What is an engine breather and why is it needed?
Everyone knows that the internal combustion engine, the same one that is installed under the hood of your car, does not run on gasoline, diesel or gas, but on their mixture with air. Moreover, it is air, which costs nothing (unlike fuel, for which we regularly pay a tidy sum at the gas station), that is required many times more. But in addition to the influx of clean air and the removal of exhaust gases through the exhaust pipe, parasitic gases are formed during the operation of the internal combustion engine.
A breather is nothing more than a breathing valve that constantly relieves excess pressure that forms inside the engine during operation. The need for this simple, relatively inexpensive part is difficult to overestimate.
Where is the engine breather located?
From engine to engine, different car manufacturers may place the breather in different places. But in most cases it is located on the valve cover, next to the filler neck. Although there may be options: it is better to clarify in the description instructions for the car or find out on thematic forums.
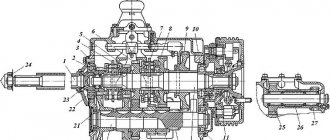
In the picture on the right is the crankcase ventilation system of the VAZ 2111 engine, which includes a breather:
- Crankcase.
- Breather.
- Hose from the breather to the valve cover pipe.
- Oil separator under the valve cover.
- A thin hose from the valve cover to the fitting with the throttle body nozzle.
- Fitting with jet on the throttle valve block.
- Thick hose from the valve cover to the intake pipe..
But the breather is installed not only in internal combustion engines. It is in:
- Gearbox. Otherwise, the gearbox would begin to operate jerkily, and the wear of the gears on the secondary shaft would increase many times over. Something similar is observed when the breather becomes clogged and ceases to perform its function.
- If the design of the car provides for a separate transfer case, then a similar mechanism may be in it.
- Front, and in rear-/all-wheel drive vehicles - in the rear axle. Moreover, this inconspicuous detail not only equalizes pressure, it protects the mechanisms from dirt and moisture when overcoming water obstacles.
However, even their appearance is often similar, and often identical: they perform the same function.
Difficult to eliminate causes of oil leakage from the gearbox
To eliminate an oil leak, you will have to spend time and sweat. The reasons require the participation of car repair specialists, but if you set a goal, you can cope without them.
Replacing oil seals.
If the obvious causes of oil leakage have been eliminated, but leaks continue to appear with enviable frequency, the seals are examined.
Special rubber seal in a metal frame. Serves to prevent leaks and oil on the moving elements of the engine and gearbox.
Long-term use of the oil seal wears out the rubber base. Oil pressure does not hold. If the oil seals have been replaced recently, you need to think about the quality of the oil used.
The replacement procedure is as follows:
- oil is drained;
- the wheel bearing mount is dismantled;
- the bolts securing the ball joint are unscrewed;
- the steering knuckle is retracted;
- the axle shaft is dismantled;
- remove the oil seal using a regular screwdriver;
- Before installation, the oil seal is lubricated with oil;
- Installation of the cuff is carried out by lightly tapping the hammer through the mandrels.
Breather device
Typically, the internal structure of the breather is very simple. Let's look at it using the example of a breather for a gearbox/axle.
- External breather housing. It is made of metal, so it cannot be damaged while driving.
- Pressure spring. Thanks to it, the mechanism does not need an electrical/mechanical drive, everything is autonomous.
- Rubber gasket. It is this that ensures tightness when excess pressure is not released.
- Lock nut. The simplest method of fixation: although in other models there are a variety of options.
- The breather body itself. The through hole allows the unit to “breathe”, relieving excess pressure.
Although this breather is not used for engines, the principle is the same. An elementary module that you simply cannot do without.
Why is there smoke coming from the breather?
There can be only one malfunction of the breather: it began to poorly pass accumulated gases, comparing the pressure inside the engine with atmospheric pressure. But the smoke coming from it can say a lot:
- The cylinder oil scraper rings were stuck or worn out. Simple decarbonization using traditional methods or special chemicals will not help here, so you will have to disassemble the engine.
- Likewise, if one/several exhaust valves burn out. A simple compression test will help determine this.
- Oil seals. Just replace them when it's time or they show signs of increased wear.
- The shaft seals, which allowed oil vapors to pass through, were worn out. Change them without hesitation, preferably without shelving them.
- The oil in the engine is old and needs replacing for a long time. No comments: as practice shows, repairing the “heart” of a car is tens of times more expensive than replacing it.
- White smoke on a hot engine - coolant enters the lubrication system. You'll have to look for where exactly the leak is.
