What is the difference between TSI and TFSI engines?
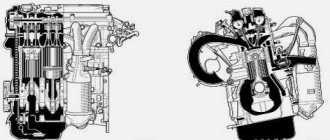
TSI motors are built on a different technology. To produce this engine, the Volkswagen concern did not take old naturally aspirated engines, but built a new unit. It has an intake manifold, two turbines, one of which is electric and runs almost constantly. The second mechanical turbine has a classic design. That is, at its core it is a bi-turbo engine.
The main differences from the TFSI also lie in the fact that Volkswagen did not provide a decent design for the cylinder block itself, so the service life of TSI engines does not always reach 200,000 km. And the turbines themselves bring owners a lot of trouble, especially if maintenance regulations are violated. 1.4 TSI engines developed before 2012 have special vagaries.
Today, various design bureaus are engaged in the development and continuation of the series of these two units. TFSI technology was taken over by the Audi concern, and TSI is installed on VW, Skoda and Seat. However, there are already rumors about the creation of a new single platform for the production of smaller turbocharged engines.
Decoding
It’s easy to guess that in this abbreviation “T” stands for turbine. And therefore, one of the main differences from FSI engines is the presence of a turbine. The engine has a turbocharger, which is driven by exhaust gases. The gases are re-burnt. The TFSI engine is even more economical, environmentally friendly and friendly - during operation, a very minimal amount of harmful gases and CO2 will be released into the air.
And now, regarding the abbreviation TFSI. Explanation: turbocharged power unit with stratified injection. This is a system that is now deservedly considered revolutionary for this time. This is an injection system directly into the cylinders with a turbine.
Due to the presence of a turbine, the developers were able to achieve very high performance. Thus, the engine power has increased even more. Now you can get everything that it is capable of and even more from a small-volume engine. Naturally, along with the power, the torque also increased. Fuel consumption remained relatively low, although the engine, equipped with turbochargers, is not particularly economical.
First acquaintance with the engine
To begin with, some car enthusiasts do not even understand what kind of TFSI engine this is and how this abbreviation stands for.
This means Turbo fuel stratified injection. In translation here we are talking about a turbo engine with stratified fuel injection. Yes, this is indeed in many ways an analogue of the FSI, only additionally equipped with a turbocharger.
The system was revolutionary for its time, since it was the Germans who were the first to use direct injection into the chamber for each piston separately, managing to connect this with a turbine.
But the decoding of the TFSI marking itself does not yet make it possible to fully recognize this engine. And be sure to compare with TSI.
Many theories, conjectures and myths were built around the motor with the designation TFSI. Some are sure that the letter F has no meaning at all, and this was done solely for the sound of the name, or for the difference in the model range of cars. Allegedly, TSI comes on Volkswagen and Skoda models, and TFSI exclusively on Audi.
You have already become familiar with how the TFSI value is deciphered. But it is equally important to understand what this same TFSI actually means, how it differs from its supposed counterpart, and what the situation looks like in reality.
The technology of the engines in question is based on older internal combustion engines, which have already been discussed here. This is FSI. One of these 2.0-liter engines was actively used in various models under the Seat, Skoda and Volkswagen brands. This is an atmospheric internal combustion engine equipped with a direct injection system. The engine has a reliable base, high-quality design and long service life.
But now cars of more recent generations are equipped with TFSI engines. Their decoding has already made it clear that we are talking about a turbo engine with direct injection. But it has its own important features. In many ways, this will allow us to understand the operating principle of the TFSI series units.
- Other pistons. To improve the performance of the turbocharged engine, the upper part of the pistons has undergone certain changes. New larger recesses are provided here, which allows you to work effectively in conditions of reduced compression.
- Increased efficiency of the internal combustion engine with a parallel reduction in the amount of harmful emissions. This distinguishes the turbocharged version from the naturally aspirated one. This was done in order to comply with new stringent environmental standards.
- Crankshafts and shafts. The principle of operation has changed largely due to the modified form. Additionally, designers use high-strength materials for their manufacture, which allows them to withstand the loads from the turbine.
- Intake and exhaust system. And here changes have occurred. They were aimed at increasing precision and efficiency, since this is one of the main requirements for an internal combustion engine when using a turbocharger.
- Fuel pump. It has become more powerful and reliable. Due to this, it was possible to improve the elasticity of operation at high speeds.
We recommend: Oil level sensor VAZ 2114: operating principle, check and replacement
The changes made and the announced features of the engine in question largely make it clear what kind of engine it is, how it works and what its strengths are.
But there is still no escape from comparison with FSI, although most often it is compared with TSI, since both engines are turbocharged.
