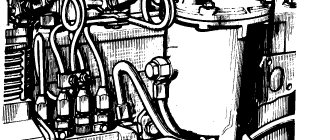
How to properly install the ignition on a Yamz 236 engine
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING THE ANGLE OF FUEL INJECTION ADVANCE OF ENGINES YaMZ-236N, YaMZ-236NE2, YaMZ-236NE, YaMZ-236BE2, YaMZ-236BE, YaMZ-236B
To adjust the fuel injection advance angle, two hatches are provided on the flywheel housing (see Fig. 63), and the angle values are marked on the flywheel in two places. For the lower indicator 3, these values are made on the flywheel in digital expression, and for the side indicator 4 - in alphabetic expression,
in this case, the letter “A” corresponds to the numerical value of 20°; letter “B” -15°; letter “B” -10°; letter "G" -5°.
Rotate the engine crankshaft clockwise (as viewed from the fan side) until the marks on the crankshaft pulley and the timing gear cover or on the flywheel with the indicator align, corresponding to the installation angle of the fuel injection advance:
Rice. 63. Combination of marks on the flywheel with flywheel housing indicators: 1-flywheel housing; 2-flywheel; 3, 4 - flywheel housing indicators; 5-top hatch plug; A - direction of rotation of the crankshaft
In this case, the valves in the 1st cylinder must be closed.
You can rotate the crankshaft with a wrench using the crankshaft pulley mounting bolt or a crowbar using the holes in the flywheel (Fig. 61) with the flywheel housing hatch cover removed.
When the marks are aligned, mark “A” on the end of the coupling (Fig. 64, 65) should align with mark “B” on the indicator. If the marks are not aligned, adjustments must be made.
The procedure for adjusting the injection advance angle of YaMZ-236NE2, BE2 engines (Fig. 64):
• loosen the tightening of bolt 2 of the terminal connection: flange 3 - drive coupling half 1;
• by turning the damper coupling, align the indicated marks;
• without disturbing the aligned position of the marks, tighten the terminal connection bolt to a torque of 16.18 kgf-m. In this case, the deviation of the plate package from its position in one plane should be within ±1 mm. Take measurements near the places where the plates are attached. If corrugations appear on the plates 4, they are eliminated by alternately loosening and then tightening with a torque of 11.12.5 kgf-m the four bolts 5 securing the plates to the flange of the coupling half and to the damper coupling;
• check the correct setting of the injection advance angle.
Rice. 64. Drive coupling for the high-pressure fuel pump of YaMZ-236NE2, BE2 engines: 1-drive half-clutch; 2-bolt terminal connection; 3-flange of the coupling half; 4-plate drive; 5-bolts for fastening the drive plates; 6-washers; 7-damper clutch; 8-pointer; 9- high pressure fuel pump; A-mark on the damper coupling; B-mark on the index
Rice. 65. Drive coupling for the high-pressure fuel pump of YaMZ-236N, B, NE, BE engines: 1-drive shaft; 2-drive plates; 3-driving coupling half; 4-bolts; 5-bolt terminal connection; 6-bolts; 7-half-coupling driven; 8-fuel injection advance clutch; 9-high pressure fuel pump; A-mark on the coupling; B-mark on the index
The procedure for adjusting the injection advance angle of YaMZ-236N, B, NE, BE engines (Fig. 65):
• check the tightness of the coupling half 3 on the drive shaft 1 and the tightening of the terminal bolt 5 (tightening torque 43.2.58.9 N-m (4.4.6 kgf-m));
• unscrew (loosen) two bolts 4 and by turning the advance clutch, use the oval holes on the flange of the coupling half to align the marks “A” and “B”;
• without disturbing the aligned position of the marks, tighten the bolts 4 of the drive with a tightening torque of 43.2-58.9 Nm (4.4.6 kgf-m). In this case, the deviation of the plate package from its position in one plane should be within ±1 mm. Take measurements near the places where the plates are attached;
• turn the crankshaft and check that the injection timing is set correctly. The discrepancy between the marks should be no more than one division or 1° of rotation of the crankshaft.
