Sudden knocking noise in the engine while driving
Car service › Articles ›Sudden knocking in the engine while driving
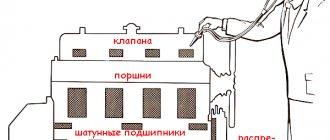
A critical increase in the size of the working gaps between the components of the internal combustion engine leads to knocking noise during engine operation. An indirect sign of the cause of the knocking is its tone, which in most cases makes it possible to determine the source of the sound indicating a malfunction of a particular component. The progression of knocking depends on the technical characteristics of the materials from which the parts are made. When contacting timing parts made of high-strength material wear out, engine knocking does not change in intensity and character for a long time. Extraneous sound quickly intensifies with wear of soft parts working in tandem with elements made of hard material (connecting rod and main bearings, as well as camshaft bearings).
If the pistons knock
A dull tone of sound, reminiscent of tapping on pottery, indicates that the problem is localized in the cylinder block. Extraneous noise may sometimes be accompanied by clicking sounds. The appearance of a gap of 0.3 - 0.4 mm leads to the appearance of piston knocking in the cylinder. Piston knocking most often occurs when the engine is cold, as well as at low speeds or when the gas pedal is suddenly released while driving. A knock of this origin disappears when the engine heats up due to thermal expansion of the piston.
If the piston pins are knocking
The sound when knocking the piston pins is metallic, ringing and high-pitched. Extraneous noise that appears at a gap of 0.1 mm is clearly audible when changing the gas, during acceleration, and also when releasing the gas. The sound is localized in the cylinder block. A similar knocking noise (detonation) can occur when using the wrong fuel, as well as under high engine load at low crankshaft speeds when driving up a steep hill in high gear.
Knock of crankshaft liners
Wear of the crankshaft main bearings results in a slightly muffled metallic noise localized in the area of the engine crankcase. An extraneous sound is heard with a sharp increase in speed, a sharp release of gas, as well as at low speeds when the engine is warm (low engine oil pressure). The use of low-quality motor oil that does not meet the requirements for the engine in use can also cause crankshaft knocking. In this case, an urgent oil change is necessary with mandatory flushing of the lubrication system.
Knock of connecting rod bearings
When the connecting rod bearings wear out, the sound is in many ways similar to the noise when the main bearings fail, being more distinct. A sharply increasing sound intensity when the crankshaft speed changes indicates the need for urgent repairs. Operating a vehicle with such noise is unacceptable due to the high risk of engine seizure.
FAQ
- When to get a vehicle inspection in 2021
- What to do when the check engine light is on? We provide comprehensive services for current and major repairs. Preliminary diagnostics of gasoline engines allows us to most accurately determine the causes of malfunctions and
- Why is the battery light on? We provide comprehensive services for routine and major repairs. Preliminary diagnostics of gasoline engines allows you to most accurately determine the causes of the malfunction and
What is engine knocking?
The appearance of engine knocking in most cases indicates that in the area of mating of certain parts there has been a critical increase in the gaps between the elements.
If the engine lubrication and cooling systems are functioning normally, then noise and knocking begin to appear at clearances that, on average, are double or more times the permissible parameters. The rate at which further wear increases will depend on the size of the gap, materials of manufacture, load, lubrication efficiency and a number of other factors. For this reason, some components can go through tens of thousands of kilometers with a knock without serious consequences (the timing belt), while others (CVM and CPG) can fail after just a few kilometers.
- detonation and heavy loads on the internal combustion engine;
- distortions of parts inside the engine;
- jamming of individual elements;
- loss of protective and other properties by motor oil;
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The variety has more advantages:
- it is a self-pollinating variety;
- attracts with beautiful, large fruits;
- the fruits ripen quickly - the harvest is harvested already in the third year;
- the variety is compatible with other crops (quince rootstocks);
- plants are frost resistant;
- trees are not prone to fungal diseases and are often resistant to pest attacks.
The Bryansk beauty pear is a unique variety that has virtually no drawbacks. The only disadvantages include deterioration in taste and the presence of defects in the appearance of the fruit, but only with a lack of moisture or drought.
Causes and solutions
This phenomenon can be caused by a large number of factors. They have varying degrees of danger. Sometimes, a small detonation is quite acceptable. All possible options for the occurrence of this phenomenon will be discussed below.
The most harmless is detonation, which occurs with a sharp increase in speed. If at 1000 rpm
sharply depress the gas pedal, accelerating the work to 4000-5000 rpm
, you can hear a brief detonation. This is quite a common occurrence. There is no need to be afraid of this; in this case, detonation will not lead to dire consequences. The reason is a sharp increase in the fuel supplied to the engine; the amount of air initially remains at the same level, this causes premature oxidation of the fuel, which is accompanied by explosions. The only way to combat this phenomenon is to avoid a sharp increase in speed.
Detonation and knocking of fingers in the engine: causes and solutions
Many motorists are concerned about the question, why do the fingers knock in the engine when accelerating the car? It is worth saying that the formulation of this question is initially incorrect.
