What oil to pour into a Cummins engine, what you need to know about oil tolerances...
Oil technologies are constantly evolving due to increased engine manufacturer requirements (e.g., rising combustion temperatures) or regulatory restrictions (e.g., emissions). There are a number of international organizations developing standards for oils. This includes:
- American Petroleum Institute (API)
- European Automotive Manufacturers Association (ACEA)
- Japan Automobile Manufacturers Association (JAMA)
Such standards are not enough to select oil for a Cummins engine. Oil should be selected according to Cummins standards (CES). Table 1 below compares each of these standards ( only ).
The API requires a series of laboratory and field tests that each grade of commercially available oil must successfully pass to ensure compliance with modern requirements. API classes determine the composition of such tests and the properties of oils for each production technology. Examples are given below.
- The CI-4 category was introduced in 2002 and updated in 2004 to accommodate the advent of exhaust gas recirculation technology to improve soot control and shear rate stability.
- Category CJ-4 was introduced in 2007 to address emissions regulations and the availability of ultra-low soot diesel fuel for reliable aftertreatment performance, limiting wear, piston deposits and soot emissions, and high resistance to overheating.
- The CK-4 category was introduced in December 2021 with all typical viscosity grades as the CJ-4 category. The current practice of increasing engine temperatures and reducing emissions requires improving oil quality. The SK-4 category has increased oxidation resistance, shear rate stability and limited aeration. Oils of this category can be used instead of oils of the CJ-4 category, but not vice versa.
- The FA-4 category was introduced in December 2021 primarily for the 10W-30 viscosity grade. These oils also have increased oxidation stability, shear rate stability and limited aeration, like the CK-4 category. FA-4 oils also reduce greenhouse gas emissions (while reducing fuel consumption) by reducing viscosity at high temperature or shear rate (HTHS ). As a result, the oil film between metal surfaces becomes thinner. Oils of category FA-4 cannot be used instead of oils of earlier categories. Use only in accordance with the oil selection instructions in Section V of the owner's manual or the appropriate engine owner's manual for CES 20087 oils.
Other international organizations, such as ACEA and JAMA, may require additional or different testing.
| Table 1. Comparison of the requirements of CES standards and other standards | ||
| CES | Closest API class | Closest class according to international standards |
| Not allowed for use | CG-4 | ACEA E1 |
| CES 14615 | — | — |
| CES 20074 | — | — |
| CES 20075 | CF-4 | ACEA E2, ACEA E3 |
| CES 20071 CES 20076 CES 20077 | CH-4 | ACEA E5, JAMA DH-1 |
| CES 20078 CES 20088 | CI-4 | ACEA E7 |
| CES 20081 | CJ-4 | ACEA E9, JAMA DH-2 |
| CES 20085 | — | — |
| CES 20086 | CK-4 | — |
| CES 20087 | FA-4 | — |
When selecting oil for a Cummins engine, should be taken into account, such as the use of aftertreatment or exhaust gas recirculation systems, as well as fuel quality.
For the same Cummins engine, a number of oil classes may be permitted, but subject to a reduction in the time required to replace it. Engines with exhaust gas treatment systems require oils with lower sulfated ash content.
The quality of the fuel at the operating site plays an important role in the selection of oil. Where fuel sulfur content is above 15 ppm and no exhaust gas treatment is used, do not use CES 20081, CES 20086, CES 20087 oils as their original total base number (TBN) is typically lower, which may require shorter oil change intervals .
It is recommended to use CES 20078 oils for these fuels. NOTE: CES 20086 oils are recommended for use in place of CES 20081 oils. CES 20086 oils can be used with extra low sulfur fuels.
| Recommendations for applying CES standards for oils based on Cummins engine configurations | |||
| CES | Without exhaust gas recirculation system Without exhaust gas treatment system | With exhaust gas recirculation system Without exhaust gas treatment system | With exhaust gas purification system |
| CES20075 | Is not allowed | Is not allowed | Is not allowed |
| CES 20071 CES 20076 CES 20077 | Allowed | Shortened term oil changes | Is not allowed |
| CES 20078 | Recommended | Recommended | Allowed for some engines |
| CES20081 | Allowed | Allowed | Allowed |
| CES 20086 | Recommended | Recommended | Recommended |
| CES 20087 | Is not allowed | Is not allowed | Allowed for some engines |
| CES 20088 | Allowed for some engines | Allowed for some engines | Allowed for some engines |
A list of CES compliant oils can be obtained from your local Cummins distributor.
