Purpose of the synchronizer
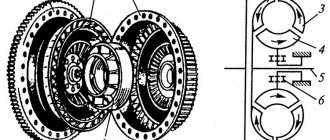
General view of the synchronizer All gears of modern passenger car gearboxes, including reverse gear, are equipped with a synchronizer.
Its purpose is as follows: to ensure equalization of the rotation speed of the shaft and gear, which is a prerequisite for shock-free gear shifting. The synchronizer not only ensures smooth gear shifting, but also helps reduce noise levels. Thanks to the element, the degree of physical wear of the mechanical parts of the box is reduced, which, in turn, affects the service life of the entire gearbox.
In addition, the synchronizer simplified the principle of gear shifting, making it more convenient for the driver. Before the advent of this mechanism, gear shifting occurred by double squeezing the clutch and shifting the gearbox to neutral.
How does the gearbox synchronizer work?
Synchronizers are installed in passenger cars on all gearboxes, even reverse gears. They work according to a certain principle: equalizing speed using friction . If the difference between the rotational speed of the shaft and gears is large, then the friction force between them must reach a slightly higher level in order to synchronize their action. This phenomenon is expected when shifting to the highest gears.
The required condition is met when the contact area of the surfaces increases, and for this purpose additional friction rings are installed.
The main element of the synchronizer is the hub, which has external and internal splines. Internal splines are used to connect to the secondary shaft, and it is possible to move the shaft axially in different directions. The lower splines, in turn, are connected to the engagement clutch, which should provide a rigid connection between the shaft and gears of the gearbox. On the outside, the clutch is connected to the fork to change gear.
The gearbox synchronizer also includes a locking ring. It is needed in order to ensure good synchronization and so that the clutch does not close at the moment when the speeds are equalized. Inside the ring there is a conical surface, it is intended to exchange action with the friction cone of existing gears. But in order to create conditions for blocking the engagement clutch, splines are installed on the outside of this locking ring.
Operating principle of the gearbox synchronizer
Scheme of operation of the synchronizer When the clutch is turned off, it occupies the middle position, and the gears rotate freely on the shaft. In this case, no torque transmission occurs. In the process of selecting a gear, the fork moves the clutch towards the gear, and the clutch, in turn, moves the locking ring. The ring is pressed against the gear cone and rotates, making further advancement of the clutch impossible.
The principle of operation of the gearbox synchronizer - what happens under the hood?
The operating principle of the gearbox synchronizer is complex, but despite this, all actions occur in just a split second. If the gearshift lever is in the neutral position, then the clutches are in the middle, and the gears rotate freely without transmitting power flow. When we increase the speed and shift the gearbox, then the lever moves the clutch to a position in the direction of the gear. What happens in the system?
When we turn on the desired gear (speed) in our car, in a split second the system manages to do approximately the following. The nuts on the coupling (small gates) move, which act on the locking ring, and it converges with the gear cone. Because of this, a frictional force is activated, which in turn turns the ring until it stops. After this, the speed of the shaft and gear is synchronized. The engine adjusts to new speeds, and we can increase the speed without much effort.
Operating principle and design of a three-shaft manual transmission
The fundamental principle of the operation of a manual transmission is the gear interaction of gears, which are enveloped in transmission fluid located in the gearbox housing.
This manual transmission includes:
- driving and driven shafts;
- intermediate and additional shafts;
- frame;
- synchronizers;
- gear sets;
- gear switching mechanism with locks and locking mechanisms;
- gear shift lever.
Bearings located in the housing ensure rotation of the shafts. Each shaft has a set of gears with a different number of teeth.
The drive shaft is connected to the engine via a clutch basket, the driven shaft is connected to the cardan shaft, and the intermediate shaft transmits torque to the secondary shaft.
There is a drive gear on the input shaft, which spins the intermediate gear with a firmly fixed set of gears located on it. The driven shaft has its own set of gears moving along splines.
Between the gears of the secondary shaft there are synchronizer clutches, which equalize the angular speeds of the gears with the revolutions of the shaft itself. The synchronizers are firmly attached to the shafts and move longitudinally along splines. On modern manual transmissions, such clutches are located at each stage.
Principle of operation
The work happens in a fraction of seconds, but the process is really difficult to describe in a few words.
Neutral gear - the clutches are not engaged and the gears rotate freely.