I would like to remind you that in the middle class of cars, the naturally aspirated FSI is considered one of the best engines in the world. Many such engines can easily cover a range of 400-500 thousand kilometers without requiring expensive repairs or serious intervention. The only condition for long-term operation is high-quality maintenance and the use of suitable motor oils.
Now, having figured out what TFSI means, you should compare TSI and TFSI, look at their capabilities and understand whether the new generation is really noticeably superior to its conventional predecessor.
Characteristics
Often the letters TFSI, which we have already deciphered above, can be seen on Audi cars. On Volkswagen models, the VAG concern installs FSI and TSI, traditional for the brand.
For the first time, a turbocharged engine with stratified direct injection was installed on the Audi A4. The engine had a volume of 2 liters and was able to produce as much as 200 horsepower with this volume. The torque is also quite high - as much as 280 Nm. To get such results on earlier engine models, its volume had to be about 3-3.5 liters, and the engine had to have six cylinders.
But the matter did not end there and in 2011 the TFSI engine was upgraded. The decoding of letters remained the same, but the power increased. With the same volume of two liters, the engineers managed to get 211 horsepower at 6000 rpm. Torque is 350 Nm at 1500-3500 rpm. The engines have excellent traction at low and high speeds.
For comparison, just look at the six-cylinder 3.2-liter FSI with 255 horsepower at 6,500 rpm and 330 Nm of torque at 3,000-5,000 rpm. Let's also look at the technical specifications of the TFSI 1.8 engine for the 2007 model year. It is capable of producing 160 horsepower at 4500 rpm. The maximum torque that can be obtained (250 Nm) is available at 1500 rpm. This engine accelerates the car to a speed of one hundred kilometers per hour in 8.4 seconds. Fuel consumption in the city with a manual transmission is only ten liters.
Even with the naked eye it is clear that FSI engines are losing, and TFSI is a step forward for VAG engineers. Although the company didn’t do anything special - they only installed a turbocharger. But the main nuances of the TFSI engine are there and we will look at them.
TSI and TFSI
It's no secret that Skoda, Seat and Audi belong to Volkswagen, which implies joint development of engines. So it turns out that the abbreviation TSI is used on Skoda and Seat Volkswagen models, and TFSI on Audi cars, but the letter designation serves to identify identical engines. The difference between Turbo Fuel Startified Injection and Turbo Startified Injection is only the absence of the word Fuel (from English - fuel) in the designation. Let us immediately note that there is no universal injection internal combustion engine called TFSI or TSI. This is only a general designation for a series of engines with direct injection and additional air charging. We have already looked at the principle of operation of TSI, so we will not dwell on this. In this case, the engine can only have a mechanical supercharger or a supercharger working in tandem with a turbocharger. Depending on the year of production, the abbreviation can be used both by engines with conventional, if this is appropriate, direct injection, and by internal combustion engines using the Miller-Atkinson cycle.
It would be wrong to talk about these engines in the singular, putting them all under the same brush. The same applies to the list of the most common problems and malfunctions that occur when operating TFSI engines. By the way, even now there are enough materials on the Internet written by people incompetent in this matter or compiled before the time when there was a need to separate engine models.
Generation Models
TFSI is a logical development of the direct fuel injection system called Fuel Startified Injection. The main feature of FSI, which allows an atmospheric engine to be both economical and powerful at the same time, is layer-by-layer mixture formation. Thanks to the features of the intake manifold, fuel injection and “tamed” turbulence, the engine can operate both on an ultra-lean and on a homogeneous mixture.
- 2004 - the naturally aspirated 2.0 FSI receives a turbine and some design changes, thereby becoming the first TFSI engine. Initially, the marking could be found not only on Audi, but also on charged versions of the Skoda Octavia (RS), Seat Leon (FR), but later the Octavia RS and Leon FR received only the TSI nameplate. Power – 147 kW. An interesting feature is that the BWA engine has only two operating modes: warm-up (two-stage fuel injection, which allows you to quickly warm up the catalytic converter) and normal (operation on a homogeneous mixture). This means that there is no talk of any layering, which is what the word Startified means. A turbine is used to pump air. 2.0 series EA888, power – 162 kW. The design uses a combined injection system; a mechanical supercharger works in tandem with the turbine. Depending on the car model and year of manufacture, the power of the two-liter “heart” could vary from 170 hp (BPJ, intended for the Audi A6) to 271 hp (Audi TT, Audi S3). Particularly noteworthy are the 2.0 Gen3B units, which use the Miller-Atkinson cycle, and the design involves the installation of the proprietary Valvelift system.
