov, who tested their vehicles for the first time in a major tank battle.
Using this example, we can talk about a number of advantages of the T-34 tank: its versatility; optimal combination of firepower, protection and mobility; the most powerful cannon weapons at each stage of the war; the most rational form of anti-ballistic armor corps; the highest speed among tanks of this type (55 km/h), the largest fuel range (up to 420 kilometers at one refueling); efficiency - thanks to the unique high-speed tank diesel engine V-2, which consumed relatively little fuel and at the same time was extremely unpretentious in terms of its quality.
Confirming that Hitler really understood the advantages of the T-34 tank is evidenced by the fact that in August 1941, when only about three hundred kilometers remained to Moscow, he ordered the 2nd Panzer Group of the mentioned Colonel General Heinz Guderian to turn to the south - to Kharkov to capture the plant that developed and produced thirty-fours. The Germans failed to launch full-scale production, but they managed to repair over 300 T-34 tanks damaged on the battlefields and put them into service in the Panzerwaffe. They were distributed among 11 tank divisions, including the elite Grossdeutschland grenadier division and the SS division Das Reich.
After inspecting the captured T-34 and KV, the Fuhrer ordered the designers to create at least the same combat vehicles, even copying them. But the Germans failed. They were unable to reveal the secret of Russian alloy steel, technologies for manufacturing cast turret hulls, submerged arc welding of oblique armored hull sheets and much more. The worst situation was with copying the V-2 diesel engine: they didn’t come up with anything even close to similar.
Duel (Tiger and T-34 tanks). Artist Valery Petelin.
The asymmetrical response of German tank builders was the appearance of the Panther tanks, which largely repeated the outlines of the T-34, Tiger, and also the Royal Tiger. The answer turned out to be powerful, but incorrect: the last of the named vehicles weighed more than twice the T-34 tank, the other two vehicles were lighter, but they were still heavy tanks, and the IS-2 and KV-2 were more suitable for them. But what is curious: the “Royal Tiger” tank, used for the first time on that day by the enemy on the Soviet-German front, was destroyed on August 12, 1944 by the crew of the T-34 tank, junior lieutenant A.P. Oskina. The success was not accidental and not isolated: in two days of fighting, only this crew burned three “Royal Tigers”, one was damaged, and three more were captured intact in the village of Oglendow (Poland).
In capable hands, the thirty-four was an inimitably formidable weapon. From the cannon of the T-34 A.M. tank. Fadin, later a Hero of the Russian Federation, shot down a German plane flying low above the ground. And the crew of the T-34 tank, senior lieutenant D.F. Lavrinenko (Hero of the Soviet Union posthumously) from October 6 to December 18, 1941 destroyed 52 enemy tanks.
Some of the best tankers of the Great Patriotic War who fought on the T-34 A.P. Oskin (left) and A.M. Fadin.
The T-34 tank is a real Russian miracle, and therefore more than one Churchill could not understand “how such a tank appeared...”. Too many “accidents” came together to make it happen. It took the successful director of the Vyatka confectionery factory, who switched to party work and was quickly rising through the ranks, Mikhail Ilyich Koshkin, to suddenly decide to “give up everything” and, under the patronage of S.M. Kirov was able to enter a technical university. So that he would be “noticed” by the People’s Commissar of Heavy Industry of the USSR G.K. Ordzhonikidze and appointed to Kharkov, at the Comintern KhPZ (plant No. 183) to the position of head of the tank KB-190. Koshkin needed to accurately grasp the trend of correct development of tank building and, contrary to the approved wheeled-tracked experimental tank "A-20", proactively build a purely tracked A-32, which became the prototype of the T-34. Overcome the powerful resistance of the powerful enemy of this machine, Deputy People's Commissar of Defense of the USSR, Marshal G.I. Kulik, and “over his head” enlist the support of the People's Commissar of Defense of the USSR, Marshal K.E. Voroshilov and personally I.V. Stalin. To embody the tank in metal and march it through the autumn muddy roads to Moscow, gaining the required mileage for testing, and then present it brand new to the country’s leadership on Ivanovskaya Square in Moscow.
The creators of the T-34 tank M.I. Koshkin (left) and A.A. Morozov.
The T-34 tank was adopted by the Red Army on December 19, 1939: on the day of St. Nicholas the Wonderworker, one of the most revered saints in Rus' (is it a coincidence?) However, this did not end his thorny path into the army. The all-terrain vehicle seemed to be firmly stuck in the bureaucratic mire of all sorts of approvals, technological inconsistencies, and technical difficulties: its production plan in 1940 and the first half of 1941 was completed by less than 30 percent. Of the planned 3,400 vehicles, the army received only 1,100. In 1940, the chief designer of the tank also passed away: the Kharkov-Moscow-Kharkov run undermined his health, a cold and overwork led to pneumonia, and removal of a lung with an intensive course of rehabilitation did not help: September 26 in a sanatorium M.I. Koshkin died.
