In a car transmission, the constant velocity joint, better known as the CV joint or grenade joint, is a fairly heavily loaded unit. In short, it is through the CV joint that the torque from the gearbox is transmitted to the wheels of the car. By the way, on front-wheel drive cars or all-wheel drive versions, this joint must be designed so that the force is transmitted to the steered wheels at changing angles.
In general terms, the drive shaft is connected to the transmission or axle through an inner CV joint, while the connection to the wheel hub is through an outer CV joint. Of course, during the operation of the car, these joints tend to wear out and fail. Please note that with regard to CV joints, signs of malfunction (even subtle ones) are a good reason for conducting in-depth diagnostics.
Sounds and symptoms of breakdown
There are several signs of a hinge failure:
- Anther rupture. It is enough to go to a service station, where the faulty element will be replaced, and the need to repair the CV joint itself will disappear.
- The sound of a grenade. The sound is very reminiscent of the friction of brake pads worn down to metal.
- Jerks. When the car starts moving, the driver may feel slight shocks. This behavior indicates broken grenade grooves.
- Clicks. They appear at the moment of movement, and their number varies from 2 to 5. When moving, the unpleasant sound disappears, but the next time you try to move, it appears again. This also indicates a malfunction of the grenade.
- Crunch. If the sound appears directly when moving, then this is an alarming signal. The CV joint is not only worn out, it is about to seize. Driving with such damage is dangerous, so it is best to call a tow truck and send the car to a workshop.
If at least one of the listed symptoms of a malfunction appears, then it is better to send the car for diagnostics. Experienced drivers can inspect the joint themselves and identify the source of the problem.
This is interesting: How to learn how to operate the clutch correctly
The simplest diagnostic methods
The driver needs to determine which CV joint has become unusable. For this, there are several verification algorithms that you can carry out yourself.
Outer
The test must be carried out on a site with a flat surface, but a regular road surface will also work. The wheels of the car must be turned all the way in one direction.
To provide more load to the hinge, you should move sharply. If you hear a familiar sound, the CV joint is faulty.
You can listen on your own by opening a window or inviting an assistant.
The second option is especially relevant if you suspect a malfunction of the right CV joint, since the sound from the distant side reaches the driver worse. By turning the steering wheel to the left, you can test the right CV joint, and turning the steering wheel to the right - the left one.
Interior
Diagnostics of internal hinges occurs differently. Instead of a smooth road, you need to find an area with deep potholes and drive along it. If the CV joint is faulty, then it will definitely make itself felt.
There is a second method, which involves significantly weighting the rear of the car. It is necessary to seat passengers and fill the trunk so that the front of the car rises and the axis of the inner CV joint bends as much as possible. When moving, a faulty part will definitely make a familiar sound.
Checking the serviceability of the CV joint
Malfunctions of the internal and external CV joints manifest themselves in different ways. To check the external hinge, you need to turn the steering wheel as far as possible and slowly drive around the site. With this position of the steering wheel, maximum bending is formed between the axle shafts. In this case, a faulty outer CV joint will produce a crunching sound, depending on the speed of movement.
Diagnostics of the serviceability of the CV joint. Video:
Achieving maximum curvature of the internal joint is more difficult. To do this you need to do the following operations:
- hang the wheels by lifting the car with a jack or lift;
- start the engine;
- turn on the transmission.
In this position, the faulty internal hinge will make a distinct crunching sound.
How to check the CV joint on a VAZ 2109 and 2114, 2110
A standard test and determination “by ear” does not always make it possible to accurately determine the serviceability of the hinges. Before buying expensive parts, you need to find out and make sure that the problem lies precisely in them. To do this, perform the following operations:
- Place the car on the pit and hang the wheels;
- inspect the condition of the anthers;
- check the play between the axle shafts.
On Kalina, the front wheel drive can be checked similarly to the VAZ 2109
How to check the serviceability of the CV joint on a Ford Focus 2
The algorithm for checking Ford hinges is no different from the one given above.
How to check the CV joint on a Renault Logan
The breakdown of parts is indicated by a characteristic crunch (sound) and play of the axle shafts.
CV joint malfunction - diagnostics, how to determine a breakdown by characteristic signs
Hello, dear motorists! Enjoying all the benefits of front-wheel drive on modern cars is more than offset by the problems that some chassis parts can create.
