During operation, a layer of soot deposits on the parts of the piston group of a car or motorcycle engine, leading to a drop in compression and difficult starting. The owner of used equipment who wants to restore the characteristics of the power plant must first find out how to decarbonize the engine and what is the best way to carry out the procedure. It should be noted that particles of dissolved dirt can clog oil channels and worsen lubrication conditions, which will lead to accelerated wear of rubbing parts.
For what reasons does oil enter the combustion chamber?
The materials used to lubricate the power unit are characterized by increased fluidity and enter the chamber through worn piston rings or oil seals on the valve stems. When heated, some of the lubricant burns out, and some settles on the engine parts, forming carbon deposits.
Foreign deposits are formed due to additives added to gasoline to increase the octane number.
Long-term idling of the engine or short trips in city traffic contribute to accelerated contamination of the chamber walls.
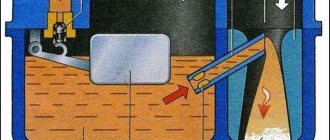
Areas of soot formation
Foreign loose or hard deposits settle on surfaces:
- piston bottom and grooves for installing piston rings;
- the upper part of the cylinder mirror, not in contact with the rings;
- vault of the chamber;
- valve plates and seats;
- spark plug electrodes and insulator;
- walls of channels for exhaust gas removal.
Carbon deposits impair heat transfer from parts, which leads to local overheating and premature (glow) ignition of the mixture. Deposits on the seats do not ensure tight closing of the valves, reducing compression and causing burnout of the working mixture in the exhaust manifold and the cavity of the catalytic converter (if there is an exhaust gas emission control system). Deposits block the movement of the rings, which reduces the compression ratio and leads to a drop in power and increased fuel consumption.
Decarbonization of VAZ 2109 rings
To do this you will need:
- new set of spark plugs. The replacement algorithm can be found here;
- new oil filter (An article on replacing the oil filter is here);
- 3.7 liters of oil;
- spark plug key;
- decarbonizing liquid LAVR ML-202 (or its equivalent);
- LAVR Motor Flush Five Minutes oil system cleaning fluid (or its equivalent);
- clean rag measuring 50x30 cm;
- car compressor with needle;
- set of screwdrivers and keys.
It is useful to read the article : Self-cleaning of VAZ 2110 injectors
Self-decarbonization of the engine is carried out on a flat surface. It is advisable to have an inspection hole nearby, because after decoking it is necessary to replace the old oil.
- Turn off the engine.
- Disconnect the high voltage wires from the spark plugs.
- Use a compressor with a needle at the tip to blow out the spark plug wells.
- Use a spark plug wrench to remove the spark plugs.
- At 4th speed, push the car until the pistons are aligned. You can verify their correct location with a feeler gauge or several screwdrivers installed in the spark plug wells.
- Put the car on the handbrake.
- Fill the cylinders with decoking liquid (35-40 milliliters is enough). It is more convenient to do this with a syringe (it is included with the liquid).
- Re-light old candles.
- Engine decarbonization takes 2-12 hours (the time is directly dependent on the degree of contamination). After a few hours, the pistons can be moved down or up.
- After a few hours, remove the old spark plugs and use a syringe to remove the used fluid from the cylinders.
- Cover the candle wells with a clean cloth.
- Remove the car from the handbrake, put it in neutral
- Press the gas pedal all the way, turn the engine 3-4 times with the starter for 5-10 seconds. The interval between actions is 15-30 seconds.
- Screw the spark plugs back in, connect the wires, start the engine. Wait until it warms up to operating temperature. In this case, deviations from its normal operation are possible: excessive amounts of smoke, interruptions. The reason for this is the final burnout of coke deposits and soot.
- Turn off the engine.
- Add 5-minute oil system cleaner, start the engine again, and leave it idling for 5 minutes.
- Drive the car onto a viewing hole or lift, replace the oil filter and oil, install new spark plugs.
After decarbonization of the rings is completed, the car should operate at high speeds for the first 10-20 kilometers. Then the remaining coke and burning will finally come out.
Worth a look: Self-adjustment of VAZ 2101 valves
Features of engine decarbonization
Decoking refers to the procedure for removing deposits without removing the cylinder head and dismantling the pistons and crankshaft.
For cleaning, chemicals are used that soften and wash away carbon deposits, which are released with the flow of exhaust gases and are partially captured by the oil filter.