The management team of plant No. 183 named after. Comintern, creator of the T-34 tank in 1940.
His undoubted merit is in creating the concept of this extraordinary machine, which had an almost inexhaustible resource for modernization, and in creating a team capable of further leading this difficult process. His deputy A. A. Morozov became the chief designer and head of the design bureau. All further modernization of this machine is an undoubted achievement of Alexander Alexandrovich and the team he leads. During the war, without slowing down production rates, tank builders constantly improved the combat vehicle. This is how the most rational form of the projectile-resistant armored hull was achieved; adaptability to serial production at various factories, even those not originally intended for the production of tanks; possibility of carrying out repairs in the field. The design idea was constantly ahead of its time: already in 1940, in parallel with overcoming bureaucratic barriers, the T-34M tank, a more advanced one, was created (the production of which had to be curtailed in favor of the previous, more streamlined model for serial production); later the T-44, T-64 and others appeared, the “genealogy” of which can be traced back to the current “Armata”, and a whole family of combat and engineering vehicles created on the basis of the legendary thirty-four.
Creator of the V-2 engine for the T-34 tank K.F. Chelpan (left) and cannon armament - V.G. Grabin.
As is known, hidden under the armor of the tank is a “fiery engine”: this perfect 500-horsepower V-2 engine was created by the design bureau of the diesel department of the Kharkov Locomotive Plant under the leadership of K. F. Chelpan, who was repressed in 1937; his work was continued by his deputies Konstantin Fedorovich Ya. E. Vikhman and I. Ya. Trashutin. The firepower of the T-34 was provided first by 76.2 mm tank guns (for the T-34-76), and then by 85 mm (for the T-34-85), developed under the leadership of the talented designer V.G. Grabin, from which many more fascist beasts like “Tigers” and “Panthers” were stuffed than from the vaunted English “17-pounder”.
The T-34 tank is a favorite character of not only domestic but also foreign artists. Here are the paintings by Canadian artist Vincent Way “T-34 “go on the attack” (left) and “The Red Army on the outskirts of Berlin.”
“T-34” is truly “the very best”: the most beloved tank of veteran tankers, the most common character in books and films about the Great Patriotic War, the most common symbol of Victory, erected on pedestals of monuments of military valor. This is the most exhibited example of weapons and military equipment in museums around the world - and the only example of weapons in the world to which a personal museum complex is dedicated (the village of Sholokhovo, Moscow region). Of all his brothers, he is most often depicted in artistic paintings and posters, envelopes and postcards, postage stamps and medals, certificates and memorial signs, in scale models and as prizes in competitions in military-technical sports and in army competitions. Because he is our glory and pride. Because it is unique. And unique.
T-34 at the parade in Donetsk
... In 2014, the Donbass militia removed the T-34 from the pedestals on which the tanks stood as monuments to Soviet tankers who liberated the cities and towns of the mining region. It turned out that the cars could be put into motion, and they became participants in Victory parades in the republics.
And in 2016, a T-34 firing was caught on camera in distant Yemen.
In the title photo: T-34 in Berlin
The main difficulties are behind us
In 1937, the design team was supplemented with military engineers. At the same time, the diesel engine was given the name B-2, under which it went down in history. However, the improvement work was not completed. Some technical tasks were delegated to the Ukrainian Institute of Aircraft Engine Engineering. The design team was supplemented by employees of the Central Institute of Aviation Engines.
In 1938, state tests of the second generation of V-2 diesel engines were carried out. Three engines were presented. None passed the tests. The first one had a jammed piston, the second one had a cracked cylinder block, and the third one had a leaking crankcase. In addition, the high pressure plunger pump did not produce enough output. It lacked precision manufacturing.
In 1939, the engine was modified and tested.
Subsequently, the V-2 engine was installed in this form on the T-34 tank. The diesel department was reformed into a tank engine plant, the goal of which was to produce 10,000 units per year.
The newest Russian tank T-14 “Armata” will not be able to go abroad yet
Strange events are happening to our newest T-14 Armata tank.
Quite recently, the manufacturers of this combat vehicle informed the people that they had managed to eliminate its “childhood diseases”, and some ministers promised that mass production and deliveries of the tank to the army would begin only in 2021, but then almost a sensation fluttered out in the media - “Armata “I received a passport: the Russian tank is being exported.”
And this is a half-truth. I have a passport, but the car is not going anywhere abroad yet. Moreover, it is not known when it will go. Here it is worth remembering that even at the time when Vladimir Putin was the prime minister of the government, a decree was issued according to which it was prohibited to sell new military equipment beyond the border until the needs of the Russian army were fully met. And our army has enormous needs. Back in 2020, the head of Uralvagonzavod (manufacturer of the T-14) Oleg Sienko “opened his cards”:
— There is a decision according to which we must supply the army with more than 2,000 units.