Check the presence of oil in the fuel injection advance clutch (YAMZ-236N, B, NE, BE engines), and, if necessary, add oil. To check, install the coupling with the holes in the upper position and remove the plugs. When the clutch is slowly turned 70°, oil should begin to flow out of one hole. After adding oil, tighten the plugs.
Source
YaMZ 236 thermal gap adjustment technology
The scheme for adjusting thermal gaps with your own hands is practically no different from a similar operation on other cars. After checking that the axle mounting bolts are securely tightened, the crankshaft is turned clockwise until the intake valve of cylinder 1 is completely closed. Then you need to turn the shaft a third of a turn, and only after this can you measure and adjust the gaps in the first cylinder. To set the gap, use special feelers of the appropriate sizes, and after adjusting the first cylinder, carry out the adjustment in the order of work that we gave above.
After installing the gaps, check the condition of the valve cover gaskets, start the engine and test its operation, first at idle, and then under load. The adjustment operation is carried out as necessary or after repair or dismantling of the cylinder heads.
Engine Specifications
| Production | "Avtodiesel" Yaroslavl Motor Plant |
| Engine make | 236 |
| Years of manufacture | 1962-present |
| Cylinder block material | cast iron |
| engine's type | diesel |
| Configuration | V-shaped |
| Number of cylinders | 6 |
| Valves per cylinder | 2 |
| Piston stroke, (mm) | 140 |
| Cylinder diameter, (mm) | 130 |
| Compression ratio | 16.5 |
| Engine capacity, (cc.cm.) | 11150 |
| Engine power, (hp/rpm) | 250/2000 |
| Max. torque, (Nm/rpm) | 1078/1100-1300 |
| Environmental standards | Euro 0 Euro 1 Euro 2 |
| Turbocharger | TKR 90 |
| Engine weight, (kg.) | 890 (YaMZ-236M2) 950 (turbo) |
| Average fuel consumption at a speed of 60 km/h, l/100 km (when installed on a URAL 4320 vehicle) | 35 |
| Oil consumption, % of fuel consumption, up to | 0.5 0.2 (Euro 2) |
| Recommended engine oil: – for summer – for winter (at temperatures less than +5° C) | M-10-G2k M-8-G2k |
| Volume of engine oil in the engine, (l.) | 21 (atmospheric) 24 (turbocharged) |
| Oil change frequency, (motor hours) | 500 1000 (Euro-2) |
| Overall dimensions, (mm): - length - width - height | (YaMZ-236B) 1276 1045 1100 |
| Engine life - declared by the factory - in practice (on average) | 8000+ engine hours 800 t.km. |
| Applicability of YaMZ-236 | Download table |
Adjustment of YaMZ 238 and 236 valves
For the Yaroslavl Motor Plant, this engine layout option is the most typical, since the manufacturer strives for maximum unification of power units. Therefore, the YaMZ-236, YaMZ-238 and YaMZ-240 engines can be considered, with a certain stretch, as variants of one engine with a different number of cylinders - from 6 to 12. Thanks to the unification of diesel engines, adjustment of YaMZ valves with a V-shaped arrangement is performed in a similar way.
All work is done in two revolutions of the crankshaft, the only difference being the rotation angles between the settings of the individual valves.
- The adjustment of engine valves 236 (BE/NE, BE2/HE2 and other modifications) is carried out in the order of operation of the cylinders (1–4–2–5–3–6). Before this, the tightening of the rocker arm axles must be checked; the factory-standardized force is 120-150 N*m.
- The adjustment on the 238 engine is in a different order (1-5-4-2-6-3-7-8). The gaps are set using similar feeler gauges within 0.35-0.3 mm for all valves.
- The YaMZ-7511 engine is actually a forced version of the old 8-cylinder engine; the setting is absolutely similar to how the clearance in the YaMZ-238 valves is adjusted.