Break-in oils
Special break-in oils not recommended for use in any Cummins engines. They do not meet Cummins durability requirements and may reduce engine life.
Additives from other manufacturers
Cummins does not endorse or deny the use of additives from other manufacturers. Engine failures or performance problems due to their use are not covered under the Cummins warranty.
Oil viscosity
Selecting an oil with the correct viscosity is critical to optimal engine performance and maximum engine life. If the oil is too viscous, the internal resistance of the engine increases with the following consequences:
- Difficulty starting
- Power reduction
- Poor cooling
- Accelerated wear
- Overheating of parts
- Increased fuel consumption
Consequences of low oil viscosity:
- Increased wear due to metal-to-metal contact
- Increased oil consumption and leaks
- Increased engine noise
The viscosity grade of the oil (for example, SAE 15W-40) on the container with it is indicated for information only This designation, in and of itself, does not imply that the product meets Cummins requirements.
Some suppliers of low viscosity oils may claim significant reductions in fuel consumption when using them. Check that the oil viscosity grade complies with the engine documentation and CES standards. Otherwise, obtain from the supplier his willingness to accept warranty obligations or do not use the product.
For general recommendations on the dependence of oil viscosity class on outside temperature, see the figure below
Not oil viscosity grades are approved for use in all Cummins engines. Refer to the documentation for the specific engine, which indicates the permitted viscosity grades and provides recommendations for operating at low temperatures.
Engine oil change period
Oil quality deteriorates in all engines at varying rates, regardless of their design. There are limits to how much deterioration can be tolerated without affecting the oil's function. Cummins oil change requirements depend on the type of duty cycle and the degree of oil degradation.
Factors influencing the deterioration of oil quality:
- Duty cycle
- Fuel type Sulfur content in the fuel: the higher it is, the faster the oil ages, requiring shorter replacement periods. For example, if it is above 500 ppm, the oil needs to be changed more often.
- Biofuel: the higher the content, the higher the corrosion rate in engines with certain exhaust gas treatment systems.
Refer to the engine documentation for acceptable methods for determining oil change intervals.
They include the following:
- By mileage or operating time
- Condition: As fuel consumption increases, the rate of deterioration of the oil properties increases.
NOTE: The use of synthetic oils does not affect stated oil change intervals unless otherwise stated in the engine owner's manual or engine operation and maintenance manual. NOTE: Fleetguard oil filters must when changing the oil.
Specifications
This car is equipped with a Cummins diesel engine. This is a Chinese ISF series power unit that meets Euro-3 environmental requirements. Note that the technical characteristics of the GAZ-33104 Valdai car may differ, since the installed power units have different volumes. The base engine is 2.8 liters. This four-cylinder inline unit produces 136 horsepower. In addition, the GAZ Valdai truck is equipped with a 3.8-liter Cummins. Its maximum power is 152 horsepower.
As for fuel consumption, this parameter depends on the height of the cargo box and operating conditions (city or highway). On average, a car consumes about 12-15 liters of diesel per 100 kilometers. The most economical mode is highway (the speed should be 70 kilometers per hour). The service life of Cummins engines is 500 thousand kilometers. Moreover, the engine warranty lasts two years or 100 thousand kilometers.
Among the disadvantages of Chinese engines, it is necessary to note the rupture of the rubber couplings that are installed between the turbine and the intercooler. Also on these engines the speedometer and tachometer are lying. As practice has shown, the readings are underestimated by about a third.