Although the phrase “knock fingers” itself is very common, it is still incorrect. The piston pins cannot knock, but in fact we hear the sound of a shock wave of exploding fuel.
Fuel combustion in a working engine occurs sequentially. Starting near the spark plug, the flame gradually occupies the entire combustion chamber. However, there is another type of combustion called detonation.
During this phenomenon, the entire fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber explodes sharply, while the pressure and temperature in the engine cylinder increases significantly. Such an explosion is called detonation. And the sound from this explosion is the very knocking of fingers in the engine that many people talk about.
It is worth noting that there is also the concept of engine vibration, which is often confused with detonation. If detonation is associated with fuel combustion, then vibration is the process of vibration of the power unit caused by a malfunction or improper installation.
How to remove detonation and prevention methods
The choice of method for eliminating detonation depends on the reason that caused this process. In some cases, to get rid of it you have to perform two or more actions. In general, methods to combat detonation are:
- Use fuel with parameters recommended by the car manufacturer. In particular, this applies to the octane number (it cannot be underestimated). It is necessary to refuel at proven gas stations and not fill the tank with any surrogate. By the way, even some high-octane gasolines contain gas (propane or other) that unscrupulous manufacturers pump into it. This increases its octane number, but not for long, so try to pour high-quality fuel into the tank of your car.
- Set the ignition later. According to statistics, ignition problems are most often the cause of detonation.
- Perform decoking, clean the engine, that is, make the volume of the combustion chamber normal, without soot and dirt. This can be done independently in a garage, using special decarbonization products.
- Inspect the engine cooling system. In particular, check the condition of the radiator, pipes, and air filter (replace it if necessary). Also, do not forget to check the antifreeze level and its condition (if it has not been changed for a long time, then it is better to change it).
- For diesel engines, the fuel injection timing must be set correctly.
- Operate the car correctly, do not drive in high gears at low speed, do not reflash the ECU in order to save fuel.
As preventive measures, it can be advised to monitor the condition of the engine, periodically clean it, change the oil on time, perform decarbonization, and prevent overheating. Similarly, maintain the cooling system and its elements in good condition, change the filter and antifreeze on time. Another trick is that periodically you need to let the engine run at higher speeds (but without fanaticism!), This needs to be done in neutral gear. At the same time, under the influence of high temperature and load, various elements of dirt and debris fly out of the engine, that is, it is cleaned.
Detonation usually occurs when the engine is hot. In addition, it is more likely on engines that are operated at minimal loads. This is due to the fact that they have a lot of carbon deposits on their pistons and cylinder walls with all the ensuing consequences. And usually the engine knocks at low speeds. Therefore, try to operate the engine at medium speeds and with medium loads.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the knock sensor. The principle of its operation is based on the use of a piezoelectric element, which converts the mechanical effect on it into electric current. Therefore, checking its operation is quite simple.
The first method is using a multimeter operating in electrical resistance measurement mode. To do this, you need to disconnect the chip from the sensor and connect the multimeter probes instead
The value of its resistance will be visible on the device screen (in this case the value itself is not important)
Next, use a wrench or other heavy object to hit the DD fastening bolt (however, be careful not to overdo it!). If the sensor is working properly, it will perceive the impact as detonation and change its resistance, which can be judged by the readings of the device
After a couple of seconds, the resistance value should return to its original position. If this does not happen, the sensor is faulty
If the sensor is working properly, it will perceive the impact as detonation and change its resistance, which can be judged by the readings of the device. After a couple of seconds, the resistance value should return to its original position. If this does not happen, the sensor is faulty.
The second verification method is simpler. To do this, you need to start the engine and set its speed to somewhere around 2000 rpm. Open the hood and use the same key or a small hammer to hit the sensor mount. A working sensor should perceive this as detonation and report this to the ECU. The control unit will then give a command to reduce engine speed, which can be clearly heard by ear. Likewise, if this does not happen, the sensor is faulty. This unit cannot be repaired, and it only needs to be replaced entirely, fortunately, it is inexpensive
Please note that when installing a new sensor into its seat, it is necessary to ensure good contact between the sensor itself and its system. Otherwise it will not work correctly
Causes
When the power unit operates correctly, the sequence of the fuel combustion process is maintained. It starts from the spark plugs, and then fills the entire chamber equidistantly.
Detonation combustion occurs in a completely different way. The entire volume of the fuel-air mixture explodes simultaneously, sharply, provoking a significant increase in the pressure and temperature of the cylinders themselves. Under such conditions, chemically active compounds are formed in places of the highest concentration of unburned fuel.
When critical values are reached, chemical chain reactions occur that promote explosive ignition. The resulting wave moves quite quickly, strongly impacts the walls of the chamber and the surfaces of the cylinders, and at the same time new points of spontaneous combustion are organized. The result is numerous oscillatory phenomena that provoke vibrations of the power unit.
This phenomenon is detonation, which becomes the root cause of why the fingers knock in the engine.