- Adjusting the 240 engine goes in the order 1-12-5-8-3-10-6-7-2-11-4-9 and requires a slightly larger amount of preparation (you need to release the flywheel inspection window to rotate the crankshaft, while adjusting valves on 236-238 engines are rotated from the fan side).
During disassembly, the service technician performs incidental diagnostics to the extent available - he inspects the rocker arms, rods, and adjusting elements.
Valve adjustments on the 238 and other V-twin engines should only be done when the engine is cold. The extremely short time after stopping the engine is 15 minutes.
The relatively large number of gas distribution parts in the lower mechanism makes this requirement critical, since the thermal expansion of individual components is uneven, and the gap changes nonlinearly as the internal combustion engine warms up and cools down. For naturally aspirated engines and turbo engines, the clearances are no different.
For safety reasons, before starting work, the master forcibly shuts off the fuel supply in order to avoid accidental working fuel injection into the cylinder when cranking.
Yaroslavl diesels, hope, support and torque
Perhaps the only enterprise that is capable of producing competitive diesel engines for trucks and construction equipment remains the Yaroslavl Motor Plant. YaMZ diesel engines are brutal, reliable, simple and unpretentious, sometimes even showing miracles of integration into the new century with its stringent requirements for environmentally friendly exhaust. Thus, all diesel engines that are installed today on Ural, MAZ, Ivanovo and Kostroma excavators comply with at least Euro 0 standards.
In particular, today we will be interested in the six-cylinder naturally aspirated diesel engine YaMZ 236, installed on a huge number of road and construction equipment, MAZ, Ural vehicles, diesel generators and some buses. The motor was developed 55 years ago, but due to the lack of an alternative, it continues to be in demand. By modern standards, even for a diesel unit of the most utilitarian construction equipment, it simply has no equal. In the sense that there is hardly any other manufacturer in the world that sells working museum exhibits. However, the 180 horsepower extracted from the 11.2-liter V-6 cylinder engine is put to good use.
Video about the YaMZ-236 engine
The basic YaMZ 236 engine can be equipped with many improvements and attachments:
- power take-off mechanism;
- mechanism for damping torsional vibrations;
- oil-liquid radiator,
and some other devices associated with the narrow specialization of certain equipment. There is also a modification of the YaMZ 236 HE2 Turbo engine. It is equipped with a turbocharger and as a result, the power increased to 230 forces. The price of the engine, by the way, without gearbox and clutch is 460,000 rubles.
But no matter what attachments are installed on this diesel engine, maintenance and adjustments are simply inevitable. The motor is easy both to set up and to maintain, since you still need to know how to damage it. Still, some technological processes require explanation, in particular, adjustment of the valve mechanism.
History of the YaMZ 236 engine
The development of the engine started in the fifties; the country's leadership set the task of modernizing the fleet of diesel units and creating a universal traction unit. The engine had to not only replace the outdated YaAZ-204 (206) models, but also be used in multi-directional vehicles. At that time, no product had such features.
The bet was made in favor of diesel units, since fuel efficiency was at the forefront, there was no suitable model in the country, the product was developed from scratch. Not everyone was able to cope with the requirements; a galaxy of designers was involved in the work, and the group was led by scientist G.D. Chernyshev. The bet worked, and a new product soon appeared. The characteristics of the YaMZ 236 engine were satisfactory and even exceeded expectations. A reliable, economical, unpretentious, durable device led mass production, marking the beginning of a line of diesel engines.
Even today, after so many years, there is no replacement in the country capable of repeating the path of the famous motor. New six-chamber diesel engines, based on the same YaMZ-236, modified to suit the latest social conditions. With a service life of 500,000 kilometers and a design in which the ease of solutions borders on the ideal, the engine is able to “give a head start” to its competitors. Looking at the situation from the outside, it is difficult to believe that the history that began back in 1962 continues, flourishes and influences current events.
