How to distinguish a variator from an automatic: description, principles of operation, pros and cons
As you know, as of 2021, automatic gearboxes in passenger cars are very popular and exist on almost every car model.
When a car enthusiast has a choice between a CVT and an automatic, he chooses the latter option. After all, this is the most reliable transmission, proven over the years. Why take a variable one? In general, against the backdrop of such popularity, automatic transmissions are just a sea, and finding one that’s suitable and comfortable for you is not a problem. However, if you didn’t know, the words “automatic transmission” actually refers not only to the automatic transmission itself, but also to robotic and variable transmission. Each of them is different, but they have a very similar structure. That is why, in order to understand the common question of how to distinguish a CVT from an automatic, this article was created. Let's get started.
Rules for the use and prevention of automatic transmissions and CVTs during operation
The CVT is designed for comfortable, quiet and family-friendly metropolitan driving. For sporty and fast driving, an automatic transmission is more suitable. This is another solution to a problem from the category: “What are the differences between an automatic transmission and a CVT.”
Automatic transmission is an unpretentious gearbox. But when operating a CVT, the car owner must comply with the following rules:
- when stopping on a descent, use the handbrake;
- switch the rocker positions from “P” to “R” only after the car has come to a complete stop;
- tow only at neutral speed and no more than 80 kilometers at a speed of 30 kilometers per hour;
- change the oil on time;
- when 70 thousand km have been traveled, replace the belts on the pulleys;
- warm up the transmission in winter before starting;
- Diagnose problems and repair your vehicle only in qualified service centers.
Read
What is the difference and how does a robotic gearbox differ from an automatic gearbox?
The same applies to the automatic transmission, with the exception of replacing belts. Proper operation and high-quality care of the gearbox will ensure a long service life of the device.
ProVariator.RU
How to do this without starting the car
There are methods that allow you to correctly determine the type of transmission without even starting the car. They are as follows:
You can also spot differences during a test drive:
In the event that you cannot independently determine the type of box, a visit to a service station will be useful. After examining the underside of the car, a real specialist will probably be able to answer your question.
Many people, when buying a car, already know which way to choose - automatic transmission or manual. But those who have chosen an automatic transmission are faced with the difficulty of how to distinguish a CVT from an automatic transmission. After all, a CVT is, in fact, just a simple type of automatic transmission.
If you are unable to determine the type of box yourself, we recommend visiting a service station. A good specialist will be able to answer your question by looking at the underside of the car.
First way.
Second way.
Third way.
Fourth way.
Fifth way.
In terms of their technical characteristics, an automatic transmission and a variator, of course, differ in the presence of both advantages and disadvantages. When purchasing a car with a specific gearbox, each buyer must decide for himself which one is best. However, for most car enthusiasts the question remains: how to distinguish an automatic from a CVT by external features? Let's try to figure this out in this article.
How to identify a machine
First, you should carefully read the technical documentation supplied with the car, and also inspect the car and the gearbox itself for marks. As a rule, automatic transmissions are designated by the letters A or AT, while CVTs are designated CVT. Various automobile magazines and articles on the Internet will be just right to help the motorist. Familiarization with them will allow you to collect the maximum possible amount of information about the car you are interested in.
A more effective way to determine the type of transmission is to test drive it. If this is possible, you should conduct a tight drive, preferably along a straight section of the road. If your car has an automatic transmission, you will feel a noticeable jolt when accelerating and upshifting. Typically they will be smooth. This can be clearly verified with a sharp start. When moving from first to second gear there will be the most pronounced shock. You can also stop the car and release the brake pedal. If an automatic transmission is installed, the car will move smoothly forward, but will not roll back, as happens with a car with a CVT.
If, after performing these steps, doubts still arise (since most modern CVTs very accurately copy the operating principle of the machine), you can contact a car service center. Experts will certainly be able to help in this matter.