Engine
GAZ-562 Steyr diesel engines were tested as a power unit for the Valdai car; three types of Iveco engines; We first chose the Minsk D-245.7 as the base one (from 2006 to 2010). Since the beginning of 2011, all Valdai trucks have been equipped with a Chinese-assembled Cummins ISF-3.8s3154 engine.
This is an in-line, 4-cylinder, 4-stroke, liquid-cooled diesel engine with a turbocharging system and charge air cooler, with direct fuel injection. The working volume of this engine is 3.76 liters. Rated power is 111 kW, or 152 hp. (at 2600 rpm).
- The operating order of the cylinders is: 1-3-4-2.
- The direction of rotation of the crankshaft is right.
- The cylinder diameter is 102 mm, the piston stroke is 115 mm.
- Compression ratio: 17.2.
- Maximum net torque: 491 Nm (50.1 kgf-m), at a crankshaft speed of 1200-1900 min.
- Minimum stable idle speed: 800 min -1.
- Maximum idle speed limited by the regulator: no more than 2950 min -1.
The Cummins engine ventilation system is open. The engine uses a radial, 3-piston injection pump (high pressure fuel pump), with an electromagnetic pressure regulator, and a mechanical booster pump. Fuel supply equipment for the Common Rail system, manufactured by CR/CP 3S3L110-30-789S, was installed.
A mechanical fuel priming pump operates as part of the injection pump and a manual one operates in the housing of the coarse fuel filter. The high pressure fuel accumulator is cylindrical, with a pressure limiting drain valve. Bosch-0445 injectors are installed, equipped with an electromagnetic control valve.
Fuel filters:
- pre-cleaner, with a manual fuel priming pump and a water separator, with a replaceable filter element, a sensor for the presence of water in the fuel and an electric
- fuel heater; fine cleaning - with a replaceable filter element.
A combined lubrication system is used: under pressure and splashing. Oil radiator – full-flow, constantly on. The oil filter is full-flow, with a replaceable filter element. The Cummins engine uses a closed-type liquid cooling system, with forced circulation of coolant, and an expansion tank.
The turbocharging system is gas turbine, with one turbo compressor of the “HE-211W” type, with a radial centripetal turbine, with a centrifugal compressor and a tubular-plate type charge air cooler.
Fuel consumption
The Cummins ISF-3.8s3154 engine meets the requirements of the Euro-4 environmental standard. Its operating life declared by the manufacturer is 500 thousand kilometers. The maximum speed it can provide is, according to the factory, 105 km/h. Average fuel consumption is from 12 to 15 liters per 100 kilometers.
Transmission
The gearbox on the Valdai is mechanical, with five steps. It has not changed since the development of the truck. So, among the problems, the owners note increased noise of its operation and leaking seals. According to regulations, an oil change should be done every 75 thousand kilometers. But it should be noted that the box itself holds the load well. There are frequent cases when Valdai was operated with overload. The transmission and clutch can withstand these loads.
Chassis
The Valdai is equipped with a simple GAZ suspension. So, there is a pivot beam in front, and a continuous bridge at the rear. Semi-elliptical springs are used as elastic elements. There are additional springs at the rear. The suspension itself is simple and very reliable. There are no serious problems with it.
But the braking system has its own nuances. The fact is that it is pneumatic. After turning on the engine, you need to wait until air is pumped into the circuits. The brakes themselves work well. Additionally, they are equipped with ABS, which has a positive effect on safety. Steering – gearbox with hydraulic booster. Unfortunately, the power steering is not reliable and leaks over time. You have to periodically add fluid or fix the leak. As for the tie rods and rods, these elements are quite durable. The resource of the elements is about 100 thousand kilometers. But the stabilizer bar bushings have to be changed every 30 thousand. In order to somehow increase the service life, owners install stiffer polyurethane bushings on the stabilizer.
How does this car behave on the move? As reviews note, the suspension characteristics on the Valdai are the same as on the old Soviet GAZ-53. The car is tough on potholes, especially when empty. Any smooth ride can be achieved only after there is at least a ton of cargo in the back. You need to take turns in this car carefully - the center of gravity is very high. And on a straight road you won’t be able to accelerate much, as the reviews say. Neither fuel consumption nor steering characteristics contribute to this.