- Oil overflow. In an internal combustion engine, it is just as dangerous as underfilling: engine wear/fuel consumption increases significantly, so check its level with a dipstick on a level surface when the engine is well warmed up. Then you will see how well the technicians at the service station (or you yourself) performed its replacement/topping up.
- The oil is of poor quality/not suitable for the car/counterfeit. There is only one way out - replace it. Likewise, if you filled up with fuel at an unknown gas station: just don’t do it again.
- Finally, the breather itself clogged from time to time, not working at 100%. Simple cleaning and preventive maintenance will eliminate this.
Breather repair and maintenance
Due to its low cost, as well as ease of removal/installation, breather repair almost always comes down to replacing it. But even forgetful car owners who carry out its maintenance from time to time will not need this, since there is simply nothing to break.
All its maintenance comes down to timely cleaning. It is enough to wipe the outside with a rag, and if the stains are old, you will have to use a knife, screwdriver or scraper.
Cleaning the inside is a little more difficult, but still very simple. The breather must be removed (it can be bolted or firmly seated “in tension”) and cleaned with a primitive cleaning rod, which can be made from a piece of wire. We do the same with the oil trap mesh: in rare cases, when it is very clogged, mechanical cleaning will not be enough. And then you need to burn it by pouring just a little gasoline, or soak it in aggressive chemicals for several hours.
Assembly, as is quite predictable, is in reverse order. Therefore, the entire process will not take much time and will not require special tools or skills.
However, this is best done during a seasonal oil change or when undergoing regular maintenance. On most cars with average mileage, it is enough to carry out this simple operation twice a year. But it is the engine breather that confirms the immutable truth: there are no small details in a car, especially a modern one.
Breather VAZ 2110 2112 2114 2115 2109
Publication date Jul 08, 2014, Categories Spare parts for VAZ |
The breather of the VAZ 2110 2112 2114 2115 2109 “makes itself felt” when the oil seals in the car’s power unit begin to leak. Also, the cylinder head gasket may be squeezed out. If such problems are observed, therefore, it is necessary to remove the cylinder head from the engine and pay urgent attention to the technical condition of the power unit breather. The VAZ engine breather is a screening element whose task is to ensure the passage of gases that accumulate in the cylinder block under the valve cover, on the one hand, and on the other, to block access for the return passage of engine oil.
It is worth drawing the attention of motorists to the fact that the design of the VAZ 2110 2112 2114 2115 2109 breather does not present any complexity. The breather is an aluminum multilayer mesh, which is not at all intended to carry out any filtration; its task is simply not to allow access to oil. Therefore, the VAZ breather does not break, but becomes clogged, or, to put it more precisely, clogged. The reason for this may be the use of low-quality motor oil or a violation of its seasonal use; also, the failure of the breather may be caused by failure to comply with the vehicle maintenance regulations, including changing the oil and oil filter. One way or another, the technical quality of the oil and the proper operation of the VAZ 2110 212 2114 2115 2109 breather are indivisible factors.
During the operation of the VAZ 2110 2112 2114 2115 2109 engine, excess low-quality oil settles in the breather, gradually transforming into fuel oil, which finally clogs it. Partly, this happens due to changes in temperatures in the car’s power unit. As for gases, their excessive pressure, which is formed as a result of combustion of the combustible mixture and is accompanied by very high temperatures, ensures their accumulation under the engine cylinders, which leads to squeezing out and leaking of the aforementioned oil seals and cylinder head gaskets. The breather in VAZ cars is designed to remove these gases, which is not a difficult task, but extremely important for the normal functioning of the car’s power unit. All of the above factors force you to once again pay attention to the brand of motor oil that your VAZ vehicle runs on.
What is an engine breather and why is it even needed? Here's the question"
What is an engine breather and why is it even needed? Here's the question
This can save you from more expensive repairs. In fact, the breather, although it seems like an insignificant detail, in practice is of great importance for the health of the power unit.
What is an engine breather?
Before answering this question, it is important to understand what it is intended for. This is directly related to the principle of its operation. The main task of this device is to reduce the pressure in the engine crankcase. When the power unit operates, various gases collect in the crankcase. Gradually they accumulate and create quite a lot of pressure. If you do not bleed them, the engine may stop, the pressure will back up the pistons. In this case, the gas will seek an exit through any available hole. To prevent this from happening, a breather is installed.
This also happens with the help of this device. Unnecessary gases are removed from it. Thus, the temperature inside the engine is slightly reduced. The engine breather has two tasks: ventilation and releasing excess pressure. In some cases, the operation of the breather can indicate the presence of problems in the engine. or damage to the piston, gray smoke characteristic of the exhaust will fly out of the hose. This way you can diagnose these faults without disassembling the engine. In normal condition, a slightly noticeable transparent smoke comes out of the breather.