- 2006 – appearance of 1.4 TFSI. A motor that implements the Downsizing idea. The point is that large-volume naturally-aspirated internal combustion engines are being replaced by smaller-volume turbocharged units. The TFSI 1.4 engine is found in the SAHS - 92 kW and CAVG - 136 kW modifications. A feature of the 1.4 engine series EA111 (CAVG) is the use of two-stage turbocharging - a mechanical supercharger and turbine. The main disadvantage of these engines is the stretching of the timing chain, leading to slipping and “meeting” of the valves with the pistons. In the EA211 series, 1.4 motors can produce 90 kW (SMVA) or 103 kW (CPTA).
- 1.2. Depending on the modification, the “heart” can produce from 63 to 73 kW.
- 1.8 series EA113. The BYT motor has a power of 118 kW (equivalent to 160 hp). Turbocharging – gas turbine, timing chain drive. The restyled 1.8 unit of the EA888 series already has 132 kW. The main feature is the combined injection system. This means that fuel is supplied not only to the combustion chamber, but also to the valves. A special nozzle is responsible for injection into the intake manifold. This innovation eliminates the problem of engines with the formation of dirt deposits on the intake valves.
V-shaped internal combustion engines
The TFSI line contains not only in-line models, but also V-shaped “hearts”:
- 3.0 V6 with a power of 213 kW;
- 4.0 V8. TFSI engine with power from 309 to 382 kW. To increase efficiency and reduce emissions of harmful substances, some of the cylinders can be switched off when unnecessary; an energy recovery system is used.
We recommend: Active car headrests
Problems and malfunctions
Among all the malfunctions of TFSI engines, we can highlight:
- stretching of the chain, leading to extraneous knocking during operation and the risk of valves “meeting” the pistons. Troubles can overtake the owner already at 30-40 thousand km. mileage;
- maslozhor. Unfortunately, all petrol engines from the VW-Group suffer from this problem. Constant improvements to the CPG only delay the mileage at which increased oil consumption appears. Often the problem is aggravated by the owners themselves, unknowingly operating the car in conditions that are uncomfortable for the engine. Constant careful operation with only “stroking” the gas pedal and long warm-ups at idle lead to aggravation.
When telling the story of the development of Turbo Fuel Started Injection, we used individual engine letter designations. It is by these numbers and letters that you can accurately identify the model and generation of the engine installed in a particular Audi. When buying a used car with TFSI, you should look for relevant information using these designations. To expand your search for information, match the abbreviations with the designations used for Volkswagen vehicles.
We simply do not have the opportunity to describe all the problems of specific internal combustion engine models. If you want to purchase a used or new Audi, we recommend that you refer to reviews from real users. You can find all the subtleties of the design and operating principle of each of the TFSI engine series in the Audi Self-Study Program. The materials are intended to improve the skills of employees of Audi service centers and, fortunately, are freely available.
Malfunctions and repairs
As mentioned earlier, TFSI power units are oil guzzlers. Of course, you can change the oil for summer and winter, but for most owners this is not a solution, but only a delay in increasing lubricant consumption. This problem occurs on many power units produced by the VW-Group.
TFSI engine for Skoda
The second significant malfunction, which occurs quite often, is stretching of the timing chain. At the same time, the meeting of pistons and valves begins, which causes a characteristic metallic knock that even auto mechanics have been looking for for a long time.
What is TFSI - decoding and technology features
These motors borrowed their original technology from older FSI engines. The VAG 2.0 FSI engine, which was installed on Skoda, Seat and Volkswagen, was very popular. This is a naturally aspirated engine with direct fuel injection into the cylinders. The unit has a fairly reliable foundation, a well-designed design and a fairly long service life.
We recommend: About the AFS adaptive lighting system in the car
TFSI engine stands for Turbo Fuel Stratified Injection. The name indicates that this is a turbocharged engine with direct fuel injection into the combustion chambers. Here are some features of a turbo engine:
- Changed pistons. Especially for the turbocharged version, the upper part of the pistons was changed; they received large recesses for operation with reduced compression.
- Improved efficiency and reduced emissions compared to the old FSI to accommodate the new engine's challenging environmental regulations.
- The designers changed the shape and operating features of the crankshaft and connecting rods. The changes also affected the quality of the material; the manufacturer increased it for turbo engines.
- The intake and exhaust systems also received changes, they became more precise and efficient, which was vital for the compressor version.
- Of course, the designers had to install a more powerful and reliable fuel pump. This ensured the elasticity of the engine at high speeds.