How to determine a variator
As already mentioned, first you should inspect the gearbox for the presence of the CVT designation. These letters mean that the car has a continuously variable transmission. However, it is best to get behind the wheel again and drive, both at high speed and moving smoothly. The key feature of the CVT is that each “gear” is not fixed. This means that as the level of load on the engine increases, very soft and smooth gear changes occur. That is why when driving a car that has a variator installed, there are no characteristic shocks when changing to the next gear. During rapid acceleration, a transition to a “new gear” occurs, and until the next gear change, the tachometer needle is at the same level, and only when the gear is changed does it change its position, etc.
As for the method of stopping the car and depressing the brake pedal, the car with the CVT installed will first roll back slightly, but the car will not move forward at idle speed. During rapid acceleration, the engine of a car with a CVT makes increasing noise, and then stops at a fairly loud tone, with which it continues to gain momentum.
There is a lot of debate among car enthusiasts about which gearbox is better. It is definitely difficult to answer this question. However, thanks to the smooth transition from gear to gear (depending on the load on the engine), cars with a CVT are in no way inferior to an automatic transmission.
Suggest a topic to the authors:
Few people know that, in addition to automatic and manual transmissions, there is also a variator. A manual transmission most often has five speeds, an automatic transmission has about eight, but how many gears does a variator have and what is a variator on a car? Below we will consider these issues in detail, as well as the difference between a variator and an automatic and manual transmission.
What is a variator and what does it go with?
A variator is a device that transmits between the engine and the wheels. It has the ability to smoothly change the rotation speed of the driving and driven disks. Typically, a CVT is installed on fairly expensive cars. However, such devices have long been installed on mopeds, scooters, as well as snowmobiles and jet skis. In cars, the CVT gained its popularity quite recently.
What is the difference between a CVT and an automatic?
There are several answers here, since there are quite a lot of differences.
- Firstly, the variator starts the car moving more calmly. It resembles a powerful electric motor. In addition, the variator also picks up speed quietly, without failures, with only a slight increasing noise.
- Secondly, a car with a CVT accelerates much faster than one with an automatic transmission. This is achieved due to the fact that the variator does not waste time changing gears, thereby gaining speed faster.
- Thirdly, the variator perceives changes in the car’s movement much more calmly. So, for example, a car with a CVT will not stall in a traffic jam or traffic light, and will not roll back when climbing. The start of movement, regardless of the driver’s skills, will always be smooth.
- Fourthly, the variator does not have the engine growl that many people need; it always hums smoothly and quietly. This does not suit those who like to drive loudly. It is also unusual for many that a car accelerates quickly and clearly with a quiet engine. For some this is a disadvantage, for others it is an advantage. However, for those who want to hear gear changes and the powerful sound of the engine, it is proposed to install “tiptronic”, which emulates these sounds.
- Fifthly, the variator is additionally equipped with a function that allows you to almost instantly change the gear ratio when pressing the gas all the way, as a result of which the car accelerates sharply.
How to visually distinguish a CVT from an automatic? Under the hood is the name and number of the transmission; it is by this number that you can distinguish between a CVT and an automatic. It is worth noting that you need to drive a car with a CVT; it will immediately become clear how to determine a CVT or an automatic. Sound, fast acceleration, soft movement - all this indicates that you have a CVT.
Details about CVT: the pros and cons of a CVT, how to distinguish a CVT from an automatic
Although the CVT is considered a newer modification of the gearbox, its prototype was created by Leonardo Da Vinci himself, who developed a similar system for operating a mill. But for cars, CVTs began to be used only in the 50-60s of the last century. It was first used in a DAF car, and later the idea was picked up by the automaker Ford. Today, many concerns producing high-end cars use continuously variable transmissions.
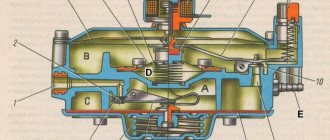
CVT design
The main difference between a CVT and an automatic is that the former has no speeds. Two pulleys located opposite each other and tied with a metal cable are responsible for the operation of the box (this is how you can visually distinguish a variator from an automatic transmission).
It is the belt that simulates gear shifting depending on the position. At the moment the drive pulley moves apart, the cable moves along a smaller diameter, simulating 5-6 gears. When the pulley moves along a larger diameter, 1st gear is simulated.