The breather is essentially a valve that bleeds air from the engine. As the pressure increases, it begins to allow a certain amount of gases to pass through it. The greater the pressure, the more air can pass through it. To prevent atmospheric air from entering inside, the valve is capable of flowing only in one direction. But on some cars this process is reciprocal. In such versions, a filter is installed in the valve to prevent dust from getting inside the motor.
Most often, the breather is located next to the oil filler neck. Much less often you can find options with its location on the side of the cylinder block. From the outlet pipe there is a hose connected to the air filter housing. This arrangement is typical for all cars. It may differ only in small nuances due to the characteristics of the body. Sometimes there are 2 pipes, in which case the second hose is connected to the injector.
How to remove the breather on a VAZ 2110
Below you can see the technical specifications of how to remove the breather on a VAZ 2110. Express your opinion about the car in the comments.
Category: Car repair
Release date: January 25, 2013
Quality: DVD Custom
Posted by admin: at the request of Calixtus
Opinion of a car owner named Ilya: Quite decent ergonomics, although the driver’s seat requires “refinement with a rasp”, an impressive reserve of carrying capacity - with oo-very small investments - some “heroes” carry 5 tons, but 2.5 is enough for me. amazing reliability and maintainability - practically “on the knee” or for quite reasonable money and “on any collective farm”. More than 750 tykil WITHOUT “capital” - only replacing the pistons with more “full” ones and rings - IMHO - they are “saying” something! Ho. ... all the advantages take place with “straight hands”, growing HE “from F...”, ABSENCE of laziness and, most importantly, the presence of “fat in the head.” Which means - DO NOT be complacent about “consumables”. Personally, my Kaza immediately after the end of the “warranty” became hooked on the “synthetic” “Hado” 5w-50. I change it every 25 tkm with an intermediate replacement of the oil filter at 9, 8, 8 tkm. The “box” is also “synthetic”. 75w-140. The brand is not important - whatever you find. The most accessible one for me is Ravenol. I change it every 150-200kil. In the “bridge” - mineral water “Hado” - 85w-140 with replacement every 100 kilos. The main “power” is propane, distributed injection! I still have the second generation, although now I already have the VI-e... Injection of the LIQUID “phase” - i.e. WITHOUT evaporator reducer. I WANT. ...but it's too late... (((
Laughter on topic: Well, what do you know about optimism? My neighbor always puts the apartment keys in her pocket when she washes her windows. In case he falls out of the window. And we live on the 9th floor.
Description: Dimensions are as follows: length - 3650, width - 1100, height - 1193 mm. The wheelbase is 2419 mm. Ground clearance 125 mm. The car is equipped with a hybrid power unit. The 2-cylinder engine is equipped with a system that provides engine power output. There are 4 valves per cylinder. The diameter of one cylinder is 76 mm, the piston stroke is 70 mm. The engine crankshaft accelerates to 3000 rpm. Maximum torque is maintained up to 3000 rpm.
Video: how to remove the breather on a VAZ 2110
Crankcase VENTILATION SYSTEM
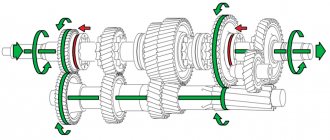
The power plant of any car is a very complex device, including mechanisms and systems that interact with each other. At the same time, the engine is not a closed hermetically sealed circuit and it also has ventilation. Crankcase ventilation is a scheme that ensures the removal of gases from internal cavities. The fact is that during combustion of the working mixture in the cylinders, exhaust gases are formed, which are under pressure, due to which part of them penetrates into the sub-piston space - the crankcase, where it mixes with oil mist and moisture formed as a result of condensation. This whole mixture is called crankcase gases. If the engine were sealed, with an increase in the amount of gases in the crankcase, the pressure inside it also increased. Because of this, a breakthrough of gases along with oil through the breather, oil seals, seals or the hole in the oil dipstick is possible. Based on this, it follows that the main task of the ventilation system is to maintain pressure inside the engine and prevent it from exceeding the permissible norm by removing crankcase gases.
Video: How to Clean the Breather VAZ 2110 16cl
Result:
What is the crankcase ventilation system made of? From the hoses, from the oil separator, from the oil separator, all these parts can be seen in the diagram below, all of this gets dirty over time, so it is necessary to dismantle the crankcase ventilation system from time to time and clean it of dirt. And the oil is inside, then the engine will work normally, and all the dirt that is in the ventilation system will not enter the engine for re-combustion, but for engines that have traveled quite a lot (200 thousand km and above), we simply recommend putting this system in a bottle so that it does not choke the engine in the car, and it drives more or less, and in order to ensure ventilation of the crankcase in the bottle, you need a screwdriver and a suitable (small) one. For information on how to do this, see the video. located at the end of the article, where everything is shown in detail.