In the case of front- and all-wheel drive vehicles, one of the most problematic areas is the constant velocity joints. Abbreviated as CV joints or, simply, “grenades”.
Studying the specialized literature, you can find statements that all CV joint elements are made of super-strong alloys, the wear of which occurs extremely slowly.
But, as practice shows, signs of a CV joint malfunction can appear even in a car that has recently left the assembly line of a car plant. There may be several reasons for this, but the most common are:
- low quality CV joints, installation of fakes or defective spare parts;
- lack or poor quality of lubricants;
- damage to the boot and the entry of abrasive debris and water into the mechanism;
- aggressive driving style and disgusting condition of the road surface.
How to independently determine a CV joint failure
The malfunction of any part in a car is caused by a change in its properties, dimensions, and the formation of wear in rubbing parts.
A CV joint is a hinge, which means its design necessarily contains elements that work in close contact under constant load. The CV joint is a kind of ball bearing, however, its races have transverse grooves, which allows you to change the angle between the drive and driven axle shafts.
In order to make the car move, the hinge transmits significant force to the wheels, and also constantly changes the angle between the axle shafts. Over time, wear develops on the rubbing parts and the gap increases. Where there is no close contact between parts, extraneous noise appears.
The signs of a CV joint failure are known to all car enthusiasts. The main one is the appearance of a characteristic “crunch”. This sound can only be produced by balls that roll along grooves, because... have too much output.
The sound can appear at any time, but usually it happens when turning, sharp acceleration, or overcoming obstacles. Car enthusiasts need to know about other options for how to check the CV joint.
To finally verify that the hinges are faulty, the following will help:
- slight jerks when starting the car or changing dynamics;
- play of the shaft located between the CV joints when trying to move it in different planes.
Signs of a faulty internal CV joint
As you know, the design provides two grenades for each drive wheel - an external one, which transmits force from the axle shaft to the wheel hub, and an internal one, which rotates the shaft from the gearbox.
Although both CV joints are links of the same chain, the outer one fails much more often and faster. This is due to the fact that the loads and rotation angles of the joint on the hub are much greater.
At the same time, the outer CV joint is smaller in size. The signs of failure described above apply more to the external hinges. In order to convince yourself that the outer CV joint is faulty, you need to turn the steering wheel as much as possible and start driving. When the angle between the axle shafts approaches its maximum, the faulty one begins to “crunch.”
The logical question would be how to check the internal CV joint, because in its natural state it is very difficult to achieve maximum curvature of the hinge. Unlike the external one, the internal one can give sound signals about a malfunction in straight-line movement.
The CV joint especially clearly signals the need for replacement when overcoming holes, ditches, and snowdrifts. A worn joint, of course, will have significant play when checking the shaft by hand, and you can finally verify the need to replace the CV joint if you lift the car on a lift.
Engaging first gear will allow the wheels to rotate in a suspended state when the inner CV joint is significantly bent. This is where that incomparable hinged “crunch” manifests itself. And this means: it’s time to go to the auto store for a repair kit and start replacing it.
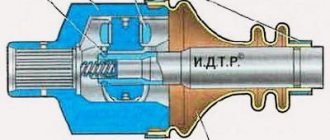
Hinge design
The transition from rear-wheel drive to front-wheel drive required automakers to develop new technical solutions. The transmission of rotation to the steered wheels is associated with large rotation angles. The driveshaft installed on rear-wheel drive cars could not cope with this task due to the limited turning angle and low efficiency. But, after changes were made to the design, it became the prototype of the modern constant velocity joint.
Automotive parts manufacturers produce two types of CV joints. The first is called "rtseppa" (better known as "six-ball"). It consists of two cages (inner and outer), steel balls and a separator separating them. Thanks to precision manufacturing and minimal clearances, the coupling can transmit high torque at high speeds and rotation angles of up to 60°.
The second type of CV joint is a “tripod”. Its design was developed in Japan, where it is used on some cars. Its structure is somewhat more complicated than that of a rzeppa, but it is capable of transmitting rotation at an angle and moving along its axis. The tripod consists of a body in which a three-rayed star with spherical rollers and a fork with profile grooves are fixedly fixed. The disadvantages of this design are the inability to work at angles exceeding 30°, the complexity of manufacturing and, as a consequence, the high price.