Brake system
The Valdai uses a dual-circuit braking system with a pneumatic drive. Disc brakes, all-round, with ABS and pad wear sensors. The service life of the pads is solid: it is 200 thousand kilometers. Spare brake system - each circuit of the service brake system. Parking brake system - with a pneumatic drive of the brake chambers, with spring energy accumulators installed on the disc brakes of the rear wheels.
Steering system and other auxiliary systems
Valdai is equipped with various auxiliary systems; they make driving extremely simple and convenient:
- power steering;
- ABS;
- Cruise control;
- ANVIS engine mount.
The type of steering mechanism “GAZ-33104” is a screw-ball nut, gear ratio is 19.8 (in the middle position). A hydraulic integral power steering is used, built into the steering mechanism. Power steering pump ( – vane, double acting.
It is especially worth mentioning the presence of devices that allow the engine to start even in severe frost: the internal manifold is equipped with a special spiral that increases the air temperature.
If necessary, it is possible to connect additional elements operating from a 220 (V) network. This allows you to warm up the unit extremely quickly, literally in a few minutes. The temperature of the coolant in the engine cooling jacket increases. The oil in the oil pan is also heated.
Additional systems
The machine was equipped with several auxiliary mechanisms that simplified work and increased comfort and safety. These included: power steering, ABS, cruise control and ANVIS engine mount.
The transport was adapted to the harsh Russian winter, equipped with a pre-heater and a gearbox from a GAZ-53. Heating was carried out due to a spiral located in the internal manifold, which heated the air. The owner also had the opportunity to connect additional heating devices to a 220-volt network. It took no more than 2-3 minutes to heat up the power unit. In addition, such a system provided heating of the oil in the oil pan.
Diesel engines of trucks and tractors. Spare parts, adjustments and repairs.
________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
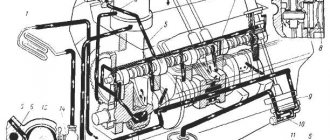
Cummins 3.8 engine lubrication system
The Cummins ISF 3.8 engine lubrication system includes the following components: Oil pump The Cummins ISF 3.8 Valdai diesel engine uses a gerotor type pump.
The oil pump, located in the front timing gear cover, is driven directly by the crankshaft. Oil Cooler The diesel engine uses a full flow plate oil cooler.
The oil cooler is located in the front timing gear cover. The oil passes through the fins of the oil cooler, where it is cooled by the engine coolant circulating behind the fins. Oil Filter A full-flow oil filter is used to filter engine oil.
The oil filter is located on the intake manifold side at the front of the Cummins Valdai engine. It is recommended to fill the filter with oil before installing it when replacing it to avoid the delay in building oil pressure that may occur when starting the engine. Oil pressure regulator The oil pressure regulator is used to prevent oil pressure from being too high.
The oil pressure regulator is located in the front timing gear cover, on the engine exhaust manifold side. The oil pressure regulator consists of a cap, a spring and a plunger. Oil Bypass Valve The oil bypass valve is mounted in the front timing gear cover, behind the oil cooler.
The bypass valve opens when the pressure drop across the oil filter becomes too great. As a result, unfiltered oil continues to flow into the engine lubrication system. Crankcase sump for Cummins ISF 3.8 diesel engine. The oil intake pipe is built into the crankcase sump. Engine Oil Heater pans of some engine models allow for the installation of additional heaters to facilitate engine operation at low temperatures. Suspended type oil pan The suspended type oil pan uses a reusable rubber gasket and a support ring at the point of its attachment to the cylinder block of the Cummins ISF 3.8 Valdai diesel engine. Oil pick-up tube -up tube is made of molded plastic and friction welded to the oil pan.