The pulleys move very smoothly. And although there are actually no gears, the gear ratios fully correspond to them, as in an automatic transmission. This allows the CVT to provide maximum efficiency, which improves the dynamics of the car and allows it to accelerate smoothly.
Why does the variator break?
The CVT box has a very complex design and is extremely demanding on maintenance. It must be carried out every 50-80 thousand mileage, otherwise problems cannot be avoided. As the practice of our workshop shows, it is the lack of maintenance that leads to a number of breakdowns:
- Untimely oil change;
- Clogged valve body;
- Problems with the belt;
- Electronics failures.
The transmission resource is about 100 - 150 thousand kilometers. Even with systematic oil changes, it is recommended to replace the belt after this gap has elapsed. This makes the CVT a more capricious gearbox.
Advantages of CVT
- A car with a CVT is an ideal option for novice drivers. The driver does not need to think about changing gears, there are no jerks;
- The efficiency of a CVT transmission is 8-10% higher compared to an automatic transmission. Therefore, the dynamics of the car are better, this is felt immediately from the moment of departure;
- Acceleration of the car is much more dynamic - a separate plus for drivers who prefer driving fast from the start;
- Consumes less fuel;
- Less oil needed
- Good car stability at high speeds.
The CVT, from the point of view of its advantages and driving sensations, is a more modern version of the gearbox. It provides comfort while driving, makes the car ride smoother, which is certainly noticeable to “experienced” car enthusiasts.
Disadvantages of a CVT gearbox
Although CVT is a newer transmission modification, it is not as popular as automatic transmission. And that's why:
- A very, very complex design. This makes repairing the CVT much more difficult and very expensive. In addition, due to the low popularity of cars with a CVT in Kyiv, and indeed in Ukraine, very few workshops repair this gearbox. As a result, the car owner has a serious problem in finding good craftsmen who can really help with repairs;
- Every 100,000 - 150,000 thousand kilometers you need to change the belt. This pleasure is by no means cheap;
- For the most part, the CVT box consists of electronics, which often fail. Finding the exact problem is not easy. Again, due to the complexity in the design;
- Oil. This is a separate topic. You need special oil, specifically for a specific car manufacturer. If you use something else, you won't be able to avoid damage. Finding special oil is not so easy, and it is expensive.
Another important nuance that needs to be indicated here. These are a number of technological nuances in the design of the variator. If a breakdown occurs, special equipment is needed to eliminate it. It's very expensive. Therefore, service stations do not tend to purchase it.
The question is brewing - why know this and what is better, an automatic or a CVT?
If you buy a new car under warranty, then there is no difference. The only difference is that the consumption, acceleration dynamics and elasticity of the ride will be better with a CVT. The situation changes dramatically when choosing a used car.
The resource of a CVT transmission is longer than that of a conventional automatic transmission. So does the cost of repairs. Usually, by 100,000 km, a CVT already requires expensive maintenance (belt replacement), whereas, like a regular automatic, it requires timely careful maintenance (oil change and gentle driving modes).
In conclusion, there is a large video comparing an automatic transmission and a CVT; the video fully describes the principles of operation of a particular transmission and collects all the pros and cons:
Make smart purchases, make smart choices.
Pros and cons of automatic transmission
The automatic transmission is equipped with a hydraulic transformer that ensures the transit of power flow from the engine to the input shaft. To change gear ratios, planetary pairs are used, working together with friction clutches. To switch stages, a hydraulic unit equipped with a pump for supplying working fluid is used. The block contains electromagnetic controlled valves that ensure the distribution of fluid flows depending on driving conditions and engine speed.
The advantages of hydromechanical transmissions include the following:
- Simplicity of the unit design, which provides increased service life. The boxes do not require major repairs for 300-350 thousand kilometers.
- Automatic gear shifting does not require the driver to manipulate the lever. Some modifications support a manual selection algorithm, in which a handle or paddles mounted under the steering wheel are used to increase or decrease speeds.
- No special equipment is required for repairs. A specially configured tool may be required when removing the box from the machine and disassembling the assembly.
