The idea of converting your car to alternative gas fuel worries the minds of many car owners. And the reason for this is one goal - savings. But some of them have doubts associated, first of all, with a lack of information. In the article we will try to give a detailed overview of the operation of a gas-powered car, since there is not enough detailed, step-by-step information in open sources or it is presented in fragments. At the same time, we will analyze emerging and existing issues regarding the operation of gas equipment.
Despite existing opinions FOR and AGAINST gas fuel, the number of cars using gas-cylinder equipment is steadily growing. For example, according to Rossiyskaya Gazeta, the number of cars running on compressed natural gas (CNG) - methane, increased 2.2 times between 2021 and 2021. This is confirmed by the fact that new automobile gas filling compressor stations (CNG filling stations) are being opened everywhere. And propane gas stations have become part of the complexes of some large branded fuel gas stations and their number is comparable to gasoline ones.
What cars are equipped with gas cylinder equipment? If converting a vehicle provides the owner with fuel savings, then first of all it is profitable to convert cars participating in a particular business project to gas, and this
- commercial transport
- passenger transport
- special equipment
Secondly, LPG works effectively on passenger vehicles of citizens who have high fuel consumption and serious mileage.
How does HBO actually work?
Today, it is advisable to install 4th generation automotive gas equipment on vehicles with engines with distributed fuel injection. This autogas system has a low cost, is characterized by quick installation, reliability and maintainability. Interacts with the engine control unit via the OBD-2 diagnostic connector, thereby ensuring correct interaction of two fuel supply systems - gas and gasoline. Also, thanks to the ability to exchange data with the ECU, it is possible to fine-tune, debug, update and calibrate 4th generation systems. The fourth generation of automotive gas equipment is the most popular in the automotive gas equipment market.
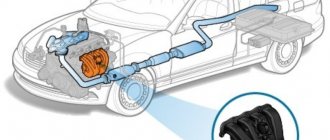
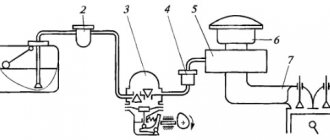
In addition to the electronic unit, the gas cylinder equipment of the car includes a gas cylinder; a multivalve, a filling device, a reducer, and an electromagnetic injector module are installed on it. But it is necessary to recall that LPG can use two types of gas in its work: methane and propane-butane mixture. Due to different physical properties, the technical design of the equipment is also somewhat different.
Gas cylinders
Methane is stored in automobile gas cylinders under high pressure, so methane cylinders are thicker-walled than propane cylinders. Cylinders for propane-butane mixture are toroidal and cylindrical, methane cylinders are only cylindrical. Accordingly, gas lines are designed for significantly higher pressure. Methane reducers come in two and three sections to reduce pressure. And propane reducers, in addition to reducing pressure, are designed to transfer the propane-butane mixture from a liquid state to a gaseous state, which is the working state. Otherwise the designs are identical.
Let's consider the operating cycle of the HBO system from start to finish. When starting the engine, it always starts on gasoline. When the coolant temperature reaches about 65-70 0C, the solenoid valve is activated, which opens the supply of the gas mixture. Let us remind you that the propane-butane mixture is in a cylinder under a pressure of 15-16 atm. in a liquid state. The propane cylinder can be filled to 80% according to established safety standards. We will describe why this is so below. When the solenoid valve opens, gas driven by its own pressure is supplied through the multivalve via lines, bypassing the solenoid valve itself to the evaporator reducer.
Multivalve HBO
Let's focus on the multivalve. The role of this element in the system is enormous. It performs a number of functions
- Fence. Gas enters the main line through the intake pipe
- Test. A float is built into the multivalve mechanism, with the help of which the gas filling of the cylinder is limited and it is possible to control the remaining gas mixture in the cylinder
- Constipated. If the pressure in the cylinder increases, a valve is provided to release excess gas. Also, in the event of a sharp increase in fuel consumption through the multivalve, which may indicate an emergency situation and a break in the line, another valve will shut off the supply. Many multivalves are also provided by the manufacturer with solenoid valves, which “allow” the supply of gas only when power is applied to them. This is also intended to protect the system and the car as a whole in case of emergency situations.
GBO reducer
On approaching the gearbox, the gas fuel is still in the liquid phase. In this state of aggregation, it bypasses the liquid phase purification filter and enters the 4th generation LPG reducer. In the gearbox, due to an increase in the volume of the chamber, the pressure decreases, and the heat supplied to the gearbox from the cooling system promotes the evaporation process. As is known, when a liquid evaporates, heat is absorbed. Therefore, heated coolant also prevents the gearbox from frostbite. At the outlet of the reducer, propane-butane is in a gaseous state and under a pressure of 1-1.4 atm. depending on engine size. The performance of the gearbox can vary depending on the level of vacuum in the intake manifold, thereby regulating the amount of gas supplied to the injectors.