It can occur for various reasons, the most common are:
Fuel composition. If air and fuel are in a 9-0 ratio, which violates the average, then in the event of penetration into a chamber with elevated temperature and pressure, various oxidative reactions are formed in remote areas, which are the primary source of the process of self-ignition, that is, detonation. The magnitude of the ignition timing. An increase in this indicator provokes a shift in the maximum pressure peak, which becomes a factor in the occurrence of detonation processes. Octane number of the fuel mixture. The lower this indicator, the greater the likelihood of detonation. A decrease in this criterion leads to an increase in the chemical activity of the fuel to the oxidation process. Therefore, car owners using 76-octane gasoline notice the knocking of the piston pins much more often than drivers who fill the tank with 92-octane gasoline. Compression ratio. An indicator characterizing the ratio of the volume of one cylinder to the total volume of the combustion chamber. Its increase leads to the fact that pressure and temperature invariably begin to increase, which means that the risk of detonation increases. Therefore, if a power unit with a sufficiently high compression ratio is installed, then the car owner is recommended to use high-leaded gasoline. Glow ignition, which causes spontaneous combustion of the fuel mixture in the cylinders. Occurs due to the presence of burning soot or high temperature in the chamber
It is equally important to choose the type of spark plug correctly. There are “cold”, “warm” and “medium” candles, characterized by different heat indicators
This is necessary so as not to cause a fire if the insulator of the central electrode of the spark plug overheats. Increased load on the motor. If the driver tries to start every time, for example, from third gear, then at some point he will invariably hear the fingers of his engine knocking.
Causes of internal explosions
Detonation is precisely the root cause of finger knocking in the internal combustion engine. But to eliminate such a malfunction, you need to understand why it occurs.
Here experts highlight several reasons:
- Composition of the mixture. The air-fuel mixture consists of fuel and air mixed in certain proportions. If the proportions are violated, then oxidative reactions will gradually appear in the combustion chamber, becoming a source of further spontaneous ignition. The same detonation.
- Ignition timing. It has certain values at which the motor operates correctly. If the angle is greater, this will lead to a shift in the peak pressure. This affects the occurrence of detonation.
- Octane number. The lower the octane number of the fuel, the higher the likelihood of the mixture exploding. A low number helps to increase the chemical activity of the fuel and increases its susceptibility to oxidative processes. It is because of this that on cars that use A-76 gasoline, detonation occurs much more often than on cars with 92 and 95 gasoline.
- Compression level parameters. This indicator reflects the ratio of the volume of one cylinder in the engine relative to the total internal volume of the entire combustion chamber. If the compression ratio increases, then the internal temperature and pressure will increase proportionally. This entails an increased risk of detonation. Therefore, automakers advise using only high-leaded fuel for engines with a high compression ratio.
- Glow ignition effect. This ignition provokes spontaneous ignition of the mixture inside the cylinders. It usually appears when there is elevated temperature inside, or the remaining soot burns. It is important to choose suitable candles. Different candles have different heating characteristics. They are conventionally divided into cold, warm and medium. Correct selection will prevent spontaneous combustion and detonation due to the overheated insulator of the central electrode.
- Increased engine load. Trying to pull an unbearable load, overloading the car or starting from 3rd gear rather than first, at some point your fingers are sure to rattle. That is, the detonation process will begin.
There are more than enough reasons. Moreover, most often the provocateur of detonation is the motorist himself.
It is necessary to follow the recommendations for operating the car, do not overload the engine and maintain it on time.
This will prevent the fingers from knocking and protect against the severe consequences of detonation.
The engine is experiencing detonation: what to do?
The first thing to do when there are characteristic sounds coming from under the hood is to try to reduce the load on the car’s engine. You should not accelerate sharply and demand the maximum from the engine - this will only wear it out and shorten its service life.
If you use low octane fuel, you should switch to high octane alternatives. There is no point in buying expensive gasoline; regular 95 will do just fine. Just in case, check the high-voltage wires and spark plugs: it is because of them that detonation often occurs.
If none of the above helps, you should contact a car service for help.
The engine knocks while driving: what should the driver do?
Specialists diagnose problem nodes by the nature of the knock, its tone and area of localization. A stethoscope is widely used for diagnosis. You can also make your own device for listening to engine knocks. To solve the problem, you will need a steel rod to which you need to solder a metal can.
The tone of the sound is an indirect sign, since on different engines the knock may appear louder or muffled. For example, the conventional knock of the crankshaft main bearings on a 1.4-liter Korean car may well be louder and easier to hear compared to the knock of connecting rods on a 3.0-liter German car.
If we talk about diagnostics based on the nature of engine knocking, then it is worth highlighting a constant knocking, periodic knocking with one frequency or another, as well as occasional knocking. In the latter case, it is worth understanding the impacts that occur unevenly.
Engine knocking is usually associated with engine speed, that is, with the frequency at which the crankshaft rotates. The faster the engine spins, the higher the knocking frequency. The indicated frequency may or may not coincide with the crankshaft speed. It is also worth noting that the sound can become more or less intense (differ in strength) depending on the operating mode of the internal combustion engine.
