Features of diesel oil
Diesel fuel contains more sulfur than gasoline. When diesel fuel burns, sulfur oxides are formed, which quickly saturate the oil during operation of the internal combustion engine. The high compression ratio required to ignite diesel fuel is the reason that a greater amount of gases enters the engine crankcase from the combustion chamber compared to a gasoline unit. The above gases also lead to active oxidation of the oil.
The main requirements for diesel oil are:
- washing ability;
- high resistance to oxidation.
The base for diesel/gasoline oils is often the same; they differ only in different additive packages. Similar additives are contained in oil for both types of engines, and they also differ in composition depending on the units for cars, trucks, etc.
Diesel oil contains special binding and detergent additives. Therefore, the replacement interval for diesel oils is shorter compared to similar requirements in gasoline units. It turns out that diesel oil requires more frequent replacement due to the rapid accumulation of sulfur oxides and soot deposits.
In other words, diesel oil loses its lubricating ability more slowly, but the oxidation process is much faster. Therefore, diesel oil manufacturers add additives that most effectively neutralize the effects of oxidation products. Oils for diesel power units often have a high base number and show higher oxidation resistance.
Features of diesel engine oil
Diesel engines, due to their characteristics, have a very high compression ratio, so there is a very high probability of gases breaking through from the combustion chamber into the engine crankcase (where the oil is located). Due to the fact that it is difficult to achieve complete combustion of fuel in a diesel engine, the exhaust gases always contain a lot of soot and sulfur. Exhaust gases entering the crankcase, due to the high content of soot and sulfur, cause rapid oxidation (or else they say “aging”) of the engine oil, as a result of which the oil loses its properties . In this regard, the oil used in diesel engines must contain an additive package that prevents its oxidation and a larger amount of detergent additives.
READ Mortgage debts of Russians reached record levels
Features of gasoline oil
If we consider gasoline internal combustion engines, then gasoline itself is lighter and contains much less sulfur, which allows the fuel to burn more fully. Therefore, gasoline oil does not require special diesel additives. For gasoline oils, it is of greater importance that such power units are capable of operating at significantly higher speeds compared to diesel engines (7-8 thousand rpm). Even the highest-speed diesel engines spin up to only 4.5 thousand rpm. The operating speeds of diesel and gasoline engines operated in normal mode also differ significantly.
These features mean that gasoline engine oils are less susceptible to oxidation, and must also provide sufficient lubrication and protection of rubbing parts (stability of kinematic and dynamic viscosity during shear deformation) at high speeds, which is taken into account when creating an individual additive package.
Features of diesel oil compared to gasoline
Diesel fuel contains more sulfur compared to gasoline. The combustion of diesel fuel leads to the formation of sulfur oxides, which quickly saturate the engine oil during operation of the internal combustion engine.
The high degree of compression required for ignition of diesel fuel leads to a larger amount of gases breaking into the crankcase of a diesel engine from the combustion chamber compared to a gasoline engine. These gases also cause the oil to actively oxidize.
The main requirements for diesel engine oil are:
- washing ability;
- increased resistance to oxidation;
The basic base for gasoline and diesel oils is often the same; the differences lie only in the different packages of additives used. Such additives are included in motor oil for gasoline and diesel internal combustion engines, and also differ in composition depending on engines for passenger cars, heavy trucks, etc.
Diesel oil contains special detergent and binding additives. For this reason, the replacement interval for diesel oils is reduced compared to similar requirements for oil change intervals in gasoline engines. It turns out that diesel oil needs to be changed more often due to the rapid accumulation of soot deposits and sulfur oxides.
In other words, diesel oil does not lose its lubricating ability as quickly, but oxidation processes occur much faster in it. For this reason, manufacturers add additives to diesel oils that neutralize oxidation products as effectively as possible. Diesel oils often have a higher base number and demonstrate increased oxidation resistance compared to gasoline oils.
As for gasoline internal combustion engines, gasoline itself is lighter, it contains much less sulfur, and such fuel burns more fully. Gasoline oil simply does not need special diesel additives. For gasoline oils, it is more important to take into account that such engines are capable of operating at significantly higher maximum speeds compared to diesel engines (about 7-8 thousand rpm). Even high-speed diesel units spin up only to 4-4.5 thousand rpm. The operating speeds of gasoline and diesel internal combustion engines, at which the engines are operated in normal mode, also differ significantly.