Now the Armatas are undergoing military experimental tests and so far there is no talk of thousands of new combat vehicles - while there are reports of a little over a hundred, or even dozens. The customer (Ministry of Defense) is very meticulous and careful when testing a new product, so as not to buy it in a “damp” form. Moreover, while the car will not be produced in mass quantities, its price per unit is very steep. The same Oleg Sienko said that with mass production of the newest Russian tank it would cost 250 million rubles.
This is on a massive scale. And it is clear that the smaller the batch of combat vehicles, the more expensive it is - sometimes almost 2 times.
At the current exchange rate, 250 million rubles is approximately $3.5 million. “Cool,” you say. Well then, I give you for comparison: the American Abrams, the French Leclerc or the Israeli Merkava are valued at an average of 8 to 10 million dollars. That is 3 times more expensive. And this despite the fact that our vehicle is unique in many key parameters (combat tactical and technical characteristics). That’s why foreign buyers are already jostling in line for it. These include China, India, Egypt and many other countries. Of course, the T-14 has quite high prospects for export. Moreover, the price is suitable for foreign buyers. Even though it will be exported with reduced combat characteristics. But in any case, it should be clear that “until the needs” of the Russian army for the T-14 are fully satisfied, there can be no talk of exporting it. Of course, our exporters of military equipment and their manufacturers are very tempted to profitably trade the Armata across the border and get a fat profit, but state interests (the interests of our army) must be higher than business calculations.
Final version
At the beginning of World War II, the plant was urgently evacuated to Chelyabinsk. ChTZ already had a production base for the production of tank engines.
Some time before the evacuation, diesel was tested on the KV heavy tank.
For a long time, the B-2 was subject to modernization and improvement. The disadvantages also decreased. The advantages of the T-34 tank engine made it possible to judge it as an unsurpassed example of design thought. Even military experts believed that the replacement of the B-2 with new diesel engines in the 60-70s was caused by the fact that the engine was outdated only from a moral point of view. In many technical parameters it was superior to new products.
You can compare some of the characteristics of the B-2 with modern engines to understand how progressive it was for that time. Starting was provided in two ways: from a compressed air receiver and an electric starter, which provided increased “survivability” to the engine of the T-34 tank. Four valves per cylinder increased the efficiency of the gas distribution mechanism. The cylinder block and crankcase were made of aluminum alloy.
The ultra-light motor was produced in three modifications, differing in power: 375, 500, 600 hp, for equipment of various weights. The change in power was achieved through boosting - reducing the combustion chamber and increasing the compression ratio of the fuel mixture. An 850 hp engine was even produced. With. It was equipped with turbocharging from the AM-38 aircraft engine, after which the diesel engine was tested on the KV-3 heavy tank.
Already at that time, there was a tendency towards the development of military engines running on any hydrocarbon fuel, which in war conditions simplifies the supply of equipment. The engine of the T-34 tank could run on both diesel fuel and kerosene.
Armament
Artillery. Here, without a doubt, the T-34 is in the lead by a huge margin both from the German and from any contemporary medium tanks of other powers. Equipping the newest Soviet 76.2 mm medium tank with L-11 and, subsequently, F-34 artillery systems with a muzzle velocity quite high for 1940, amounting to 612 and 655-662 m/sec, respectively, was a huge step forward for world tank building.
In essence, it was about the fact that it was the T-34 that received a universal artillery system, suitable for combating almost all possible targets of the tank: enemy armored vehicles, field artillery, anti-tank weapons, infantry, as well as a number of field fortifications. At the same time, even at the beginning of the Great Patriotic War, a certain specialization was still preserved in the artillery armament of German tanks. Thus, the 37-mm and 50-mm guns installed on the T-3 due to the low weight of the projectile and, accordingly, the low explosive content in it, were not very well suited for hitting enemy infantry and artillery and were mostly anti-tank weapons.
Unreliable diesel
Despite the demand of People's Commissar V.A. Malyshev, diesel never became reliable. Most likely, it was not a matter of design flaws, but the fact that production, evacuated to ChTZ in Chelyabinsk, had to be launched in great haste. Materials required by specifications were not available.
Two tanks with B-2 engines were sent to the United States to study the reasons leading to premature failure. After conducting annual tests on the T-34 and KV-1, it was concluded that the air filters do not retain dust particles at all, and they penetrate into the engine, leading to wear of the piston group. Due to a flaw in the technology, the oil contained in the filter flowed out through resistance welding in the housing. Dust, instead of settling in the oil, freely penetrated into the combustion chamber.
Throughout the war, work on the reliability of the T-34 tank engine was carried out constantly. In 1941, 4th generation engines could barely work 150 hours, while 300 were required. By 1945, the engine life was increased 4 times, and the number of malfunctions was reduced from 26 to 9 per thousand kilometers.