Engaging the gear - we move the lever to the “speed” we need, accordingly it “drives” the clutch through the fork and the “slot” to the desired position. The crackers begin to move, which then act on the locking rings, which in turn goes to the gear cone. As you can imagine, friction begins between the cones, which turns the ring until it almost stops. After this, the gear is put on the shaft, that is, synchronization occurs.
The engine adjusts to new speeds, and we get either acceleration or traction.
It may be a little confusing, then watch this video.
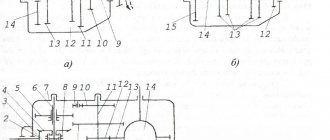
Synchronizer design
The synchronizer consists of the following elements:
- hub with breadcrumbs;
- engagement clutch;
- locking rings;
- gear with friction cone.
Synchronizer device
The basis of the unit is a hub having internal and external splines. With the help of the former, it is connected to the gearbox shaft, moving along it in different directions. Using external splines, the hub is connected to the coupling.
GEARBOX SYNCHRONIZER IN ACTION
When the gearbox selector is in the neutral position, each synchronizer clutch is located in the middle position. With this arrangement, power transmission through them is completely eliminated. In this case, the gears located on the driven shaft do not have any obstacles to rotation.
As soon as we change gear, the clutch immediately moves with the help of the gearbox fork to a position similar to that occupied by the gears, following them. The shift of the clutch is accompanied by a change in the position of the cotters, which affects the locking ring, which as a result lies close to the gear cone. Due to the friction force created at this time between the surfaces, the ring rotates until the crackers are aligned with the grooves. The stopping of the ring during this period of time occurs precisely because of turning.
This is exactly how, in its final position, this unit works according to its purpose - it does not allow subsequent movement of the engagement clutch along the path of the shaft axis. This happens because all the ends of the splines, located along the entire perimeter of the ring, without exception, stand opposite the same parts of the clutch mechanism.
cross-sectional diagram of a synchronizer
Subsequently, the speeds of the driven shaft and gears are synchronized using the friction force generated by the interaction of the surfaces. Next, when the gear alignment process is completed, the locking ring begins to rotate in the opposite direction.
Thus, the clutch, which was previously blocked and limited in its trajectory, begins to function, and its splines engage with the ring gear, having free play. Next, the gears are connected to the gearbox output shaft.
The entire process described may seem complicated not only to a novice car enthusiast, but even to an experienced mechanic who is well versed in the structure of the transmission. However, despite the versatility of the synchronizer, the switching process in practice occurs almost at lightning speed and takes no more than a few fractions of a second.
Synchronized gearboxes, what does this mean?
Nowadays, virtually all mechanical and robotic boxes are synchronized. To turn on the speed in boxes of this type, a necessary condition is to equalize the rotation speed of the gear and shaft. Synchronization is provided by a device called a synchronizer. In addition to smooth gear shifting, it can reduce noise when changing gears, reduce wear on the mechanical connection and thereby increase the service life of the gearbox. All transmission gears of a passenger vehicle, including reverse gear, are equipped with synchronizers.
Why do you need a synchronizer?
All gearboxes of modern cars are equipped with a synchronizer. This also applies to reverse gears. The main purpose of the synchronizer is to ensure equalization of the rotation speed of the shaft and gear. This is a prerequisite for the gears to be engaged without emphasis. Thanks to the synchronizer, smooth gear shifting is ensured. In addition, it allows you to reduce the noise of the device. This element reduces the degree of wear on the mechanical elements of the gearbox, which has a positive effect on the overall service life of the gearbox. It is also worth noting that the synchronizer has significantly simplified the principle of gear shifting. For the driver, this process has become as convenient as possible, because before it he had to switch by double squeezing the clutch and shifting the gearbox to neutral.
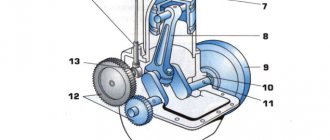
Manual transmission device
A manual transmission consists of a clutch basket and the gearbox itself.
The power unit includes:
- crankcase (housing);
- primary, secondary and intermediate shafts;
- stage selection device;
- driven and driving sets of gears;
- synchronizers;
- bearings, couplings and seals.
All these components are located in the housing and interacting with each other transmit torque.
Clutch
The clutch is an integral component of a manual transmission, which disconnects the engine and gearbox at the moment of gear shifting without consequences for the units. To exaggerate, the clutch turns off the torque, while both the engine and the wheels of the car spin at idle.
The clutch is designed to neatly connect the motor and wheels. It consists of two disks, one of which is connected to the car’s motor, the second to the wheels of the vehicle. The transmission of torque is carried out through the input shaft of the transmission.