READ How to remove the rear seats of a VAZ 2110
When should I clean the crankcase ventilation system? It all depends on how well the engine is running, if the piston rings are worn and it is constantly throwing oil into the crankcase vent it will need to be cleaned much more often, unlike a new or empty engine it is easy to clean these engines need a vent system every 40,000 thousand km Approximately (you need to clean it before changing the oil), you can more often if you have free time, it will not deteriorate, but a very dirty crankcase ventilation will make it difficult for gases to drain from the crankcase into the cylinders, so the gas pressure inside the engine will increase the gas, there is simply nowhere to go apply, except for other types of seals that come out through the seals, due to which oil will flow through the seals (mainly due to dirty crankcase ventilation. Oil begins to flow through the front crankshaft seal).
VENTILATION DESIGN FEATURES, OPERATING PRINCIPLE
The simplest diagram of the crankcase ventilation system used on internal combustion engines previously consisted of only one fitting - a breather installed in the crankcase. This breather connected the internal cavity of the cylinder block with the external environment, and crankcase gases simply escaped through it into the atmosphere. But this scheme had one significant drawback - the exhaust gases contained oil particles, which also entered the external environment. And this is not only loss of lubricant and the need for periodic refilling, but also air pollution. On modern cars the ventilation system is closed. It also has a breather, but a pipe is connected to it, allowing gases to be vented into the intake manifold or air filter housing, from where they enter the cylinders and burn. That is, the atmosphere is not polluted by them. Additionally, the system includes elements that ensure oil separation and return back to the crankcase so that it does not enter the cylinders along with the gases.
There are several options for oil separators, and on cars from different manufacturers they may differ in design and operating principle. It is worth noting that part of the exhaust gases enters the supra-valve space, and they must also be removed. Therefore, the entire circuit of the engine ventilation system on a modern car consists of a breather, an oil separator and two pipes. Additionally, a special valve can be included in the system to regulate the pressure of gases entering the intake manifold. The configuration of the system can be very different, but this does not change its purpose and operating principle. For example, consider the ventilation design of the VAZ-2110. At the bottom of the cylinder block of this car there is a breather, onto which a pipe is attached; the second end of this hose is connected through a fitting to the cylinder head cover. At the same time, an oil separator is located inside this cover at the inlet of the pipe. On its other side there is another fitting, to which a tube is connected that goes to the air inlet pipe.
The principle of operation of such ventilation is simple - gases enter the cylinder head cover space through the breather and pass through the oil separator, while the separated oil flows to the valve assembly. After this, the gases are mixed with those that have broken into the supra-valve space and are supplied to the air pipe, and then to the manifold. There is no pressure regulating valve in this car. On other machines, the oil separator may be located immediately next to the breather, and a valve is installed behind it.
Cleaning on VAZ 2101-VAZ 2107
Breeding
1. Remove the air filter housing from the car engine (for more details, see the article “Replacing the air filter housing”)
The note! Be sure to remove the flame arrester from the crankcase ventilation hose and wash it with kerosene in case of severe contamination.
2. Release the clamp by attaching the additional hose to the breathing cap (marked with a red arrow) and disconnect the additional hose. Continue unscrewing the main hose clamp (marked with the blue arrow) and remove it from the cover.
3. Remove the engine oil level sensor.
4. Unscrew the bolt securing the fan cover and remove the cover from the car engine.
5. Dampen a cloth with kerosene and wipe the inside of the oil separator.
The note! Be careful when wiping; Do not allow dirt to get inside the engine. If you are not comfortable cleaning dirt from the installed oil separator, remove it from the vehicle by unscrewing the lock nut (indicated by the red arrow). Place the removed oil separator in a prepared container with kerosene.
6. Clean the surface of the air filter from dirt by wiping it with a cloth soaked in kerosene.
READ Which Battery For VAZ 21099 Injector
The note! Remove the gasket from the filter housing and clean it of dirt.
Installation
This is done in the reverse order of removal.
The note! Replace broken or cracked gaskets with new ones. Make sure the metal shims are inserted into the air filter housing gasket (shown in photo).
Important! If a large amount of kerosene gets into the crankcase, change the engine oil! (Read more in the article “Changing Engine Oil”)
For beginners! Question: What does the oil separator look like? Answer: in the photo.