Regardless of the design and manufacturing technology, the drive components must be equipped with a boot secured with clamps and a locking ring to secure the part to the shaft. Damage to one of them is a reason to check the CV joint (grenade) on the car. The entry of water, sand or dirt into the internal cavity is unacceptable. Foreign substances will cause intense wear on the working surfaces and damage the drive.
For your information!
The appearance of traces of grease on the outer surfaces of the boot is one of the signs of a faulty CV joint.
The hinge, whether it be a hinge or a tripod, cannot itself transmit rotation to the wheel hub. It is an integral component of a drive consisting of a shaft and two CV joints (internal and external). The first is made of thick-walled pipe with a diameter of 25-35 mm. The internal one is installed on the gearbox, and the external one on the wheel hub. The first one works at rotation angles not exceeding 30°, which allows you to install a tripod there. A CV joint of the CV type is fixed on the outer side.
However, during operation, the drive perceives not only torque loads. While the car is moving, the suspension swings, which leads to a change in the distance between the hinges. To compensate for this, the drive shaft in the inner CV joint can move along splines. In premium cars, a tripod with a rigidly fixed axle shaft is installed in this place. This design is more reliable, but more expensive than a drive assembled on the basis of simple CV joints.
Which inner CV joint is better?
How to check and change fuel pressure regulator VAZ 2110?
Currently, we can talk about two main types of internal joints - Rzepp six-ball CV joints and tripoid constant velocity joints. You can answer the question of which internal CV joint is better by taking a closer look at the characteristics of both.
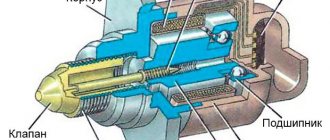
1. CV joint with ball bearings.
Structurally, the part consists of a housing with a driven shaft (trunnion), inside of which there is a holder (knuckle). The inner surface of the body and the outer side of the holder are supplemented with guide grooves along which 6 balls move, held by a separator.
The splined part of the drive shaft is inserted into the central hole of the knuckle. To protect the CV joint from the negative effects of the environment, it is filled with lubricant and covered with a sealed rubber or silicone boot. Ball CV joints are filled with thick lubricants containing molybdenum disulfide.
The small design with six balls is characterized by high reliability and wear resistance. The load is distributed over a large contact area, so the inner CV joint can transmit high-intensity torque without negative consequences for the assembly.
When thinking about which internal CV joint is better, keep in mind that the ball unit is characterized by a significant angle of rotation of the cage, minimal play between the elements, and low vibration loads when starting the car.
The inner ball CV joint with straight grooves is characterized by:
- bending angle reaching 22°;
- maximum axial movement – up to 50 mm.
An external CV joint with radius grooves is characterized by:
- bending angle reaching 54°,
- structural impossibility of axial movement.
2. Tripoid CV joint with needle bearings.
Often, modern cars are equipped with tripoidal internal CV joints.
They consist of a housing, inside of which there is a three-beam fork, pressed onto the splines of the driven shaft. The fork teeth end with three working rollers that move along the grooves of the housing during rotation or axial displacement of the unit.
To protect tripod joints from wear and scuffing, they use special synthetic lubricants that do not contain solid additives.
Needle bearings increase the wear resistance of tripoids and reduce losses from friction of elements in the CV joint.
When choosing which inner CV joint is better, check out the characteristics of tripoid joints:
- bending angle reaching 18°;
- possibility of maximum axial movement of 55 mm;
- vibrations of the internal combustion engine and transmission are compensated by more than 60%.
In addition, for this type of hinges, it is impossible for one-time failure to prevent the vehicle from continuing to move. Fans of off-road driving should take this into account. Even after hearing a loud crunch and feeling vibrations indicating an emergency condition of the joint, the driver will be able to drive to the service station under his own power.
The opinions of experts regarding which internal CV joint is better - tripoid or ball - vary, but the majority is inclined to believe that the tripoid unit is most effective due to such qualities as:
- reliability and durability, impossibility of immediate failure;
- increased longitudinal movement compared to ball movement, resulting in increased load compensation;
- better resistance to loads when turning the inner CV joint at a significant angle;
- greater resistance to torsion;
- increased efficiency achieved due to low losses during axial movement and needle bearings;
- ease of installation, replacement and maintenance, due to the sufficient amount of space at the location of the CV joint;
- possibility of replacement with the same type of hinges;
- Fewer elements, resulting in cheaper production.