It should be taken into account that with natural wear of the piston group (with runs of more than 200 thousand km), the volume of oil entering the chamber increases. In this case, cleaning will help for 2-5 thousand km, and then a layer of sediment settles on the walls again.
Methods for decoking piston rings
To restore the mobility of the piston rings and increase compression to standard values, harsh and delicate chemicals are used, after which the engine oil and filter must be replaced (without flushing the lubrication system). The maintenance algorithm depends on the location of the cylinder blocks (vertically, horizontally or V-shaped); the carbon layer from the surfaces of the combustion chambers, plates and valve stems is removed separately.
Soft
Soft technology involves pouring a special washing liquid into the pan; after 100-200 km of engine operation, the oil is drained in a gentle mode and the filter is removed, in which particles of washed-out carbon deposits remain. The method does not allow cleaning the chamber roof and parts of the gas distribution mechanism. Dimexide can be used for cleaning, but in this case there is a risk of clogging the oil channels with particles of sludge and paint washed off from the internal surfaces of the crankcase and engine sump.
Tough
The technique involves pouring a detergent composition into the cylinders of a preheated power unit through the holes for spark plugs or injectors. The spent solution is removed with a rubber bulb, and then the engine is started and the car is operated in a gentle mode for 40-50 km.
After the test run, drain the engine oil and change the filter and spark plugs.
The technology is used to restore engine performance with your own hands and at service stations.
Disadvantages of hard decarbonization
Disadvantages of the rough cleaning procedure:
- When using homemade liquids (for example, a mixture of kerosene and acetone), it is impossible to completely fill the combustion chamber, so contaminated areas remain. The use of foamed decarbonizers (for example, Mitsubishi Shumma) allows for complete softening of the sludge.
- When pouring the washing solution, dirt may enter from the spark plug wells, so it is necessary to first clear the channels of debris (for example, with a stream of compressed air and brushes).
- The most active reagents are toxic; when cleaning the engine in a confined space, there is a risk of vapor poisoning. It should be noted that the dissolution rate depends on the temperature of the parts; in winter, when working outdoors, the washing process becomes ineffective or takes a long time.
- The difficulty of dosing drugs and the risk of damage to the crankshaft and camshaft oil seals from aggressive components that get into the engine oil.
- Risk of damage to the cylinder mirror by solid carbon particles at the moment of starting the power unit. The active substance washes away the oil film and dry friction occurs within 2-3 seconds.
Procedure for boxer engine
Power units with horizontal cylinders are used in Subaru or Porsche cars; a spark plug located in the center of the combustion chamber will not allow the cylinder to be filled with liquid solution.
In this case, it is necessary to select a foamed reagent that will evenly cover the walls, ensuring the dissolution of deposits.
An additional problem will be difficult access to the spark plugs (for example, on a Subaru Forester you will need to remove the power unit mounts and lift the engine up).
For V-engine
In V-shaped and some in-line engines, the blocks are located at an angle of up to 45° from the vertical, which does not allow the combustion chamber to be completely filled with liquid reagent. Additional problems arise when removing spark plugs that are covered by additional units or located in hard-to-reach areas due to the tight layout of the engine compartment. The effectiveness of cleaning depends on the material chosen for maintenance (foaming chemicals are recommended).
For rings in motion through fuel
The simplest cleaning is done by supplying the reagent along with the fuel; gradually eroded deposits burn out and leave with the exhaust gases (without contaminating the oil filter). Liquid material (for example, Edial) is poured into the tank (the proportion is indicated in the instructions for use), and then the vehicle begins to operate in standard mode without restrictions on the crankshaft speed.
For oil scraper rings
Since the oil scraper rings are located at the bottom of the piston, a combined method involving the introduction of additives into the lubricant and fuel is used to remove contaminants. The car is operated in a gentle mode for 200-300 km, periodically checking the lubricant level in the crankcase. On some engines (for example, on TFSI units from the VAG concern with direct fuel injection, carbon deposits on the surface of the intake valves) it is necessary to flush 2-3 times, and then do a hard cleaning, followed by an oil and filter change.
For valves
The parts of the gas distribution mechanism located inside the combustion chamber are cleaned by introducing Edial fluid into the fuel. When the air-fuel mixture is burned, deposits are removed and the tightness of the junction line between the valve plate and the seat is restored. At the same time, the spark plug electrodes are cleaned, which improves the performance of the ignition system.