Source
Welcome! The crankcase ventilation system is necessary to ensure that the atmosphere is not clogged and the exhaust gases are allowed to burn out again, this system has been implemented in many cars, from VAZ 2101 to cars such as Lada Priora, Lada Granta, etc., but when the engine is worn out, This system is removed by people themselves by removing all the PCV hoses, usually in a bottle or just outside, we will break it down in this article, so if your car has already been driven quite a lot, this article will be sent to you.
The note! We will look at cleaning the ventilation only on 16 valve engines, if you have 8 valves, then we will move on to the article: “Cleaning the crankcase ventilation on a VAZ 2114”, this engine is described in this article, you will need to clean the ventilation, crankcase 16 drain: pliers are not large , screwdrivers with different heads and all kinds of wrenches, in addition, you will need sealant for the cylinder head cover and a new gasket!
REASONS FOR OIL EMISSION THROUGH THE BREATH.
But there are many of them, and many of them do not relate to ventilation.
Lubricant may flow through this system due to:
1. Severe wear of the piston rings and the cylinder-piston group as a whole. Because of this, a very large amount of gases break into the crankcase, and the ventilation simply does not have time to remove them all. Therefore, increased pressure is formed inside the engine, which squeezes oil into the breather;
2. Clogged oil separator drain channel. In this case, the separated oil has nowhere to go, and it is mixed into the passing gases;
3. Air filter dirty. The engine sucks in a large amount of air, and if there is not enough air due to a clogged element, the motor will suck it in along with oil from the ventilation system;
4. Increased amount of oil in the system. If there is more lubricant in the engine than normal, then excess lubricant will enter the ventilation;
5. Jamming of the ventilation system valve;
6. Timing belt wear or valve burnout. As a result, crankcase gases enter the above-valve space, then they penetrate into the crankcase, significantly increasing the pressure.
Design and principle of operation
As was said at the very beginning, the ventilation system removes crankcase gases from the VAZ 2114 back into the engine, preventing unburned fuel oil mixture from entering the atmosphere. It includes a pair of pipes through which gases are removed, and a filter that traps solid particles and clots.
The principle of operation of the crankcase ventilation system of the VAZ 2114
The whole system functions as follows:
- the fuel mixture entering the engine burns and forms exhaust gases, most of which are discharged from the engine into the exhaust line;
- a small part of the gases leaks through the piston rings and enters the lower pipe of the ventilation system;
- From the lower pipe, gases enter the filter (made in the form of a multilayer mesh), after which, already purified, they return to the engine, where they burn out.
DIAGNOSING THE CAUSE OF OIL RUSSIAN
Since there are a large number of reasons for oil leaking through the breather, a comprehensive check of the engine is necessary to determine exactly why the problem arose. At the same time, to carry it out, you don’t even need to disassemble the power plant, it’s just enough to take measurements of some parameters, as well as visually assess the condition of the ventilation. For example, let's take the already mentioned VAZ-2110. Let's assume that in the engine of this car, plaque and oil deposits were noticed in the intake manifold, which indicates oil leakage through the breather.
To determine what caused this problem, you will need little - a set of open-end wrenches, a screwdriver, a compression gauge. We'll start the test by assessing the exhaust gases. To do this, just start the engine and look at their color shade. If it is gray or black in color, this indicates oil getting into the cylinders due to wear or sticking of the CPG rings or problems with the timing belt. Only this can help determine the cause; read more here - the causes of smoke from the exhaust pipe. It is also necessary to check the compression in all cylinders. In the normal state of the cylinder-piston group, it should be in the range of 11-13 MPa. The difference between the readings in the cylinders is allowed to be no more than 1 MPa.
If the compression in one cylinder is significantly lower, it can cause oil leakage. But why exactly this is happening - rings or valves - can be determined by the spark plug that was installed on this cylinder. Heavy carbon deposits on it will indicate a problem with the CPG.
But if the compression is low, and the spark plug has a normal working appearance without carbon deposits, you should check the valves. If the compression in all cylinders is normal, we proceed to inspect the elements of the ventilation system.
Diagram of the standard crankcase ventilation system
The crankcase ventilation system of VAZ engines consists of two circuits that operate at different load modes and speeds:
- The small ventilation circuit is connected to the valve cover and the intake manifold (behind the throttle body). This connection diagram provides intensive crankcase ventilation due to the vacuum that occurs in the intake manifold when the throttle is closed. To avoid an effect such as hyperventilation, the cross-section of the small circuit is limited by a jet in the cable throttle body with a diameter of 1.7 millimeters. This circuit operates in the region of 800-1500 rpm.
- A large ventilation circuit is connected to the valve cover and the air pipe (in the pre-throttle space). This scheme provides intensive crankcase ventilation at high speeds. The cross section of the large contour is 16-18 millimeters