HBO injectors
The essence of the operation of gas injectors is similar to the operation of gasoline injector nozzles. And it comes down to the fact that under the influence of an electromagnetic pulse, the shut-off rod rises and gas enters through hoses and screwed fittings into the engine intake manifold and further into the combustion chamber. This concludes the mechanical-physical part of the process.
Cylinder selection
When choosing a gas cylinder, you can ask for qualified help from gas equipment installation professionals, but do not forget that only you know all the nuances of your car. First you need to think about how often you use the trunk, and how exactly.
Is it loaded to capacity with essentials, or do you only carry a first aid kit, a fire extinguisher and a spare tire? Does your car have a folding rear seat feature to increase interior and trunk space?
The answer to these questions must be obtained so that the chosen type of cylinder does not bring you any inconvenience and allows you to use the car comfortably and the trunk with maximum efficiency.
What to choose
Today, the toroidal type of cylinder is installed on a car much more often than the cylindrical one. The toroidal cylinder is mounted in a place intended for a “spare spare”, which is undoubtedly convenient. But this is not a reason that you need to choose it for your car. Let's take a closer look at each type of gas cylinders.
Cylindrical cylinder
From the name it becomes clear that this cylinder has the shape of a cylinder and can be installed anywhere in the trunk of any car body. In most cases, the cylinder is installed across the car, close to the back of the rear seat.
The size of the trunk and the cylinder determines whether the latter will occupy the entire space between the wheel arches, or whether part of the trunk will remain free. With this mounting option, you most likely will not be able to transport large items by folding the rear seatbacks.
A cylindrical LPG gas cylinder can also be installed along the car, on the right or left side. This installation method provides for free space on one side of the trunk.
With this fastening method, it is possible to transport large items if the back of the rear seats are folded (given that your car has such a function). This method was popular in the absence of toroidal cylinders.
A cylindrical cylinder can also be mounted under the bottom of your car, if the design and ground clearance allow such an arrangement.
If you install a gas cylinder under the bottom of the car, you need to monitor its tightness and the integrity of both the cylinder itself and its fastenings. Because during periods of high environmental humidity (autumn-spring), the cylinder and its fastenings are exposed to the influence of both reagents (salt) and moisture.
A cylindrical cylinder will fit most organically into sedan cars with deep trunks, where, due to the depth of the luggage compartment, it is quite difficult to fully operate it.
Installing a cylindrical cylinder in such luggage racks allows you to most effectively use the luggage compartment without loss of functionality. Also, an undoubted advantage is the fact that after installing the cylindrical cylinder, the spare wheel and other necessary items that are located in the trunk remain in their places.
Toroidal balloon
Toroidal LPG gas cylinder – has the shape of a spare wheel. At the moment, this type of cylinder is the most common, since its installation instead of a “spare wheel” does not make any special changes to the functionality of the luggage compartment of the car. You will have access to the entire luggage space, both with the seats folded down and with the seats in their normal position.
In some cars, the spare wheel is located under the bottom of the car, in which case mounting a toroidal cylinder under the bottom is also acceptable. Due to the design of the toroidal cylinder, its capacity is slightly smaller relative to the cylindrical one. This means that the operating time of the engine on gas when using such a cylinder will be less.
The role of the electronic gas control unit
The entire dynamics of the gas mixture and interaction with the gasoline fuel supply system is controlled by an electronic unit, which is connected to the gasoline control unit. If, with the engine running, the coolant temperature reaches 700C, the electronic device supplies power to the solenoid valve, which opens the gas supply. At the same time, the impulse is intercepted from the gasoline electronic unit to the injectors, and they remain closed. The received electronic pulse is processed in the HBO ECU, adjusted, and, according to the stored fuel maps, a signal is issued to open the injectors for the calculated time, depending on the required volume of gas.
Main components
The gas equipment set consists of the following components:
- evaporator - converts gas into a vapor state, reduces its pressure to atmospheric level
- reducer - reduces pressure, converts gas from liquid to gaseous due to integration with the cooling system. Controlled by vacuum or electromagnet, has screws for adjusting the amount of gas supply
- gas solenoid valve - shuts off the gas supply when the carburetor or injector is operating, as well as when the engine is stopped
- gasoline solenoid valve - allows you to prevent the supply of gas and gasoline at the same time; the emulator on the injector is responsible for this
- switch - installed in the cabin, has a button for forced switching between fuels, as well as a light indicator for the gas level in the tank
- multivalve - an integral unit installed in the cylinder. Includes fuel supply and flow valve, as well as gas level. If there is excess pressure, the multivalve releases gas into the atmosphere
- cylinder - a container, cylindrical or toroidal, can be made of ordinary steel, alloyed, aluminum with a composite winding or composite materials. As a rule, the tank is filled to no more than 80% of its volume to allow gas expansion without a significant increase in pressure.