- The transmission design uses Dextron fluid, which has a lower cost compared to special oils for CVTs.
- The box is equipped with a control unit that determines the gear shift moments. The total volume of electronic components in the design of an automatic transmission does not exceed 25-30%.
Disadvantages of automatic transmissions:
- When using boxes of outdated designs that have 4 forward gears, there is increased noise from engine operation when driving at speeds of more than 100 km/h. If the car is equipped with a 5- or 6-speed transmission, then the engine speed is reduced, which has a positive effect on the acoustic comfort in the cabin.
- Reduced acceleration dynamics. When using the same engines, the difference between manual and automatic transmissions is 1-2 seconds (when accelerating from 0 to 100 km/h). Due to the use of friction clutches, shifts are accompanied by shocks. In modernized 6-speed units, shocks and vibrations are reduced to a minimum and are observed only at the moment of sharp acceleration.
- Increased fuel consumption due to reduced transmission efficiency. The efficiency of the box is reduced due to the use of hydraulic drives; to ensure the operation of the components, part of the power of the power plant is wasted.
- Increased crankcase capacity. When changing the oil, 8-10 liters of oil are poured into the housing of a standard automatic transmission for a passenger car. For comparison, the crankcase of a manual transmission installed on an engine with an identical displacement holds up to 4 liters of fluid, and a CVT - within 5-8 liters.
Mechanical Differences
The CVT and automatic transmission are the same in that both options are a type of gearbox that is controlled by an electronic device built inside the box. The difference is in the design features.
VKPP in technical documentation is designated as CVT (CVT). This is an abbreviation for the English words: “Continuously Variable Transmission”. In Russian it sounds like this: “constantly changing gears”
The difference between a CVT and an automatic is in the structure of the mechanism. The first difference that generalizes all CVTs is in the principle of operation: the absence of gear steps. Speeds change due to the gear ratio. The latter is controlled by parallel cone pulleys. This is a driven and driven mechanism.
There is also a difference in the fastening of the pulleys. Some pulleys in a vehicle's CVT box are connected to each other by means of metal chains, others by means of belts.
The variator works on the principle of moving pulleys apart and bringing them closer together. These actions lead to a change in the gear ratio. And changing the number accordingly changes the speed of the car.
An example of the operation of a V-belt variator in the form of a table:
| Vehicle speed | Locating the pulley in the variator space | Diameter that the belt goes through |
| Low gear (first speed) | Maximum spread | Small |
| High gear (fourth speed or higher) | Maximum shifted | Big |
Attention! The operating principle of a toroidal variator is to change the roller in relation to the friction disc. These differences will be discussed in the next block.
CVT types
The variator has two types of gearbox:
- V-belt. This variator consists of two pulleys and a belt connecting them. It is so named because the moment the pulleys are connected, the belt becomes V-shaped. The pulleys move by means of a hydraulic drive;
- Toroidal. This type of variator consists of rollers and coaxial disks. When the gear changes, the position of the rollers also changes.
But the difference between a variator and an automatic transmission lies not only in design features. CVT boxes have their positive and negative sides.
Disadvantages and positive qualities of CVT
The positive aspects of the variator are the following features:
- smooth movement of the car, without jerking;
- immediate response to changes in the route landscape: slope, country road;
- there is no slowdown in speed with an instant increase in load, unlike an automatic transmission;
- simple design and light weight;
- saving gasoline.
But no matter how much one lists the positive aspects of a gearbox without gear shifting, a vehicle with a CVT still has disadvantages:
- rapid wear of internal CVT equipment (the belt must be changed every 70,000 km);
- the vehicle is not able to move on hilly terrain due to the unsuitability of the variator for heavy loads. Not installed on SUVs;
- Service centers do not repair the variator due to the shortage of spare parts and the complexity of repairs, but only replace one box with another. The gearbox itself is expensive;
- It takes some time to switch the movement back or forward, which cannot be said about the automatic transmission. Many drivers don't like this.
Attention!
Therefore, when choosing a variator, you need to understand that it is short-lived, unlike an automatic.