We also recommend reading the article about how a turbine works on a diesel engine. From this article you will learn about the design and operating principles of a turbocharger on a diesel engine.
These features mean that gasoline oils are less susceptible to oxidation and should provide reliable protection and lubrication of rubbing parts (stability of dynamic and kinematic viscosity under shear deformation conditions) at high speeds, which was separately taken into account when creating an individual additive package for them.
What is the difference between diesel oil and gasoline
It’s worth starting with the fact that gasoline and diesel engines operate on a similar principle; they burn a fuel-air mixture in the cylinders. It is well known that the main task of engine oil is to lubricate parts at friction points. Based on this, it may seem that any oil will cope with its functions, regardless of which engine it is used with. Moreover, some time ago, lubricants for diesel and gasoline engines were clearly differentiated by area of application. Reasons for this division:
- individual characteristics of different types of internal combustion engines (crankshaft speed, method of ignition of the mixture, temperature, loads at the joints of parts, etc.);
- different types of fuel used (diesel fuel and gasoline), which differ in properties and composition.
It turns out that despite the similar principle of operation of the two types of engines, gasoline and diesel oils still have differences. If you don’t delve too deeply into the specifics of the process, oil oxidation in a diesel engine occurs much faster than in its gasoline counterparts. This happens due to the type of fuel used, as well as the compression ratio of the power unit.
In a diesel engine, after combustion of the fuel charge, which contains air and diesel fuel, an impressive amount of residual elements (soot) remains. The increased compression ratio (about 100% higher than in gasoline-powered units), required to heat the air, which then allows the existing mixture to ignite without the help of spark plugs, allows a larger volume of gases to enter the engine crankcase. These gases significantly accelerate the oxidation of oil.
Taking into account such features, manufacturing companies add special additive packages to diesel oil. Their necessity is also dictated by the fact that diesel fuel contains more sulfur compounds than gasoline. As a result, many sulfur oxides are formed in diesel fuel after combustion of the fuel charge. The resulting products have a very aggressive effect on the engine and lubricant. This means that additives are separately added to diesel oils to combat oxidation. In other words, the ash content and alkaline number in diesel oil will be significantly higher in terms of this indicator compared to lubricant for a gasoline engine.
In parallel, diesel engine oil contains active components that slow down aging and enable the lubricant to remain more stable against the background of ongoing oxidative processes. It should also be noted that a diesel engine requires more air to function properly than a gasoline engine. As a result, there is a higher tendency to coking and carbon formation. To counteract this, the oil must have improved cleaning properties, and its service life should not be significantly reduced.
Regarding oils for gasoline units, the fuel charge burns without much soot emission. Gasoline also initially contains lower amounts of sulfur compared to diesel fuel. So there is no need to include detergent components and increase the base number in the additive package for gasoline oil.
Another difference can be considered the different operating speeds of the power units. For this reason, gasoline oil contains additives that improve the protection of stressed parts at high speeds. For oil in a gasoline unit, it is important to ensure stability of kinematic and dynamic viscosity while taking into account shear deformation. For a diesel engine, which does not spin up so much, this parameter is less significant.
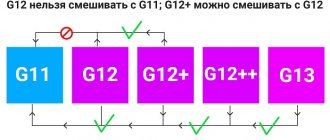
Is it possible or not?
You can pour lubricant from a diesel engine into a gasoline engine, but for a short period of time. And the lubricant from a gasoline engine will destroy a diesel engine. Since it does not contain the necessary compounds that can clean the parts of the power unit as well as diesel lubricant does.
Experienced mechanics advise using diesel lubricant wisely in a gasoline engine. This does not mean that a lubricant should be considered a panacea for all contaminants. There is no need to run headlong to the store, buy similar oil and clean the engine with it. It is better to use a universal liquid.
Universal oil
The balanced composition of modern lubricants allows such liquids to be poured into both engines. They are equally good for diesel engines and will not harm a gasoline engine. Additionally, the liquid cleans motors.
Designed specifically for operation over a wide temperature range. The base number is neutralized by additives. The oxidative processes that the oil puts into action when it enters the engine are also strictly regulated by special additives.