A detailed review of flushing oils from the most popular manufacturers. Let's figure out how to determine which engine flushing oil is best for your car.
Methods to combat coking
Dozens of manufacturers of components and car care products, hoping to occupy all the niches of this market segment, produce chemicals that can remove carbon deposits from parts of internal combustion engines. The principle of their action can be different: it is either an increase in the combustion temperature of the fuel, or the dissolution of carbon deposits using certain chemical reactions. In addition, there are several ways to achieve these goals.
Fuel additives (mild decoking)
How to decarbonize oil scraper rings without extra costs and additional work? That's right, you can use special fuel additives. One such product is the chemical EDIAL. The mechanism of use is quite simple. In the case of this product, you need to pour about 50 ml of liquid into a 50-liter gas tank before visiting a gas station. In addition, this decarbonization method is ideal not only for gasoline engines, but also for diesel engines.
Among the advantages of this decarbonization method, the following points are worth highlighting:
- No unnecessary physical activity. This method does not require removing spark plugs and injectors;
- Fast fluid injection time;
- There is no need to change the engine oil after decarbonization;
- Protects engine elements from carbon deposits for a long time after the drug has been removed.
But the soft decarbonization technology also has disadvantages that should not be kept silent about:
- This method is a prevention, but not a treatment for clinical cases of coking of piston and oil scraper rings;
- Additives will not cope with coking of the cylinder walls and valves.
Simply put, mild piston ring carbon cleaners are detergents that can remove light deposits on the rings and their grooves.
Hard engine decoking method
Motorists who consider engine decarbonization a vital undertaking most often prefer the method of hard cleaning of rings and other elements. An obvious disadvantage of this technology is the mandatory oil change after decoking. For example, we can consider a domestically produced product called LAVR.
The cleaning technology itself will not cause problems or complexity even for novice car enthusiasts who have at least the slightest idea about the design of the engine in their vehicle.
- The car is placed on a flat surface, started and warmed up to operating temperature. The main thing is that it should not be heated to the limit.
- All spark plugs or injectors and glow plugs are unscrewed one by one when decarbonizing the diesel engine.
- Next, you need to set the pistons at the same level. To do this, you can jack up the car, set the maximum gear on the gearbox and rotate the wheel of the drive axle. Alternatively, you can turn the crankshaft clockwise with a belt.
- After this, using a syringe, a certain amount of liquid is poured into the combustion chambers through the holes. The dosage of the product is usually indicated on the packaging. Afterwards, the candles are screwed back in to prevent small debris from getting inside.
- The mixture must remain in the engine for at least one hour, but it is better to carry out work in the evening and leave the solution overnight.
- After a few hours or the next day, if the liquid was left overnight, the candles or nozzles are unscrewed, and a rag is placed over the holes.
- Next, you need to remove any remaining cleaner to prevent engine water hammer. To do this, it is enough to crank the engine with the starter for 5-10 seconds, not forgetting to first set the neutral speed. Along with the liquid, plaque residues will also be removed.
- The spark plugs are screwed in, the engine is started, and it remains to idle for literally 10 minutes.
- Finally, all that remains is to change the oil. If desired, you can repeat the procedure after 100 km.
If you are thinking about how to decarbonize the piston rings on an engine, you can safely choose the presented cleaning technology and the LAVR product (or its analogues). This method is used in almost all auto repair shops, and the solution has proven to be an excellent and reliable assistant in the matter of removing carbon deposits.
Types of coking of piston rings
Piston rings become coked in 2 positions:
- In a recessed state. The elements are held in the grooves by a layer of carbon deposits on the end edges. After removing foreign deposits with reagents, the rings return to their normal position, which makes it possible to restore engine performance.
- In extruded form. Deposits accumulate between the ring and the piston, leading to accelerated wear. After cleaning, the parts will fall into place, but due to the increased gap, oil consumption will remain unchanged or increase. To eliminate the defect, a major overhaul of the power plant will be required with the replacement of piston group parts or boring of the cylinder mirrors.
What means are used
The rating of carbon removal products, compiled based on customer reviews, includes:
- Mitsubishi Shumma Engine Conditioner is petroleum based and contains detergent additives based on ethylene glycol and volatile ethers. The foamed material is introduced into the combustion chamber through an extension tube and does not have an aggressive effect on rubber elements, but when it gets on the body or plastic glass of lighting equipment it leaves cloudy spots.