How the YaMZ-236 model was created and production today
Before the development of this engine, YaAZ models were used, which became obsolete by the fifties. Therefore, in the 50s of the last century, the Yaroslavl plant, under a state special order, was tasked with creating a more powerful and economical engine. In addition, we needed a unit that could be installed on a wide variety of equipment.
The development of the YaMZ-236 engine was undertaken by the honored scientist and outstanding designer of the USSR G.D. Chernyshev, who also developed other diesel engines in those years.
This is how a new internal combustion engine was born, which later became a celebrity. It was distinguished by high power, reliability and easy repairs, simple maintenance and cheap spare parts. With proper use, this mechanism will last for many years.
YaMZ-236 is still produced today, regularly modernized and at the same time already has a successor - an improved modification, YaMZ-530.
YaMZ-236 diesel engines are still relevant, their sales are not falling, despite the appearance of more modern models.
Engine Features
YaMZ 236 is a four-stroke V-shaped 6-cylinder diesel engine with a working volume of 11.15 liters (11,150 cm³). The cylinders have a 90° camber. And each cylinder has two valves: one intake and one exhaust. Thus, this power unit is equipped with 12 valves.
Unlike newfangled engines, the cylinder block material is cast iron. In many ways, this is what determines the high reliability of the power unit and its maintainability.
An important positive factor is that the entire engine is designed with ease of maintenance in mind. All attachments are located on the top of the motor and are convenient for replacement and repair.
The main disadvantage of this power unit is that, due to its antiquity, the engine does not meet any environmental standards.
Ignition installation
Ignition installation is the process of adjusting and controlling fuel injection. You can set the ignition of YaMZ 236 m2 yourself or with the help of service station specialists.
The adjustment must be made as follows:
- find the mark on the coupling near the fuel pump and fix the part with this mark facing up;
- turn the engine to get a value of 20 degrees on the scale;
- loosen the bolted connection fixed on the coupling, turn it to the late ignition position;
- unscrew the tube supplying fuel to cylinder No.1;
- wipe parts and remove dirt;
- Rotate the clutch slowly until fuel is visible in the recess located on the primary cylinder;
- tighten the bolts on the coupling.
Setting the advance angle
The required advance value is located next to the special mark. The YaMZ 236 fuel injection advance clutch is where this risk is applied. The normal value is 20 or 18 points. The angle of the fuel mass itself is determined by the primary cylinder.
Control is carried out using a conventional pump. So, they work on the power supply system of a car engine, without fail, first opening the valves through which air escapes from the engine. After the air masses have come out without any residue, the plugs are wrapped. Next, you should connect the momentoscope device to the fittings of the special section from the fuel pump. Before carrying out the procedure, it is necessary to remove the injection pump of the Yamz 236 cylinder.
Read also: Test drive Nissan Primera 2006 video
The advance is adjusted as follows:
- the bracket from the working power apparatus is transferred to the working state;
- drain all the fuel from the glass container until the volume of liquid reaches the mark in the middle part of the tube;
- carefully turn the crankshaft.
All movements must be made strictly in the direction of torsion. The current position of the meniscus in the tube must be constantly observed and monitored. Its sharp rise signals the start of fuel start-up by a certain section. The line marked on the pulley should be opposite the line with the number marks. The procedure for setting the angle requires special accuracy up to 1 value.
Problems and weaknesses of the YaMZ-236 engine
Let’s immediately talk about the weaknesses of the YaMZ-236. Problems may be related to the gear drive of the injection pump. To check whether everything is normal with this unit, it is recommended to start the engine “cold” and “hot” several times; the start should be instantaneous. Old engines suffer from running out on the key, as a result, the injection angle changes at start-up, and under traction loads, the output power will drop and change, the engine will smoke more.
Structurally, the timing drive was also not very well placed. There are a lot of torsional and vibration vibrations, which is why gears and keys wear out faster.