How does it work and what does it consist of?
The design of the synchronizer provides for the presence of such elements as a hub with nuts, locking rings, gears with a friction cone and an engagement clutch. The hub acts as the basis of the unit and consists of internal and external splines. With their help, it is connected to the shaft and to the coupling itself. The grooves in it are located at a certain angle (120 degrees). They already contain spring-loaded crackers that fix the clutch in the neutral position. The coupling itself provides a rigid connection between the shaft and gear.
When the clutch is disengaged and in the middle position, the gears begin to rotate freely on the shaft. In this case, there is no transmission of torque. When selecting a gear, the fork moves the clutch toward the gear. The clutch moves the locking ring, which is pressed against the cone and rotates. Synchronization occurs under the influence of gear and shaft speeds. When the clutch begins to move and connect the gear and shaft, torque transmission begins. Accordingly, the car begins its movement at a given speed.
The operating principle of the gearbox synchronizer will be described in more detail in this video:
Published: November 20, 2021
Synchronizer resource
In case of any malfunctions related to gear shifting, it is first necessary to rule out problems with the clutch and only then check the synchronizer.
You can independently identify a unit malfunction using the following signs:
- Noise when the gearbox is running. This may indicate that the locking ring is bent or that the cone is worn out.
- Spontaneous gear shutdown. This problem can be associated with the clutch, or with the fact that the gear has outlived its service life.
- Difficulty engaging the gear. This directly indicates that the synchronizer has become unusable.
Repairing a synchronizer is a very labor-intensive process. It is better to simply replace the worn mechanism with a new one.
Compliance with the following rules will help extend the service life of the synchronizer and gearbox as a whole:
- Avoid aggressive driving style and sudden starts.
- Select the correct speed and gear.
- Carry out gearbox maintenance in a timely manner.
- Timely change the oil intended specifically for this type of gearbox.
- Fully depress the clutch before changing gears.
Manual transmission synchronizer operation
If you decide to install this device in your car, you should find out how this product works. The operating principle of the gearbox synchronizer is as follows: when the switch is fixed in the “neutral” position, the device clutches are in the middle position. At the same time, the transmission of power through them is completely excluded, and the gears located on the main shaft do not create obstacles to rotational movements.
The principle of operation of the synchronizer
If the driver decides to change the speed, the clutch instantly moves and takes a position identical to that occupied by the gears. This is accompanied by a change in the location of the cracks, which influence the synchronizer blocking ring. As a result, the ring fits close to the gear cone. The frictional force created when the surfaces come into contact leads to the fact that the ring inside the synchronizer begins to rotate until the very moment the crackers come into contact with the grooves.
Signs of breakdown/wear of the synchronizer or its individual parts
Transmission problems often look the same, although they have different causes. Please note that if the owner is not familiar with the structure of individual components of the car, unscrupulous craftsmen can take advantage of this. For example, instead of repairing or replacing the gearbox synchronizer, they may offer to replace or overhaul the entire gearbox.
To avoid unreasonable expenses, it is worth knowing what signs indicate possible malfunctions of the gearbox synchronizers. Synchronizer problems may be indicated by:
- noise when changing gears;
- you have to make a lot of effort to engage the gear;
- the transmission does not engage or does not engage clearly;
- spontaneous transmission shutdown; We also recommend reading the article about how a manual transmission works and works. From this article you will learn about the main elements that make up a manual transmission, as well as the principle by which this type of box operates.
In order to check the synchronizers, you will have to disassemble the gearbox and try to move them by hand. The coupling should move easily along the splines. If you have to make an effort or you can’t move it, then you need to remove the synchronizer and disassemble it to inspect the surfaces of the parts for damage. If necessary, worn or damaged elements must be replaced. A complete replacement of the synchronizer can also be carried out immediately.
Synchronizer malfunctions and ways to eliminate them
If any difficulties arise with shifting gears, most car owners who have at least basic knowledge about the structure and principle of operation of the gearbox believe that the synchronizer is to blame. This often turns out to be true, although you should first rule out clutch malfunctions, which also quite often cause problems in the operation of a manual transmission when the system operates with jamming, a certain delay, and so on.
If the check does not reveal any violations, you can independently suspect problems with the synchronizer based on the following symptoms:
- When the gears switch off spontaneously, first of all, you need to pay attention to the release clutch and gears, which may be worn out.