Automatic transmission
In addition to the variator or robotic gearbox, an automatic transmission is installed in the car. The difference is in the complexity of the design, but it is more durable. This is the main difference between a CVT and an automatic, which is why many experienced car owners buy a car with an automatic transmission.
Differences between automatic and variator
It is impossible to visually distinguish an automatic from a variator, since there is no difference in the placement of the lever. It can be located either near the steering wheel or at the usual location of the box. The difference can only be felt when driving: with a CVT gearbox, transmission switching occurs very smoothly, almost imperceptibly; you can understand that the speed has been switched only by the sound of the engine. On an automatic, the speed is changed with a slight jerk. On the latest generation automatic transmission, shifting occurs very smoothly, especially if the gearbox is equipped with two clutches, for example, a DSG automatic transmission from Volkswagen.
In addition to the sound of operation and the feeling of switching, CVT automatic transmissions differ in structure. Thus, the basis of the variator is a mechanism that allows you to very smoothly change the speed between the drive and driven disks. This happens through a belt or chain that connects the discs to each other. There are several different types of drives available for CVTs.
A car that has a CVT as a transmission shift box has a much shorter acceleration time, while the acceleration occurs very smoothly and almost imperceptibly. Such gearboxes entered industrial production relatively recently. Also, the design has less weight and is considered very reliable. So that you can clearly see how the variator works, we suggest watching the video:
How to distinguish an automatic transmission from a CVT
As a rule, before purchasing a car with an automatic transmission, the potential owner immediately decides for himself what is better, a regular automatic, a CVT or a robot. If we take into account the fact that the traditional hydromechanical automatic transmission, although not without its shortcomings, remains the most reliable and time-tested transmission among other automatic transmissions, it is not surprising that such a gearbox is in the greatest demand on the secondary market.
Please note that often the initial knowledge of how to distinguish a CVT from an automatic by lever is simply not enough. The main reason is the deliberate replacement of the lever (selector) by the unscrupulous owner himself, tuning the lever using covers for the gearshift knob, reupholstering the selector with leather, etc.
So, in order to correctly determine the type of gearbox visually, you need to follow a certain procedure and take into account a number of recommendations. First of all, you should start with the following:
- Before inspecting the car, you need to collect as much information as possible regarding transmission options for a specific model on the Internet; you can also use technical literature, catalogs, etc.
- When inspecting, carefully study the documents for the car, as well as the marking plates on the body and components. As a rule, if the car is equipped with an automatic transmission, then this will be indicated by the letters A or AT. In the case of a variator, the designation CVT is used.
- When trying to visually identify it, you need to inspect the gearshift lever, since CVTs often have the CVT designation printed on them. You also need to pay attention to the modes near the gear selector. In the case of a conventional automatic, in addition to the standard PRND modes, you can also see modes “L”, “2”, sometimes “3”, while CVTs have only the “L” mode.
Visual identification of CVT and automatic
Novice car enthusiasts have no idea how to visually distinguish a CVT transmission from an automatic transmission. Although there are many differences between them:
Read
How to replace an automatic transmission with a manual transmission in your garage
- CVT transmissions are usually labeled “CVT”;
- gear shift names near the scenes. On CVTs, in addition to standard PRND, there is an “L” mode. Automata have L2, L3;
- It's almost impossible to do this with a lever. In addition, unscrupulous owners replace the variator lever with a lever from an automatic transmission if there are significant differences.
In addition, how to distinguish them externally, the buyer of a car needs to be a driver: drive about five hundred meters in a car. When the car accelerates on an automatic transmission, the sound will be identical to the sound on a manual transmission.
If you put the vehicle on the rise of a hill, then with the CVT gearbox the car will roll back.
Attention! The last method will work when the car does not have a rollback system installed.
Popular models with CVT
Japanese automakers are the most committed to continuously variable transmissions. Only Mazda does not produce models with a CVT. European auto giants are not lagging behind (but on a smaller scale), among which Audi is the leader in the use of CVTs. The American auto industry does not like CVTs - of the popular models, you can about.