Basic concepts explain what a TFSI engine is, how it works, and what its main advantages are. If you have ever come across FSI engines from VAG, then you know that they were the most reliable and successful mid-class naturally aspirated engines. Many of them reach 500,000 km without repairs or intervention. It is enough to maintain the unit well and pour expensive oil at the right time.
Pros and cons of using
The positive side of the Fuel Stratified Injection engine is the presence of dual-circuit fuel injection. Fuel is supplied from one circuit at low pressure, and from the second at high pressure. Let's consider the operating principle of each fuel supply circuit.
The low pressure circuit in the list of components has:
- fuel tank;
- gasoline pump;
- fuel filter;
- bypass valve;
- fuel pressure control;
The design of the high pressure circuit requires the presence of:
- high pressure fuel pump;
- high pressure lines;
- distribution pipelines;
- high pressure sensor;
- safety valve;
- injection nozzles;
A distinctive feature is the presence of an absorber and a purge valve.
Engine FSi Audi A8
Unlike conventional gasoline power units, where the fuel enters the intake manifold before entering the combustion chamber, on FSI the fuel enters directly into the cylinders. The injectors themselves have 6 holes, which provides an improved injection system and increased efficiency.
Since air enters the cylinders separately, through the damper, an optimal air-fuel mixture ratio is formed, which allows gasoline to burn evenly without exposing the pistons to unnecessary wear.
Another positive quality of using such an aspirated engine is fuel economy and high environmental standards. The Fuel Stratified Injection system will allow the driver to save up to 2.5 liters of fuel per 100 km.
Table of applicability of TFSi, FSi and TSi
But where there are many positive aspects, there are also a significant number of disadvantages. The first disadvantage can be considered that the aspirated engine is very sensitive to the quality of the fuel. You can’t save money on this engine, because with bad gasoline, it will simply refuse to work normally and will malfunction.
Another big drawback is that in cold weather, the power unit simply won’t start. If we take into account common problems and FSI engines, problems in this line can arise with cold starts. The culprit is considered to be the same layered injection and the desire of engineers to reduce exhaust toxicity during warm-up.
Oil consumption is one of the disadvantages. According to most owners of this power unit, an increase in lubricant consumption is often noticeable. To prevent this from happening, the manufacturer recommends maintaining VW 504 00/507 00 tolerances. In other words, changing the engine oil 2 times a year - during the transition to summer and winter operating modes.
Advantages and disadvantages
The superiority of TFSI over TSI is obvious. These are larger engines, equipped with a turbine, characterized by an impressive service life. If turbines are maintained on time and correctly, they can last about 300 thousand kilometers.
The advantages include adequate fuel consumption, which is pleasantly surprising given such high power parameters.
But for now, this is where the list of advantages ends. Now it’s worth looking at the disadvantages that can characterize a car with a TFSI engine under the hood.
The technology is indeed far from perfect. Work is already underway to eliminate them, and many problems were eliminated literally after the first update. But when buying used cars with TFSI under the hood, remember that these cars with such an engine had the following problems:
- The installation of a turbine on an initially naturally aspirated engine led to the fact that engines became more demanding of fuel quality. You need to choose your gas station carefully, otherwise problems will soon arise.
- Due to the turbine and other innovations, the cost of maintenance has increased significantly.
- Increased maintenance requirements have led to the need for such internal combustion engines to use expensive oil and filters.
- The cost of repair work is extremely impressive for many clients. This is largely due to the fact that only original parts have to be used. And they cost a lot.
- Due to design changes, oil consumption has increased. Therefore, it is important not to forget to top it up periodically. If you forget, the process of oil starvation will begin.
- The timing belt uses a chain that stretches over time. Replacing it is expensive.
In many ways, these problems are typical for engines manufactured before 2014.
Then Audi worked on the errors and eliminated many of them. So the current generation TFSI causes much less criticism.
Improvements
If you look for the difference between TFSI and TSI technologies, the difference lies in the piston crowns. The cylinders in the TFSI are smaller, but the area they occupy is larger. Due to this shape, the engine operates efficiently with low compression.
The engineers also modified the cylinder head - it is equipped with two camshafts made of a more durable alloy. The valves were also made from the same alloy. The intake and exhaust have been significantly modified, and the fuel supply channels have been corrected. The fuel supply itself has also been improved.
In general, motors with TFSI technology operate on the same principles as other units of the concern. There are two fuel circuits - high and low pressure. The low pressure circuit is a tank, a low pressure pump. There are also filters and sensors. In the high pressure circuit there is an injection system and high pressure fuel pump.
The operating modes of all devices and systems in the circuit are fully controlled by electronics operating according to fairly complex algorithms. During operation, various parameters are analyzed, and then the corresponding commands are sent to the actuators.