The production capacity of ChTZ Uraltrak was not enough for the military industry. Therefore, it was decided to build engine factories in Barnaul and Sverdlovsk. They produced the same B-2 and its modifications for installation not only on tanks, but also on self-propelled vehicles.
ChTZ “Uraltrak” also produced engines for a variety of equipment: heavy tanks of the KV series, light tanks BT-7, heavy artillery tractors “Voroshilovets”.
The forerunner of a new generation of Soviet tanks: T-44
The T-44 was not produced in large quantities, like the BT, or the T-34, and did not survive the entire war.
It did not become the main tank for the army. But it is still a worthy representative of Soviet tank building. Its creation began at the end of 1943, at the Design Bureau of the Ural Tank Plant, under the leadership of A. A. Morozov.
In the creation of the T-44, the developments of three tanks were widely used, the famous T-34, T-34M and T-43.
T-34M
The T-34M began to be developed in 1940, in parallel with the T-34. It was planned to install more powerful 60 mm frontal armor, a 600-horsepower engine, and an 8-speed gearbox. Chassis with 6 support rollers and 3 support rollers. They wanted to place the engine across the hull, turning it 90 degrees, they could reduce the length of the vehicle and increase the ammunition load of the 76 mm cannon to 100 rounds (the T-34 has 77). This tank promised to surpass the T-34 in all respects (armor, firepower, mobility). But in the end, the military command did not support the designers’ innovations; apparently they did not want to scatter their forces by concentrating on the T-34, and the project was canceled. The designers were assigned another task - designing the T-43.
At the same time, the creation of tanks weighing 30, 40, 50 tons, with frontal armor of 75, 90, 120 mm, guns of 57, 76 and 107 mm caliber was interrupted. But the meeting of the Germans in the summer of 1941 with the T-34 and KV became, according to their own recollections, a very unpleasant “surprise”. I think a meeting with the T-34M would not have pleased them either.
T-43
The T-34 tank was modernized several times during the war and reached its ceiling. The Red Army needed a new medium tank class vehicle. The design of the T-34 was completed by June 1943. The main requirement for it was maximum protection, with a minimum increase in the mass of the tank.
The hull had 75 mm all-round armor, the frontal part of the turret was 90 mm (for comparison, the T-34 had 45 mm). But the length of the engine-transmission compartment could not be reduced, so the fighting compartment was smaller. To provide the crew with more space, the designers for the first time installed a torsion bar suspension on a medium tank, smaller than a spark plug suspension, with vertical springs, like on the T-34.
The T-43 surpassed the T-34 in armor protection, approached the KV in firepower, but greatly increased the specific pressure on the ground, which had a bad effect on mobility and power reserve. Yes, and its design came out to the limit. Excluding the possibility of major modernization. Therefore, when the T-34 was equipped with an 85 mm cannon, the need for the T-43 disappeared.
But the experience of its creation was not lost, for example: its test run of 3 thousand km clearly showed the correct installation of the torsion bar suspension. It became clear that a fundamentally new vehicle was needed - it was called the T-44.
T-44
It also featured a transverse engine arrangement, but also a number of new technical innovations; as a result, the design of the T-44 determined the development of tanks in the USSR for several decades.
The height of the MTO was reduced by moving a new type of air cleaner from the V-engine camber to the side. The V-44 diesel engine was equipped with improved fuel equipment, which made it possible to increase power from 500 to 520 hp. s., with the same cylinder volume as on the B-34. In place of the fan, which protruded beyond the dimensions of the crankcase, a compact flywheel was installed. This made it possible to install the diesel engine on a low, rigid and light engine frame. Thus, the height of the case was reduced to 300 mm. The fan was moved towards the rear sheet, this improved the cooling of the transmission units.
The water and oil radiators were placed horizontally (on the T-34 they stood vertically), under the transmission compartment cover, in a uniform air flow, so the cooling system became more efficient.
The engine was connected to a new 5-speed gearbox, an overdrive gearbox with a gear ratio of 0.7. The side clutches and gears were taken from the T-34.
The new MTO scheme made it possible to move the turret with the 85-mm cannon (as on the modernized T-34) to the center of the hull, where the crew was less subject to angular vibrations and the cannon was not at risk of sticking into the ground. When moving over rough terrain, shooting accuracy also increased.
The frontal armor of the hull was increased to 120 mm, the driver's hatch was moved to the roof of the hull, and the ball mount of the course machine gun was removed. And a fuel tank was installed in the vacant space.
The T-44 successfully passed all tests and was adopted by the Red Army.
At the end of the 40s, a new turret with a 100 mm D-10T, or LB-1 (Lavrenty Beria, because he was the deputy chairman of the State Defense Committee and was in charge of armaments) was developed. A turret with a DShK anti-aircraft machine gun was installed on the roof of the loader's hatch; the sides and chassis were covered with 6 mm cumulative screens. This modernization was called T-44-100.