CVT Nissan Primera, Honda Civic, Honda HR-V, and almost all Audi models are common on the Russian market. In instructions and brochures, the transmission may be called Multitronic, X-Tronic, Hypertronic or Multimatic - all these are brand names for CVTs. The abbreviation CVT, adopted for technical specifications, is more understandable. It stands for Continuously Variable Transmission.
DSG gearbox - what is it?
DSG (Direct Shift Gearbox - synchronized shift gearbox) is an evolutionary continuation of robotic gearboxes. It is also called preselective transmission - this is the second generation of “robots”.
These boxes are by far the most advanced. They are equipped with two clutch discs at once - one switches even gears, and the second – odd ones. Essentially, these are two gearboxes in one housing.
The highlight of the DSG box is that it has two gears constantly engaged: while driving, only one of the 2 clutch discs is closed, and the second is in constant readiness and engages its gear as soon as the first disc opens. Thanks to this scheme, switching occurs almost instantly, and the smooth operation is comparable to a CVT.
But even such a seemingly ideal gearbox as the DSG has its drawbacks. The design of preselective transmissions is extremely complex. All this leads to the fact that its maintenance cannot be called cheap.
In addition, even large service stations often do not undertake to repair DSG gearboxes. And their repair, in most cases, is simply impossible. Therefore, in the event of a breakdown, it is often necessary to change the entire preselective transmission assembly, and only sometimes can one confine oneself to replacing the electronic control unit.
Also included in the list of disadvantages of DSG gearboxes is overheating of the clutches after a long drive, as a result of which shocks appear over time when shifting.
Taking into account all of the above, we believe that preselective transmissions, despite all their manufacturability, are still quite “crude”, too expensive and cannot be repaired.
Automatic and variator design
The machine contains two main components - a torque converter and a gearbox.
- The torque converter is designed for smooth gear shifting; to put it simply, it replaces the clutch.
- The automatic transmission gearbox is a complete mechanism with several stages, in which all paired gears are in constant mesh.
Stepless variator . The mechanism works without the usual gear shifting.
How it is designed: it has 2 cone pulleys (driven and driven), which are located opposite each other and are connected to each other by a metal trapezoidal belt, or on some models there may be chains.
This is how the pulleys are connected using a belt
How does a variator work?
Cone pulleys are not solid, but consist of sliding parts.
- When the drive pulley is extended as far as possible, the metal belt runs along a small diameter (low gear), which is equivalent to first gear.
- When the pulley is shifted, the belt passes over a larger diameter (high gear), which is equivalent to fifth or higher gear.
This is how a variator works, moving and spreading the pulleys, which leads to a change in the gear ratio and, accordingly, the speed of the car changes.
Watch an interesting video, the device and principle of operation of the variator:
How to determine a variator or automatic
Question from a reader:
“Good afternoon Sergey. Firstly, I would like to say thank you for your site, it is very useful for novice drivers like me. Secondly, I really liked the article where you discussed two automatic transmissions (CVT and automatic). My question is, is it possible to identify these two transmissions purely visually, looking out the car window? Or this is not possible. Thank you in advance. Anna"
A very popular question on my site, so I decided to answer it anyway, read the answer below...
Visually identifying two automatic transmissions is almost impossible. That is, if you look inside the car, the automatic and the variator will have the same set of modes - gears on the panel behind the lever. I mean the letters P, N, D and so on, read the article for more details. There will be one shift lever, there will be no additional levers, so the differences, as you can see, are minimal.
Why is this being done?
Everything is simple - for versatility. If you change from an automatic to a CVT or robot, so that you do not experience any inconvenience in using this or that transmission, everything will be as you are used to doing. If the mode is “P” and “D”, then it will be the same on all transmissions.
So there’s no way to determine it at all?
Visually, you can still find out something. If you read the article about modes, then you understand that there can be many modes on the panel near the lever. However, a CVT may have fewer such modes than an automatic. Usually these are modes “P”, “N”, “D”, “R” and that’s it. But an automatic transmission may also contain modes “L”, “M”, “OD”, etc. However, that’s not all.