- GZox Injection&Carb Cleaner, originally created for cleaning jets and valves in carburetors. The composition includes ammonia, which destroys aluminum parts, so the solution should be poured for 15-30 minutes.
- The water-based carburetor cleaner ICC300 dissolves sludge well due to its reduced volatility, but it takes 10-12 hours to achieve results. When the air temperature drops, efficiency decreases; the manufacturer recommends warming up the engine and then pouring the reagent into the cylinders.
- VeryLube preparation from the Hado company in aerosol packaging, designed for treating engines with a thin layer of deposits on the piston group. The manufacturer claims the possibility of using liquid to flush the lubrication system.
- Greenol Reanimator Professional is distinguished by the use of components that dissolve paint on the surface of power plant parts. The liquid is supplied in an oversized package, which is enough to clean an engine with a volume of up to 3.5 liters. Additives have a negative effect on rubber elements (for example, oil seals on valve stems).
- Lavr ML202 Anti Coks Fast, designed to dissolve light contaminants, does not restore ring mobility and compression. It takes 12 to 24 hours for surface deposits to soften.
The average price of reagents and packaging volume are shown in the table.
| Name | Capacity, ml | price, rub. |
| Mitsubishi Shumma | 220 | 750 |
| GZox Injection&Carb Cleaner | 300 | 545 |
| ICC300 | 300 | 480 |
| VeryLube | 320 | 470 |
| Greenol Reanimator Professional | 450 | 900 |
| Lavr ML202 Anti Coks Fast | 515 | 520 |
Features of decarbonization of boxer and V-shaped engines
Decarbonization of engines of different designs has its own subtleties. For example, boxer power units are located horizontally, so it will be difficult to pour anti-coke into the combustion chamber. Setting the pistons to the middle position on such an engine is even more problematic. Even if everything works, the flushing agent will only clean the lower half of the combustion chamber and the lower segment of the rings.
The same can be said about multi-cylinder V-shaped engines - access to their spark plugs and injectors is difficult with attached units. They often require special tools to remove them. The copper sealing washers found under the injectors are not reusable and will need to be replaced. Since the pistons are angled, more flushing agent will be needed to evenly attack the carbon deposits.
What is the best way to decarbonize an engine?
The effectiveness of cleaning piston group parts with preparations was assessed on a 1NZ-FE engine with high mileage. The solutions to be tested were poured into the cylinders, and the removed valves were lowered into containers with reagents. Before testing began, the elements were heated to a temperature of +60°C, the processing time was 14 hours for the piston group, and the gas distribution mechanism parts were checked in accelerated mode (for 60 minutes).
The tested liquids showed the following results:
- The leader was Mitsubishi Shumma, which is characterized by ease of application and destroys dense deposits of sludge. Carbon deposits remained only in the corners of the recesses for the valve plates.
- Composition BG-211 was slightly inferior to the winner, retaining some of the deposits on the milled plane of the piston crown.
- The LAVR preparation was much inferior to its competitors; the varnish sludge remained untouched.
- FENOM liquid washed away only the loose surface layer of carbon deposits.
None of the solutions tested were able to flush the oil supply channels located under the rings. It should be borne in mind that decarbonization will not restore engine performance in a neglected state. The reagents will allow you to remove some of the sludge from the surface of the parts and push back the time for major repairs by several thousand km.
Do not use Dimexide for washing, which destroys the paintwork of the internal surfaces of the engine crankcase, as well as household cleaners for stoves.
The active substances included in the composition (for example, caustic soda) destroy aluminum alloys, and abrasive particles accelerate the wear of rubbing surfaces. It is allowed to use materials to remove carbon deposits when disassembling the engine (short-term exposure does not have a negative effect on aluminum, and the abrasive is removed when washing the power plant parts before assembly).
Complex decoking of the cylinder-piston group using BG technology
Over time, during the combustion of fuel, combustion products accumulate in the engine cylinders; this process is called coking of the piston rings. Coking occurs especially quickly due to low-quality fuel and when motor oil enters the combustion chamber. Burning together with gasoline or diesel fuel, the oil forms soot deposits, so-called coke deposits.
Engine decarbonization is a procedure that can extend the service life of the cylinder-piston group (CPG) and other critical engine elements without major repairs, by removing carbon deposits and deposits from the CPG.
Why does the engine get dirty?
The main source of carbon deposits in engine cylinders is oil that gets into the chamber, which burns together with the fuel. Oil can enter the combustion chamber by leaking from under the piston rings or valve stem seals.