Replacement
Replacing a CV joint is not an easy operation. And although it can be carried out by a car enthusiast with certain locksmith skills, before you begin, you need to soberly weigh your capabilities. After all, it is impossible to deliver a car with a dismantled “grenade” to a service station without a tow truck. Therefore, it is best to entrust the replacement of the constant velocity joint to a specialist who, in addition to performing this procedure faster and with better quality, will also provide a guarantee for his work.
- Computer diagnostics of the Priora heater control unit
- How to fix the stove in a Lada Priora car
- How Photon engines are repaired
- What to do if Lada Priora has trouble starting
This is interesting: Why does black smoke come out of the exhaust pipe?
How to replace a CV joint with your own hands
To replace the hinges you will need the following tools, parts and materials:
- new CV joint;
- molybdenum grease;
- new outer joint fastening nut;
- chisel;
- new boot;
- punch;
- hammer;
- set of wrenches;
- puller for ball and steering rods;
- wheel wrench;
- mount;
- jack and support.
Doing the job alone is difficult. So ask a friend to help you.
Photo report on dismantling and installing CV joints on a VAZ 2110-2112
First of all, when the car is still on the ground, you need to pry up the protective cap of the hub nut and remove it. Then, using a powerful lever and a 32mm socket, unscrew the hub nut, but not all the way:
After this, unscrew all the wheel bolts and remove it, after first lifting the front of the car with a jack. After this, we finally unscrew the hub nut and remove the washer.
Then unscrew the two bolts securing the ball joint from the bottom:
After this, you can move the steering knuckle with the stand to the side and remove one end of the CV joint from the hub:
If it is the outer CV joint that needs to be replaced, then you can now use a hammer to knock it off the shaft, but you should do this carefully so as not to damage anything. And the ideal option, of course, is to completely remove the drive. To do this, use a pry bar to pry up the inner CV joint and disconnect it from the gearbox:
As a result, you can completely remove the CV joint from the VAZ 2110 gearbox and remove the drive assembly outward. Then, using a vice and a hammer, we disconnect all the necessary CV joints, both internal and external.
Be sure to pay attention to the condition of the anthers. If they are damaged, they should be replaced with new ones.
The installation takes place in the reverse order and everything is clearly visible on the same video clip that was presented at the beginning of the article. It is also worth mentioning the cost of new spare parts. So, the price of an outer CV joint on a VAZ 2110 can range from 900 to 1,500 rubles. For an internal one you will have to pay from 1200 to 2000 rubles.
In the 80s of the last century, an important stage began in the mass production of passenger cars: the transition from the classic design with a driveshaft and rear axle to front-wheel drive. Front-wheel drive with MacPherson strut suspension has proven itself to be a simple and reliable system with a number of advantages:
- increased handling and cross-country ability due to the weighting of the front part of the car;
- stable directional stability of the machine, especially on slippery surfaces;
- increase in usable interior space due to the compact size of the engine compartment and the absence of a driveshaft;
- reduction in vehicle weight due to the absence of a gearbox and rear-wheel drive elements;
- increasing the safety of the design and increasing the dimensions of the luggage compartment by installing a fuel tank under the rear seat.
However, to transmit rotation to the drive wheels, a number of vulnerable parts and assemblies were introduced into the design. The main, heavily loaded transmission element in front-wheel drive cars is constant velocity joints (CV joints).
Main causes and signs of failures
Experience in operating and repairing cars suggests that problems with the drive can occur even in a new car with low mileage. There are a number of reasons why a CV joint may fail:
- Lack of grease. The latter can be washed out through loose connections between the boot and metal parts or through damaged areas of the protective coating. Lack of lubrication or its complete absence leads to increased wear of the contact surfaces.
- Damage to the boot. Dirt, road dust, and sand can get into the CV joint through cracks and holes. When mixed with lubricant, the smallest particles become an abrasive material that wears out working surfaces.
- Low quality parts. Due to high contact stresses in the assembly, alloy steels with increased hardness are used. If a manufacturer deviates from manufacturing technology using “soft” metal, the parts will quickly exhaust their service life.
- Aggressive driving or towing heavy trailers. The safety margin of the unit is designed by the designers in such a way that its lifespan is sufficient for the average driver. Exceeding operating loads leads to a reduction in the service life of the drive.
- Mechanical impact. If a wheel gets into a deep pothole or a car gets into an accident, damage to the drive elements may occur.