With the advent of the T-54, the T-44 was not withdrawn from service; in 1961, the engine, power transmission, and chassis units were unified with those installed on the T-54. Night vision devices were installed. In 1966, a weapon stabilizer was installed in two planes. It remained in service with the Soviet army until the end of the 70s.
They did not participate in hostilities, except for participation in the operation to suppress the rebellion in Hungary in 1956. Participated in the filming of Ozerov’s epic “Liberation” - in the role of the German “Tigers”
Artillery, tank tractors, and engineering vehicles were produced on the basis of the T-44. A total of 1,823 tanks of this type were created; the tank was produced until 1947.
Performance characteristics of the T-44 medium tank
Weight, t – 31.5 Armament – 85 mm ZIS-S-53 cannon, 2 DTM machine guns Armor, mm, hull – 120-45, turret 90-75 Engine – V-44 diesel power 520 hp With. Max. Highway speed, km per hour – 55 Cruising range, km – 235 Length with gun, mm – 7650 Hull length, mm – 5850 Width, mm – 3100 Hull width, mm – 2000 Height, mm – 2400 Ground clearance, mm – 430 Crew - 4
The weight of the modernized T-44M reached 32 tons, maximum armor 120 mm, speed - 57 km per hour.
The weight of the T-44-100 reached 34 tons, the speed was 55 km per hour. Armament: 100-mm LB-1 or D-10T cannon, DShK anti-aircraft machine gun, two DTM or GVG machine guns.
Tank engine in civilian life
The career of the T-34 tank engine did not end with the end of the war. Refinement of the design continued. It formed the basis for many modifications of tank V-shaped diesel engines. B-45, B-46, B-54, B-55, etc. - all of them became direct descendants of the B-2. They had the same V-twin, 12-cylinder concept. Various hydrocarbon mixtures could serve as fuel for them. The body was made of aluminum alloys and was lightweight.
In addition, the B-2 served as a prototype for many other engines that were not related to military equipment.
The civilian ships “Moskva” and “Moskvich” received the same engine that was installed on the T-34 tank, with minor changes. This modification was called D12. In addition, diesel engines were produced for river transport, which were 6-cylinder V-2 halves.
The 1D6 diesel engine was equipped with shunting locomotives TGK-2, TGM-1, TGM-23. In total, over 10 thousand units of these units were produced.
MAZ mining dump trucks received 1D12 diesel. The engine power was 400 hp. With. at a rotation speed of 1600 rpm.
Interestingly, after modifications, the engine’s potential increased significantly. Now the assigned engine life before major repairs was 22 thousand engine hours.
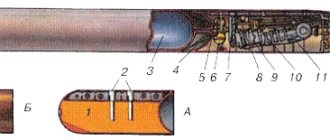
MANAGEMENT OF THE COMMANDER OF ARMOR AND MECHANIZED FORCES OF THE RED ARMY For official use “APPROVED” - Deputy.
N-K-KA Red Army General Lieutenant General of the Engineering Service I. Lebedev on June 7, 1944 Tank T-34 leadership of the second fixed publication Military Publishing House of the People’s Commissariat of Defense Moscow-1944 in the preparation of this leadership was attended by engineers of the exploitation department and design bureau of the plant No. 183 named after the Comintern vol.: Kaganer B.A., Levchuk E.K., Mitnik A.Ya., Nechaev L.N. and major engineer of the GBTU of the Red Army Kachur I.S. The manuscript was half-prepared for publication by the officers of the Editorial and Publishing Department of the State Administration of the Fleet and the BP BTMV of the Red Army, engineer-lieutenant colonel Goryushin N.Kh., engineer-lieutenant colonel Chufarovsky B.I., engineer-captain Kotlyar S.I. and senior technician-lieutenant B.M. Sytin. Editor: engineer-lieutenant colonel Goryushin N.Kh. Technical editor Strelnikova M.A. Proofreader Kurashov A.A. CHAPTER ONE GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF THE TANK The T-34 tank is a tracked combat vehicle with a rotating turret that provides all-round fire from a cannon and a coaxial machine gun. The tank is armed with a 76-mm F-34 cannon or an 85-mm S-53 cannon and two machine guns (one is paired with the cannon, the other is installed in the bow of the tank). T-34 tank crew: 4 people. The main parts of the tank: · armored hull and turret (they accommodate the crew, as well as weapons, ammunition, surveillance and communication devices, electrical equipment and tank mechanisms); · engine: diesel engine brand V-2-34, V-shaped, water-cooled; · transmission mechanisms: main clutch, gearbox, side clutches, brakes, final drives; · control drives: side clutch levers, main clutch and foot brake pedals, gear shift mechanism; · chassis: drive wheels, track chains, idler wheels (sloths), road wheels with balancers, suspension; · equipment and gear. Inside, the tank hull is divided into four compartments: control, combat, engine, and transmission. The control compartment is located in the bow of the