Even when using high-quality fuel and oil, over time, combustion products form in the combustion chambers and carbon deposits accumulate, and some moving metal elements inside the engine become covered with a viscous coating (varnish). The oil supply system fails due to the formation of sludge - the result of polymerization of used or spoiled oil.
The formation of carbon deposits accelerates significantly if:
- the engine regularly overheats or operates at high temperatures, like BMW engines - the oil ages faster, loses viscosity, and forms polymer deposits on the parts of the CPG and lubrication system;
- the engine is operated at low temperatures, and the water vapor generated during fuel combustion comes into contact with cold oil, causing the formation of sludge in the crankcase;
- the engine is operated in city driving mode, that is, short trains alternate with idle time in traffic jams, fuel does not burn efficiently and incompletely;
- motor oil is of dubious quality or is not changed according to regulations, that is, the engine runs on old oil
- the turbocharger is worn out and hot exhaust gases enter the oil, changing its properties;
- low-quality fuel is used, which does not burn out completely;
- Soot is formed due to a drop in compression or late injection on diesel internal combustion engines.
In all these cases, if the piston group, combustion chamber, lubrication system and other important engine elements are not decarbonized in time, there will be obvious consequences of malfunctioning internal combustion engine and the need for expensive repairs will arise.
It doesn’t matter whether the engine is diesel or gasoline, active soot formation and general wear of the CPG reduce the service life of the engine.
Particularly dangerous are deposits in different areas of the piston, on the back side of the intake valve. This causes wear on the cylinders, blockage of the oil drainage channels, leanness of the fuel mixture, loss of compression and detonation in the cylinders. Deposits on the piston bottom interfere with heat dissipation and can cause burnout of the valve and melting of the piston, up to its complete destruction.
If the situation is advanced, the CPG parts are badly worn out, decoking the engine will only give a temporary effect, and you will have to do a major overhaul of the engine. If the prognosis is more favorable, it will be necessary to replace the compression and oil scraper rings along with decoking.
In what cases is decarbonization necessary?
It is recommended to decarbonize piston rings and other parts of the CPG in cases where:
- there is a sharp increase in oil consumption, the so-called “oil burn”;
- the smokiness of the exhaust increases, a burning smell appears in the cabin, which indicates incomplete combustion of fuel in the engine;
- the engine is idling unsteadily and has difficulty starting when cold;
- The traction characteristics of the engine decrease due to a decrease in compression in the cylinders.
Experts recommend not to let the situation lead to serious malfunctions, but to carry out preventative soft cleaning of the CPG every 20 thousand kilometers. It is recommended to remove carbon deposits and coke deposits using specialized equipment every 60 thousand km or when malfunctions occur.
When is the best time to perform the procedure?
It is recommended to decarbonize the engine CPG when the indicated malfunctions occur.
If you plan in advance, then ideally the best time is after winter , when soot forms especially intensely for the following reasons:
- driving with a cold engine
- cold start
- standing idle in traffic jams
- engine idling
- frost influence
It is also recommended to carry out professional decoking of the CPG before an oil service, that is, when it is planned to replace the engine oil and filter.
What methods of decarbonization exist?
The most expensive and time-consuming way to clean an engine from carbon deposits and other deposits involves disassembling it. This only makes sense if you plan to replace worn rings and CPG elements.
To clean the engine from carbon deposits and combustion products without disassembling, there are 2 strategies - hard and soft decarbonization. Both of them work through special means that chemically dissolve carbon deposits or increase the flash point in the combustion chamber to remove deposits, but this result is achieved in different ways.
Soft cleaning . It involves adding a flushing agent to the engine lubrication system with the effect of decarbonizing carbon deposits, for example, BG 109.
The additive is added when there are about 200 km left before the scheduled oil change. All this time the car is operated in a gentle mode, without reaching high speeds and preventing overheating. The liquid circulates in the system, cleaning the oil scraper rings and compression rings, and is removed along with the used oil when replaced.
The main disadvantage of the method is that it is not possible to remove carbon deposits and deposits from the walls of the combustion chamber and valves.
That is, soft cleaning is a simple and inexpensive preventive measure that prevents engine contamination, prevents carbonization of the lower piston rings and reduces oil consumption due to waste. But such a cleaning additive will not cope with serious problems.
Tough cleaning. Involves supplying a cleaning agent through the fuel system. This method allows you to clean fuel injectors, intake valves, decarbonize the upper compression rings, remove carbon deposits from the walls of the combustion chamber and exhaust valves.