For example, with an increase in the speed and load on the engine, there is a natural increase in the loads on the moving parts of the crank mechanism and the timing belt. In this case, the worn elements will knock more strongly than when the engine is idling. At this stage, when diagnosing, it is important to determine whether the knocking increases with increasing speed. This often requires experience, since it is necessary to listen for knocking against the background of the general increasing noise of the operating unit.
In parallel with this, it is necessary to separately take into account the fact that the oil pressure in the engine lubrication system also increases with increasing speed. In some cases, the engine oil itself acts as a “damper”, and the knocking itself may become less intense even with increased load on the engine. For this reason, an important parameter is the temperature of the internal combustion engine.
When you experience engine knocking, the first thing you need to do is check the engine oil level. The appearance of a knock may well be due to a drop in pressure in the lubrication system. If everything is in order with the level, then at the initial stage it will be necessary to more accurately localize the fault, eliminating possible knocking noises from fuel equipment, drives, attachment pulleys, etc.
If the knocking frequency is two times different from the crankshaft rotation speed, then problems with the timing belt are likely. This is because the crankshaft rotates twice as fast as the camshaft. Warming up the engine in such a case can lead to increased knocking, since with increasing temperature the valve clearances increase.
When knocking occurs on a cold or hot engine, that is, depending on the temperature, you need to additionally take into account the possible expansion of worn parts as they warm up and a decrease in clearances (the knocking weakens). At the same time, the dilution of the heated oil can lead to increased knocking. The first case is typical for CPG, the second affects the bearings of the crank mechanism.
Based on the conclusions drawn about the nature of the knock, you can decide whether to go to the service center on your own or call a tow truck. Finally, we would like to add that increased knocking under load and its rapid progression when driving is a clear sign that it is better to refuse independent movement. In this case, the engine should be turned off to prevent further destruction of the power unit.
- The connecting rod bearing has turned: solution to the problem
Why the crankshaft bearings are turning: the main reasons. What to do if the connecting rod bearing has turned, how to change the connecting rod bearings correctly. - Engine knocking when cold
Why a cold engine may knock: various malfunctions. Analysis of the nature of the knock in the power unit: ringing, metallic, muffled, etc.
- Valve knocking on a cold engine
Valves knock on a cold engine or after warming up the engine: possible causes of valve mechanism knocking. Fault diagnosis, useful tips.
- Why do my fingers knock in the engine when accelerating a car?
For what reasons does piston pin knocking occur during vehicle acceleration and operation under load: fuel quality, ignition, mixture composition, and others.
- A grinding, whistling, or knocking noise is heard when starting the engine.
What can knock, whistle, rustle and make other extraneous sounds under the hood after starting the engine. Diagnostics and determination of faults.
- The engine knocked (knocked): what is it?
What should be understood by the definition of “engine knocked”. Why does the engine start knocking? In what cases does a knocking sound in the engine indicate a breakdown of the internal combustion engine.
The first thing to do when there are characteristic sounds coming from under the hood is to try to reduce the load on the car’s engine. You should not accelerate sharply and demand the maximum from the engine - this will only wear it out and shorten its service life.
If you use low octane fuel, you should switch to high octane alternatives. There is no point in buying expensive gasoline; regular 95 will do just fine. Just in case, check the high-voltage wires and spark plugs: it is because of them that detonation often occurs.
If none of the above helps, you should contact a car service for help.
Cause of knocking fingers
Regardless of the reason for which the fingers begin to knock, such a phenomenon is still abnormal and it is necessary to open the engine, carry out diagnostics and appropriate repairs. Only on certain engine modifications during sudden acceleration can such a knocking sound occur for natural reasons when the engine is subject to increased loads. But if such sounds appear at idle or smooth acceleration, then the engine has problems that need to be corrected as soon as possible.
By the way, the cause of this knocking of fingers may be the poor quality of the gasoline used. Under no circumstances should the octane number be lowered, as the car manufacturer requires. This is the main reason for the unpleasant knocking of fingers. Such breakdowns can also occur due to a malfunction of the air flow meter or a breakdown of the knock sensor. In any case, if changing the fuel did not help solve the problem, you will need to initially perform computer diagnostics of the engine, and then open it and check the injection.
Another reason for such problems is a malfunction of the ignition system. Ignition settings can go wrong even in the most modern cars, which leads to incorrect detonation and the appearance of pronounced extraneous knocks in engine operation. In such a case, it is necessary to reconfigure the injector and ignition, which is performed under service conditions using special equipment.
It is much worse when the cause of knocking fingers is the general wear and tear of the car. In such a case, a comprehensive repair will be required, which falls into the category of capital and has an appropriate cost. However, this is observed only on heavily worn cars that have already run 300-400 thousand kilometers or more. For such restoration, appropriate repair kits are used, but it is much easier to replace the engine with a used contract one than to try to restore it.