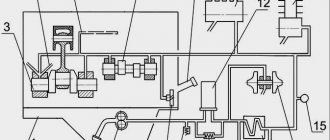
The part of the tube immersed in oil is perforated to prevent large foreign particles from entering the lubrication system. The oil pick-up tube is sealed to the front timing gear cover when the oil pan is installed. Oil pressure sensor A sensor is used to monitor oil pressure. If the oil pressure drops below the set level, the ECM registers a malfunction and a warning lamp lights up on the instrument panel, notifying the driver of engine abnormalities. The oil pressure sensor is located on the rear of the front timing gear cover, directly above the oil filter head. Diagram of the operation of the lubrication system of the Cummins Valdai ISF 3.8 diesel engine Oil pump The Cummins ISF 3.8 engine uses a gerotor type oil pump.
Oil enters the lubrication system through an intake tube, through which it enters a gerotor-type oil pump. After the pump, oil under pressure is supplied to the pressure control valve installed in the oil cooler cover. Pressure Regulating Valve The pressure regulating valve is designed to keep the lubricating oil pressure within 320 kPa.
If the oil pressure after the pump becomes more than 320 kPa, the valve opens, allowing oil to flow into the unloading channel, through which it returns to the oil pan. Taking into account technological tolerances for the manufacture of parts and oil pipelines, the lubricating oil pressure in different engines can vary up to 69 kPa. Bypass valve Next, the oil flow, having passed through the oil cooler, enters the bypass valve, which opens if the pressure drop across the filter exceeds 345 kPa.
The valve opening pressure can vary within ± 34 kPa. Cummins Valdai diesel oil filter After the oil cooler, the oil passes through a full-flow oil filter.
The oil that has passed through the full-flow filter is sent to the main oil line of the cylinder block and the turbocharger. Turbocharger lubrication The Cummins ISF 3.8 diesel turbocharger is the first unit that receives filtered, cooled oil, passing under pressure through a pipeline from the front timing gear cover. A drain pipe connected to the bottom of the turbocharger housing returns oil to the oil pan through a channel in the cylinder block. Load Lubricant Main Oil Line In addition, lubricating oil from the oil filter enters the main oil line through a passage at the front of the cylinder block, behind the front timing gear cover. In addition, pressurized oil from the main oil line is supplied to lubricate the main bearings, valve train and auxiliary drives. In addition, oil under pressure from the main oil line is supplied to other components and parts of the power transmission (connecting rods, pistons and camshaft). Oil from the main oil line is supplied to the main bearings, crankshaft, piston cooling nozzles and idler gear of the Cummins Valdai 3.8 engine. The crankshaft then supplies oil to the connecting rods. The valve mechanism is lubricated through separate channels drilled into the cylinder block. Oil passes through the holes and slot in the cylinder head gasket. Valve Mechanism Lubrication The channels drilled into the cylinder block continue into the cylinder head, leading to holes in the rocker arms and camshaft journals. Through a channel in the support, oil flows to the rocker axis, its roller and the crosshead pad. Through a channel in the cylinder block, oil is supplied to the vacuum pump drive, as well as to the camshaft chain tensioner. Lubrication of the rear timing gears The rear timing gears and the camshaft chain drive are lubricated by a stream of oil coming from a hole in the cylinder head.
The oil is then drained back into the oil pan through the flywheel housing.
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
- Injection pump D-245 - design and adjustments
- Timing belt and valves D-245
- Engine lubrication system D-245
- Fuel system parts D-245
- Operations for adjusting YaMZ-236
- Operations for disassembling and installing fuel injection pump YaMZ-236
- Cooling system and lubrication system YaMZ-238
- Fuel injection pump YaMZ-238
- Characteristics of Cummins ISBe, ISLe, ISB, QSB
___________________________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________
- Repair and replacement of Cummins ISBe, ISLe, ISB crankshaft
- Cummins ISBe, ISLe, QSB cylinder block repair
- Connecting rod and piston group Cummins ISBe, ISLe, ISB
- Diesel cooling system ISF 2.8
- ISF 2.8 diesel cylinder block and pistons
- Cummins ISF 3.8 Fuel System Components
- Cummins 3.8 engine lubrication system
- Cummins ISF 3.8 Cooling System
- Cylinder head YaMZ-7511
- YaMZ-7511 cylinder block
- Diesel crankshaft YaMZ-7511