tank. It contains the seats of the driver and gunner-radio operator, control drives for the tank mechanisms, instruments that control the operation of the engine and electrical equipment, a DT machine gun in a ball mount, part of the ammunition, a radio station, two compressed air cylinders for air starting the engine, spare parts, tools and accessories. The fighting compartment is located in the middle part of the tank. Above it there is a turret mounted on a ball support, which houses weapons, part of the ammunition, surveillance devices, as well as seats for the tank commander and turret gunner. A fan motor is installed in the tower ventilation hatch. The main part of the ammunition is stowed in the fighting compartment - on the floor and near the sides. Behind the removable iron sheets of the bulwarks, between the suspension shafts, there are fuel tanks. The engine compartment is located in the middle part of the tank, behind the fighting compartment, from which it is separated by a partition. This compartment contains: an engine, two water radiators, two oil tanks and four batteries - in pairs, on brackets, between the lower half of the engine crankcase and the radiators. The transmission compartment is located in the rear of the tank. It contains the main clutch with a centrifugal fan, a gearbox, side clutches with brakes, an electric starter, final drives and two fuel tanks. COMBAT AND TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE TANK General data Vehicle type Medium tracked tank Combat weight 30 t Tank dimensions T 34 Length 6070 mm Width 2950 " Overall height 2604 " Height without turret 1697 " Track width (distance between the centers of the track chains) 2450 " Ground clearance 400 " D Lina bearing surface on tracks 3840 » Estimated travel speeds at 1700 rpm of the engine shaft (in km/h) Travel speeds are rounded Five-speed gearbox: Four-speed gearbox In 1st gear 6.65 7.40 In 2nd » 14, 25 15.45 In 3rd » 20.00 25.60 In 4th » 30.50 48.30 In 5th » 48.30 — In reverse gear 7.50 6.90 Fuel and lubricant consumption and reserve Fuel consumption per 1 km of travel: on a dirt road 2.3 liters on a highway 1.6 » Fuel consumption for 3 hours of engine operation: on a dirt road at an average speed of 25 km/h. 50 » on the highway at an average speed of 30 km/h 48 » Fuel range (considering only the main tanks): on a dirt road approx. 250 km by highway approx. 300 » Oil consumption per 1 km: on a dirt road 0.10 liters on a highway 0.05 » Oil consumption per 1 hour of engine operation: on a dirt road at an average speed of 25 km/h 2.00 liters on a highway at an average speed at 30 km/h 1.50 l Armament Cannon brand F-34, S-53 caliber 76 mm, 85 mm horizontal firing angle 360° 360° elevation angle 28° 22…25° descent angle 5° 5° Machine guns quantity 2 brand DT placement one is paired with a cannon, the other is located in the bow of the tank horizontal angle of fire of a machine gun installed in the turret 360° horizontal angle of fire of a machine gun installed in the bow of the tank ±-12° maximum elevation angle of a machine gun installed in the bow of the tank 16 ° maximum angle of descent of a machine gun installed in the bow of the tank 6° Submachine gun (stowed in the turret) brand PPD or PPSh quantity 1 Transportable combat kit for the F-34, S-53 gun shells for the gun 100, 56 machine gun discs 50 (3150 cartridges) 31 (1953 cartridges) cartridges for a submachine gun 4 disks 4 disks F-1 hand grenades 25 20 Tank engine T34 engine brand V-2-34 cylinder arrangement V-shaped at an angle of 60° cylinder numbering order from the fighting compartment to transmission (separately for each group of cylinders) number of cylinders 12 cylinder diameter 150 mm piston stroke: left row 180 mm right row 186.7 mm displacement of all cylinders 38.88 l compression ratio 14 - 15 direction of rotation of the crankshaft clockwise (if view from the fighting compartment) Engine power: nominal at 1750 rpm 450 hp. operational at 1700 rpm 400 hp. maximum at 1800 rpm 500 hp minimum stable idle speed 600 rpm maximum permissible idle speed 2050 rpm specific fuel consumption in normal and operating modes 160-175 g/hp. hour Gas distribution Intake valve number of valves in cylinder 2 opening to TDC in degrees of crankshaft rotation. 