Universal lubricating fluids are completely synthetic. They do not contain natural minerals. They were bred in chemical laboratories specifically to solve problems comprehensively.
Similar article Installing a VAZ engine on a LUAZ
However, the opinions of some experienced mechanics differ from the opinions of other mechanics. Some argue that multi-purpose lubricants are a real and high-quality solution that increases the life of the power unit. Others are categorically against the use of such oils.
For example, the latter claim that only strictly profiled oils are suitable for use in different engines. Otherwise, the durability of the engine is reduced.
It is impossible to say anything specific about this. Since everything depends not so much on the oil, but on how the car owner operates his car. If you don’t take care of the engine and don’t send it for preventative maintenance on time, then you can kill the engine in two years.
Diesel oil
Filling diesel oil into a gasoline engine is necessary only in rare cases. Because initially it is impossible to mix different oils according to the internal parameters of lubricants. What can we say about the types of oils for different engines.
Autodiesel is recommended to be used only in extreme cases. First, thoroughly flush the system to remove any remaining lubricant for the gasoline power unit. And only then add fresh diesel lubricant.
If it is necessary to add lubricant, and there is none nearby except diesel, then experienced mechanics recommend adding any lubricant to avoid oil starvation. After such a maneuver, it is recommended to visit a service center. It is necessary to completely flush the engine and change the fluid.
Use of universal oils
The different additive packages in diesel and gasoline oils create certain inconveniences when servicing large vehicle fleets. Such fleets usually contain passenger cars, minibuses, and heavy trucks with various power units.
And the emergence of universal oils is intended to solve this problem. Such oils comply with ACEA and API approvals for both types of engines; they can be poured into any units. Since the base oil is the same, its versatility is ensured by a balanced and effectively selected additive package. The available components make it possible to neutralize processes characteristic of both diesel and gasoline engines.
It must be separately taken into account that the oil for a diesel unit is much more sensitive to the quality of the diesel engine in comparison with similar gasoline engines. The use of universal oil requires the operation of a diesel engine exclusively on high-quality diesel fuel with limited sulfur content.
If you are not confident in the quality of the fuel, the use of universal oil in a diesel unit is not recommended. Diesel oil, which was originally developed for engines of this type, often has a high base number and ash content, and also contains active detergent and dispersant additives.
Universal motor oils
Manufacturers have begun to release universal types of oils onto the market, which should solve problems with the selection of materials for filling into the engine. They must comply with API and ACEA approvals, and this means that they can be used with any motors.
Manufacturers must correctly select the amount of additives that will not interfere with the stable operation of the engine. If you choose the right active components, this will neutralize the negative consequences of gasoline and diesel engines.
But you need to use universal oil carefully, especially in cases where the motorist is not sure of the quality of the fuel used. Diesel engine oil has a special composition that has a high base number and ash content, and also contains the necessary additives in sufficient quantities.
Consequences of gasoline oil getting into a diesel engine
Many modern oils created for passenger cars can be used for both types of engines. The “diesel” marking on such oils is largely a marketing ploy. Motor oils only for gasoline engines are distributed mainly in the North American market.
Gasoline oil differs from universal gasoline in its reduced content of additives, especially ash ones. High-quality gasoline contains few contaminants and acids that need to be neutralized (there are significantly more of them in diesel). The fewer additives there are in the fuel, the less insoluble deposits appear in oil waste, an inevitable product of the operation of any engine.
Diesel oil requires more detergent qualities in the oil used, so the oil contains more additives. If exclusively gasoline motor oil contains no more than 5% additives, specialized diesel oils have a figure of up to 15%.
So, if you pour gasoline oil into a power unit using a diesel engine, its cleaning properties will not be enough and the engine will quickly coke.
Consequences of diesel oil getting into a gasoline engine
When engine oil enters the combustion chamber through valve stem seals or a worn piston group, deposits remain inside it. This provokes glow ignition and detonation. As a result, it is necessary to use fuel with a higher octane number. If there is low consumption of engine oil for waste between shift intervals, the ash content is reduced to almost zero.
In more understandable terms: if the engine oil consumption during the interval between its replacement is less than 0.5-1 liters, then diesel lubricants can be poured into the engine without negative consequences.