Let's sum it up
On most engines, the appearance of a characteristic metallic knocking sound of the fingers is a sign of a malfunction of the ignition system or other engine failures. First of all, the car owner should try changing the gas station; if this does not help, he needs to take the car to a service center, perform computer diagnostics, identify existing faults and carry out prompt repairs. Such malfunctions should not be ignored, as subsequently the coating of the cylinders burns out and problems with the valve group appear. Ultimately, you have to perform an expensive overhaul of the engine.
21.10.2019
Why do engine fingers knock when accelerating?
Accelerating a car is a stressful situation for the engine, especially when it comes to a sharp increase in speed. When pressing the pedal to the floor for a sharp increase in speed, for example, from 1000 to 5000, the driver may hear the fingers knocking in the engine, and this is normal. To quickly gain speed, more fuel is supplied to the engine with the same amount of air, which can lead to detonation.
However, the situation when, during a quiet car start and acceleration, the driver hears fingers tapping, is not considered normal. In such cases, it is necessary to identify the cause of the problem as soon as possible and eliminate it in order to avoid serious engine damage.
The following reasons can be cited why fingers knock during normal engine operation:
Air flow sensor failure. If the air flow sensor does not work correctly, the electronic control unit will receive erroneous information and give the wrong signal;
The ignition timing is incorrectly set. For this reason, the point of maximum fuel combustion approaches top dead center, which leads to increased cylinder pressure and dangerous detonation; Damage to the knock suppression sensor. It is imperative that if there is a knocking sound in the engine, you need to check the knock damping sensor. If you find a problem, replace it; Incorrect gasoline. Car manufacturers indicate what kind of gasoline should be poured into the engine. If you use fuel with a lower octane rating than the manufacturer recommends, compression problems will occur. They are also possible if low-quality gasoline was poured into the tank at a gas station.
It is worth noting that the knocking of engine fingers is not always a problem acquired during operation. There are situations where a car comes from the factory with sensors connected incorrectly, which leads to this problem. This situation is especially dangerous because the new engine can be seriously damaged. If you hear knocking noises in the engine, have the problem corrected immediately.
Many motorists are concerned about the question, why do the fingers knock in the engine when accelerating the car? It is worth saying that the formulation of this question is initially incorrect.
Although the phrase “knock fingers” itself is very common, it is still incorrect. Piston pins cannot knock, but in fact we hear the sound of a shock wave of exploding fuel.
Fuel combustion in a working engine occurs sequentially. Starting near the spark plug, the flame gradually occupies the entire combustion chamber.
However, there is another type of combustion called detonation. During this phenomenon, the entire fuel-air mixture in the combustion chamber explodes sharply, while the pressure and temperature in the engine cylinder increases significantly. Such an explosion is called detonation. And the knock from this explosion is the answer to the question of why the fingers knock in the engine.
There is also the concept of engine vibration, which is often confused with detonation. If detonation is associated with fuel combustion, then vibration is the process of vibration of the power unit caused by a malfunction of its installation.
Why do my fingers knock in the engine?
The octane number of fuel is an indicator characterizing the coefficient of fuel resistance to combustion during compression. In other words, it shows the detonation resistance of the fuel. Accordingly, an engine with a high compression ratio must use gasoline with a high octane number.
All modern engines have a high compression ratio and if low-octane fuel is used in them, the likelihood of detonation is very high. With small deviations in gasoline parameters, the so-called knocking of fingers in the engine can be observed under load on the engine or when accelerating the car. In more serious cases - in any engine operating mode. Even though high-octane gasoline is more expensive than low-octane gasoline, it’s not worth saving on it for that reason.
Another cause of detonation is glow ignition, that is, spontaneous combustion of fuel in the engine cylinders. The reasons for this phenomenon may be burning soot or high temperature in the combustion chamber. The problem most often appears on worn engines that consume a lot of oil.
Another reason may be spark plugs that are not suitable for a particular engine. It is very important to select spark plugs for the engine with the appropriate heat rating. There are “cold”, “medium” and “warm” candles. Otherwise, the overheated insulator of the central electrode of the spark plugs can cause premature combustion of gasoline in the cylinders, the combustion of which will be accompanied by knocking of the fingers in the engine.
A lean fuel mixture, that is, an increase in the amount of air in the mixture compared to gasoline, can also cause detonation. If a lean mixture enters the engine cylinders, it is much more likely to cause detonation than a normal mixture.
Detonation can also occur due to high engine load. And it’s not necessarily about any malfunctions, but especially about the operation of a particular engine. Therefore, when wondering why your fingers are knocking in the engine when accelerating a car, it is worth familiarizing yourself with the nuances of the operation of your car’s power unit. Perhaps this is its drawback, which manifests itself when the engine is overloaded. However, if you try, for example, to start right away in third gear, then with a high probability you will not even hear a dull knock, but a loud clang on many engines.
Causes of engine detonation
The engine can detonate in any car: new, old, modern or no longer in production. The type of power unit does not really matter, whether it is carburetor or fuel injection.
On new cars, a special engine knock sensor is installed (only for injection power units). This device allows the on-board computer to regulate the operation of the engine so that it does not detonate.