- Natural degradation of the node. In a CV joint that has reached the end of its life, there is an increase in working gaps, which leads to its rapid destruction.
For your information!
Increased vibration, which is a consequence of wear of suspension parts (ball joints, ends, struts), negatively affects the condition of the CV joint, reducing its service life.
At the first sign of a problem with the joints, you need to check the drive trains of a front-wheel drive vehicle. If the defect is not detected in a timely manner, damage to the CV joint may exceed critical values and it may collapse while driving. In the worst case, the car may get into an accident, and in the best, it will have to be delivered to the repair site by tow truck or the faulty part will have to be replaced right on the road. Drivers need to quickly respond to signs of a CV joint failure:
- Crunching (clicking) sounds when cornering.
- Gaps between hinge parts.
- Noise when starting to drive or when accelerating hard.
- Jerks during acceleration.
Elimination of crunches and knocks, restoring the operation of CV joints
How to find out which CV joint is crunching - we figured it out, now about the measures that should be taken to fix the problem, since it is undesirable to operate a car with problematic joints.
One of the disadvantages of CV joints is their non-repairability, that is, if the joint crunches, then it is worn out and requires replacement. The only thing that can be done is to “extend the life” of the node and delay its replacement.
Since the main reason for the appearance of crunches is dust and dirt, when they appear, you should immediately inspect all the anthers for damage. If none are found, we determine which CV joint is crunching using one of the above methods.
After identifying the problematic hinge, we try to extend its service life. To do this you need:
- Remove the drive from the car;
- Disassemble the CV joint;
- Thoroughly wash all components with gasoline, solvent or other means (white spirit, etc.);
- Apply new CV joint grease or equivalents (see above) and assemble the hinge;
- Install a new boot;
- Install the rebuilt drive on the car.
At the initial stage of wear, these measures are enough to get rid of the crunches, but they will eventually return (when the wear intensifies) and then the hinge will have to be replaced.
How to check a "grenade"?
- First way . Turn the steering wheel all the way to the right or left, then shift into gear and try to quickly move away. If during such a jerk you hear a crunch, most likely the “grenade” is gradually failing, or already requires replacement. Listen to which side the crunch is coming from and get ready to replace it.
- Second way . We lift the car on a lift or hang the front wheel (you can hear a crunch on the side with the bark). Next, we perform a visual inspection and also check the backlash. There shouldn't be any play, maybe just minimal.
- Third way . We hang the front end or lift the car on a lift. We turn on first gear or turn on “D”. If the unit is faulty, you will hear a characteristic distinct crunching sound when the wheels rotate.
Replacing a CV joint is not an easy task, and not everyone can do it, so before you replace a CV joint with your own hands, you need to realistically assess your capabilities and knowledge in this area. If there is no time and desire, it is better to entrust the replacement of the “grenade” to professionals. They will do the work quickly and efficiently, and you will most likely be provided with a guarantee for the work done.
Prevention of CV joint failures
Inner CV joint boot
First of all, you need to monitor the condition of the rubber covers of the CV joints. In general, the manufacturer, as a rule, prescribes replacing the hinges themselves if their covers are damaged. But in practice, if the “grenade” has not yet “picked up” sand and water, sometimes it is possible to get by by thoroughly washing it and replacing the lubricant.
The manufacturer, as a rule, prescribes replacing the hinges themselves if their covers are damaged.
You also need to pay attention to how tightly the clamps on the covers are fastened. A properly tightened clamp does not allow the boot to rotate on the hinge body. In general, make it a rule to pay attention to the condition of the covers (they are often called boots) in every suitable case - when you change a wheel, or you can ask them to be examined at a car service center where you went to change the oil. Despite the fact that we examined the operation of the hinge, using the VAZ drive as a sample, the principle of operation of such units is quite similar, even if your car is not equipped with the “usual” CV joint, discussed above, but a tripod, which is often installed as an internal hinge.
Diagnosis of damage
It is not enough to know the signs to determine a malfunction of the internal or external CV joint. Noise can also occur due to other defects in suspension parts. You should identify the symptoms to find out about a CV joint failure. Defects in internal and external hinges are diagnosed differently. What they have in common is working under increased loads and in extreme positions. This is the only way to determine critical wear without removing the hinges from the car.