Other weak points of the YaMZ-236 include: valve lifters, fuel equipment, especially injectors, difficulties in replacing these same injectors, injection pump with flow-through lubrication and a not very successful drive. There are also several cases when the cylinder head burst in the area of the injector holes, but this is rather an exception to the rule, but still.
Adjustment of UOVT in YaMZ 238
To set the spray advance angle, there are two control holes on the rotary wheel (flywheel) housing. And on the rotation wheel itself, angle reference points are marked at two points. The lower indicators are expressed in numbers, and the side indicators are expressed in letters.
To adjust the fuel spray advance angle, open the hole on the flywheel housing, rotate the engine crankshaft until the notches on the shaft pulley align with the timing gear housing or on the flywheel with a reference point. The resulting value should correspond to the setting angle of advance of the VT (6°–7°). These actions are performed, as a rule, with the valves in the 1st cylinder of the engine closed.
The crankshaft can be turned either with a wrench using the mounting bolt of the shaft wheel, or with a crowbar attached to the holes in the flywheel.
When aligning the marks, the indicators “A” on the end of the clamping device (coupling) must coincide with the arrow of the indicator or the letter “B” on the indicator. If the marks are not level, you need to continue adjusting.
YaMZ-236 device
The cylinder block is cast from low-alloy, gray cast iron with wet liners (0.1 mm projection). The crankshaft stands on four supports inside the cylinder block.
- The piston stroke is 140 mm.
- Neck diameter – 110 mm.
- Crankpin – 88 m.
- Connecting rod length – 265 mm.
- Piston diameter – 130 mm.
- Piston height – 100 mm.
Two 6-valve cast iron cylinder heads are installed on the cylinder block. Inlet/exhaust valve - 61/48 mm, with a stem thickness of 12 mm. YaMZ-236 belongs to the lower engine type, so its camshaft is located in the cylinder block. Camshaft characteristics: phase 246/266, lift 13.5 mm.
The clearances of the intake and exhaust valves are 0.25-0.30 mm. Adjustment order: 1-4-2-5-3-6. It is recommended to carry out valve adjustment work every 500 operating hours.
- Boring of the seats of the main bearing shells is carried out together with their covers; therefore, the covers are marked for each shell separately.
- Cylinder liners are cast from special cast iron. They are sealed on top with a cylinder head gasket, and on the bottom with rubber rings.
- The crankshaft is made of steel and is manufactured by hot stamping. It has 3 crankpins and 4 main bearings.
- The cylinder head is cast from low-alloy gray cast iron, just like the cylinder block itself. The cooling system of the block head is a “jacket”, which is connected to the “jacket” of the main block. The cylinder head and the block are joined through a gasket.
- Timing mechanism is overhead valve with lower camshaft. The shaft is made of carbon steel with hardened bearings and cams and is located in the camber of the cylinder block.
- The valve seats are made of heat-resistant alloy and are pressed into their seats. Springs, timing valves, pushers and injectors are located in the cylinder head.
The oil pressure in a warm engine should be within 4-7 kgf/sq.cm.
The YaMZ-236 itself is a simple diesel engine with direct fuel injection. It has a lot of modifications and each of them contains different injectors, pumps, turbochargers, generators and other attachments.
Repair
The YaMZ-236 engine is repaired only in car repair shops, because it requires special equipment and appropriate tools. The category of special equipment includes stands: for dismantling and assembling the power unit and its components, adjustment, balancing, testing.
Special equipment includes a boring and honing machine; devices for grinding and polishing crankshafts; stand with bath for crimping; reamers, which are used to grind the seats of valve seats; equipment for mounting guide valves; turning and milling machines; stand for cleaning injectors; a press on which oil seals and bearings are pressed; argon welding (in some cases). Other tools and special-purpose equipment for repairing diesel engines may also be useful.
As you can see, you will need quite a lot of equipment, which not every car service can afford. Repair of the YaMZ-236 engine is carried out in several stages. They are quite complex. A specialist of a narrow profile is responsible for each.