Hard cleaning can be done simply by hand or using high-tech equipment. The processes are similar, but the execution technology and efficiency are radically different.
Manual method:
- it is necessary to remove the spark plugs or injectors on the combustion chambers
- the cylinders are brought to the middle position
- Cleaning liquid is supplied to the combustion chambers of a heated engine.
- spark plugs or injectors are returned to their place, loosely screwed in
- wait the allotted time - from half an hour to 12 hours
- remove spark plugs/injectors
- The cleaner, along with dissolved deposits, is removed with a syringe and by cranking with a starter without spark plugs
- the engine operates at variable speeds
- The oil is being changed.
This is the method used in most auto repair shops. And in Soviet times, car enthusiasts carried out such decoking right in the garage, pouring a “vigorous” mixture of kerosene and acetone into the cylinders.
Disadvantages of the manual hard cleaning method:
- insufficient cleaning of the walls of the combustion chamber and valves, that is, the composition does not penetrate there;
- if the temperature is low and the motor cools down quickly, efficiency decreases even more;
- Not every type of engine has convenient access to the combustion chambers; for example, in boxer and V-shaped engines it is impossible to clean the cylinders in this way without special service equipment.
Options for engine protection against carbon deposits
To reduce the rate of deposit formation it is necessary:
- use motor oils with tolerances specified by the vehicle manufacturer;
- use high quality fuel and refuel the car at pumps of large oil refining companies;
- regularly change filters that remove impurities from fuel;
- reduce the number of trips with the power unit partially warmed up or with long periods of idle time in traffic jams;
- periodically go on the highway to drive at higher speeds, which allows you to partially remove deposits.
Common myths about decoking
Despite the start of mass production of synthetic oils and improved fuel quality, engines become contaminated with deposits because the clearances between mating parts are reduced. Carbon deposits reduce compression and lead to increased fuel and lubricant consumption. But it should be remembered that decoking will not restore the performance of a power unit with worn rings and cylinder mirrors.
The maintenance procedure depends on the configuration adopted for the cylinder block. With an inclined arrangement of combustion chambers, it is necessary to fill in a larger volume of cleaning agent than with a vertical arrangement (with the same displacement and number of cylinders). At the same time, it should be taken into account that excess solution should not be filled, since the penetration of the reagent into the oil pan through the piston ring locks leads to damage to the seals.
Reagents should not clean parts to their original factory condition; excessive aggressive action leads to the formation of cavities on the metal surface. The remaining liquid poured into the cylinders burns and forms a smoky exhaust, which is not a sign of an emergency condition of the engine and does not harm the catalytic converter or soot trap. Owners with experience in decarbonizing power units recommend changing the oil immediately after completing the cleaning procedure.
When using foreign liquids, a layer of cleaning agent remains on the surface of the cylinders and electrodes of the spark plugs, so when starting, it is necessary to crank the engine crankshaft several times before the power plant begins to operate without interruption. What other piston ring decarbonizers can be used when servicing engines and what difficulties will the car owner encounter when performing the work independently?
- Which antifreeze is better: Syntec or Felix?
- Rating of air filters for cars
- Which wheel bearing is better?
- Which H7 low beam lamps are the best?
- Which brand of silent blocks is better to buy?
- Which jack is better to buy for a passenger car?
Decarbonization with kerosene - instructions
The occurrence of piston rings due to carbon deposits can be “cured” with kerosene. The method is especially good if deposits on rings and channels have created an insurmountable layer of coke. You will need a 50:50 mixture of kerosene and acetone .
Step-by-step description of removing carbon deposits:
- Unscrew all spark plugs.
- Pour about 100 mg into each hole in the cylinders (to distribute the mixture evenly, it is preferable to install them in one line).
- Install the spark plugs and leave the car overnight (at least 8 hours).
- Unscrew the spark plugs and place a rag on the spark plug wells.
- Start the starter so that the remaining solution comes out through the wells.
- Tighten the spark plugs, start the engine, 15 km of driving is enough to eliminate the residue (it is advisable to choose a busy road, cleaning will cause a lot of smoke).
- Change the oil.
Decarbonizing piston rings with kerosene is a simple procedure that can be done alone. As a result, we get normal oil consumption without excessive consumption, improved vehicle dynamics, clean injectors, and no detonation due to accumulated coke.