Checking the internal hinge
To check the internal grenade and determine the faulty CV joint, you need to load these parts. When driving a car, drivers use two diagnostic methods: driving over obstacles and overloading the car. In the first case, they drive along an uneven road with potholes and bumps. To do this, select a section of the canvas so that the obstacles are located on one side. Alternately drive at a speed of 15-20 km/h over uneven surfaces with the right and left wheels. If there are defects, when you hit potholes there will be a characteristic knock in the area where the hinges are attached.
The second method is to overload the car so that the front of the car lifts slightly. In this case, the internal hinges will work at critical angles, which will provoke the appearance of more obvious noise. To make the car heavier, drivers place passengers in the back seat and load heavy objects into the trunk. When the front of the car is slightly raised, drive through a flat section of the road, preferably with an upward slope. Under increased load, the joint should knock more.
For your information!
It's not just the drive that can make noise when the car is moving. To accurately determine the failure of the internal CV joint, you need to diagnose the unit at a service station or service workshop.
Outdoor
Once the signs appear, it will not be difficult to identify a malfunction of the outer CV joint. The driver needs to choose a flat area where he can freely drive in different directions without disturbing anyone. To diagnose, you need to alternately turn the wheels to the right and left, and quickly move away. The joint with the groove will make a crunching noise. Due to the large distance between the parts, it will be easy to determine the side where the defective CV joint is located.
It is better to listen to the sound coming from the transmission with the windows open. You can choose a site next to the wall. In this case, the effect will be amplification of sound waves when they are reflected from an obstacle and reach the driver. You can also ask an assistant to listen to the noise coming from the transmission parts. As a rule, when turning right, the left CV joint will make noise, and vice versa. This is explained by the forces of inertia acting on the car and the redistribution of the load.
Universal joint test
The diagnostic algorithm allows you to more accurately determine which parts are damaged. Sequencing:
- Place the car on a level surface, secure the rear wheels with the hand brake, and place wheel chocks.
- Use a jack to jack up the front right and left wheels one by one. For safety, it is better to install supports under the body.
- Start the engine and engage first gear. At this time, the hanging wheel will begin to rotate.
- To diagnose the internal joint, smoothly press the brake pedal, loading the drive. The appearance of noise near the gearbox indicates wear of the part.
- To check the outer CV joint, turn the steering wheel completely, alternately to the right and to the left. If only the inner joint is faulty, the sound will not change. When the external one wears out, tapping will also be added to the general noise.
How do malfunctions of the internal CV joint manifest themselves?
VAZ 2110 how to check the crankshaft position sensor
The most characteristic symptom of a malfunctioning internal CV joint is the characteristic crunch that accompanies the operation of the hinge. But the “dying” outer CV joint makes exactly the same sound, so sometimes it’s difficult to figure out the “culprit”.
How can you determine whether the inner or outer CV joint is faulty?
When diagnosing, you need to take into account the operating features of the hinges. The outer “grenade” crunches when the car turns or moves away sharply with the wheels turned out - it is at such moments that the outer joint experiences the greatest loads.
Sometimes it happens that wear of the internal CV joint parts leads to vibration felt by the driver when driving on a flat road.
In order to test the internal “grenade” in motion, you need to choose the most uneven road - for example, a dirt road with numerous gullies from puddles. When driving on such a road, the front suspension will be constantly in operation, thereby causing axial and angular displacements of the inner CV joint cage. If the hinge is worn out, it will make exactly the same sounds as the outer one.
But sometimes it happens that wear of the internal CV joint parts leads to vibration felt by the driver when driving on a flat road. Diagnosing the operation of the drive in this case is much more difficult. Sometimes even hanging the car on a lift does not allow us to reliably determine the malfunction - after all, the load on the CV joints during “idle” rotation is minimal.
Often in such cases, the experience of the technician inspecting the car comes to the rescue. A good specialist with solid experience is able to detect the slightest play or jamming in the operation of the mechanism. The most meticulous craftsmen will not be too lazy to disassemble the suspension and remove the entire drive in order to uncover the CV joint, thoroughly rinse and blow it with compressed air and see for themselves whether the parts are damaged or not.
But a strong backlash - such that even a “grenade” standing still “clangs” when it is shaken - can be seen by an inexperienced driver.
On almost all German cars (VW, Audi, Skoda), the inner CV joint is attached to the gearbox with bolts, loosening or breaking of which can also cause vibration.