Disassembly
It is clear that the engine can be disassembled using an expanded set of tools and an air gun. Malfunctions will be diagnosed and a list of spare parts required for replacement will be determined. The crankshaft is being ground. The cylinder block is being prepared. All spare parts and components are washed. As a rule, washing is performed with hot kerosene. Next comes the assembly of the elements. The engine disassembly procedure lasts about 6-8 hours. It will take approximately 16-20 hours to prepare the parts for assembly (this depends on the complexity of the problem). Assembly takes up to 36 hours. The process depends on the degree of wear of the main units and components, and how well the elements were prepared for the last stage of work.
Save and share:
Ignition adjustment
To carry out adjustments, there are two special hatches in the flywheel housing design. The angle values are indicated on the body of the part. In this case, the bottom column expresses the values in numbers, and the side column – in letters.
The crankshaft rotates only in a clockwise direction. The view is directed from the side of the fan. Rotation can be done using a wrench hooked onto a bolted connection. The crankcase cover must be removed.
During the process of aligning the marks, the letter “A” printed on the end of the coupling must align with the mark “B” on the lower indicator. If the connection does not occur, then it is necessary to fine-tune the parts.
Malfunctions, their causes and solutions
- Engine overheating. Possible causes are a dirty radiator, faulty pump or thermostat.
- The revolutions “float”. It is necessary to check the fuel injection pump and adjust it if necessary. Air in the fuel system is also possible.
- Troubles or jerks at low speeds. First of all, you need to look at the fuel system (fuel pump, injectors, fuel line, fuel filter). It is also worth checking the ignition system.
- It starts poorly or stalls. There may be air in the fuel system, where it is being sucked in, a damaged tube, etc., or the fuel filter may be clogged. If you don’t find anything, then we look towards the fuel injection pump.
- Engine knock. It’s unlikely that it will be possible to do without an autopsy. Again, injectors, valves, rings, and liners may knock. You can also look at the ignition and fuel pump.
- White smoke from the exhaust. The cause may be water in the tank or coolant entering the cylinders through a crack in the cylinder head or a worn gasket.
- Black smoke. The mixture is very rich, you need to reduce it by tightening the lower power screw on the injection pump, perhaps it is turned to the maximum.
- Blue smoke. The oil gets into the cylinders and burns there.
- Strong vibration of the motor. The cause of the vibration may be the flywheel, worn engine mounts, an unregulated ignition, or the driveshaft. Well, as a last resort, an unbalanced crankshaft.
- It won't start at all. Look towards the fuel system, namely the injection pump and injectors.
Features of the mechanism
In order for the mechanism to work smoothly and for a long time, you need to know and observe certain features.
First of all, it is necessary to carefully carry out all routine maintenance provided for in the manufacturer’s instructions.
When running in a new engine, all its rubbing surfaces are run-in, so it is important to follow the running-in rules - they are usually indicated in the corresponding section of the instructions.
It is also important to lubricate the engine according to the appropriate table. All approved lubricants are listed in it.
The coolant in a running engine should have a temperature of 75 to 98 degrees. A cold engine should not operate under load. When starting a cold engine, you cannot sharply increase the speed, as the thick oil does not have time to reach the crankshaft bearings, and they fail.
The oil level should not fall below 300 kPa, otherwise the rubbing surfaces may quickly wear out.
Cylinder head fastenings that are tightened with nuts must be tightened with strict frequency, sequence and specified torque. If this is not observed, the seal will fail and the gaskets will burn out.
Gearbox YaMZ-236
Gearboxes for the YaMZ-236 family of diesel engines are five-speed, mechanical, three-way gearboxes with synchronizers in 2-3 and 4-5 gears. There are five gears for forward movement and one gear for reverse movement.