Modern car engines operate at high compression ratios, so the risk that the air-fuel mixture will detonate is quite high. If the engine knock sensor is faulty, the ECU cannot effectively regulate the operation of the unit. Problems will not keep you waiting.
The most common causes of engine detonation during acceleration, at speed or at idle:
- fuel of low quality or with an inappropriate octane number,
- too much ignition advance,
- lean air-fuel mixture,
- carbon deposits on the cylinder walls,
- low-quality or unsuitable spark plugs,
- engine overheating due to a malfunction of the cooling system.
Let's look at each point in detail to understand the root cause. Then it will be easier to fix the problem.
Fuel with the wrong octane number or low quality
If gasoline with an octane rating lower than recommended enters the engine, detonation occurs with almost 100% probability. The car manufacturer calculates the compression ratio for a certain type of fuel, so the use of low-quality or unsuitable octane fuel leads to engine detonation at idle or during acceleration.
The quality of the fuel can be corrected using the SGA additive.
Gasoline additive SGA. Cleaning injectors and injectors Cleans and lubricates fuel pumps and injectors, extending their service life. Improves injection, which reduces fuel consumption and increases dynamics. Suitable for any petrol systems, including TFSI, TSI, GDI, MDI. more reviews
Incorrectly configured ignition
In an effort to increase torque, some craftsmen change the factory settings of the ignition system. If the advance angle is set too high, the spark plug will produce a spark before the piston approaches TDC. Ignition will occur prematurely when the fuel is not completely mixed with air.
Faulty spark plugs
Sometimes the cause of detonation of a VAZ engine or another brand of car is faulty or unsuitable spark plugs. In this case, the spark may not be generated as expected by the motor manufacturer. Untimely sparking of a spark plug is one of the common causes of problems with ignition of the air-fuel mixture.
Lean air/fuel mixture
In pursuit of efficiency, motorists can deliberately lean the air-fuel mixture. This is another reason why engine detonation occurs. Due to insufficient concentration of fuel vapor, a spark cannot ignite the mixture. During the next injection cycle, on the contrary, fuel vapors become higher than normal. An overly rich mixture ignites prematurely due to compression.
Carbon deposits on cylinder walls
Often the cause of engine detonation at speed is the presence of deposits on the inner surface of the combustion chamber. The soot heats up and acts as a wick, igniting the air-fuel mixture. In addition, carbon deposits increase the compression ratio and fuel with a given octane number ignites earlier due to an increase in compression temperature.
Cleaning the engine is possible with a special long-term engine flush.
Soft engine flushing Suprotek Aprokhim For long-term (up to 200 km) soft flushing of internal combustion engines of any type. more reviews
Cooling system malfunction
Fuel also detonates if the cooling system in the power unit is faulty. With this problem, engine detonation occurs during acceleration. Under load, the engine overheats, the internal space of the combustion chamber heats up to a temperature where gasoline vapors spontaneously ignite.
If the engine oil level is above/below normal
The lubrication system is designed to reduce friction between the rubbing parts of the engine. In addition to performing its main function, the lubrication system provides cooling of engine parts, removal of carbon deposits and wear, and protection of engine parts from corrosion. Therefore, malfunctions in the engine lubrication system are very dangerous. We will talk about what to do if the engine oil level is higher or lower than the normal level and what the consequences may be.
If the engine oil level is below normal
It happens that the oil level in the engine crankcase is below normal. This can be checked using a dipstick no earlier than 5-7 minutes after stopping the engine. The oil level should be considered normal if the mark on the dipstick is halfway between the min and max marks.
If the check shows that the oil level is below normal, add oil to the engine crankcase to the required level, having previously identified and eliminated possible leaks in the connections in the engine lubrication system. By externally inspecting the engine, you can verify whether there are oil leaks from under the gaskets - camshaft drive cover, valve cover, cylinder block, oil filter, as well as from the filler plug, through the oil pressure indicator sensor fitting from under the oil separator cover and through the oil dipstick seal.
Even small oil leaks detected indicate a violation of the tightness of the lubrication system due to damaged gaskets or seals or unreliable fastenings, which is absolutely unacceptable.
If the engine oil level is higher than normal
High oil pressure is no better than low oil pressure: most likely, the problem is in the viscosity of the oil used; to do this, you need to check its viscosity and quality, and if necessary, replace the oil. It is common to see increased oil pressure when using summer oil in winter at low temperatures.
In the engine lubrication system, the required pressure is provided at normal viscosity. Therefore, for each engine, depending on the season, ambient temperature and dustiness of the area, manufacturers recommend a certain type of oil that has a certain viscosity and the necessary lubricating properties.
During the operation of the car, partial dilution of the oil occurs with that part of the gasoline that does not burn when the engine is running on an over-enriched mixture, or sometimes due to coolant getting into the oil when the cylinder head gasket is damaged. Of course, the quality of the oil decreases and its viscosity decreases if the oil is old and has long been in need of replacement. The oil pressure in the lubrication system decreases sharply, because Low-viscosity oil easily penetrates into the gaps between mating rubbing parts.