20±3 closing after BDC in degrees of crankshaft rotation 48±3 duration of suction in degrees of crankshaft rotation 248 maximum valve lift 13 mm gap between the valve stem plate and the back of the camshaft cam 2.34±0.1 mm 2 22° - at wide pursuit, 25° - with narrow pursuit. Exhaust valve number of valves in cylinder 2 opening before BDC in degrees of crankshaft rotation 48±3 closing after TDC in degrees of crankshaft rotation 20±3 duration of exhaust in degrees of crankshaft rotation 248 maximum valve lift 13 mm gap between the valve stem plate and the back of the camshaft roller 2.34±0.1 mm Operating order of cylinders 1 l - 6 p. 5 l - 2 p. 3 l - 4 p. 6 l - 1 p. 2 l - 5 p. 4 l - 3 p. Power system engine used diesel fuel fuel tanks: main onboard 6 main aft 2 additional external 3 capacity of the main tanks 570...580 l capacity of additional tanks 270 l Fuel pump supply system Fuel pump type rotary lobe BNK-12B number of pumps 1 ratio of the number of revolutions of the pump to the number of revolutions of the crankshaft shaft 0.786 fuel pressure supplied by the fuel priming pump in operational mode, measured, After the fuel filter 0.5...0.7 kg/cm2 Fuel pump type NK-1 number of pumps one 12-plunger numbering order of pump sections from the fighting compartment to the transmission section, servicing the left block even sections servicing the right block odd order of operation of sections 2 - 11 - 10 - 3 - 6 - 7 - 12 - 1 - 4 - 9 - 8 - 5 constant advance angle of fuel supply by the fuel pump in degrees of rotation of the crankshaft (clutch no advance) 30...33 direction of rotation counterclockwise if you look at the engine from the side of the fighting compartment) ratio of the number of revolutions of the fuel pump to the number of revolutions of the crankshaft 0.5 Injector type closed injector spring tension 200 kg/cm2 Regulator type centrifugal Engine lubrication system used oil aviation oil: summer - MK winter - MZ oil tanks number of tanks 2 filling capacity 80 l lubrication system combined circulation system "dry sump" three-section gear oil pump one injection section, two suction sections ratio of oil pump speed to crankshaft speed 1.725 oil pressure in operating mode after passing through the oil filter 6...9 kg/cm2 oil pressure after passing through the filter at a steady minimum engine speed of not lower than 2 kg/cm2 oil temperature when leaving the engine is not higher than +105°C specific oil consumption in operating mode is not more than 13 g/hp/hour. oil pump performance at 1600 crankshaft rpm 3750 l/hour Engine cooling system water type, forced Radiators tubular type cooling surface (both radiators) 107.36 m2 filling capacity 80 l. Water pump centrifugal type ratio of water pump speed to crankshaft speed 1.5 water pump performance at 2550 rpm impeller 500 l/min outlet water temperature not higher than +1050C Engine starting system main electric starter starting system additional (spare) compressed air starting system maximum air pressure in cylinders 150 kg/cm2 pressure of air entering the air distributor is not higher than 90 kg/cm2 and not lower in summer - 45 kg/cm2, in winter - 65 kg/cm2 the moment of air supply starts - up to TDC on the compression stroke in degrees of rotation of the crankshaft 6±3 Drive to tachometer drive type flexible shaft ratio of the number of revolutions of the flexible shaft to the number of revolutions of the crankshaft 0.5 direction of rotation of the drive shaft clockwise (when viewed from above the engine) Tank transmission Main clutch type multi-disc dry disc material steel number of driving disks 11 number of driven disks 11 number of springs 16 clutch release mechanism ball with inclined grooves in release rings maximum force required to disengage the clutch 25 kg connection to the gearbox through a gear clutch Gearbox Type three-way five-speed or three-way four-speed Number of gears five-speed gearbox five forward and one reverse four-speed gearbox four forward and one reverse gear ratios five-speed gearbox four-speed bevel gearbox 1,859 1,859 in first gear 5,570 5,000 in second gear 2,600 2,390 in third gear 1,855 1,450 in fourth gear 1.215 0.756 in fifth gear 0.756 in reverse gear 4.950 5.350 splash lubrication Onboard clutches and brakes clutch type multi-disc, dry disk material steel total thickness of disk set 137.6±1 mm number of drive disks from 17 to 21 (depending on their thickness ) number of driven disks from 18 to 22 (depending on their thickness) number of springs 18 ball clutch release mechanism with inclined grooves in the release rings maximum force on the lever handle required to disengage the side clutches 20 kg type of brakes band with cast iron pads (floating type) outer diameter of the driven drum 500 mm belt width 200 mm Final drives type single-stage reduction gearbox gear ratio 5.7 splash lubrication Tank undercarriage Drive wheels type of engagement ridge, with rollers arrangement on the splines of the final drive shafts outer diameter 634 mm Crawler chain type fine-link gearing comb number of tracks in each chain 72, of which 36 with a comb and 36 without a comb connecting the tracks with fingers having a head and without a cotter pin (the heads are facing the body) driving the fingers into place when they come out towards the body with “fists” attached to final drive cover track pitch 172 mm track width 500 mm method of tensioning the track chain by turning the crank of the guide wheel method of turning the crank by a worm pair Guide wheels (sloths) wheel