YaMZ-236 gearbox diagram:
1-clutch release; 2-primary shaft; 3 and 15 bearing caps; 4-clutch housing; 5 and 10 synchronizers; 7-ball retainer; 8 and 22 fifth gear gears; 9 and 21 third gear gears; 11 and 19 gears of the second gear; 12-gear first gear and reverse; 13-top cover; 14-secondary shaft; 16-flange; 17-intermediate shaft with first gear; 18-gearbox housing; 20-oil pump intake with magnet; 23-gear power take-off; 24-gear drive of the intermediate shaft; 25-oil pump; 26-axis reverse gear unit; 27-reverse gear block; 28-gear speedometer drive.
This is a fairly reliable box, which is confirmed by its installation on heavy-duty equipment operating in difficult conditions. Gearbox components and parts are made from high-quality materials. The good maintainability of the YaMZ-236 gearbox allows you to repair both its individual parts and replace entire units.
Modifications
Box modifications: YaMZ-236P, YaMZ-236PO, YaMZ-236N, YaMZ-236L, YaMZ-236U, YaMZ-236UO. They all have different purposes and depending on this, one or another gearbox is installed on the engine.
YaMZ 236P is considered the base model. There is a plug on the cover of the device, and on the cover of the output shaft there is a flange that ensures the operation of the speedometer and a driveshaft flange.
YaMZ 236P3 is manufactured for a diaphragm clutch. It is distinguished by the presence of a clutch release clutch and a bracket that engages the cylindrical spring of the clutch.
YaMZ 236P4 differs from P3 in the end splines on the driveshaft flange.
YaMZ 236P5 is a basic gearbox model, on which a short lever is installed on the cover instead of a plug. Cardan shaft with conventional flange.
YaMZ 236P7 is a P5 model for a diaphragm clutch. It differs from the base model in the dimensions of the clutch, which disengages the clutch mechanism, and in the presence of an engaging bracket.
The YaMZ-236U differs from the 236P in the presence of a gear shift lever and the absence of a flange for the speedometer drive mechanism on the output shaft cover.
YaMZ-236U3 is a 236U for a diaphragm clutch. It differs in the size of the clutch release clutch and the presence of a bracket for engaging the clutch release coil spring.
YaMZ-236U4 and 236U are hermetically sealed, distinguished by cast clutch starter hatch covers, a breather is installed on the top cover, and a plug on the bottom.
YaMZ-236U5 – 236U3 in a sealed design for a diaphragm clutch. It is distinguished by cast clutch starter hatch covers, a breather is installed on the top cover, and a plug on the bottom.
Gearbox Specifications
- Torque – 930 Nm.
- Weight – 240-250 kg.
- Switching – Lever/flange.
- Fastening the cardan shaft – Smooth flange for 8 bolts M10*155mm.
- Power take-off – Through the crankcase from a spur gear (up to 29.5 kW/40 hp) or from a gear coupling (up to 73.5 kW/100 hp) (additional option).
- Application: KrAZ, MAZ, ZIL, Ural vehicles, MoAZ scraper, MAZ, LAZ, LiAZ, MARZ, Neman, Volzhanin buses.
Gear ratios
| Broadcast | Gear ratio |
| 1 | 5,26 |
| 2 | 2,90 |
| 3 | 1,52 |
| 4 | 1,00 |
| 5 | 0,66 |
| Reverse | 5,48 |
Some features of the gearbox
- The gearbox lubrication system is mixed. Some components are lubricated under pressure, and others by splashing.
- The oil collector is equipped with a mesh with a magnet, which allows you to clean the oil from metal shavings and particles.
- The speedometer drive is located in the secondary shaft cover.
- The internal gearbox map communicates with atmospheric air through a breather.
- A protection system against simultaneous engagement of two gears has been introduced into the design of the YaMZ-236 gearbox.
- The spring fuse prevents you from accidentally engaging reverse gear, and it also makes it difficult to engage first gear.
- The gearbox mechanism is equipped with inertia-type synchronizers for shockless engagement of gears from 2 to 5.
- To ensure equal angular speeds of the carriage and gears, the YaMZ-236 gearbox has a friction pair consisting of a conical synchronizer ring located on the gear wheel.