To ensure a long service life of engine oil with the required viscosity and required quality, I recommend that you regularly monitor the serviceability of the crankcase ventilation system and promptly clean it and flush the parts.
If you have filled the engine oil above the level
There are situations when more oil is poured into the engine during the next replacement, and more often this happens due to inattention. What happens if you fill the engine with more oil than normal? Is it worth draining it? If you filled the oil slightly above the “max” level on the oil dipstick, then it’s okay. During operation, the oil will drain naturally and after several thousand kilometers, the oil level will be normal.
If you have filled in too much oil above the norm, then problems may arise. Especially if you already have an old car. When the oil level is higher than normal, increased pressure is created in the lubrication system, and this can lead to wear on the seals and subsequently they can be “squeezed out”.
It is advisable not to exceed the recommended oil level. And if there is a large amount of “excess” oil in the engine, then it is advisable to drain it to normal.
Knock in the engine block
The appearance of a knock in the BC, especially if the knock is localized in the lower part of the engine, often indicates problems with the crankshaft. Such knocks indicate a serious breakdown; the engine must be stopped operating. Otherwise, the crankshaft may become unusable.
If the connecting rod bearings are knocking, further driving will lead to the connecting rod cap being torn off, and then the cylinder block will be broken. In this case, it may be necessary to replace the entire engine with a contract one.
The knock of the connecting rod journals is metallic and sharp, especially if you press the gas. Also in such a situation, the oil pressure drops and the oil pressure light on the instrument panel lights up. A decrease in pressure leads to the fact that the engine can seize after just a few minutes of operation under load.
The crankshaft journals may also knock. This kind of knock is lower, vibration goes through the engine. The reason is that as a result of wear on the main journals, a gap appears between the crankshaft journals and the supports in the block. This type of knocking noise may also appear due to low pressure in the lubrication system, which leads to scoring on the shaft journals.
Note that if the problem is in the main journals of the shaft, you can get to the repair site under your own power, which cannot be said about knocking connecting rod bearings. However, even in this case, no serious loads can be placed on the internal combustion engine, and the engine itself must be repaired immediately.
Now let's move on to the CPG. If the piston group begins to knock, this indicates an increase in the gap between the piston and the cylinder, as well as the occurrence of defects both on the liner and on the piston itself.
It should also be noted that the cause of knocking can also be the piston pin and its connection with the connecting rod. For example, if the pin is pulled out of the piston, then it can hit the cylinder wall. The reason is insufficient pressing of the pin or the stopper on the piston has flown out (depending on the type of fit of the piston pin on a particular internal combustion engine, which can be “hot” and “floating”).
Solving existing problems
In each specific case, the repair technology will differ, depending on the identified faults. If this is a problem with the engine mounts or various attachments have failed, then such breakdowns are relatively easy to fix. However, if there is wear on the crankshaft and problems with the piston group, then such repairs fall under the category of capital repairs, and accordingly the car owner’s expenses will be extremely high.
In such cases, when engine noise increases, the car owner should not delay contacting service. The sooner he contacts specialized workshops, the easier and cheaper it will be to eliminate existing faults.
As a preventive measure, we can only recommend maintaining the car in technically sound condition, performing its routine maintenance in a timely manner, paying special attention to the quality of the oil used.
It is low-quality motor oil that most often causes such problems with a car engine. Lubricant can accumulate in hard-to-reach places, not providing high-quality lubrication of moving elements, and lead to increased wear. As a result, literally a few years after the start of operation, such a motor begins to operate at higher tones, and it is extremely difficult to solve such problems, since it is necessary to carry out a major overhaul of the engine.
Let's sum it up
There may be many reasons why the engine began to run louder. This is the use of low-quality fuel, improper operation of the lubrication system, problems with injectors, timing chain, wear of valves and camshafts. In such a case, it is extremely difficult to correctly identify faults and carry out repairs on your own; the car owner needs to contact workshops where specialists, using the appropriate equipment, will carry out diagnostics, identify characteristic breakdowns and restore the car.
Methods for eliminating detonation
Along with the reasons for the formation of detonation processes, there are a number of techniques to prevent it. Their goal is to actively accelerate the combustion process of the residual amount of the fuel mixture, as well as to slow down the flow of oxidative chemical processes formed in the cavity of the combustion chamber.
- Increasing the number of revolutions of a running engine.
- Organization of turbulization of fuel-air mixture flows in the combustion chamber.
- Reducing the path of the flame front.
Recently, techniques have been intensively developed using electronics to combat why fingers knock in the engine during acceleration. For this purpose, microprocessors are created to control the power unit.
The intelligent sensors being created make it possible not only to monitor all processes occurring and developing inside the cylinders, but also to correct them by changing the composition of the fuel mixture, as well as by changing the ignition timing.
The piston pin is knocking, what should I do?
Any car owner, regardless of driving experience, has heard the expression “knock of fingers.” Despite the fact that the phrase is quite common, it does not have an entirely accurate interpretation.