rims steel installation on the crank outer diameter 500 mm Track rollers type with external shock absorption (rubber-coated tires) or with internal shock absorption and steel rims (only for the 2nd, 3rd and 4th rollers) number of five rollers on each side diameter of the rollers with external shock absorption 830 mm with internal shock absorption 830 mm width of the rubberized tire 150 mm width of the disk of the roller with internal shock absorption 100 mm Suspension spring type, individual arrangement of suspensions inclined number of springs in each suspension 2 arrangement of springs at the front rollers concentric arrangement of springs at the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th road wheels, one above the other roller stroke: up 140 mm down at the front roller - 75 mm, for the 2nd, 3rd, 4th and 5th rollers - 115 mm Electrical equipment single-wire wiring system (emergency lighting - two-wire) mains voltage 24 and 12 V Sources of electricity Electric generator brand GT-4563-A power 1000 W voltage 24 V ratio number of revolutions of the generator shaft to the number of revolutions of the crankshaft 1.5 type of drive non-disengaging friction clutch direction of rotation clockwise (as viewed from the drive side) battery charging begins at 665 rpm of the engine crankshaft relay-regulator RPA-24 F Rechargeable batteries brand 6-STE-128 type acid Capacity 128 Ah number of batteries 4 voltage 12 V start of charging at 665 crankshaft rpm Electricity consumers Electric starter brand ST-700 power 15 hp voltage 24 V Electric motor of the tower turning mechanism brand MB-20A serial type, four-pole power 1350 W. Voltage 20 V speed (maximum) 5800 rpm current consumption 90...120 A gear ratio from the armature shaft to the tower ring 1257 Electric fan motor brand MV-12 power 19 W speed 1500 rpm voltage 12 V current consumption 3, 8 A Lighting devices headlight 1 (left) with two lamps of 25 and 5 W signal lamp 1 (rear) with a lamp of 5 W lighting of the control panel 1 lamp of 5 W lighting of the electrical panel 1 lamp of 5 W interior lighting 2 lamps with 10 W lamps transmitter lighting 1 5 W lamp lighting of artillery equipment 3 0.15 W lamps illumination of the protractor scale 1 10 W lamp Electrical signal type GF-4702 power consumption 60 W Radio station 9-R power consumption 150 W radio station umformers two: one RU -45V, 47 W to power the anode circuits of the transmitter and one RU-11V 35 W to power the anode circuits of the receiver. Observation and communication equipment in the driver's hatch 2 periscope viewing devices in the turret 2 viewing slits TMFD-7 and PT-4-7 aiming and observation devices, paired with a gun External communications radio type 9-R range 18 km when parked, at with the engine turned off - up to 25 km. Internal communication device type TPU-3R number of devices 3 installation location telephone set No. 1 for the driver telephone set No. 2 for the gunner-radio operator telephone set No. 3 for the tank commander CHAPTER ONE GENERAL DESCRIPTION CHAPTER TWO ARMOR CASE CHAPTER THREE ARMAMENT CHAPTER FOUR V-2 ENGINE -34 POWER SYSTEM LUBRICATION SYSTEM COOLING SYSTEM CHAPTER FIVE TRANSMISSION MAIN CLUTCH GEARBOX ONBOARD CLUTCHES CHAPTER SIX RUNNING GEAR CHAPTER SEVEN ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT GENERAL INFORMATION CURRENT SOURCES CURRENT CONSUMERS CHAPTER EIGHT COMMUNICATION CHAPTER NINE MAINTENANCE TANK REFUELING TECHNICAL INSPECTIONS TANK LUBRICATION WINTER AND SUMMER OPERATION TANK OPERATION GUN C-53 ADDITIONAL INSTRUCTIONS APPENDIX
Tank battles in World War 1 and World War 2. Performance characteristics of tanks in World War 1 and World War 2.
Identification marks
Tank aces of the USSR: list, photo galleries (1), (2)
The war is over home page
URL SP1-REAL 6.8 for Steel Panthers I ver.1.2
Mobile anti-aircraft installations of the USSR
Characteristics of various modifications of Soviet tanks
Ilya Muromets Russian bombers in World War I and Russian Civilian War
Aces of Spanish Civil War
Characteristics and design of the T-34 tank engine
The high-speed, compressorless diesel B-2 was water-cooled. The cylinder blocks were located at an angle of 60 degrees relative to each other.
The motor operation was carried out as follows:
- During the intake stroke, atmospheric air is supplied through the open intake valves.
- The valves close and the compression stroke occurs. The air pressure increases to 35 atm, and the temperature rises to 600 °C.
- At the end of the compression stroke, the fuel pump supplies fuel under a pressure of 200 atm through the injector, which ignites at high temperature.
- The gases begin to expand sharply, increasing the pressure to 90 atm. The engine's power stroke occurs.
- The exhaust valves open and exhaust gases are released into the exhaust system. The pressure inside the combustion chamber drops to 3-4 atm.
Then the cycle repeats.