- If, when switching gears, a noise appears, the identification of which is impossible and which was previously uncharacteristic, this may indicate that the locking ring is bent or that its conical part is worn out.
- Difficult gear shifting, when it is necessary to make a lot of effort and make several attempts, is virtually guaranteed to indicate a failed synchronizer.
It should be said right away that repairing this device is extremely labor-intensive and virtually impossible to do it yourself. This will require professional equipment and a lot of time, so it is advisable to entrust this matter to specialists. In addition, it is worth knowing that quite often a phenomenon such as chipping of gear teeth can be observed - owners of trucks and those who like sudden starts from a standstill are most susceptible to this danger. Operation of such a box is unacceptable.
Malfunctions and methods for their elimination
The main malfunctions of manual transmissions occur due to high wear or improper operation. As a rule, shafts and gears are quite strong products, so they are extremely difficult to break, and they practically do not suffer. However, the weak link is precisely the synchronizers, because they have the largest number of small, easily “erasable” elements. If the oil in the transmission is bad, it cannot reliably lubricate all parts, so increased wear occurs. Thus, the synchronizer rings are the first to suffer. This appears:
— Increased crunching noise when switching
— Difficulty shifting gears, or not turning on at all
— Spontaneous shutdown of the gear, for example, when the speed is reduced, the clutch itself may be damaged
In any of these cases, the synchronizer or its rings are covered (which most often happens), or the clutch needs to be completely checked for wear.
The repair is complex and requires a fairly highly qualified technician, I would not allow just anyone to do my manual transmission, because incorrect actions entail repeated repairs, and this means removing the transmission, etc.
In your case, the technician outlines the replacement of other rubbing elements, such as bearings. This is fair, because your synchronizers are out of order, and this indicates high wear of the entire mechanism. So my advice to you is that if you plan to drive this car for a long time, then change everything as the master tells you!
And that’s all for me, read our AUTOBLOG.
Similar news
- MPI engine
- What is a G-sensor in a DVR
- What is an electrolyte?
Add a comment Cancel reply
Preventive actions
Synchronizers do not belong to the category of mechanisms that fail with enviable regularity and require constant attention, repair or replacement.
But if we take into account the fact that the replacement procedure is quite labor-intensive, requires certain skills from the car owner, or additional financial costs for paying for the services of car service specialists, a more correct solution would be to extend the service life of the unit.
In order for the synchronizer to work for a long time, efficiently and effectively, you need to follow literally a few simple rules.
- Minimal use in aggressive conditions. Try to avoid aggressive driving. Do not try to constantly start abruptly, brake and accelerate again, literally tearing apart the gearbox. Smooth and moderate control of the gearbox will significantly increase the already quite impressive life of the synchronizers.
- Do not forget about the correct correspondence between the speed of the vehicle and the selected gear on the gearbox selector. Each gear has its own specific and optimal speed range for the machine. This is taught in the first lessons at a driving school. And such information should be remembered very carefully. If the speed matches the gear, and the gear speed, then the optimal load will begin to affect the synchronizers. This will have a positive effect on the service life of the mechanism and will significantly delay the replacement of the synchronizer on your car.
- In accordance with the regulations and requirements of the car manufacturer, carry out maintenance of the box. Often, the recommendations in the instructions for foreign cars do not quite coincide with the actual mileage and timing in relation to our operating conditions. Therefore, from the mileage indicated in the manual to the replacement of the same transmission oil or other consumables, it is usually recommended to subtract 15-25%. This means that maintenance needs to be done a little earlier. It all depends on the conditions under which the car and the gearbox in particular are operated.
- Use suitable oils for the box. Here again you need to look at the instruction manual. Manufacturers clearly state which transmission oils should be used for your specific transmission. It is better not to deviate from these recommendations. If you cannot find or purchase oils of the specified brand with the recommended characteristics, look among other manufacturers of working fluids for compositions that are as close as possible to the properties of the original oil.
- Before changing gear, be sure to fully depress the clutch pedal. Some drivers do not press the pedal all the way, as a result of which a large load begins to affect the synchronizer and wear accelerates. Regular operation of the clutch pedal in this manner will lead to breakdowns and malfunctions. By following this simple rule, you will be able to avoid unnecessary problems.
The synchronizer is truly a useful and effective addition to the design of modern mechanical and robotic gearboxes.
The vast majority of gearboxes installed on modern cars are synchronized. This is a completely justified and correct move on the part of the manufacturers. The unit has wide functionality, while simultaneously extending the service life of the entire box.