In modern cars, the characteristic sound is not produced by the piston pins; the driver and his passengers catch the sound vibration from the shock wave formed during the explosion of the fuel-air composition directly in the combustion chamber.
In cars of the “grandmother’s” model year, it was the piston pins that could knock. Low wear resistance, strength of metal parts, exposure to high temperatures and significant loads of the piston pin seat contributed to the formation of various gaps, which became the cause of the characteristic sound.
The modern automotive industry uses exclusively steel of the proper quality, applies high-precision techniques for processing each part, so damage and the appearance of any defects of the fingers themselves are practically eliminated. But, nevertheless, the term “knocking fingers” has not disappeared from the professional vocabulary of car owners.
Causes
When the power unit operates correctly, the sequence of the fuel combustion process is maintained. It starts from the spark plugs, and then fills the entire chamber equidistantly.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=coJGgbMJjwg
Detonation combustion occurs in a completely different way. The entire volume of the fuel-air mixture explodes simultaneously, sharply, provoking a significant increase in the pressure and temperature of the cylinders themselves. Under such conditions, chemically active compounds are formed in places of the highest concentration of unburned fuel.
When critical values are reached, chemical chain reactions occur that promote explosive ignition.
The resulting wave moves quite quickly, strongly impacts the walls of the chamber and the surfaces of the cylinders, and at the same time new points of spontaneous combustion are organized.
The result is numerous oscillatory phenomena that provoke vibrations of the power unit.
This phenomenon is detonation, which becomes the root cause of why the fingers knock in the engine.
It can occur for various reasons, the most common are:
- Fuel composition. If air and fuel are in a 9-0 ratio, which violates the average, then in the event of penetration into a chamber with elevated temperature and pressure, various oxidative reactions are formed in remote areas, which are the primary source of the process of self-ignition, that is, detonation.
- The magnitude of the ignition timing. An increase in this indicator provokes a shift in the maximum pressure peak, which becomes a factor in the occurrence of detonation processes.
- Octane number of the fuel mixture. The lower this indicator, the greater the likelihood of detonation. A decrease in this criterion leads to an increase in the chemical activity of the fuel to the oxidation process. Therefore, car owners using 76-octane gasoline notice the knocking of the piston pins much more often than drivers who fill the tank with 92-octane gasoline.
- Compression ratio. An indicator characterizing the ratio of the volume of one cylinder to the total volume of the combustion chamber. Its increase leads to the fact that pressure and temperature invariably begin to increase, which means that the risk of detonation increases. Therefore, if a power unit with a sufficiently high compression ratio is installed, then the car owner is recommended to use high-leaded gasoline.
- Glow ignition, which causes spontaneous combustion of the fuel mixture in the cylinders. Occurs due to the presence of burning soot or high temperature in the chamber. It is equally important to choose the type of spark plug correctly. There are “cold”, “warm” and “medium” candles, characterized by different heat indicators. This is necessary so as not to cause a fire if the insulator of the central electrode of the spark plug overheats.
- Increased load on the motor. If the driver tries to start every time, for example, from third gear, then at some point he will invariably hear the fingers of his engine knocking.
Negative consequences of detonation
Detonation, by its nature, is destructive in nature, can lead to breakdown of various parts and assemblies, and can also become a fundamental reason for engine overhaul. Therefore, modern internal combustion engines operating at high speeds can fail in a short time, precisely because of detonation processes.
There is a very common misconception among car owners that an increase in pressure due to an increase in speed has a positive effect on increasing engine power. But the situation is exactly the opposite. The duration of the blast wave is very short (0.0001 s).
The same time is allocated to increase the pressure on the pistons. Consequently, they will not be able to affect the engine power in such a tiny amount of time. And it is quite likely to cause significant damage to various components and parts.
When the blast wave hits the cylinder walls with enormous force, it significantly destroys the oil film. This film protects the CPG parts not only from “dry” friction, but also from corrosion, so its destruction will inevitably lead to partial mechanical wear and damage to the parts.
In addition, when a shock wave is formed in a sharp form, the thermal output from the burnt gas begins to increase towards the cylinder walls, which causes overheating of the internal combustion engine. This, in turn, will affect the condition and performance characteristics of gaskets, seals, spark plugs, pistons, etc.
Methods for eliminating detonation
Along with the reasons for the formation of detonation processes, there are a number of techniques to prevent it. Their goal is to actively accelerate the combustion process of the residual amount of the fuel mixture, as well as to slow down the flow of oxidative chemical processes formed in the cavity of the combustion chamber.
- Increasing the number of revolutions of a running engine.
- Organization of turbulization of fuel-air mixture flows in the combustion chamber.
- Reducing the path of the flame front.
Recently, techniques have been intensively developed using electronics to combat why fingers knock in the engine during acceleration. For this purpose, microprocessors are created to control the power unit.
The intelligent sensors being created make it possible not only to monitor all processes occurring and developing inside the cylinders, but also to correct them by changing the composition of the fuel mixture, as well as by changing the ignition timing.
Source: https://avtoreview-msk.com/stuchit-palets-porshnya-chto-delat/